COPMAN WK 1: Introduction to Operations Management
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Operations
Operations refer to the part of an organization that is responsible for producing goods and/or services.
Goods
are physical items inclusive of raw materials, parts and subassemblies such as engine system used in a car, and final products such as computers and machineries.
Services
are activities that provide a combination of time, location, form and psychological value.
Operations Management
The business function responsible for planning, coordinating, and controlling the resources needed to produce products and services for a company.
Finance
Responsible for securing financial resources at favorable prices and allocating those resources throughout the organization, as well as budgeting, analyzing investment proposals, and providing funds for operations.
Marketing
Responsible for assessing consumers' needs and wants, and selling and promoting the organization's goods and services.
Operation
Is responsible for producing goods and or providing services offered by the organization
Operations Management (OM)
transforms inputs to outputs.
Inputs
Resources such as People, Material, and Money.
Outputs
Goods and services produced by the organization.
Value Added
The difference between the cost of inputs and the value or price of output.
Efficiency
means performing activities well for least possible cost
Manufacturers
Organizations that produce tangible products that can be inventoried.
Service Organizations
Organizations that provide intangible products that cannot be inventoried.
Operations Function
Includes many interrelated activities such as forecasting, capacity planning, scheduling, managing inventories, assuring quality, motivating employees, and locating facilities.
System Design
Involves decisions related to system capacity, geographic location, facilities arrangement, placement of equipment, product and service planning, and acquisition of equipment, typically requiring long-term commitments.
System Operation
Involves management of personnel, inventory planning and control, scheduling, project management, and quality assurance, generally involving tactical and operational decisions.
Strategic Decision Making
The process of charting a course based on long-term goals and long-term vision.
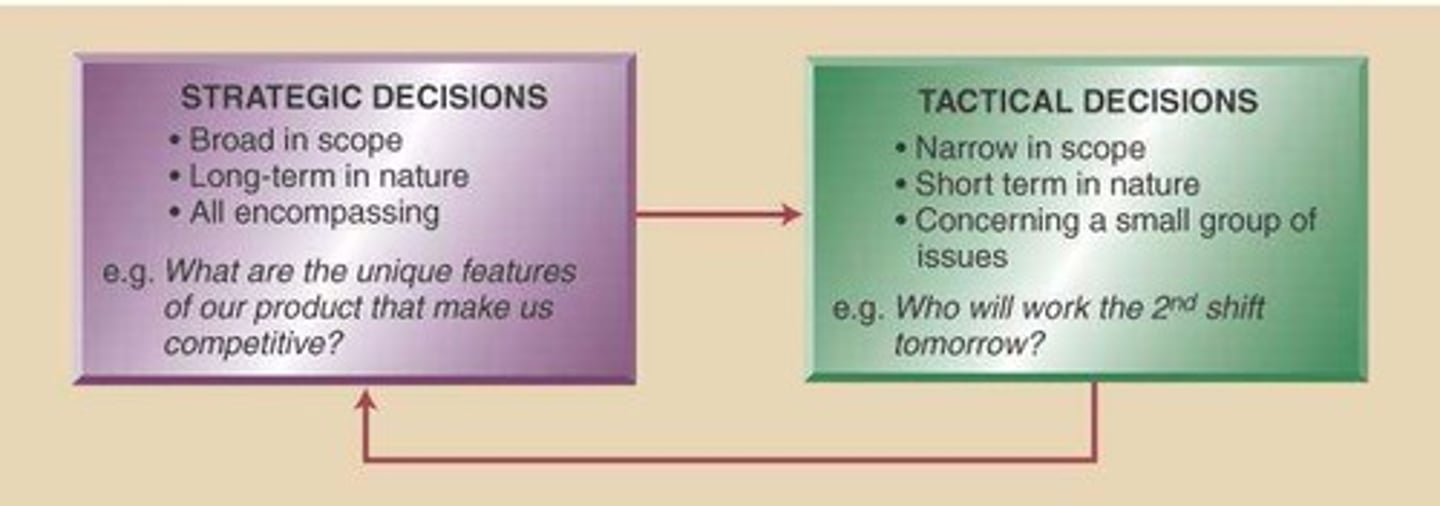
Tactical Decisions
Medium-term, less complex decisions made by middle managers focusing on specific day-to-day issues like resource needs, schedules, and quantities to produce an output.
Models
An abstraction of reality, a simplified representation of something, used as a key tool by all decision makers.
Physical Models
One classification of models that represent physical objects.
Schematic Models
One classification of models that represent concepts or systems in a diagrammatic form.
Mathematical Models
One classification of models that use mathematical expressions to represent relationships.
Quantitative Approach
A problem-solving method that often attempts to obtain mathematically optimal solutions to managerial problems.
Performance Metrics
Metrics used to manage and control the operation.
Analysis of Trade Offs
Decisions that involve considering the trade off between increased customer service and the increased cost of inventory.
System Approach
Emphasizes interrelationship among subsystems such as Marketing, Finance, and Operation.
System
A set of interrelated parts that must work together
Ethics
mangers must consider how their decisions affect the stakeholders of the organization
Industrial Revolution
Began in the 1770s in England and spread to Europe and the United States during the 19th century.
Craft Production
Early manufacturing method where highly skilled workers used simple and flexible tools to produce goods according to customer specifications.
