lf206 lecture 10 - protein modification (cytosolic events)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
most protein synthesis starts in free ______ ribosomes
cytosolic
protein synthesis in the cytosol
cytosolic ribosomal ________ are used to assemble _______ on mRNA encoding ______ proteins
these proteins remain in the _______.
multiple ribosomes assemble and produce __________ (polysomes)
newly made protein are released and the ribosomes are _______ and recycled
subunits, ribosomes, cytosolic
cytosol
polyribosomes
dismantled
the cytosol is ______ crowded
so estimates may differ by _____ of magnitude
a single mRNA translated by multiple ribosomes (__________) the nascent proteins are prone to __________
very
orders
polysomes/polyribosomes
aggregation
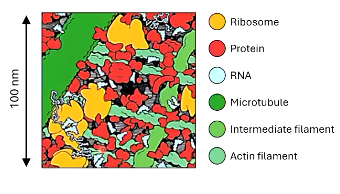
newly synthesised proteins are often non-________
unfolded proteins are prone to ________
folded proteins are stable, functional and resistant to _______
_______ are proteins that ensure correct polypeptide folding
functional
aggregation
proteases
chaperones
how do chaperoned correctly fold proteins?
________ patches on nascent/unfolded proteins are recognised and bound by ____ _____ _____ __ (Hsp 40 co-chaperone)
Hsp 40 delivers the substrate to an ____ conformation Hsc 70 chaperone to stimulate its ______ activity
when ___ bound it has an open conformation
this hydrolysing activity results in ___-bound (closed conformation) Hsp70 which then _____ the hydrophobic _____
this prevents ______ and allows for time to ___ correctly
upon _______ exchange of ADP to ATP, Hsc70 adopts an open conformation, releases the partly folded substrate which will then __ into its final conformation.
hydrophobic, heat shock protein 40
open, ATPase
ATP
ADP, shields, patches
aggregation (clumpi/cluster), fold
nucleotide, snap
why is studying in vivo chaperone interactions hard?
the cytoplasm is very crowded
studying chaperones in vitro
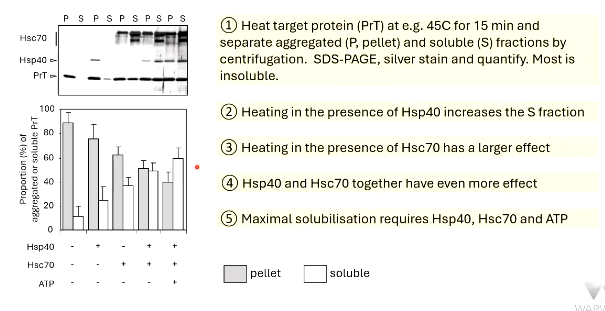
________ of unfolded proteins leads to insolubility
heat target protein to separate aggregate (P, pellet) and ______ (S) fractions by ________
heating in presence of Hsp40 increases _ fraction
heating in presence of Hsc70 has a ______ effect
maximal solubilisation requires Hsp40, Hsc70 and ___
aggregation
soluble, centrifugation
S
greater
ATP
Hsc70 is an anti-aggregation device.
it doesn’t determine a protein’s ________
the protein can have a productive (folding, activation) or __ -______ (destruction, inactivation) fate
productive → released & finds stable conformation, passed onto other ______ for further folding
non-productive → transported to a ______ or passed on to proteasomes for _______
conformation
non-productive
chaperone
lysosome
degradation
how is Hsc70 released
requires _______ ____ _____ (NEF) to bind to Hsp70:____ complex and removes ADP _______-binding site
this promote nucleotide _____ allowing entry of ATP
nucleotide exchange factors
client
nucleotide
exchange
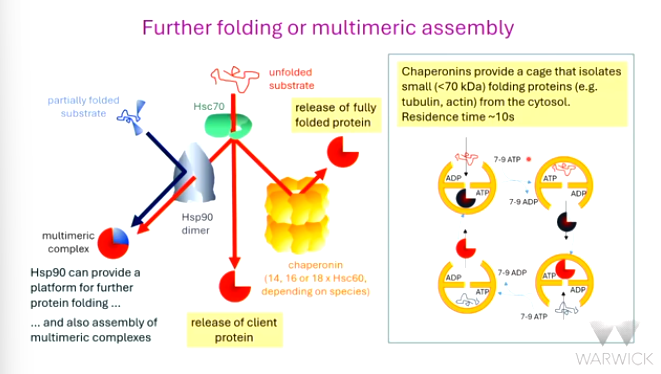
Hsp90 can provide a platform for the assembly of _________ complexes by bringing in other partially folded substrates.
chaperonins (for example _____) are composed of two rings of 7 or 8 or 9 subunits per ring depending on ______
they can interrupt/join after Hsc70: client complex to release a _____ folded protein
the chaperonins provide a cage that _______ small folding proteins like _______ and actin.
multimeric
Hsc60
species
fully
isolates
tubulin
__-chaperones determine the fate of protein/chaperone client complex by _______ with others.
provide an example.
co-chaperones
competing
HOP transfers clients from Hsc70 to Hsp90
BAG-1 releases Hsc70 clients to proteasome = destruction
BAG-2 releases clients away from proteasome = folding
HIP competes with NEFs to maintain Hsc70 client interaction
what does Hsc70 stand for?
heat shock cognate protein 70
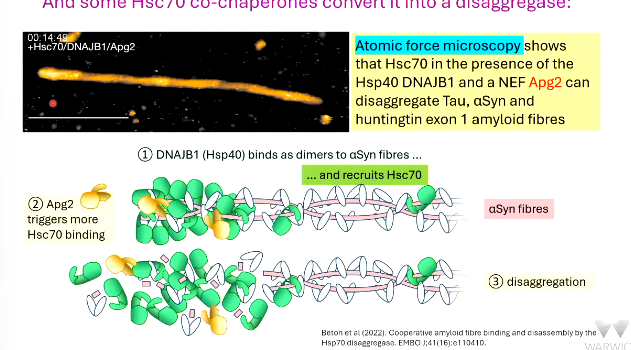
atomic ____ microscopy shows Hsc70 in the presence of Hsp40 and NEF ____ can disaggregate
DNAJB1 (a ______) binds as dimers to aSyn fibres
this recruits Hsc70
____ triggers more Hsc70 binding
the binding stretches the target causing _______ -
force
Apg2
Hsp40
Apg2
disaggregation
PROTEASOME STRUCTURE
has a central core of 2 ring of 7 ______ subunits
flanked by a ring of 7 ____ subunits above and below it
the central core is flanked by a 19S _________ ___ (RP) cap ontop to be described as a __S proteasome
or a 30S proteasome with an RP ______
the active sites of the proteasome are at/encoded by ____ subunits.
beta
alpha
regulatory particle
26
below it
beta
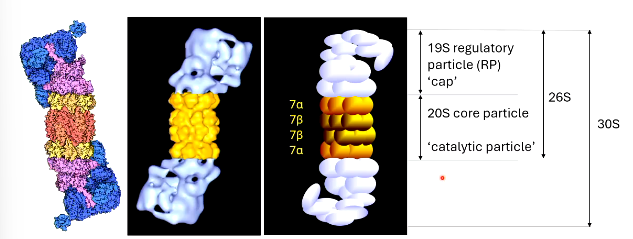
the 20S core particle of a __________ has 3 proteolytic activities.
what are they?
proteasome
chymotrypsin-like
trypsin-like
caspase-like (peptidylglutamyl-peptide hydrolysing).
proteins are targeted to the proteasome by _________ (Ub).
this is a conserved protein of __ amino acids found in all __karyotic cells
proteins marked with a chain of _____ Ub proteins means it is doomed for ____________
monoubiquitinated proteins are targeted to the _______ instead.
ubiquitin
76
eukaryotic
4
degradation
lysosomes
a protein that has failed Hsc70-mediated _______could be targeted to the proteasome.
Ub is activated by __ ubiquitin-activating enzyme
there are roughly _ of these enzymes in mammalian cells
activated Ub is transferred to __
there a roughly __ of these enzymes in mammalian cells
the E2-Ub conjugate associates with E3 ubiquitin _____
there are roughly ___s of E3 ligases in mammalian cells
the __-__-__ conjugate binds to the target ________ and transfers Ub to the target
folding
E1
9
E2
30
ligase
100s
E2-E3-Ub, protein
features of a protein that E3 targets. [4]
extended residence in a chaperone system
their N-terminus
misfolded regions
exposure of a degradation signal
the chain of 4 Ub is detected by ________ _____ ___ of the proteasome
regulatory particle cap
PROTEASOME DESTRUCTION
polyubiquitylated proteins bind to the 19S _______ _____ of the proteasome
RP uses ___ for energy to unfold the protein
_________ (DUBs) remove Ub molecules and they are recycled
protein drawn through proteasome core and degraded - the _____ proteolytic activities are encoded by ____ subunits of 20S core.
