Fluids & Hydration
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
what percentage of our BW does extracellular fluid take up?
~20%
what percentage of our BW does intracellular fluid take up?
~40%
what percentage of our BW is fluid?
~60%
what is the movement of water from low solute concentration (ISF) to high concentration (blood)?
osmosis
what is defined as excessive amount of fluid in the interstitial compartment (in the tissues/not bloodstream)?
edema
what are the 4 causes of edema?
1. Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure
2. Loss of plasma proteins: Particularly albumin. Results in decreased plasma osmotic pressure
3. Obstruction of lymphatic circulation: Causes localized edema. Excessive fluid and protein. Not returned to general circulation
4. Increased capillary permeability
What is caused by higher BP or increased BV? Forces increased fluid out of capillaries into tissue. Cause of pulmonary edema
Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure
Increased capillary permeability usually causes localized edema. May result from an
inflammatory response or infection. Histamines & other chemical mediators increase capillary permeability
what are the effects of edema?
Pain: Edema exerts pressure on nerves locally. Headache w/ cerebral edema. Stretching of capsule in organs (kidney, liver)
Impaired arterial circulation: Ischemia leading to tissue breakdown
Susceptible to tissue breakdown in skin from pressure
How does the body regulate fluid thru thirst?
Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus
How does the body regulate fluid thru Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)?
reabsorption of water from the kidney tubules
How does the body regulate fluid thru Aldosterone?
reabsorption of sodium and water in kidneys
How does the body regulate fluid thru Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)?
Synthesized by myocardial cells
Regulation of fluid, sodium, & potassium levels
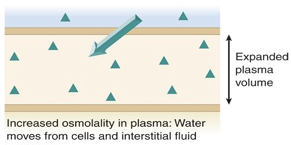
what kind of IV causes water to move from interstitial space to plasma
Hypertonic intravenous fluid (enter)
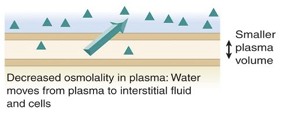
what kind of IV causes water to move from plasma to interstitial space
Hypotonic intravenous fluid (out)
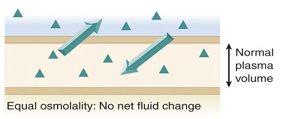
no fluid shift
isotonic intravenous fluid
what kind of IV solutions has electrolytes?
●Used to replace fluids & promote urine output
●Capable of leaving plasma & moving to interstitial spaces & intracellular fluid (dependent on tonicity)
Crystalloids IV Fluids
What IV fluids have Molecules too large to easily cross capillary membrane?
colloids (isotonic but have hypertonic effect) (albumin)