2. transporting CO2
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
CO2 TRANSPORT- 1 AND 2
CO2 transported through circulatory system in 3 ways:
dissolved in plasma (5%)
associated w/ Hb to form carminohaemoglobin (10%)
CO2 TRANSPORT- 3 DIAGRAM
85% of CO2 is transported as hydrogen carbonate ions in erythrocytes
enzyme carbonic anhydrase catalyses reversible reaction between CO2 and H2O
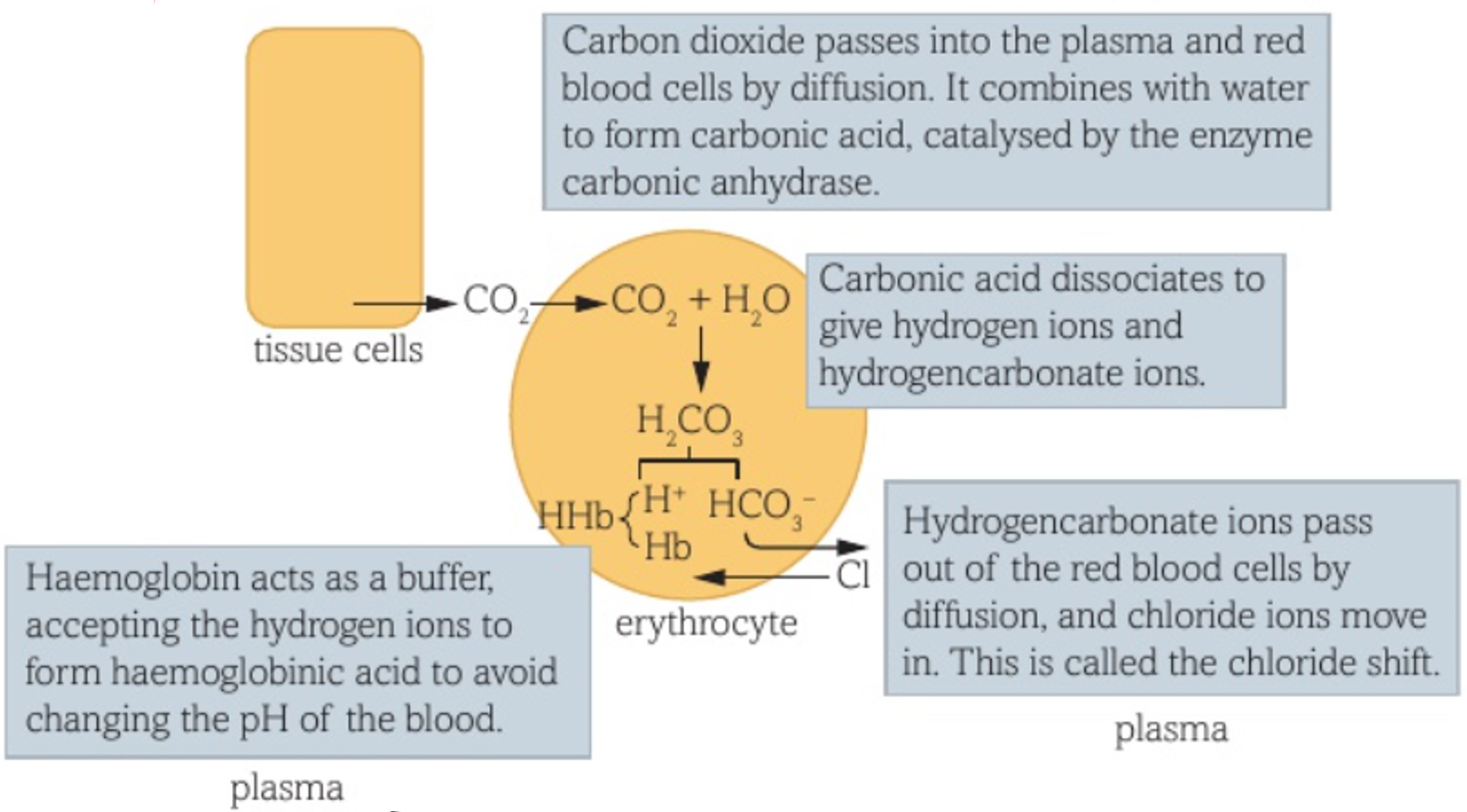
CO2 TRANSPORT- 3
CO2 dissolves in H2O to form carbonic acid (carbonic anhydrase catalyst)
CO2 + H2O —> H2CO3
carbonic acid releases H+ protons (acid dissociation)
H2CO3 —> HCO3^- + H+
HCO3^- (hydrogencarbonate) ions diffuse out of erythrocyte
Cl- diffuse into cell to balance charge —> CHLORIDE SHIFT
H+ ions will bind w/ Hb to form haemoglobinic acid
CO2 EFFECT ON O2 DISSOCIATION
O2 dissociates from oxyhaemoglobin where pO2 is low (i.e. respiring tissues)
if H+ ions can bind w/ Hb, they must compete w/ O2
in respiring tissue:
more CO2 produced
more carbonic acid formed
more H+ dissociated
more competition for Hb
more O2 dissociation
O2 released more readily to muscle cells
BOHR EFFECT
in CO2 rich env (i.e. at respiring tissue) more O2 dissociates from oxyhaemoglobin
O2 dissociation curve shifts right
(requires higher pO2 to saturate Hb due to H+ competition)
known as bohr effect
