Section C (add river landscapes)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
coastal management case study
location:
Lyme Regis, west of Dorset. popular tourist destination, with up to 20,000 tourists every year. this scheme 'Hold the Line' cost £60 million.
what was done + did it work?
PHASE 1 + 2 - rock armour to absorb wave energy + rock armour extension to protect harbour, beach nourishment
PHASE 3 - not undertaken as cost outweighed benefits
PHASE 4 - new 390m recurved sea wall, nailing, piling and drainage to stabilise cliffs + protect 480 homes
benefits + disadvantages
benefits - more tourists, defences work against storms, harbour better protected for boats + fishermen, increased property values
disadvantages - litter + traffic increased due to more visitors, less fossils revealed as cliffs stabilised, spoilt natural landscape
explain some soft engineering methods
beach nourishment - beach widened using sand + shingle, increases distance wave has to travel, expensive, has to be repeated
dune regeneration - new dunes created / old ones restored by either nourishment or planting vegetation to stabilise, dunes provide barrier to prevent flooding / erosion, stabilisation cheap, nourishment expensive
managed retreat
explain how a sand dune forms
at low tide, sand in blown inland
obstacles (e.g. driftwood) means the wind is slowed so sand is deposited, forming embryo dunes
the dune is colonised, meaning specialised plants grow there and the dune stabilises.
over time, older dunes move inland as newer embryo dunes form. mature dunes can reach heights of up to 10m.
how is a beach formed? what is a sand beach and what is a shingle beach?
beaches are formed by constructive waves depositing material. sand beaches are gently sloping and wide - weak backwash can move them back down the beach. shingle beaches are steep and narrow - weak backwash cannot move the shingle back down.
explain some hard engineering methods
sea wall - concreate wall that reflects waves back to sea, prevents erosion, expensive, strong backwash erodes under wall
gabions - absorb wave energy, cheap, ugly, wire cages can corrode
rock armour - boulders piled up along the coast, absorb wave energy so reduce erosion, can be moved by strong waves so need replacing
groynes (wooden / rock) - fences that stop longshore drift, create wider beaches, cheap, starves beaches further down the coast
define hard engineering
the use of concrete and man-made structures to defend land against natural erosion processes
define soft engineering
managing erosion by working with natural processes to reduce the effects of flooding and erosion.
what is managed retreat + case study?
Medmerry case study
total cost: £28 million
sea wall was becoming too expensive + not worth the cost
a 2km embankment was constructed around the perimeter of areas to be flooded, protecting caravan parks, farmland, etc
rock armour placed at seaward edges of the embankment
benefits - properties protected, new footpaths, new habitat for wildlife, no maintenance cost
disadvantages - locals annoyed about losing land, expensive for low population, farmland lost
what is a tombolo?
it is when a spit begins to form, but then joins an old island to the mainland.
draw a labelled diagram of a tombolo
explain how a bar forms
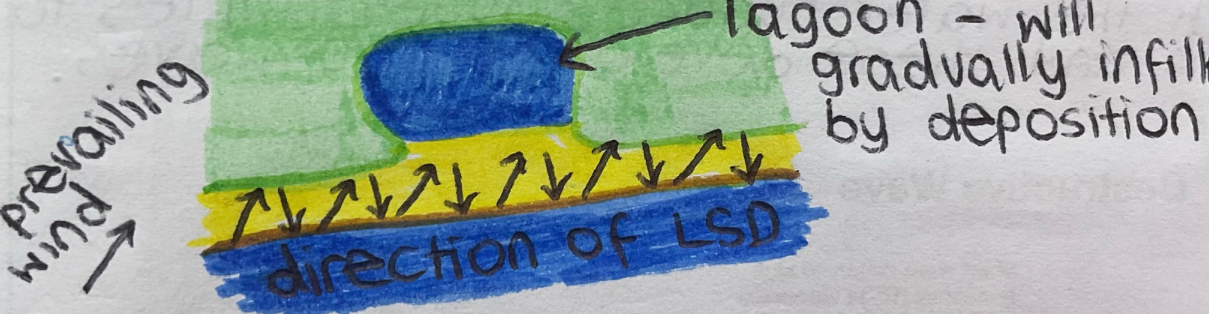
a bar is formed when a spit joins two headlands together
the bar cuts off the bay between the headlands from the sea
this means a lagoon forms behind the bar
draw a labelled diagram of a bar
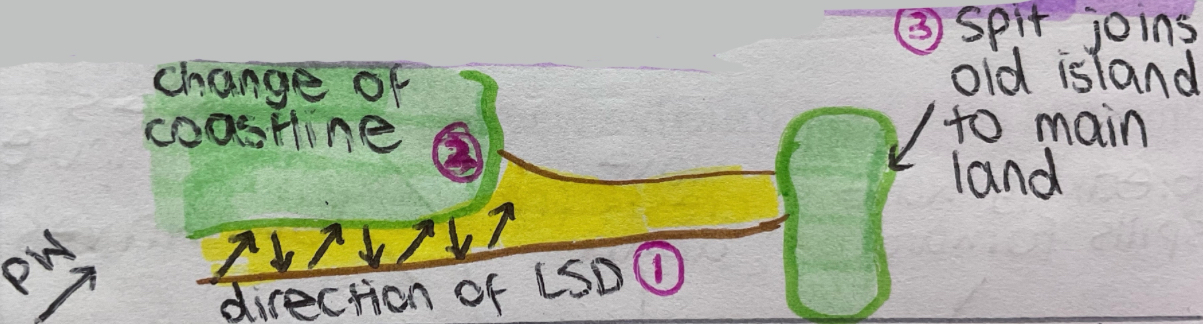
explain how a spit forms
longshore drift transports material along the coast
there is a change in direction of the coastline, and as sediment builds up, it forms an extension
strong wind + waves can curve the end of the spit, forming a recurved end
the area behind the spit is protected - lots of material accumulates, forming a salt marsh or mud flat.
draw a labelled diagram of a spit

where and why does coastal deposition occur?
deposition is when material being carried by seawater is dropped on the coast due to waves slowing down. more deposition may occur when lots of material is available due to lots of erosion elsewhere on the coast.
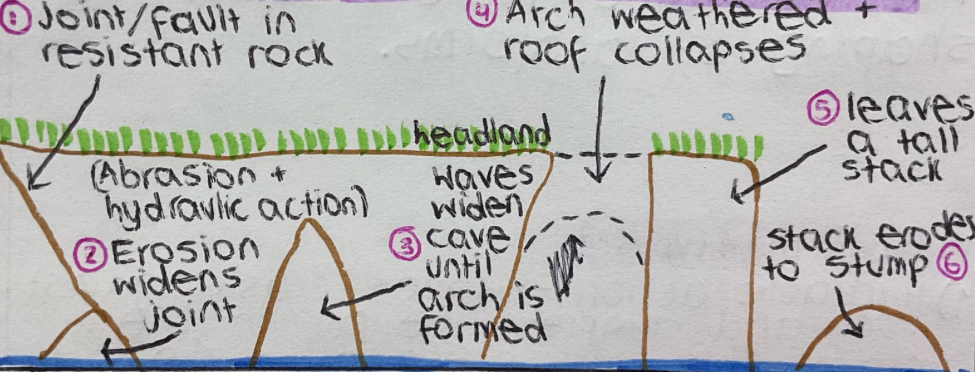
explain how a cave, arch, stack, and stump form
cracks form in resistant rock
hydraulic action and abrasion enlarge the cracks, causing a cave at the cliff base.
continued erosion deepens the cave until it breaks through the headland to form an arch.
the arch is weathered chemically + mechanically and the roof collapses.
this forms a stack, which eventually erodes + collapses to form a stump.
draw a labelled diagram of a cave, arch, stack, and stump
how is material transported along the coastline depending on its size?