Scientific Management
Began in 1900, based on observation, measurement, analysis, and improvement of work methods and economic incentives.
Frederick Winslow Taylor
Known as the Father of Scientific Management, emphasized maximizing output.
Frank Gilbreth
Industrial engineer who developed principles of motion economy applied to small portions of tasks.
Henry Gantt
Recognized the value of non-monetary rewards to motivate workers and developed the Gantt Chart for scheduling.
Harrington Emerson
Applied Taylor's ideas to organizational structure and encouraged the use of experts to improve efficiency.
Henry Ford
Industrialist who employed scientific management techniques in his factories.
Mass Production
Production method where low-skilled workers use specialized machinery to produce high volumes of standardized goods.
Interchangeable Parts
Parts made to such precision that they do not have to be custom fitted.
Division of Labour
Breaking up of a production process into small tasks, allowing each worker to perform a small portion of the overall job.
Human Relation Movement
Began in the 1930s, emphasizing the importance of the human element in job design.
Lilian Gilbreth
Psychologist who focused on the human factor in work alongside her husband Frank Gilbreth.
F. W. Harris
Developed one of the first mathematical models for inventory management in 1915.
Japanese Manufacturers
Developed management practices that increased productivity and quality, emphasizing quality, continual improvement, worker teams, and customer satisfaction.
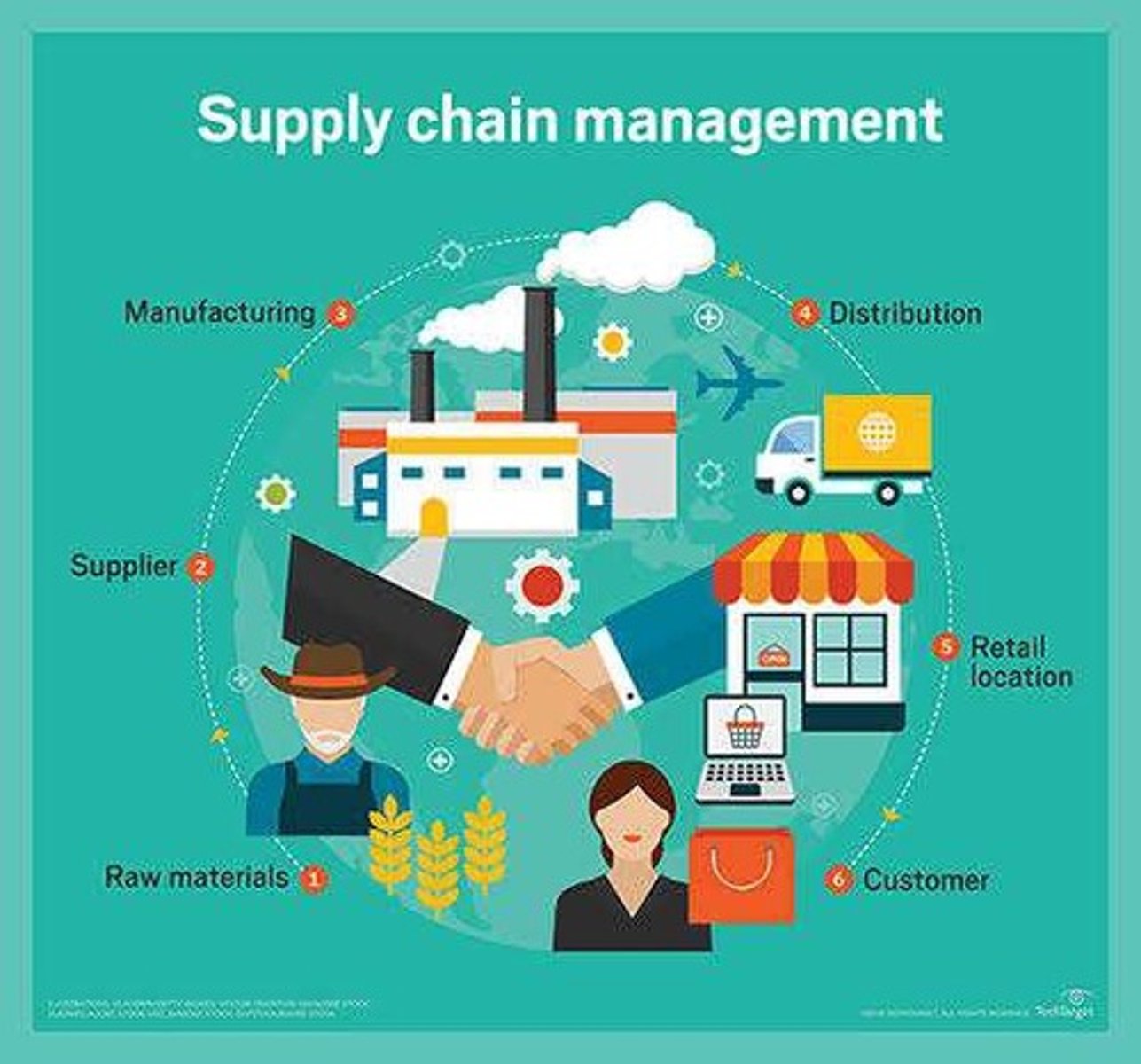
Supply Chain
A system that encompasses the flow of goods and services from origin to consumer.