protein degraded into small peptides. ~7-9 ____ acid residues long
regulatory particle
ATP
deubiquitylases
three, beta
amino
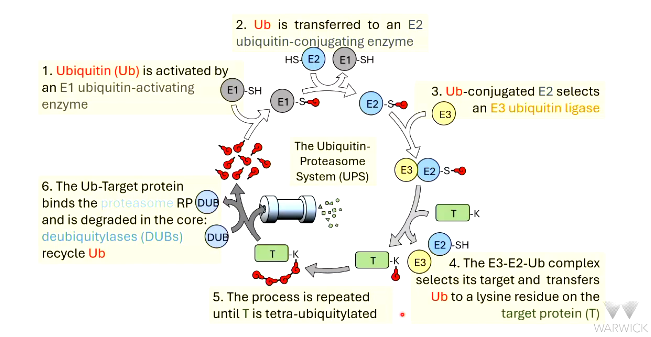
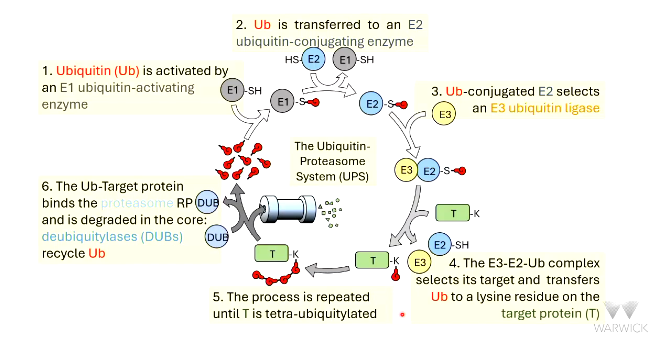
the proteasome is not just a destructive machine
in the RP subunit, there is a chaperone called _____
it directs some proteins to be __-_______
RPT5
re-folded
when proteasomes/E3 fails
proteins ________
can lead to formation of aggregates - driving _________ diseases
if cell cycle proteins aren’t degraded properly it can lead to cell _________ (cancer)
overactive proteasomes
have been implicated in ________ disease. e.g systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis
accumulate
Alzheimer’s
proliferation
autoimmune
proteolytic cleavage to ______ a protein
inactive precursor procaspase 3 is cleaved by CASP8, 9 & __
they all cleave in the _____ place
________ into an active procaspase 3
activate
10
same
rearranged
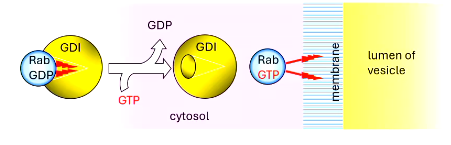
some proteins like ___ are modified by the addition of lipids
Rabs are ______ prenylated
the prenylated lipids are either a __ C farnesyl or __C geranylgeranyl
the prenyl groups are masked by GDI (___ _______ ______)
Rab GDP becomes Rab ___ and GDI dissociates, Rab___ can now enter target ________
Rabs
doubly
15
20
GDP dissociation inhibitor
GTP
GTP
membrane
addition/removal of phosphates can alter protein _______
______ ______ ______ (CAK) makes cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinase and active complex
Wee1 kinase adds more _______ inactivating the complex
cdc25 phosphatase _______ - activating the complex
activity
cyclin activating kinase
phosphates
reverses this
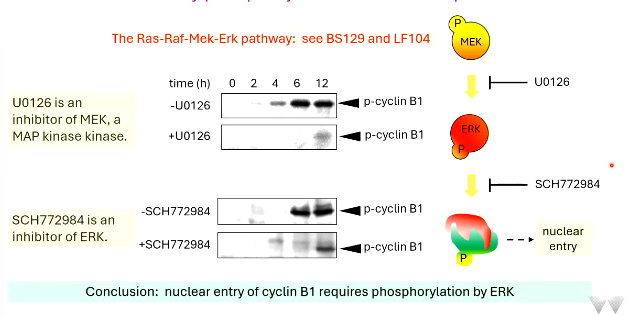
what is the ras-raf-mek-erk pathway?
signalling pathway transmitting signals from cell surface receptor to transcription factors/nucleus
SCH772984 is an inhibitor of ___
in it’s presence ___ p-cyclin B1 was produced
so, nuclear entry of cyclin B1 requires the phosphorylation of ___
ERK
less
ERK
p53 is _________ during stress
has 24 known phosphorylation _____ - each produces a different conformation
phosphorylated p53 ______ and binds to DNA
it acts as a ____-activator of a number of genes
phosphorylated
sites
tetramerises
trans
name 5 cytosolic post-translational modifications
proteolytic cleavage
addition of lipids (prenylation)
phosphorylation
ADP ribosylation (cholera toxin is an ADP-ribosylase)
methylation (histone methylation)