ch9: software evolution
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
evolution and servicing stages
Organizations must maintain value of software by changing and updating it.
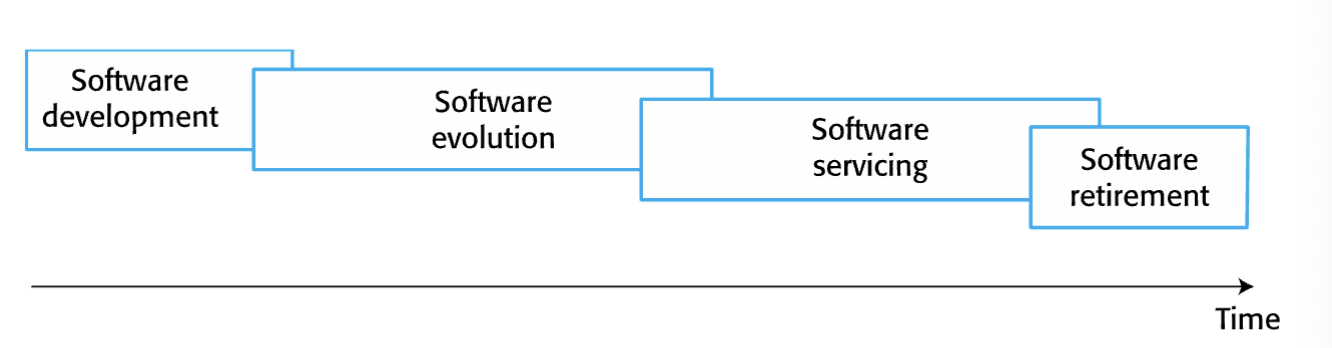
software evolution
An iterative stage in a software system’s life cycle where it is in
operational use and is evolving as new requirements are
proposed and implemented in the system.
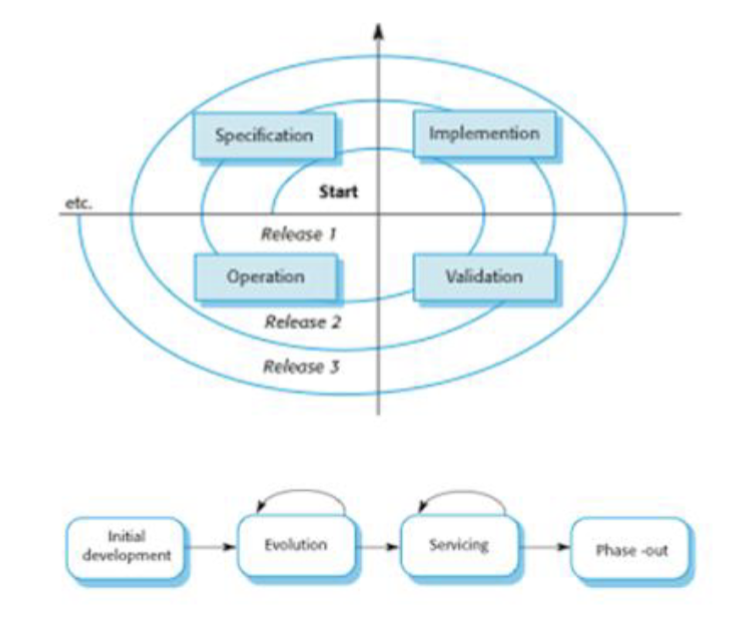
software servicing
At this stage, the software remains useful but the only changes
made are those required to keep it operational, i.e. bug fixes and
changes to reflect changes in the software’s environment. No
new functionality is added.
software retirement
The software may still be used but no further changes are made
to it.
