Biology VI Babylon's Ashes
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The End of 1st Semester
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Crucial Roles of Cell Division
It makes possible for a fertilized egg to develop into an adult organism
It ensures the continuity of life through asexual or sexual reproduction
Cell Cycle
series of stages in the life of a cell
Interphase, Mitosis/Meiosis, Karyokinesis & Cytokinesis
3 sections of cell cycles
Gap
Meaning of G in cell cycle
Synthetic Phase
Meaning of S in cell cycle
Interphase Parts
G1 - Growth and Metabolic Roles, S - Replication of DNA occurs, G2 - Growth and more preparation
G1
Protein supply increases number of cell organelles, size of the cell increases
S
Most important phase, because it replicates DNA
G2
Prepares cell for actual cell division, it ensures the cell is ready for meiotic/mitotic division.
Mitosis Parts
Prophase, Metaphases, Anaphases, Telophases
Interphase
referred to as the preparatory stage. It is the longest phase in the cell cycle for most cells. Typically, it lasts for at least 90% of the total time required for the cell cycle.
Mitosis
division of the nucleus with it’s contents into two identical nuclei
Prophase
1st part of mitosis, where chromosomes condense into chromatin. Divided into two parts, early ****, where the chromosomes duplicate and nucleoli disappear, and late ****, where spindle fiber begins to form on centrioles, and nuclear envelopes disappears.
Metaphase
2nd part of Mitosis, where chromosomes align at cell center
Anaphase
3rd part of mitosis, where replication of DNA occurs
Telophase
4th part of mitosis, where growth and more preparation for karyokinesis and cytokinesis occurs
Karyokinesis
process of nucleus division
Cytokinesis
process of cytoplasmic division
Cell Division
process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells.
Meiosis
a special form of cell division for reproductive cells. This is mostly similar to mitosis aside from 4 daughter cells, daughter cells having half the no. of chromosomes (haploid no.) of the parent cell, and the daughter cells being non-alike and not having the same exact copies of chromosomes
Homologous Pair
same pair
Haploid Cell
1 complete set of chromosomes
