Reflex, Eyes, & Ears - A&P
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Patellar Reflex
A reflex extension of the leg resulting from a sharp tap on the patellar tendon.

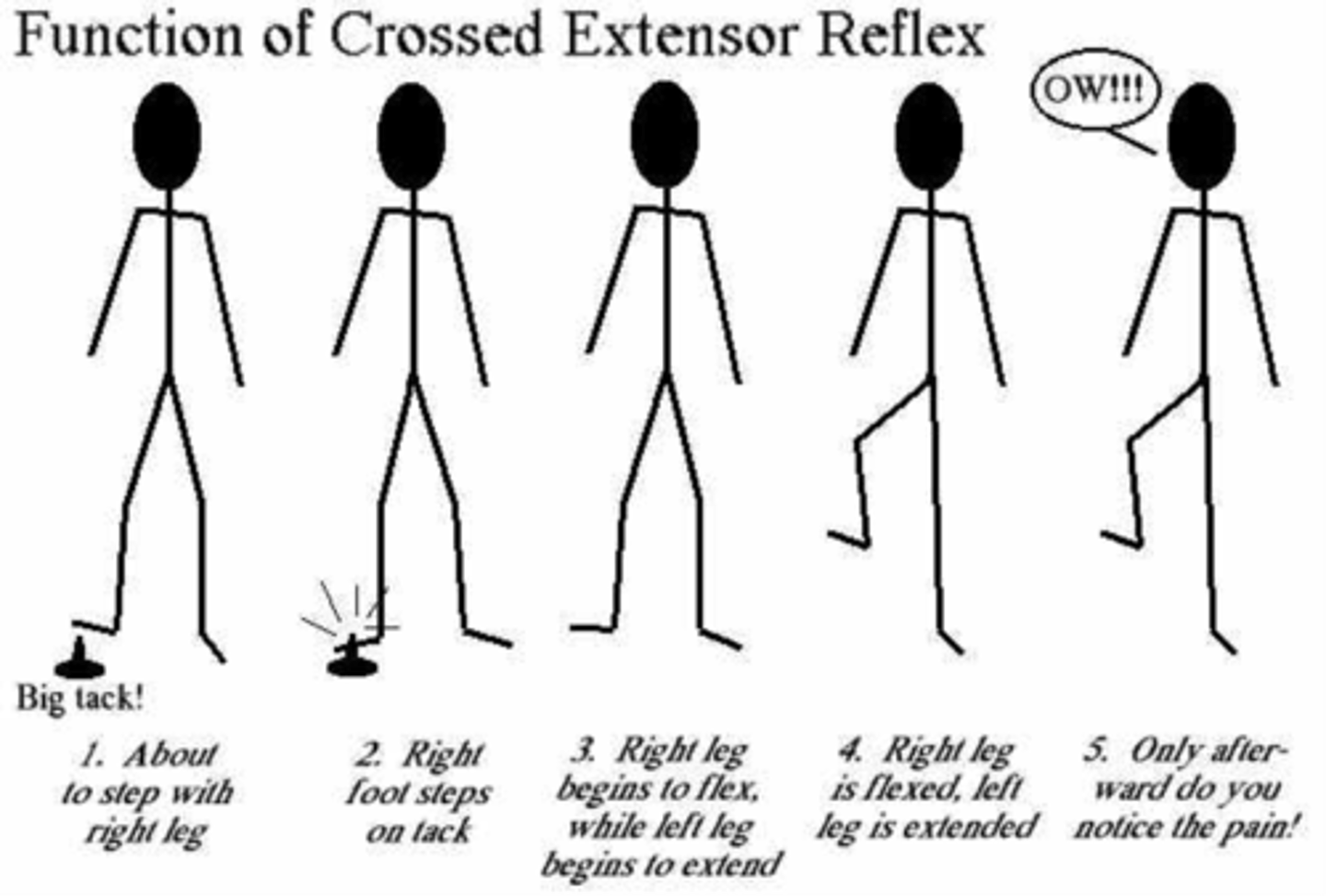
Crossed Extensor Reflex
Opposite limb supports body during withdrawal of injured limb.
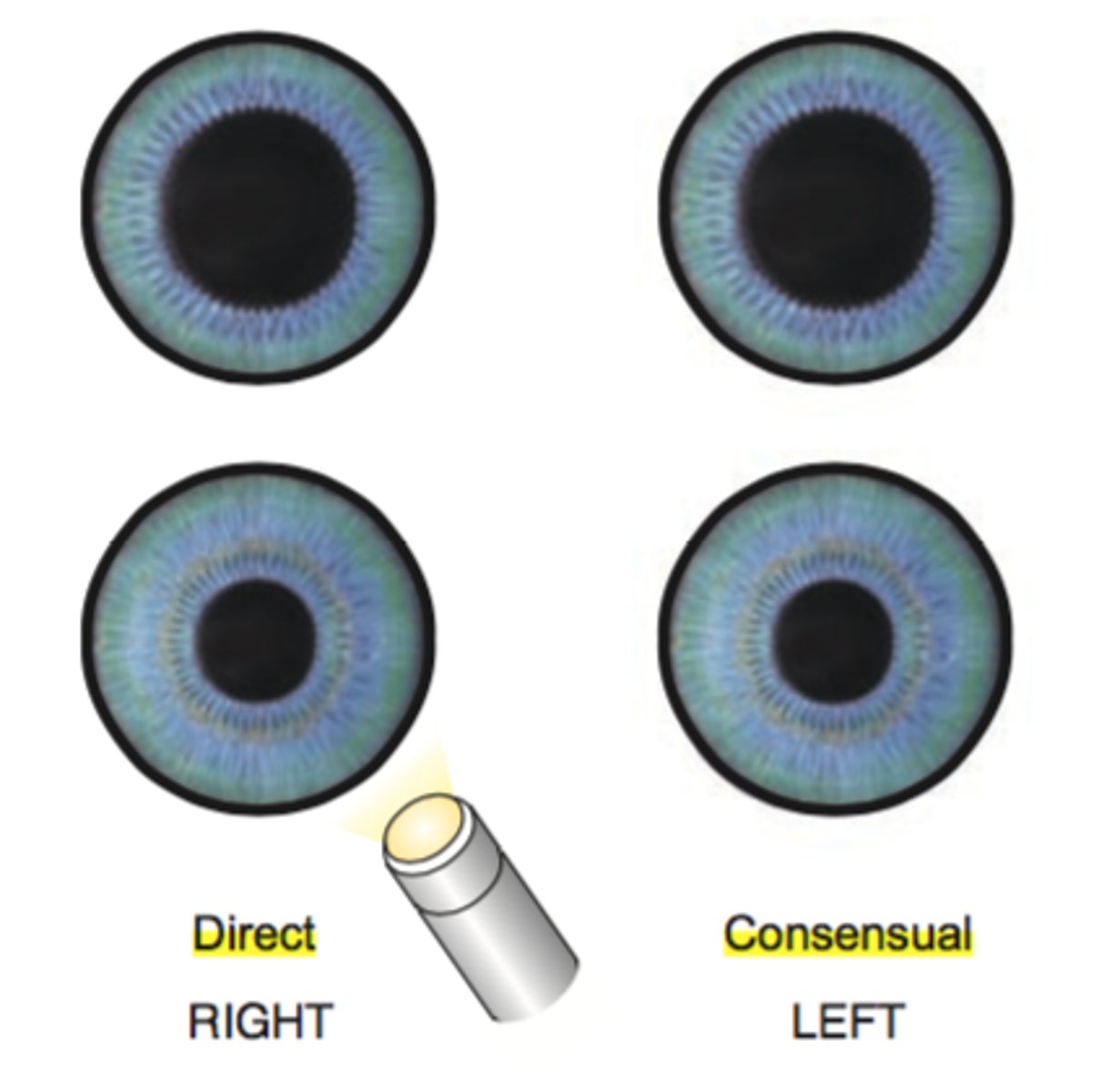
Pupillary Reflex
Both pupils constrict when light is directed at one eye.
Intrinsic Reflexes
Reflexes we are born with for primitive protection.

Learned Reflexes
Result from practice or repetition.
Two Point Threshold
Minimum distance necessary between two points of stimulation on the skin such that the points will be felt as two distinct stimuli.
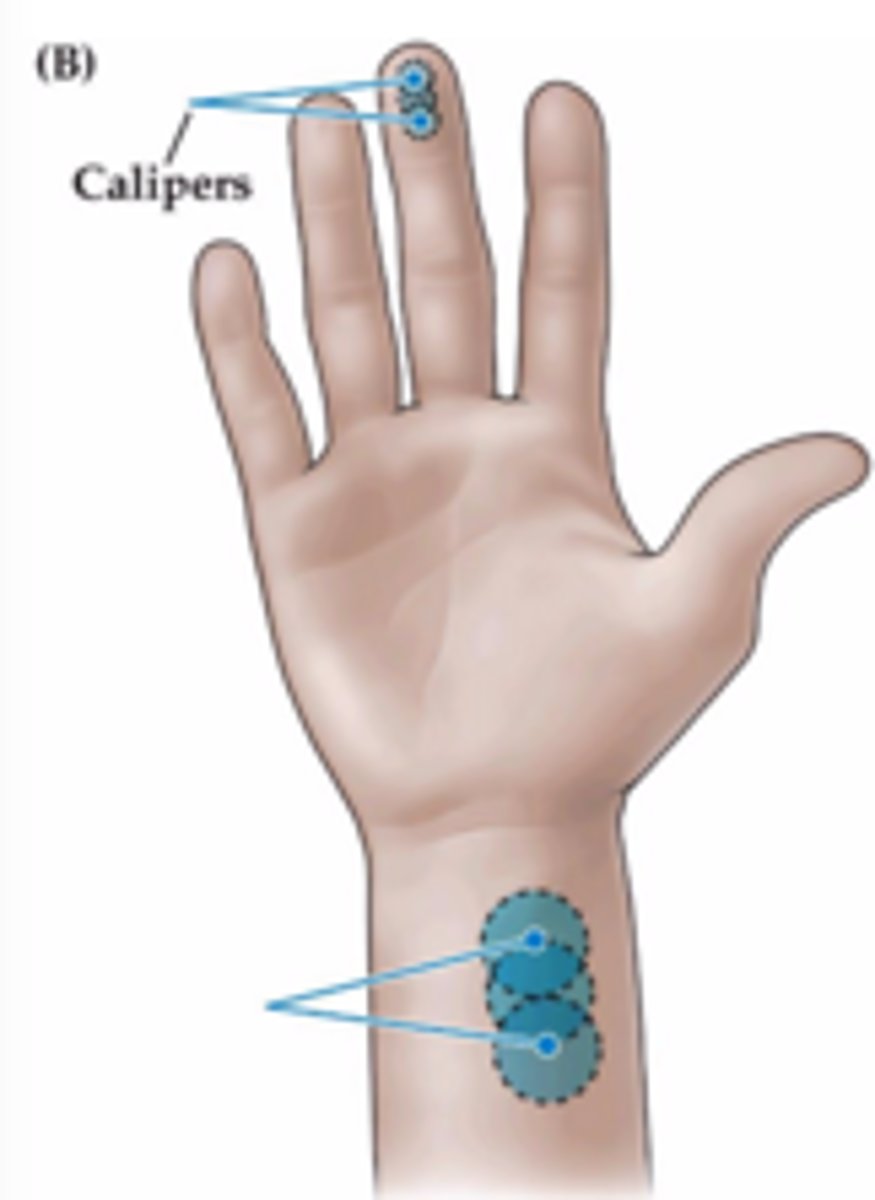
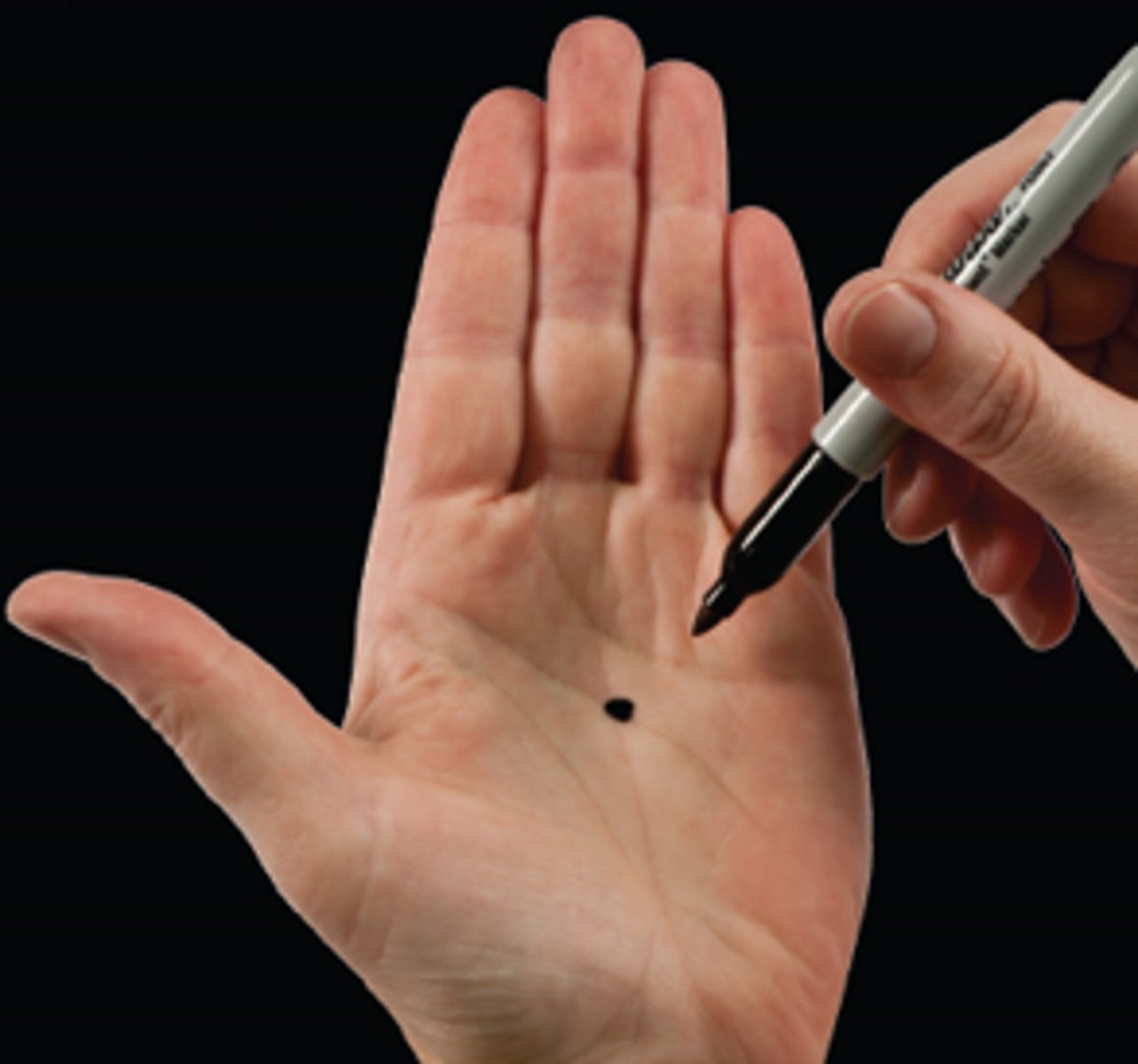
Tactile Localization
The ability to determine which portion of the skin has been touched.

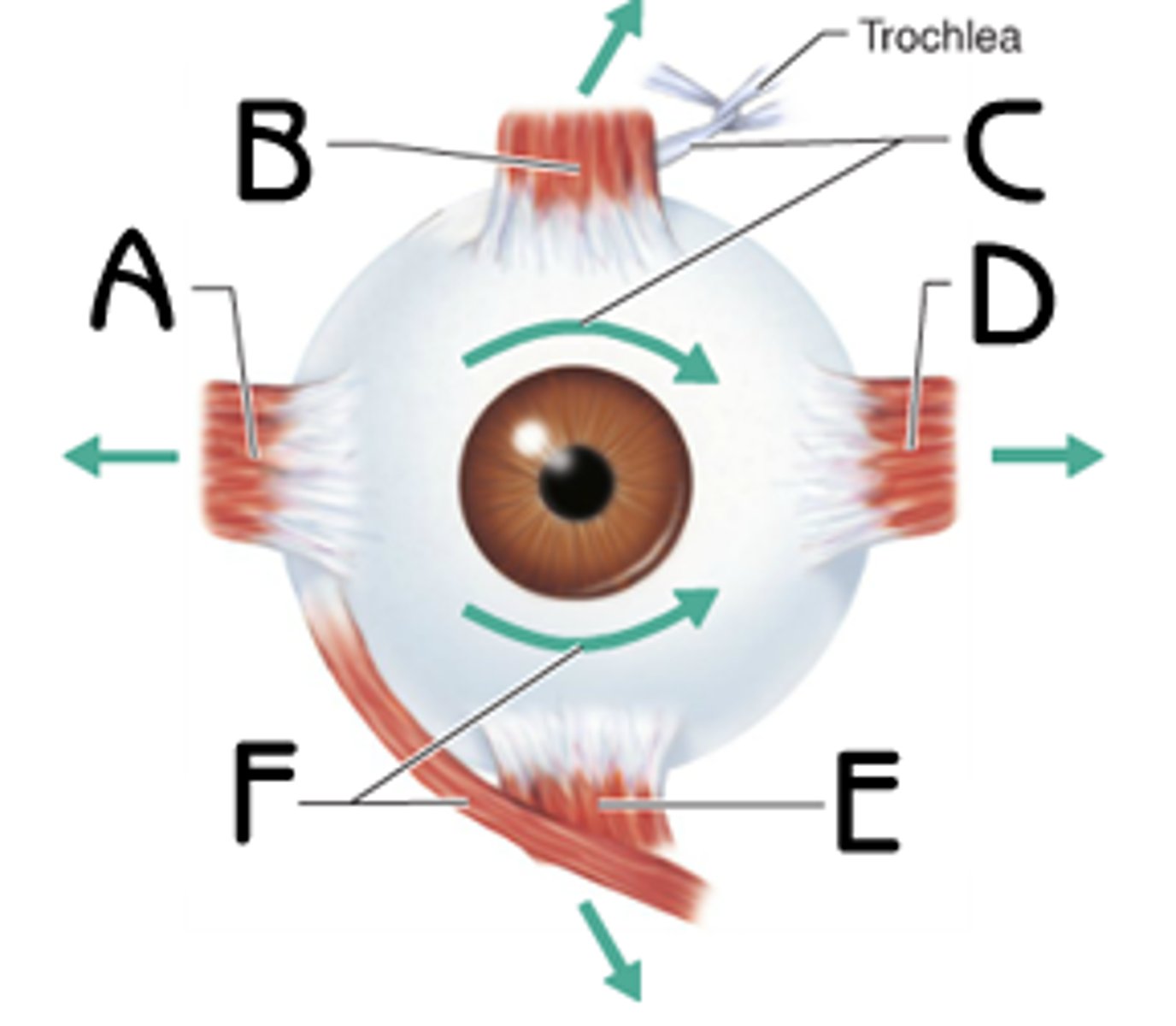
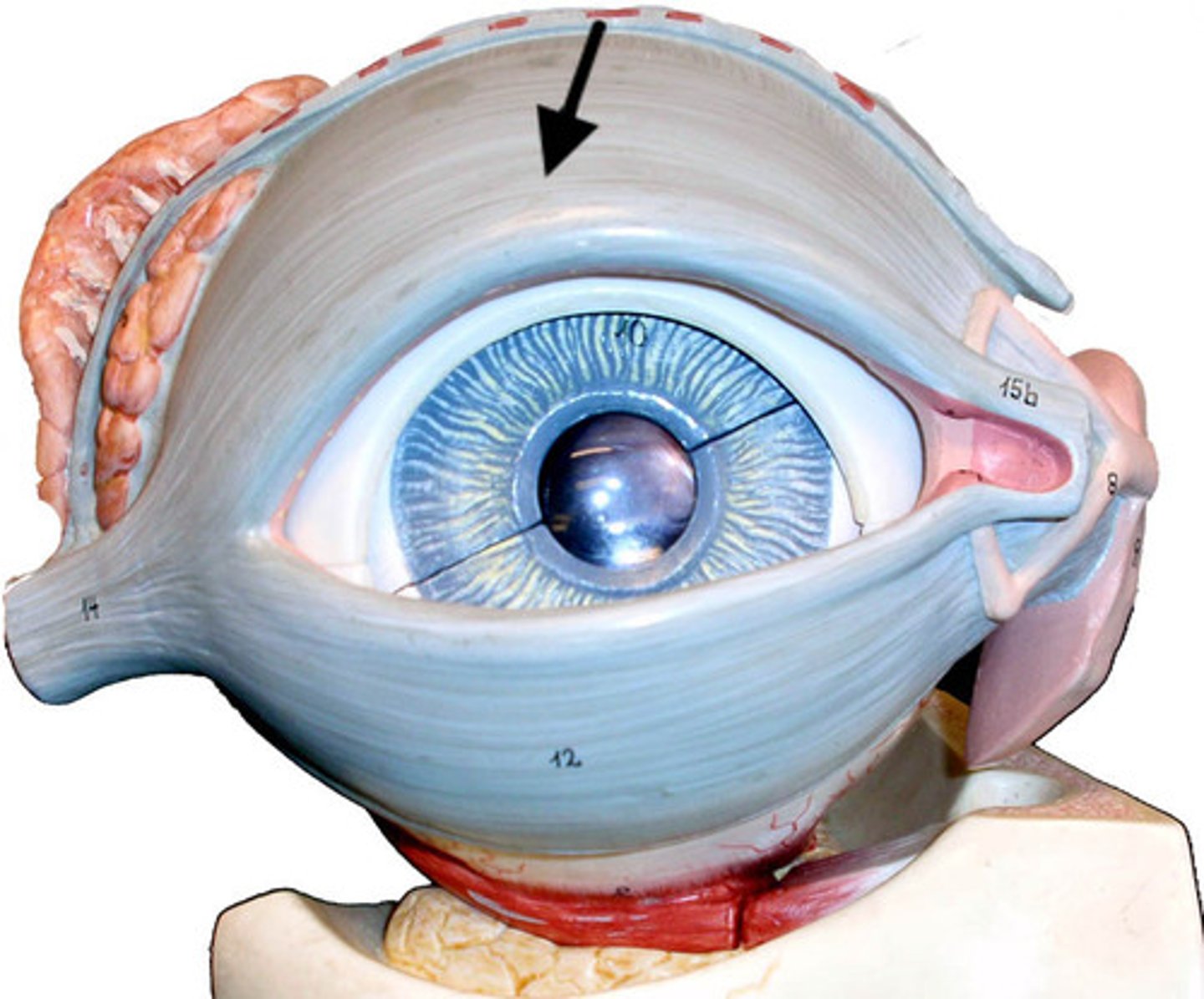
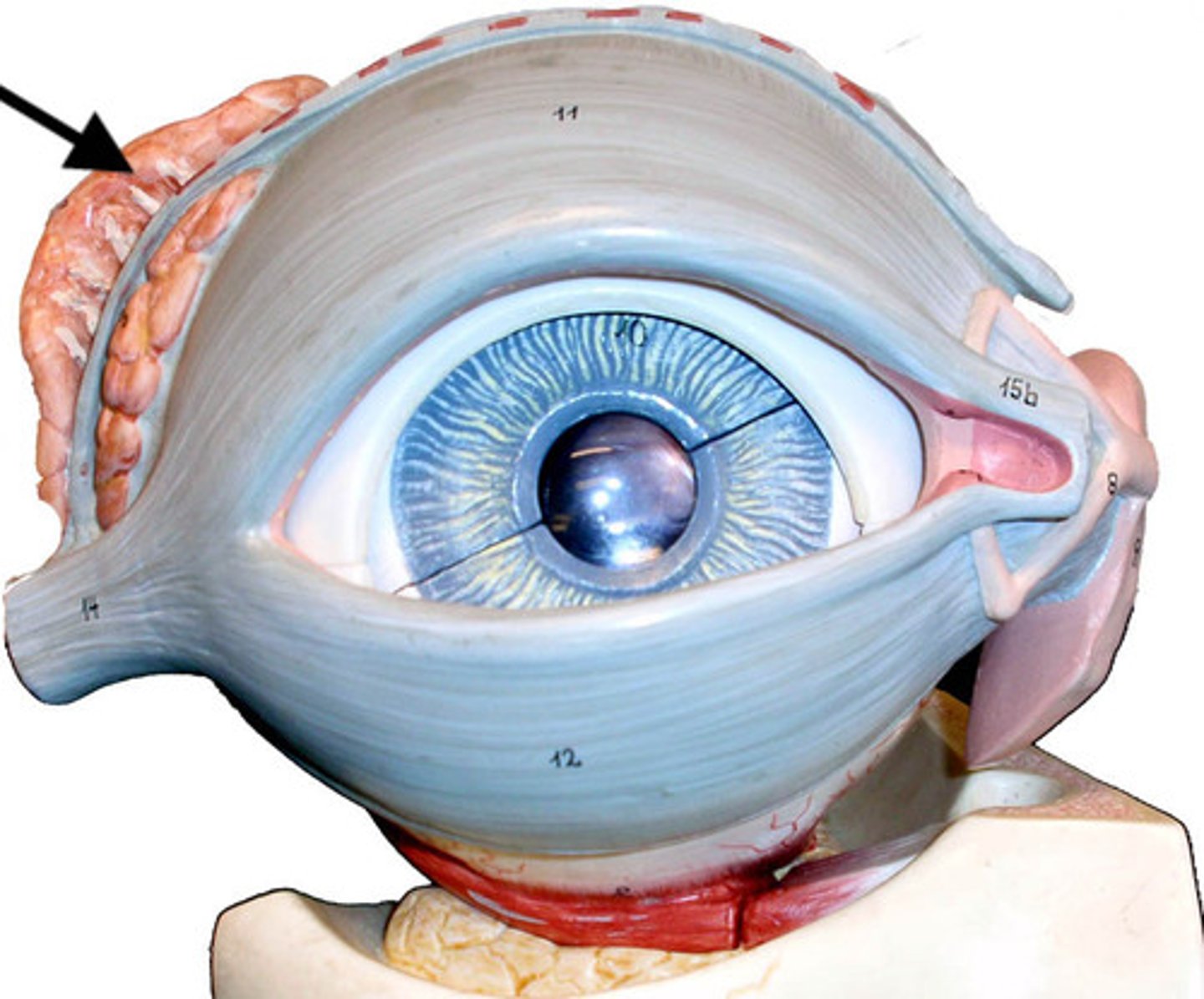
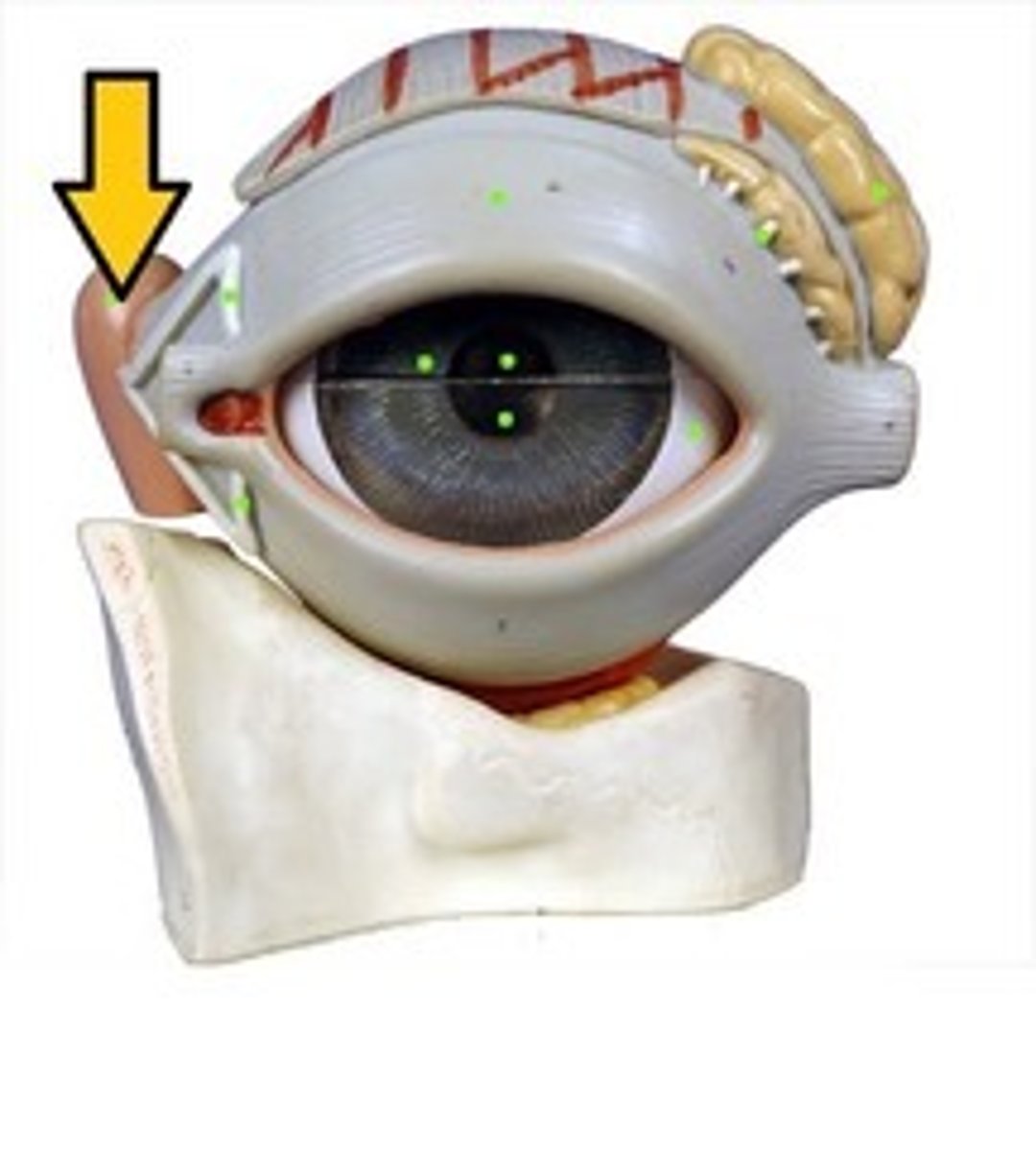
Extrinsic Eye Muscles
Six muscles attach to the outer surface of the eye and produce eye movements.
Conjunctiva
Delicate membrane lining the eyelids and covering the eyeball.
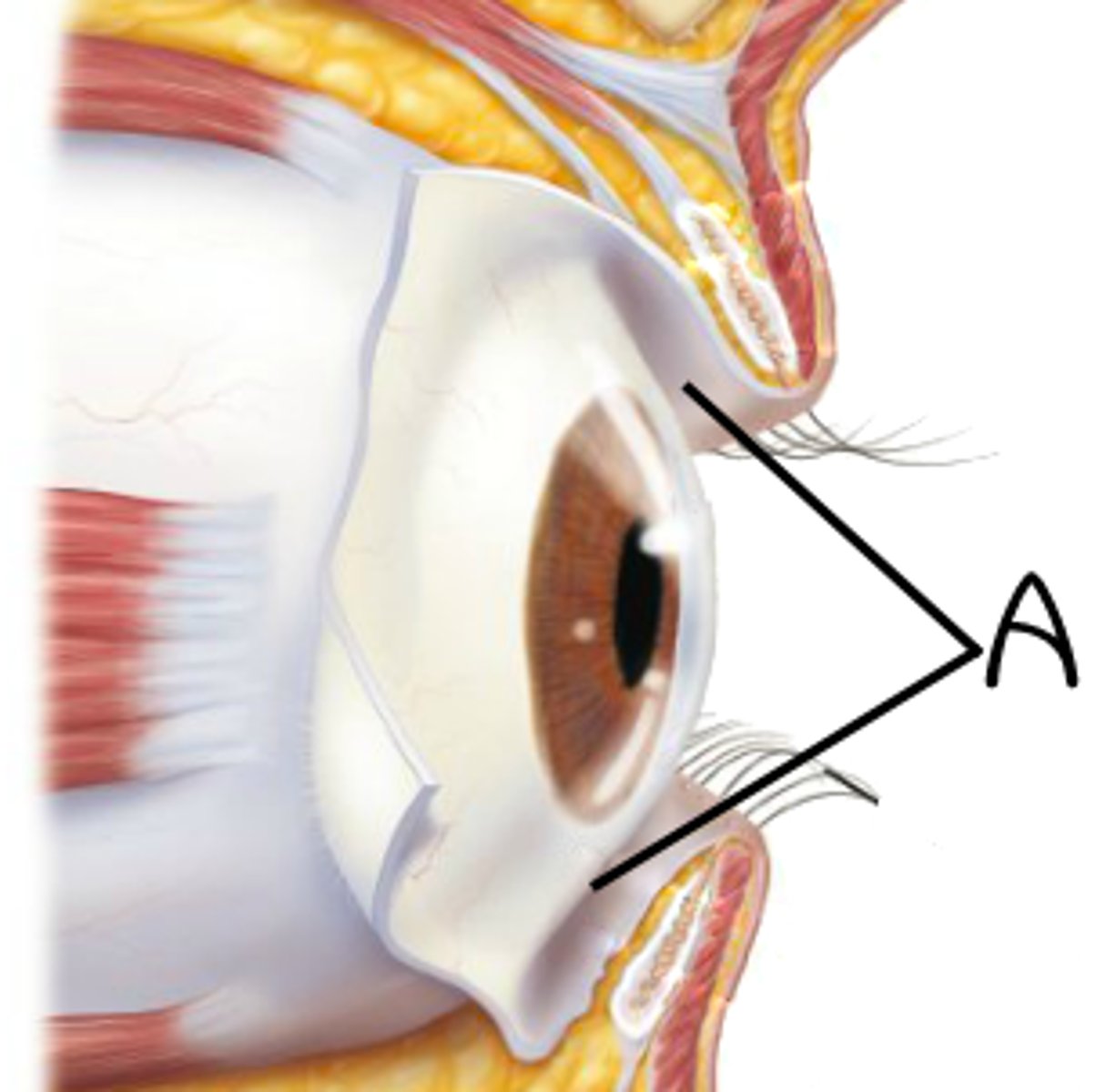
Eyelids
Two movable flaps of skin which cover and uncover each eyeball.
Eyelashes
Nerve endings of follicles initiate reflex blinking.

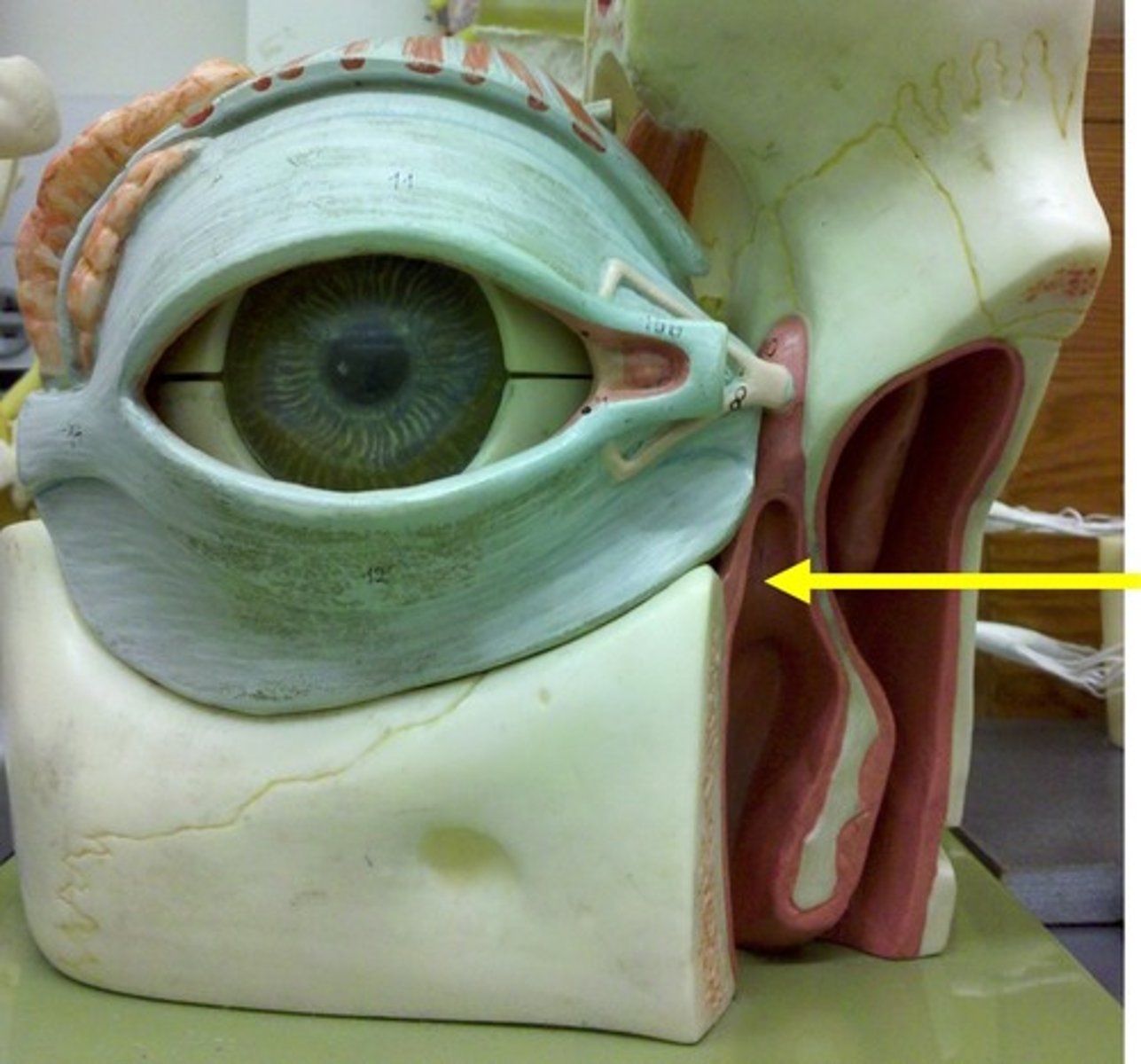
Lacrimal Gland
Produces tears.
Lacrimal Sac
Structure that collects tears before emptying into the nasolacrimal duct.
Nasolacrimal Duct
Passageway for tears from the lacrimal sac into the nose.
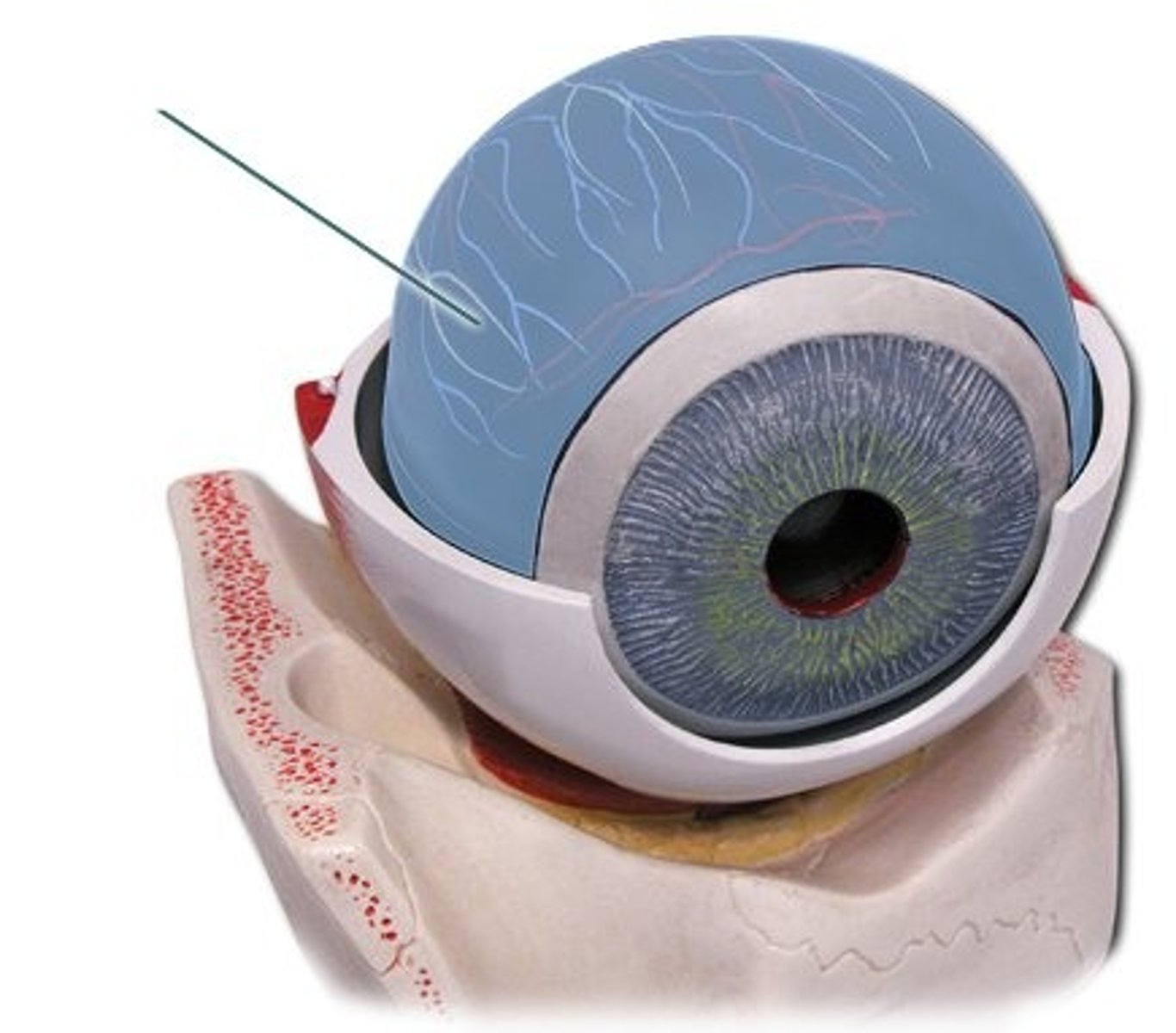
Sclera
White part of the eye.
