Lecture 7: Skeletal Muscle Structure and Functions
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
function of mucles
movement, maintain posture, stabilize joints, generate heat
functional characteristics of muscles`
excitability, elasticity, contractility, extensibility
types of muscles
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
smooth muscle characteristics
Location: wall of hollow organs, vessels, respiratory passageways
Cell characteristics: tapered at each end, branching networks, nonstriated
Control: Involuntary control
Action: Produce peristalsis- contracts and relaxes slowly, may sustain contraction
cardiac muscle characteristics
Location: wall of heart
Cell characteristics: branching networks, special membranes (intercalated disks) between cells, single nucleus; lightly striated
Control: Involuntary control
Action: pumps blood out of heart; self-excitatory but influenced by nervous system and hormones
skeletal muscle characteristics
Location: attached to bones
Cell characteristics: long and cylindrical; multinucleated; heavily striated
Control: Voluntary control
Action: Produces movement at joints; stimulated by nervous system; contracts and relaxes rapidly
hierarchal organization of muscle
bones
muscle
surrounded by epimysium
fascicles
surrounded by perimysium
muscle fibers (cells)
covered by endomysium
myofibrils
surrounded by sarcoplasmic reticulum
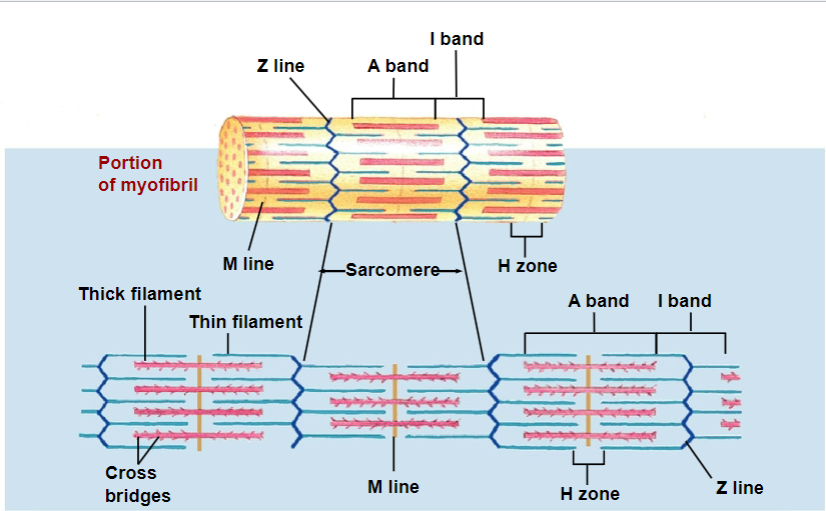
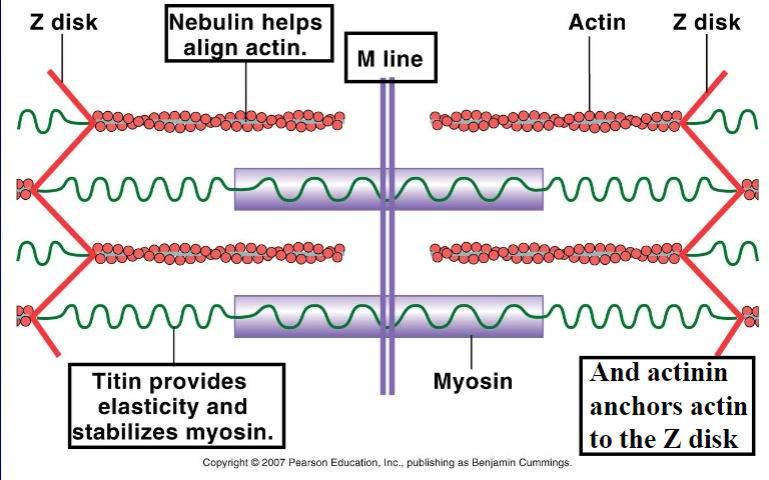
sarcomere
thick and thin filaments (myosin and actin)
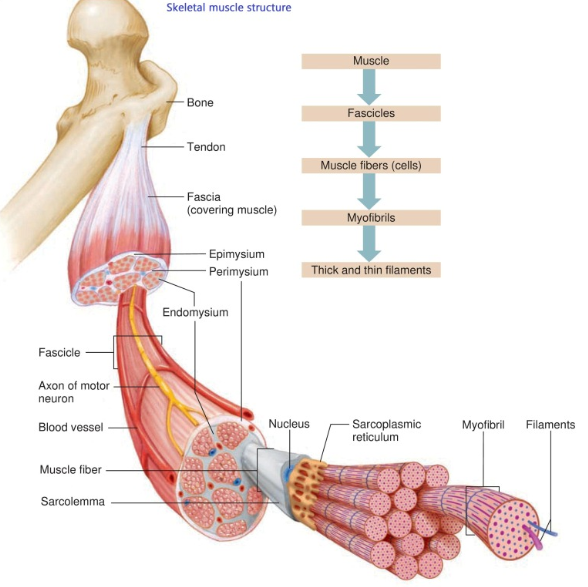
the muscle fiber is surrounded by _____ and contains _______
endomysium, myofibrils
myofibrils are surrounded by _______, and contains ________
sarcoplasmic reticulum, sarcomeres (Z line to Z line)