Diploid Cell
2 complete sets of chromosomes
Haploid Number
no. in a haploid represented 1N
Diploid Number
number of chromosomes in a diploid represented by 2N
Zygote
fertilized egg cell
Meiosis phases
Meiosis I, composed of Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, and Meiosis II, composed of Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and Telophase II.
Meiosis I
Meiosis II
Synapsis
the fusion of chromosome pairs at the start of meiosis.
Crossing Over
the exchange of DNA between paired homologous chromosomes (one from each parent) that occurs during the development of egg and sperm cells
Gametogenesis
process by which gametes or reproductive cells are formed by meiotic division
Spermatogenesis
Sperm cell formation
Oogenesis
Egg Cell Formation
GnRH
Gonaditropin Releasing Hormone
FSH
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
LH
Lutenizing Hormone
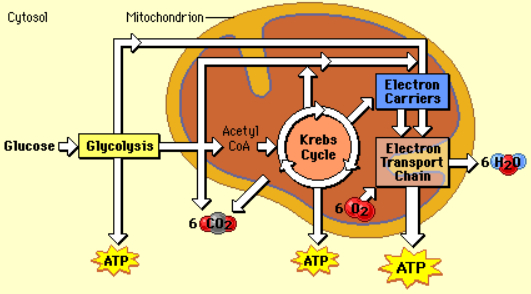
Cellular Respiration
process by which the chemical energy of “food” molecules is released and partially captured in the form of ATP
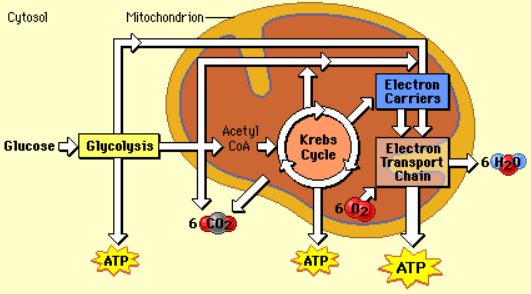
Stages of Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis, Krebs or Citric Acid Cycle, and Electron Transport Chain
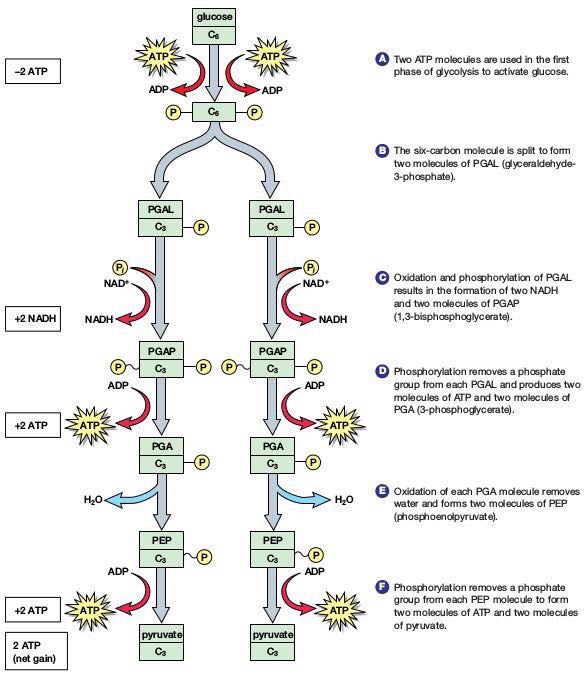
Glycolysis
1st stage of cellular respiration, which occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell, the process is anaerobic (O2 not required), requires input of 2 ATP and glucose to start. Produces pyruvate, pyruvic acid, and 4 ATP, 2 NADH
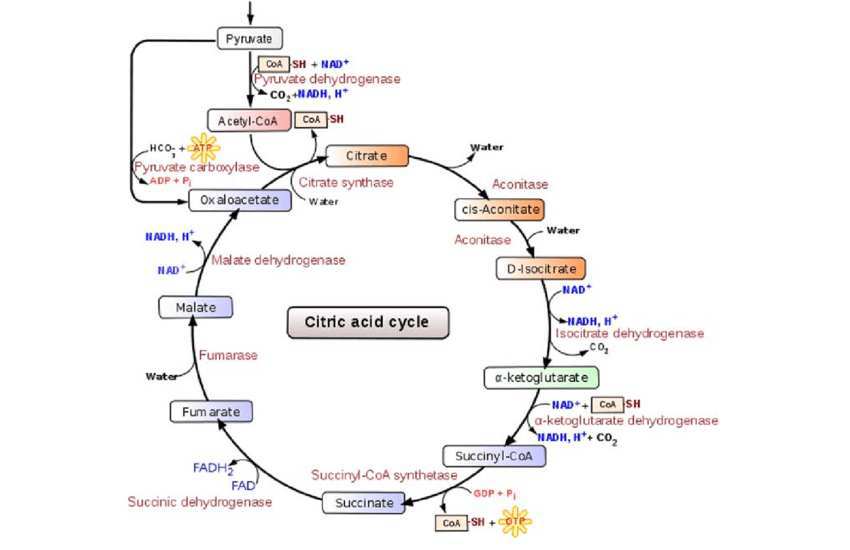
Krebs or Citric Acid Cycle
2nd stage of cellular respiration, which occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria, the process is aerobic (O2 required), cyclical series of oxidation that give off CO2 and produced one ATP per cycle, turns twice per glucose molecule, produces 2 ATP as a result. Overall, the Krebs cycle produces 6 NADH, 4 FADH2, 4 CO2, 2 ATP.
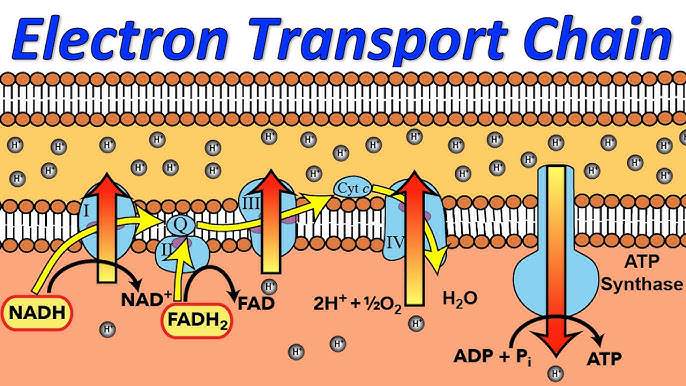
Electron Transport Chain
3rd stage of cellular respiration, which occurs in the the cristae of the mitochondria, the process produces the most ATP (34) as well H2O. It uses coenzymes NAD+ and FAD+ to accept e- from Glucose. NADH = 3 ATPs, and FADH = 2 ATPs.