traction - large pebbles rolled along the seabed by the force of the water
saltation - pebble-sized particles are bounced along the seabed
suspension - particles are carried along in the water
solution - soluble materials dissolve in the water and are carried along
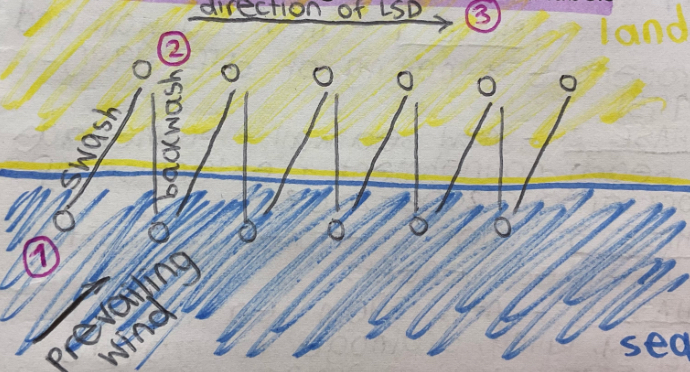
explain longshore drift
the waves move up the beach in the direction of prevailing wind. they hit the coast at an angle.
the swash carries material up the beach.
the backwash then carries material down the beach in a straight line due to gravity.
over time, material is carried along the coastline.
draw a labelled diagram of longshore drift
explain how headlands and bays form
soft rocks have low resistance to erosion, so erodes quickly to form bays (gentle slope)
hard rocks have high resistant to erosion, so eroded slowly to form headlands (steep sides)
these occur on discordant coastlines.
draw a diagram of headlands and bays

define discordant coastline
different rocks + different erosion speeds across the coastline. headlands and bays form.
define concordant coastline
the same rock + erosion speed along the coastline
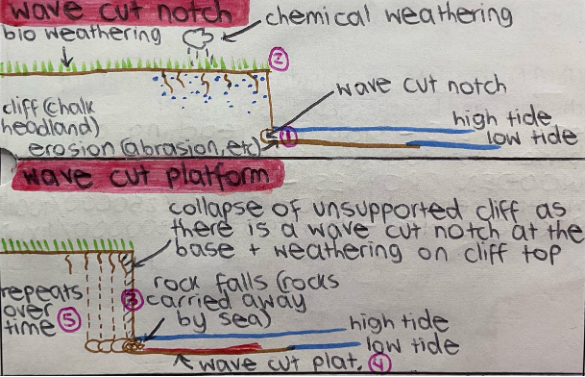
explain how a wave cut platform + wave cut notch forms
at high tide, erosion (name types) is caused at the cliff base, forming a wave cut notch.
the top of the cliff is weathered (name types); it's now unsupported.
the rock above the notch becomes unstable + collapses.
the collapsed material is washed away and a new WCN is formed.
repeating collapsing results in the cliff retreating.
a wave-cut notch platform is left behind as the cliff retreats.
draw a labelled diagram of a wave cut notch and wave cut platform
describe the 3 types of erosion
hydraulic action - waves crash against rock and compress the air in the cracks. this puts pressure on the rock. repeated compression widens the cracks and forces out bits of rock.
abrasion - eroded particles in the water scrape and rub against rock, removing small pieces.
attrition - rock fragments carried by the sea knock against eachother, causing them to become smaller and more rounded.
define erosion
when rocks are broken down and carried away by something (e.g. seawater) + shaping of landforms
describe the 3 types of mass movement
sliding - material shifts in a straight line
slumping - material shifts in a rotation
rock falls - material breaks up and falls down slope
define mass movement
the shifting of loose material + rocks down a slope. it causes coasts to rapidly retreat.
describe the 2 types of weathering
MECHANICAL: freeze thaw weathering - water collects in rock cracks, and at night (if temperature is below 0º), it freezes. when it freezes, it expands, meaning the ice thaws + water seeps deeper into rock. this repeats, breaking up the rock
CHEMICAL: carbonation weathering - rainwater is a weak carbonic acid. it reacts with rocks containing calcium carbonate, dissolving them
define weathering
the breakdown of rocks where they are
what are the features of a constructive wave?
long wave length so low frequency (6-8 waves per minute)
low waves
strong swash, weak backwash
sand + pebbles dropped
breaking wave spills forwards
gentle waves + little energy
what are the features of a destructive wave?
short wave length so high frequency (10-14 waves per minute)
steep waves
weak swash, very strong backwash
erodes sand
wave plunges onto steep beach, energy directed downwards
how do waves form?
by wind blowing over the sea - friction with the water surface causes ripples to form and these develop into waves