sarcomeres contain
thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments
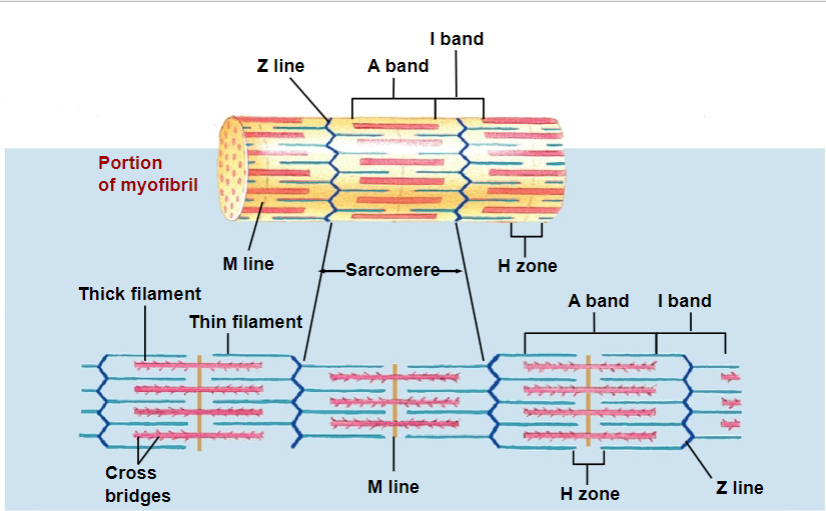
sarcomere
basic unit of contraction
has repetitive units of overlapping filaments w/ myofibrils
Z-disc/line forms boundary b/w adjacent sarcomeres
myofilaments: M line
cytoskeletal proteins that stabilizes myosin
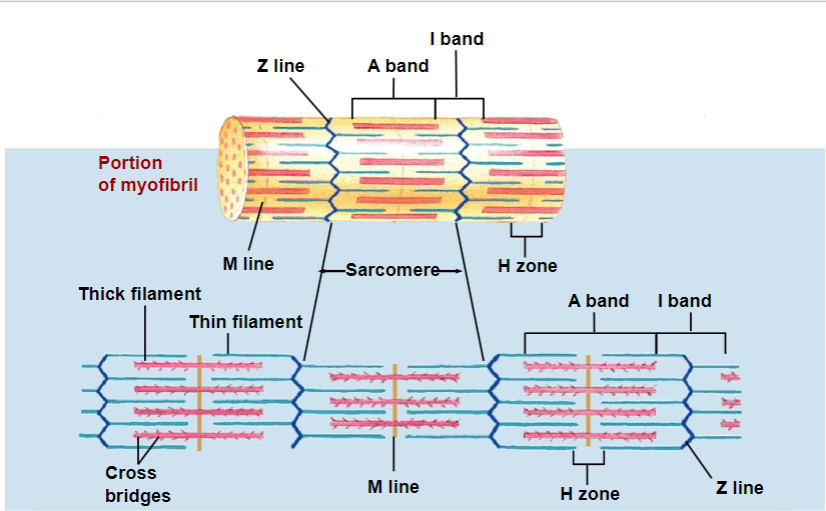
myofilaments: H zone
myosin only (no actin overlap)
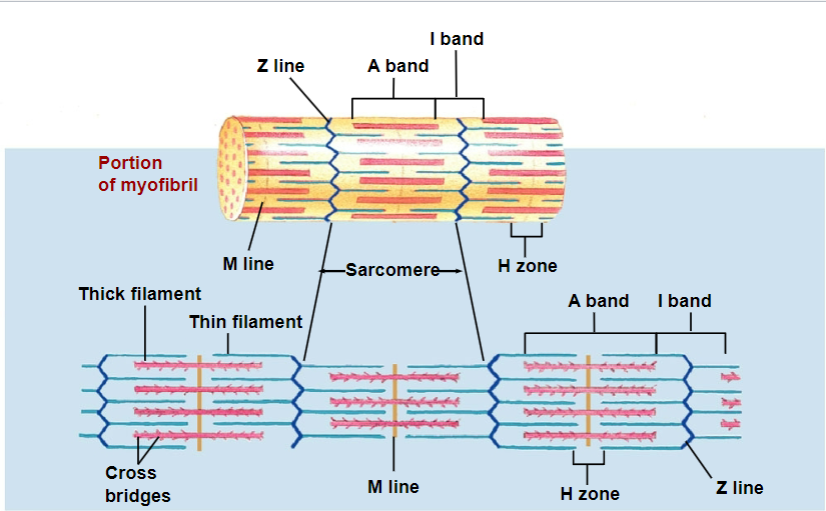
myofilaments: A band
length of myosin (w/ some actin overlap); thick filaments
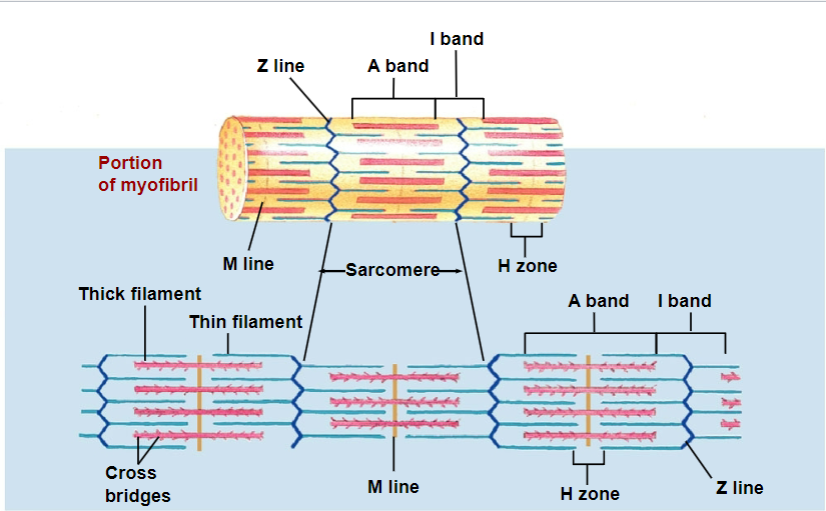
myofilaments: I band
actin ONLY (no myosin overlap); thin filaments
Nebulin
protein that aligns actin
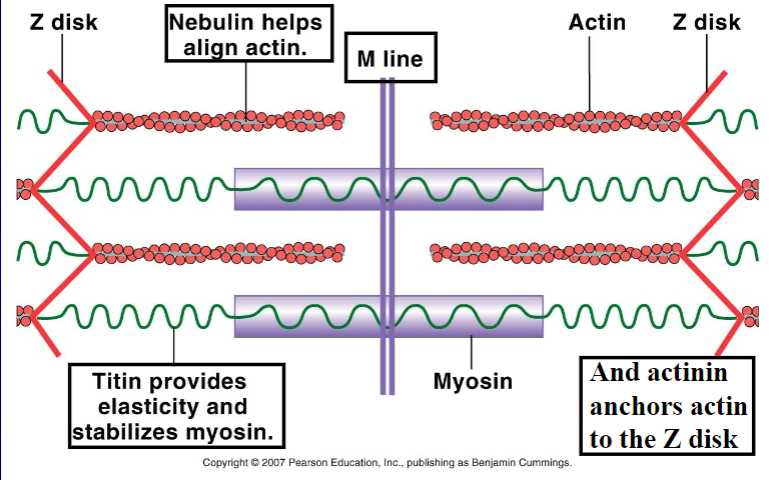
actinin
protein that anchors actin to z-disk/line
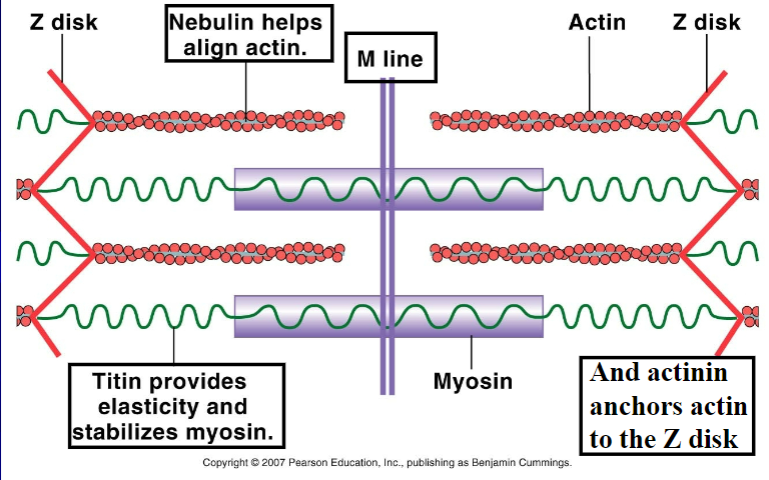
titin
protein that provide elasticity and stabilize myosin
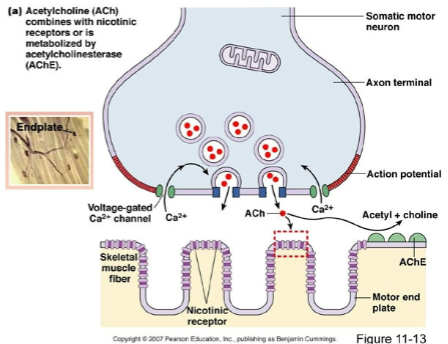
which nervous system branch is involved in skeletal muscle
somatic nervous system (of the peripheral nervous system)
skeletal muscle and nerves are organized into ________
motor units (neuron + all muscle fiber it innervates)
small motor units
has high precision BUT low force control
a single motor neuron triggers fewer than 10 muscle fibers
example: in the eye and fingers
large motor units
has high force BUT low precision actions
a single motor neuron triggers 1000-2000 in quadriceps, biceps, gastrocnemius
motor end plate
is the postsynaptic membrane of the muscle fiber
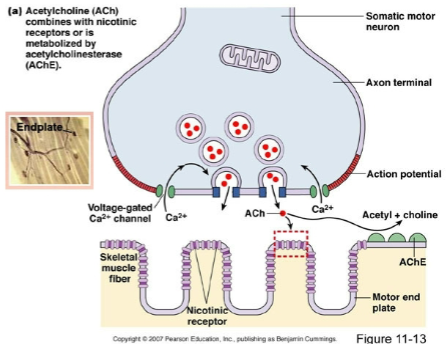
ACh combines with ________ _________ or is metabolized by ____________________
nicotinic receptors; acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
what are the effects of botulinum toxin (botox)?
blocks the release of ACh; interferes with synapsins that move vesicles containing ACh = prevents muscle contraction (paralysis)
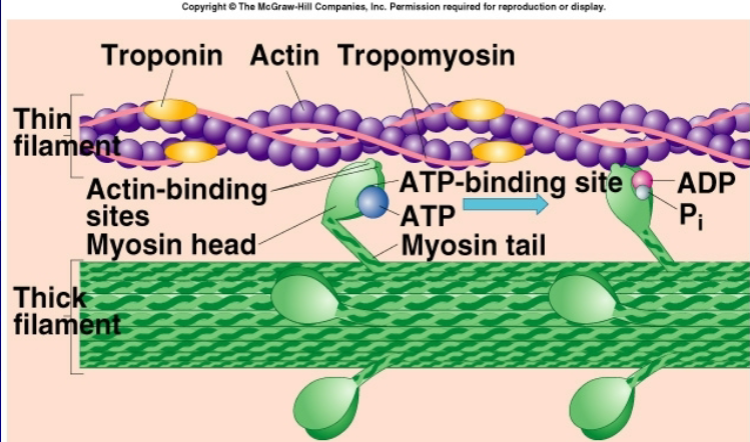
what causes sliding of myofilaments?
sliding of myofilaments is triggered by myosin-actin cross bridge formations
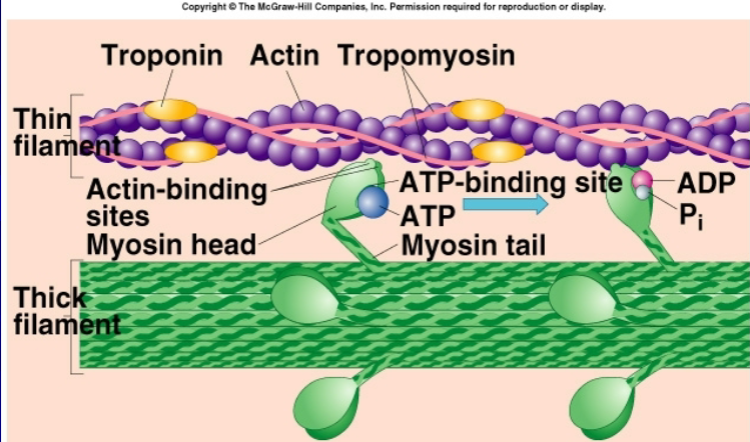
what causes cross bridges?
when myosin head that extend out toward actin
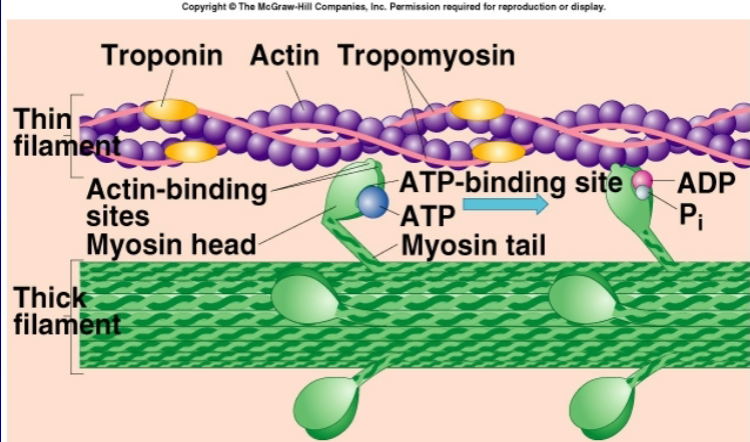
myosin head contains
actin binding site
ATP binding site (location of myosin ATPase)
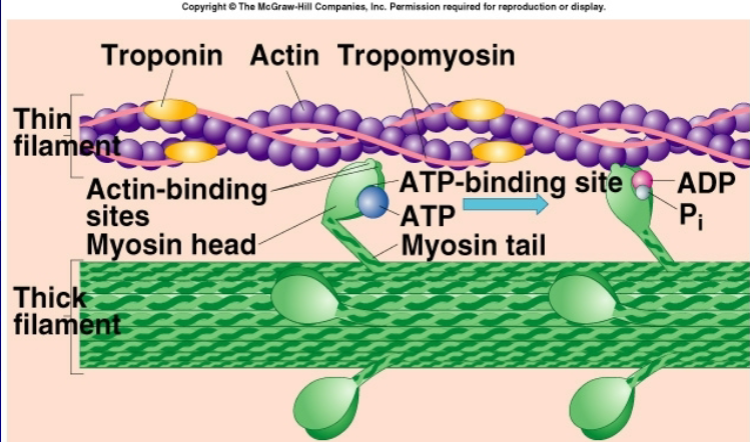
troponin
promote muscle contraction; frees binding site of actin filaments
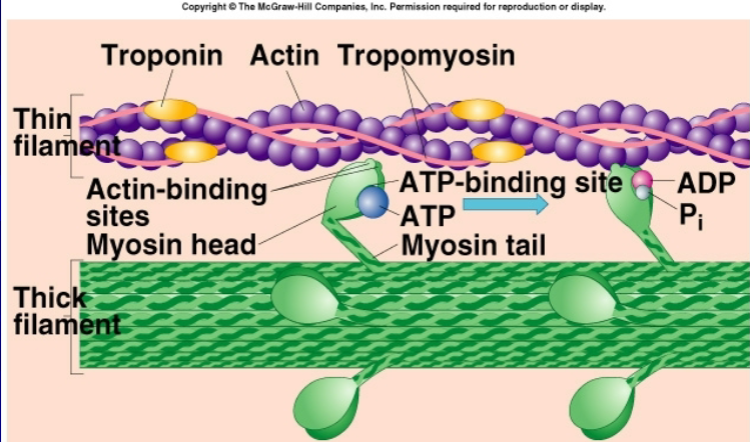
tropomyosin
inhibit contraction; blocks binding sites
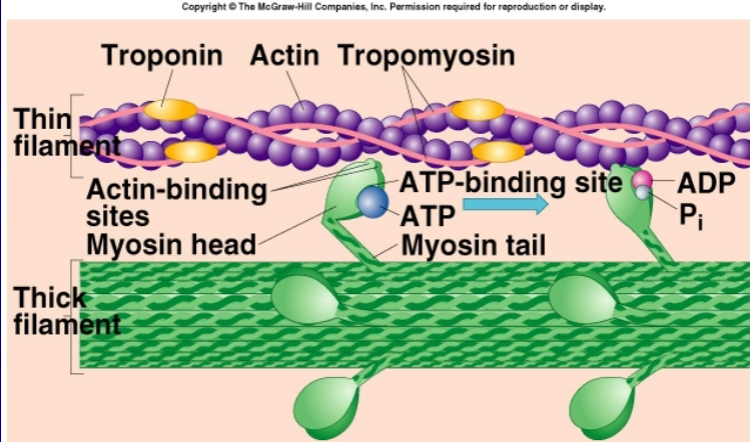
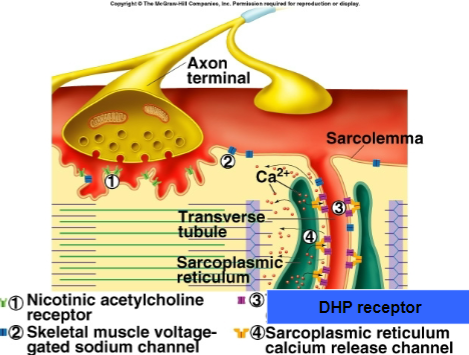
mechanism of skeletal muscle contraction (from motor end plate to cross bridge formation)
AP to motor end plate (NMJ)
releases ACh into synaptic cleft
ACh binds to receptors on sarcolemma (muscle cell membrane)
opens Na+ channels, sodium enters muscle fiber leading to depolarization and generation of new AP
AP propagated and travels along sarcolemma and down through T-tubules
causing Ca2+ to be released to cytosol from the SR
Ca2+ binds to troponin, changing its shape
Tropomyosin moves away from myosin binding site on actin filament
Myosin head attach to actin, forming cross bridge
Binding of myosin trigger release of ADP and Pi causing myosin head to pivot and pull actin filament toward center of sarcomere = power stroke
sliding of actin over myosin shortens sarcomere = muscle contraction
in muscle contraction, which bands shorten and which DOES NOT shorten?
I and H bands: shorten
A bands: do not shorten
Role of ATP in muscle function
ATP hydrolyzed by ATPase and yields ADP, Pi and stored energy necessary for muscle contraction
myosin ATPase splits ATP to ADP and Pi
ADP and Pi remain attached to myosin
myosin attaches to actin
Pi is released, triggering power stroke
ADP then detaches to myosin and another ATP binds, causing cross-bridges to break
cross bridges detach and is ready to bind again
Role of Ca2+ in muscle function
Ca2+ binds to troponin
tropomyosin-troponin complex conformational change
exposures of myosin binding site in actin filament
cross bridges of myosin head with actin
role of Ca2+ in muscle contraction; receptors
DHP receptors detect the change in membrane potential as the action potential travels down the T-tubules; their activation opens ryanodine receptors in the SR, facilitating Ca²⁺ release
calcium is released from SR terminal cisternae thru calcium channels (ryanodine receptors - responsible for the release of calcium from the SR into the cytosol thru depolarization of T-tubules)
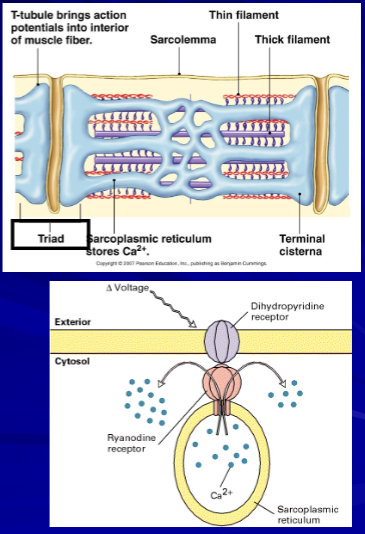
big picture: excitation-contraction coupling
NT release
depolarization (Na+ influx) of motor end plate
voltage activation of t-tubules (DHP receptor) that results in
activation of SR Ca2+ channels (ryanodine receptor)
what happens in muscle relaxation?
AP stop
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) degrades and recycles ACh
DHP receptors returns to original conformation
Ca2+ release channels (Ry receptors) close
Ca2+ pumped back into SR through Ca2+-ATPase pumps (SERCA)
types of muscle fibers
slow twitch (type I)- red (red d/t myoglobin protein that carry oxygen)
intermediate (type IIa)
fast twitch (type IIb/x) - white (bigger stronger contractions)
classified on basis of contraction speed
ATP generation of each of the muscle fibers
Type I - oxidative phosphorylation (36 molecules of ATP)
Type IIa - glycolysis (2 molecules of ATP)
**Type IIb/x - creatine phosphate (1 molecule of ATP)
Type I fiber characteristics
aka slow oxidative (SO)
red fibers
aerobic metabolism
fatigue-resistant
well vascularized (high blood supply)
numerous mitochondria (enzymes for aerobic metabolism)
high myoglobin concentration
small diameter
ex) long distance race (marathon) “endurance”
myosin ATPase activity is slow
rate of Ca2+ uptake by SR is slow to intermediate
Type II fiber characteristics
fast twitch (type IIb or IIx fibers)
aka fast glycolytic (FG)
white fibers
anaerobic metabolism (few mitochondria)
large stores of glycogen (glycolysis)
poorly vascularized
highly fatigueable
large diameter (POWER)
intermediate (type IIa fibers)
aka fast oxidative glycolytic (FOG)
aerobic metabolism
moderate resistance to fatigue
myosin ATPase activity is fast
rate of Ca2+ uptake by SR is high