Equation for Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 —> 6 CO2 + 6H2O + e- + 36-38 ATP
NAD+ is an energy carrier
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
NADH
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide + Hydrogen
FAD+ is an alternative electron carrier
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide
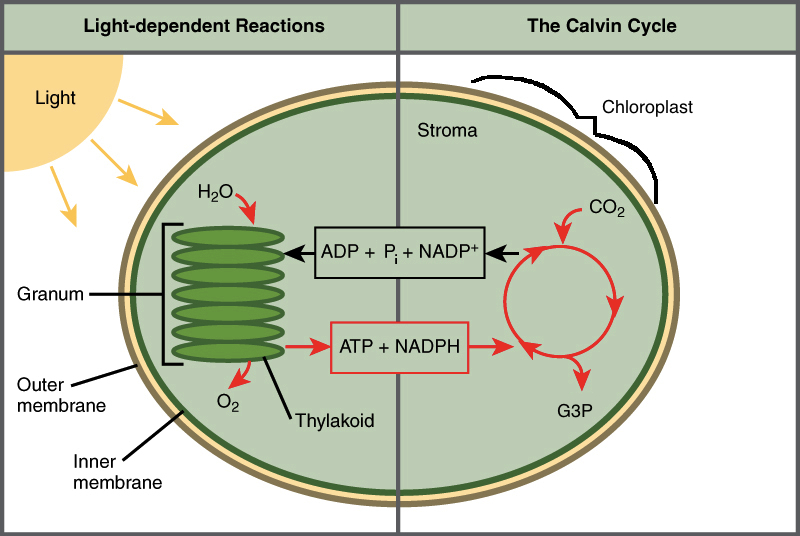
Photosynthesis
process by which plants convert solar light energy into glucose. It is the process that drives the food chain on earth
Photos
“light” in Greek
Synthesis
“put together” in Greek
Photosynthesis Equation
6 CO2 + 6 H2 —→ C9H12O9 + 6 O2
Mesophyll
Middle layer of the plant cell
Stoma (plural: Stomata)
Tiny openings in the middle layers of plant layers where gases enter and exit the leaves
Chloroplasts
have a double membrane (inner and outer membrane). Contains the chlorophyll pigment
Stroma
is a thick fluid contained in the inner membrane of the chloroplast, where it holds chloroplasts, DDNA, ribosomes, and enzymes
Thylakoids
tiny disc shaped interconnected membranes sacs, which enclose another internal compartment, and are suspended within the stroma. Chlorophyll pigments are embedded on these sacs which absorb light.
Grannum (Plural: Grana)
A stack of Thylakoids
Photosystems
Light-absorbing molecules, different from chlorophylls embedded within the thylakoid membrane.
Stages of phoyosynthesis
Light-dependent stage, and the Light-independent stage
Light-dependent stage
occurs in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast, where the chlorophyll pigment absorbs the light energy from the sun and converts it into glucose together with water. Oxygen is released as a byproduct.
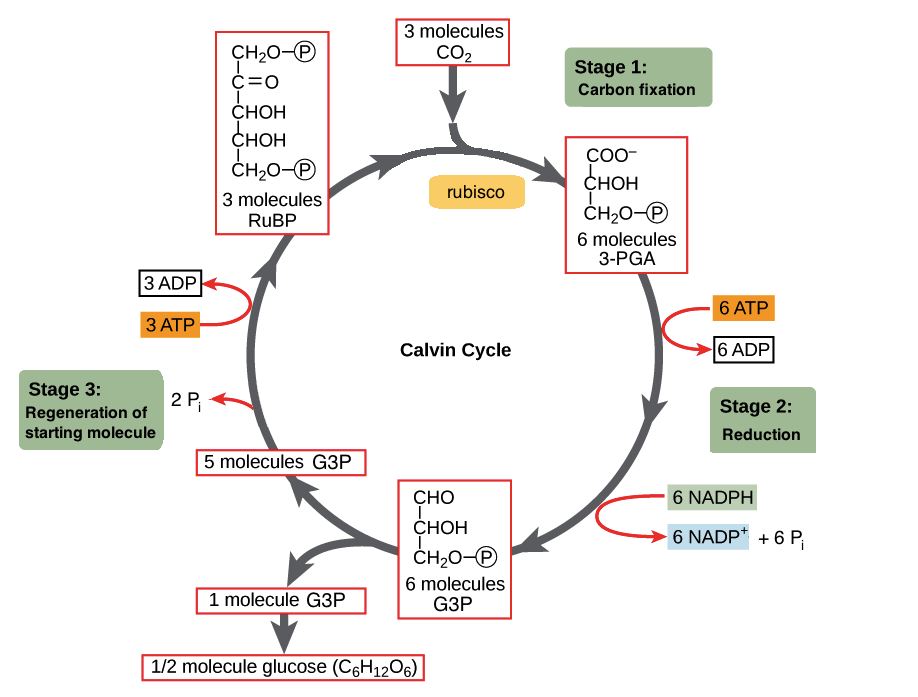
Light-independent stage
also known as Calvin, Calvin-Benson, and/or Calvin-Benson-Bessham Cycle, which occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast.