Ch.17 Cell Growth and Division
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
What is the surface area and how is it calculated?
It is the amount of covering of the object. You calculate it by using the formula: LxWx6
What is volume and how is it calculated?
It is the amount of space inside the object. You calculate by using the formula: LxWxH
What is Asexual Reproduction?
Is the production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. All the genes come from one parent, so the offspring are identical to the parent. Many single celled organisms such as bacteria reproduce this way.
What is Sexual Reproduction?
It involves the fusion of two reproductive cells, an egg cell and a sperm cell from two parents. Offspring produced by sexual reproduction inherit some of their genetic information from each parent.
How many parents are involved in Asexual Reproduction?
One singular parent
How many parents are involved in Sexual Reproduction?
Two parents.
Are the offspring identical or different in Asexual Reproduction?
Identical
Are the offspring identical or different in Sexual Reproduction?
Different
How many offspring are produced in Asexual Reproduction, few or many?
Many
How many offspring are produced in Sexual Reproduction, few or many?
Few
Is it a fast or slow process in Asexual Reproduction?
Fast
Is it a fast or slow process in Sexual Reproduction?
Slow
What happens to the offspring if the environment changes in Asexual Reproduction?
In a changing environment the offspring do not adapt well and die.
What happens to the offspring if the environment changes in Sexual Reproduction?
In a changing environment genetic diversity is beneficial.
What are some Advantages in Asexual Reproduction?
Reproduce offspring quickly
Produces many offspring
You don't need a partner/mate
In stable environments genetically identical offspring thrive
What are some Disadvantages in Asexual Reproduction?
The offspring are genetically identical to the parents and lack variation
In a changing environment the offspring do not adapt well and die
What are some Advantages in Sexual Reproduction?
It produces offsprings that are genetically diverse and different
In a changing environment genetic diversity is beneficial
What are some Disadvantages in Sexual Reproduction?
Produces fewer offspring
You need a partner/mate
It's a slower process
What is a consequence that can happen if a cell gets too large?
The larger a cell becomes the less effective it is in moving nutrients and waste materials across the cell membrane.
Prokaryotic cells reproduce through asexual reproduction, through a process called:
Binary Fission
What is Binary Fission
It is a type of asexual reproduction where a single-celled organism divides into two identical daughter cells.
How does interphase prepare a cell to divide?
By growing, copying its DNA, and making the necessary parts for cell division.
What is the cell cycle?
Is a series of events where the cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form two daughter cells.
What are the 3 phases of Interphase? What happens in each phase of interphase?
Gap 1- The cell grows.
Synthesis - new DNA is synthesized as the chromosomes are replicated. By the end of the S phase the cell has twice as much DNA.
Gap 2 - the organelles and molecules required for cell division are produced. At the end of Gap 2 the cell is ready to enter the M phase and begin the cellular division.
What are the three checkpoints in the cell cycle?
G1 checkpoint: allows entry into the S phase or causes the cell to leave the cycle
G2 checkpoint
M checkpoint
What happens to a cell that does not pass a checkpoint?
If a cell does not pass a checkpoint, it either pauses to fix the problem, or if the damage is too serious, it may self-destruct through a process called apoptosis (programmed cell death).
True/False. Telophase happens first, followed by cytokinesis.
False
Mitotic spindles help with cellular division and they come from:
Centrioles
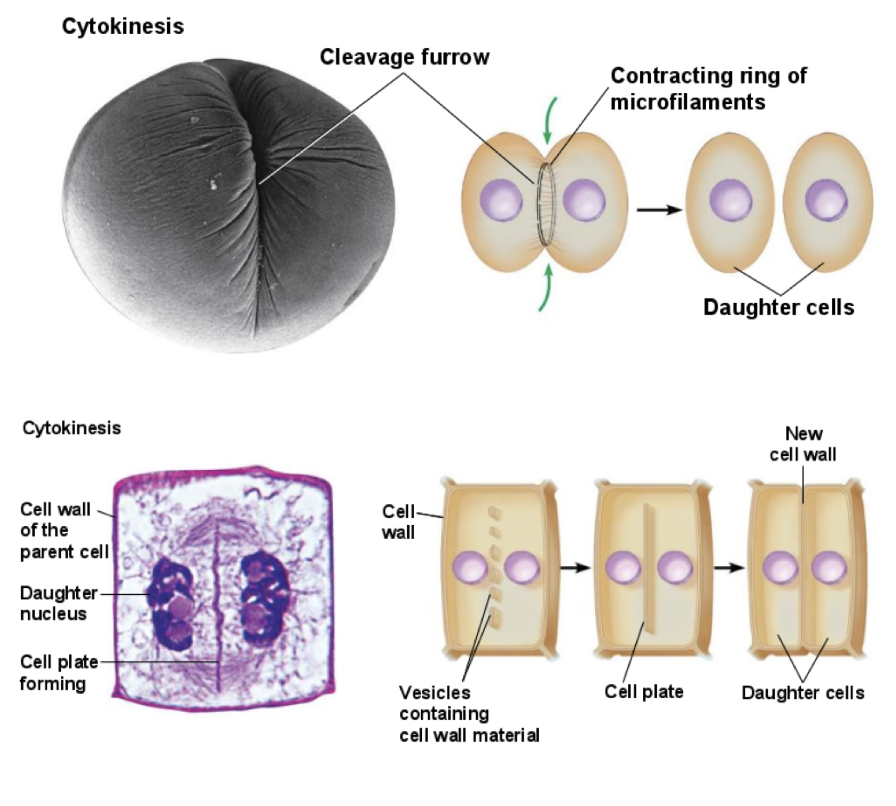
How is cytokinesis different in animal and plant cells?
It is different in animal and plant cells because animal cells form a cleavage furrow that pinches the cell in two, while plant cells build a cell plate that develops into a new cell wall between the two daughter cells.
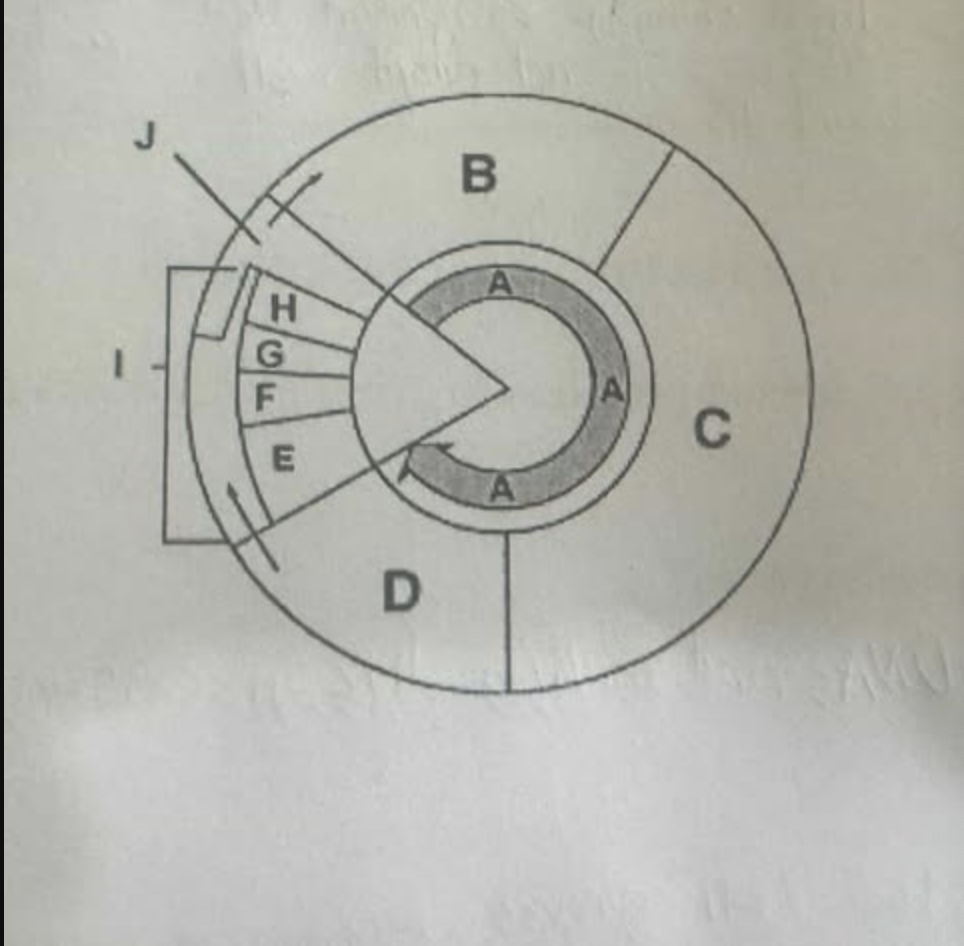
What are all the phases of the cell cycle that is shown?
A = Interphase
B = Gap 1
C = Synthesis
D = Gap 2
E = Prophase
F = Metaphase
G = Anaphase
H = Telophase
I = Mitosis
J = cytokinesis
What are the number of cell division in Mitosis?
One
What is the function of Mitosis?
Growth, regeneration of new cells.
Is Mitosis Diploid or Haploid cells?
Diploid
Does Mitosis have genetically different or identical cells?
identical
Where is Mitosis located in your body?
In your body cells
What is the type of reproduction that is associated with Mitosis?
Asexual reproduction
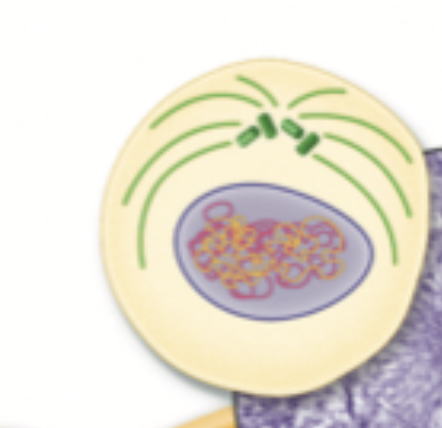
What phase is this?
Interphase
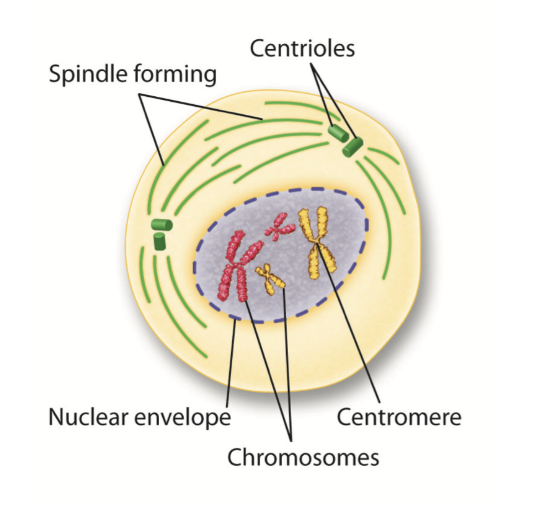
What phase is this?
Prophase
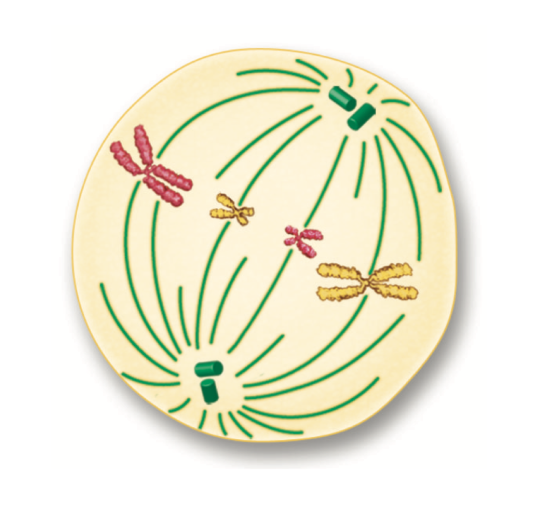
What phase is this?
Metaphase
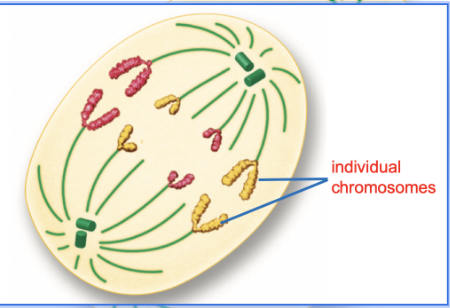
What phase is this?
Anaphase
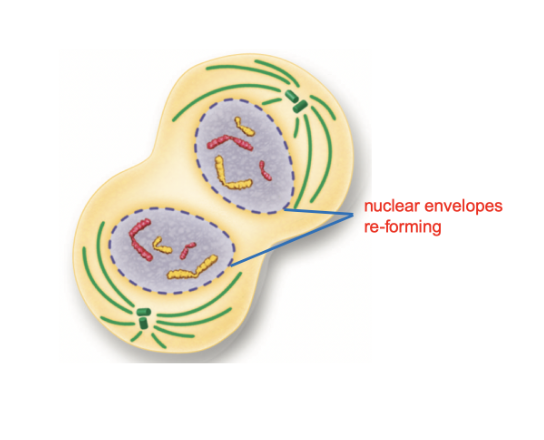
What phase is this?
Telophase
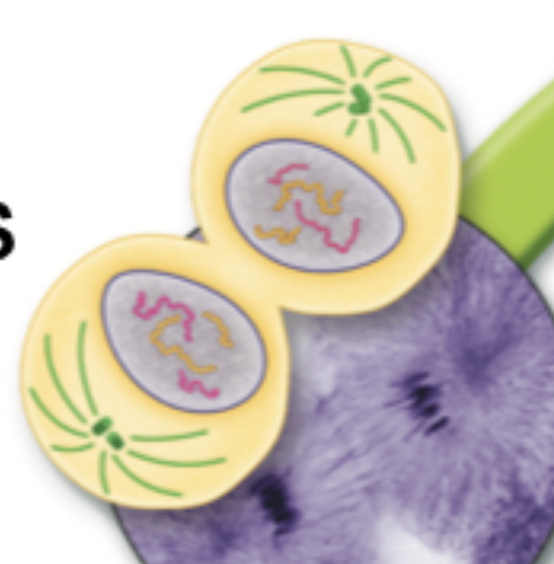

What phase is this?
Cytokinesis
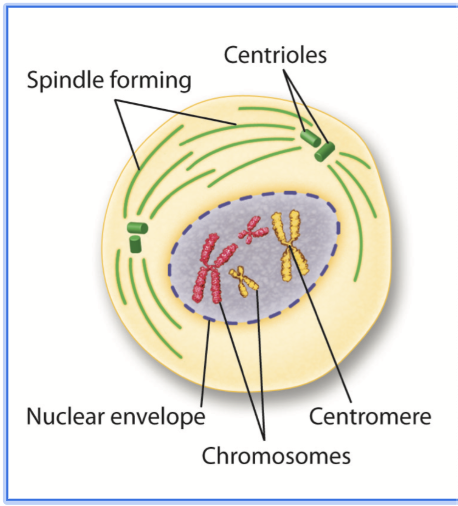
What happens in Prophase?
It's the longest phase
Genetic material inside the nucleus condenses into chromosomes, they duplicate, and become visible.
Each chromosome condenses into sister chromatids that are attached in the center by a centromere.
Centrioles appear, they move towards opposite ends of the cell, and mitotic spindle fibers begin to form.
Spindle fibers will help to separate the chromosomes.
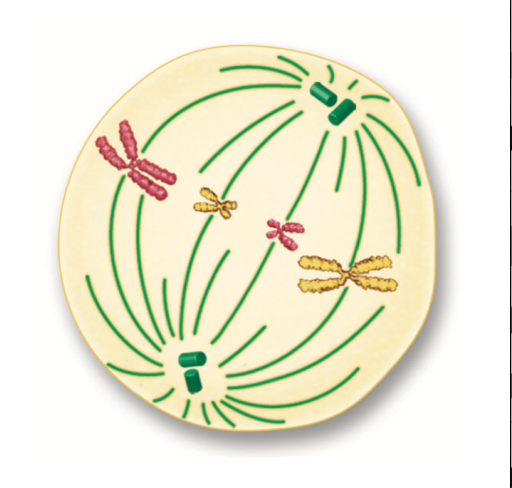

What happens in metaphase?
The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell.
Spindle fibers connect to the centromere of each chromosome.
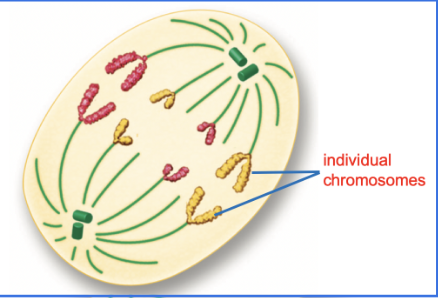
What happens in anaphase?
The sister chromatid separate and begin to move apart towards opposite ends of the cell.
The mitotic spindle fibers help to pull the chromosomes apart.
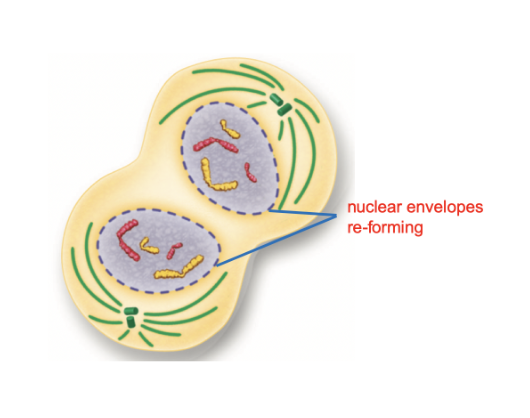
What happens in Telophase?
The chromosomes begin to spread out.
The nuclear envelope re-forms around each cluster of chromosomes until a nucleus becomes visible in each daughter cell.
The mitotic spindle disappear into the centrioles.
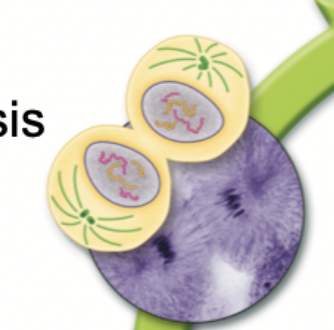
What happens in Cytokinesis?
The division of the cytoplasm to form two daughter cells.
It happens at the same time as telophase.
It completes the process of cell division by dividing one cell into two cells.
At the end you have two identical daughter cells.
What is the cell plate?
It is a structure that forms in the middle of a dividing plant cell during cytokinesis, eventually becoming the new cell wall that separates the two daughter cells.
What is centromere?
It is the region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids are held together and where the spindle fibers attach during cell division to help pull the chromatids apart.
What is sister chromatid?
It is one of two identical copies of a chromosome that are joined together at the centromere after DNA is replicated.
What are Internal Regulators?
Proteins that respond to events inside the cell.
They act as a checkpoint that allows the cell cycle to proceed only when certain events have taken place.
Ex: one checkpoint ensures that a cell does not enter mitosis until the chromosomes have been replicated.
What are external regulators?
Proteins that respond to events outside the cell, such as growth factors, which simulate the growth and division of cells
They direct the cell to speed up or slow down the cell cycle.
This happens during embryonic development and wound healing.
When a person breaks a bone, cells at the edge of the injury are stimulated to divide rapidly.
Others are found on the surface of neighboring cells, They cause cells to slow down or stop their cell cycle, preventing excessive cell growth.
What is Cyclin?
It is a type of protein that helps regulate the cell cycle by controlling when a cell should start dividing, making sure everything happens at the right time. (When injected into a nondividing cell, a mitotic spindle would form.)
What are mitotic spindle?
Is a structure made of microtubules that forms during cell division to pull chromosomes apart and move them to opposite ends of the cell.
What is apoptosis?
Is a process of programmed cell death. Once its is triggered, a cell undergoes a series of controlled steps leading to its self-destruction.
What is cancer?
Is uncontrolled cell growth. The body loses the ability to control cell growth. These cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the cell cycle causing cells to grow and divide uncontrollably.
What are Benign tumors?
They are noncancerous tumors, which don’t have cancer and they don’t spread / metastasise to surrounding tissue or to other parts of the body.
What are Malignant tumors?
They are cancerous tumors and they invade and destory surrounding healthy tissue.
What happen when cancer spreads?
As the cells spread to surrounding healthy tissue, they absorb the nutrients needed by other cells, block nerve connections, and prevent the organs they invade from function properly.
The balance in the body are disrupted and life threatening illness happen.
What causes Cancer?
Defects, smoking, chewing tobacco, radiation exposure, and viral infection can cause cancer.
What happens when cancer comes into effect?
The control over the cell cycle has been broken.
Some cancer cells will no longer respond to external growth regulators, while others fail to produce the internal regulators that ensure orderly growth.
How does Cancerous tumors remover work?
Since cancer cells divide very quickly, so they constantly copy their DNA. Because of this, they are more easily harmed by high-energy radiation, which can damage their DNA so badly that they can’t divide anymore and eventually die.
Radiation therapy focuses directly on the tumor (localized) to kill cancer cells and shrink the tumor, but it can also accidentally harm nearby healthy cells.
What are chemotherapy?
Are chemicals that kill or slow the growth of cancer.
Why do chemotherapy treatments cause side effects, and what are researchers doing to improve cancer treatment?
Chemotherapy drugs don’t just kill cancer cells — they also harm healthy cells that divide quickly, like those in the hair, skin, and stomach. That’s why many patients have serious side effects like hair loss, nausea, or skin issues. Since chemo travels through the whole body, it affects more than just the cancer. Scientists are working on better treatments that only target cancer cells without hurting the healthy ones.
How does T cell therapy enhance the immune system’s ability to fight cancer?
T cell therapy involves removing immune cells called T cells from a patient's blood, genetically modifying them to recognize cancer cells, and then injecting them back into the patient to help the immune system target and kill the cancer cells.
Why is childhood cancer research underfunded, and what impact does this have on treatment and survival rates?
Childhood cancer is the second leading cause of death among children, but only 4% of the national cancer research budget is spent on researching it. As a result, only 3 new drugs have been developed for children in the past 30 years, while 23 new drugs were developed for adults in 2012 alone. There are also no screening methods for early detection, so children are often diagnosed with cancer only at stage 4, when it is more advanced. Every day, 7 children die from cancer, and 36 children are diagnosed with it.
What is cellular differentiation?
It Is the process by which a cell changes into a more specialized type with a specific function.
True/False. Once a cell differentiates, it stays that type of cell until it dies.
True
What is blastocyst?
A hollow ball of cells with a cluster of cells inside knowns as the inner cell mass.
What happens to the outer cells of a blastocyst?
It forms tissues that will be attached to the embryo to its mother. which is the placenta. The placenta will help providing nutrients and oxygen to the developing embryo and removes waste products.
What happens to the inner cells of a blastocyst?
It becomes the embryo itself
What are stem cells? And where are they found?
Are the unspecialized cells from which differentiated cells develop. Stem cells are found in the early embryo and in many places in the adult body.
A zygote is totipotent, what does totipotent mean?
It means its able to do everything to develop into any type of cell in the body, including the cells that made up the embryonic membranes and placenta.
Where are Embryonic Stem cells found?
Inner cell mass of a blastocyst
Where are Adult Stem cells found?
Brain, heart, skeletal muscles, and bone marrow
What does multipotent mean?
Are cells that can develop into several types of related cells, but not all cell types. For example, adult stem cells are multipotent because they can form different types of cells, like blood cells, but cannot form cells from other unrelated tissues like nerve cells.
What does pluripotent mean?
Cells that can develop into almost any type of cell in the body, but not extra-embryonic tissues like the placenta. An example is embryonic stem cells, which can give rise to all of the body's cell types, including muscle, skin, and nerve cells.
Are Embryonic stem cells multipotent or pluripotent?
pluripotent
Are Adult stem cells multipotent or pluripotent?
multipotent
Is there ethical issues over Embryonic stem cells?
Yes, obtaining these cells involves destroying embryos, which some people believe is morally wrong because they view the embryo as having the potential for life.
Is there ethical issues over Adult stem cells?
No, because they are usually collected from fully developed tissues.
How can stem cell therapy help repair damage caused by heart attacks, and what challenges might it face?
Heart attacks damage the heart by cutting off blood supply to part of the heart muscle, causing the muscle cells to die. To help repair the damage, stem cells harvested from the bone marrow might be cultured and injected into the damaged area of the heart. Once injected, these stem cells would transform into the type of cells needed (heart muscle cells) by observing the surrounding healthy cells, a process called differentiation. This could help the heart muscle regenerate and improve its function.
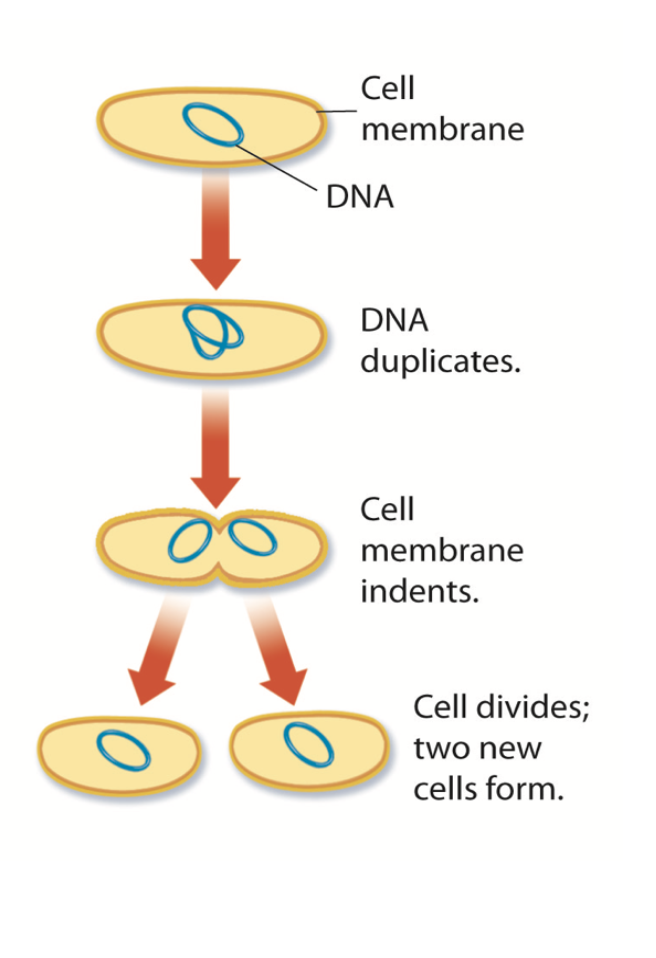
How does Binary fission work?
The cell makes a copy of its DNA (its genetic material).
The DNA copies move to opposite sides of the cell.
The cell starts to split down the middle.
It fully separates into two new cells that are genetically identical to each other.
True/False. Volume and surface area do not increase at the same rate, this is why cells divide instead of continuing to grow without limits.
True