change identification and evolution processes
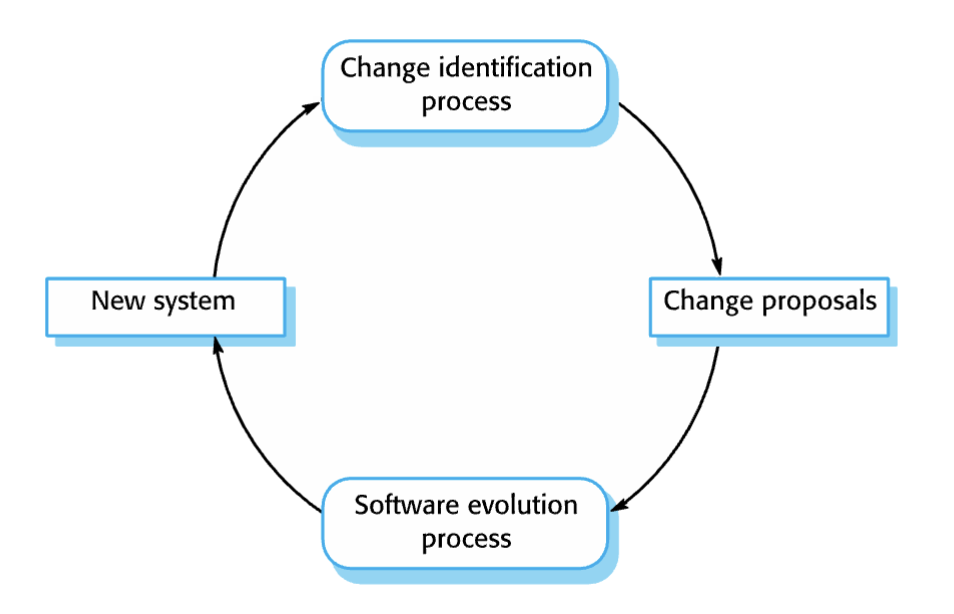
change implementation
Iteration of the development process where the revisions
to the system are designed, implemented and tested.
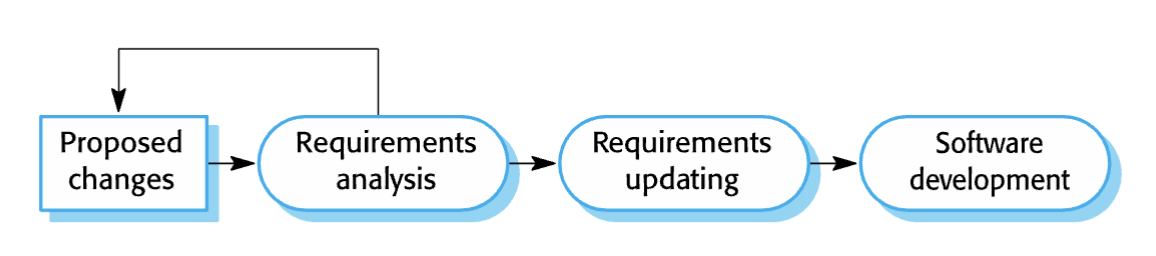
urgent change requests
Change requests that may have to be implemented without
going through all stages of the software engineering process.
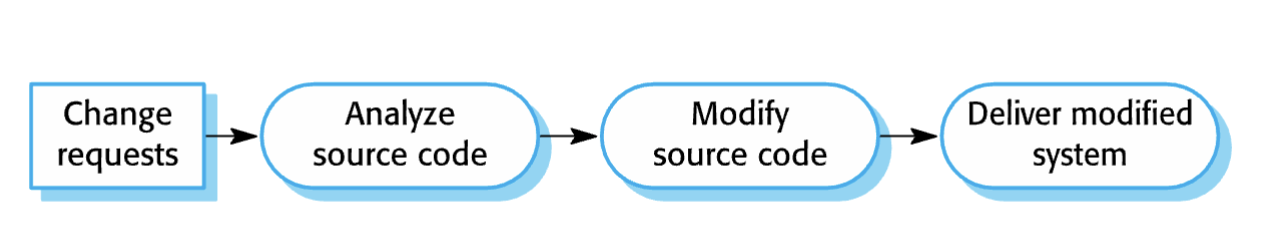
software maintenance
Modifying a program after it has been put into use. Three types:
Bug fixing
Modifying for new environment
Implementing new/changed requirements
types of maintenance
a) fault repairs
b) environmental adaptation
c) functionality addition and modification
maintenance effort distribution
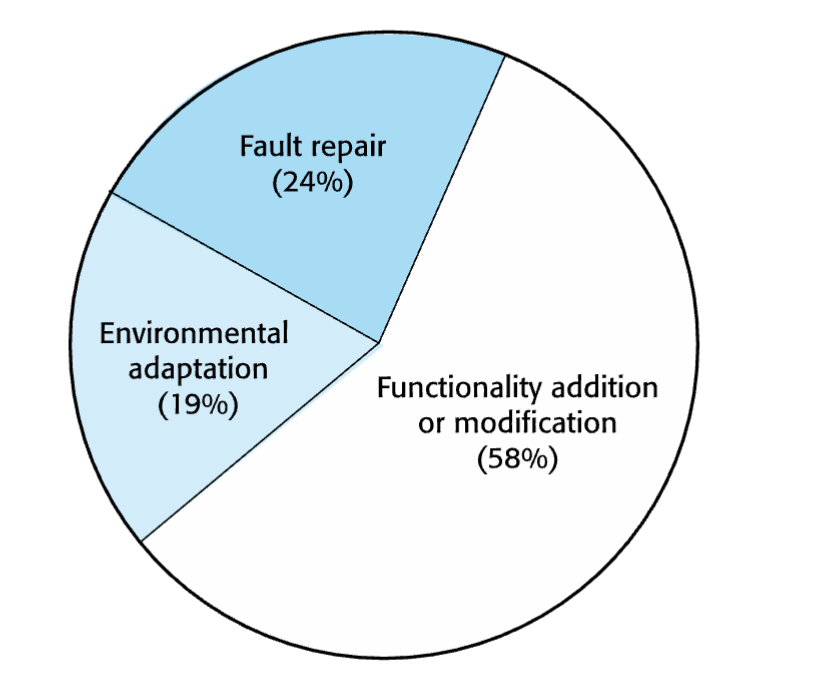
maintenance costs
Costs of preserving software, which is usually greater than development cost.
software reengineering
Restructuring or rewriting part or all of a legacy system
without changing its functionality, after a system has been maintained for some time.
advantages of reengineering
reduced risk
reduced cost
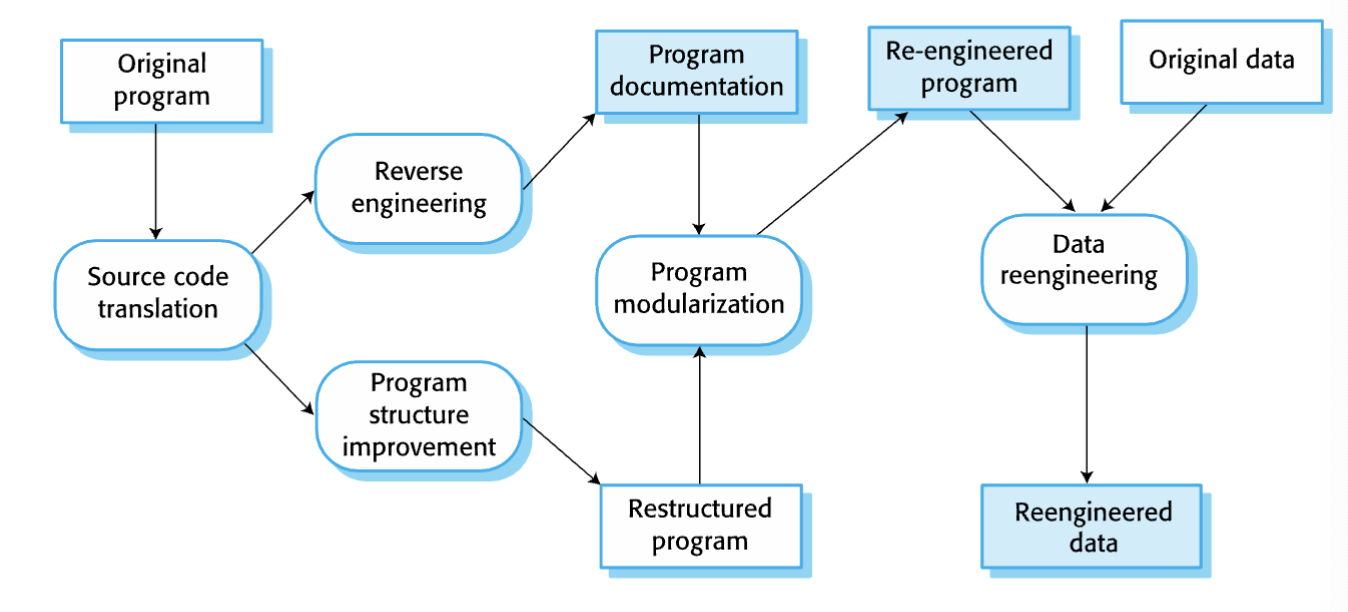
reengineering process activities
source code translation
reverse engineering
program structure improvement
program modularization
data reengineering
reengineering cost factors
software quality
tool support
extent of data conversion required
availability of expert staff
refactoring
‘Preventative maintenance’; Process of continuously making improvements to a program to slow down degradation through change.
bad smells
duplicate code
long methods
switch statements
data clumping
speculative generality