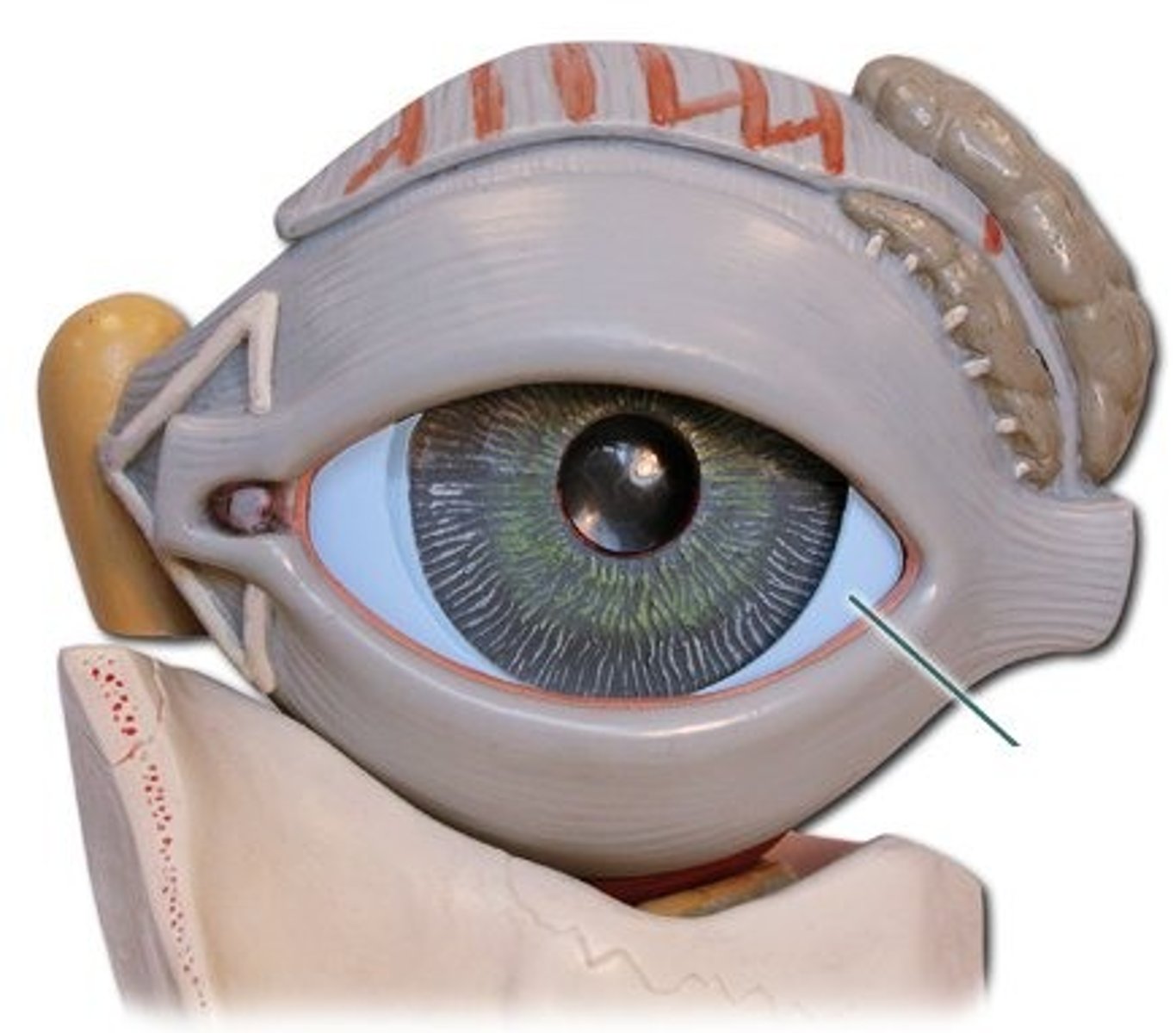
Cornea
The clear tissue that covers the front of the eye.
Choroid
Middle, vascular layer of the eye, between the retina and the sclera.
Ciliary Body
Rng of tissue behind the peripheral iris that is composed of ciliary muscle and ciliary processes.
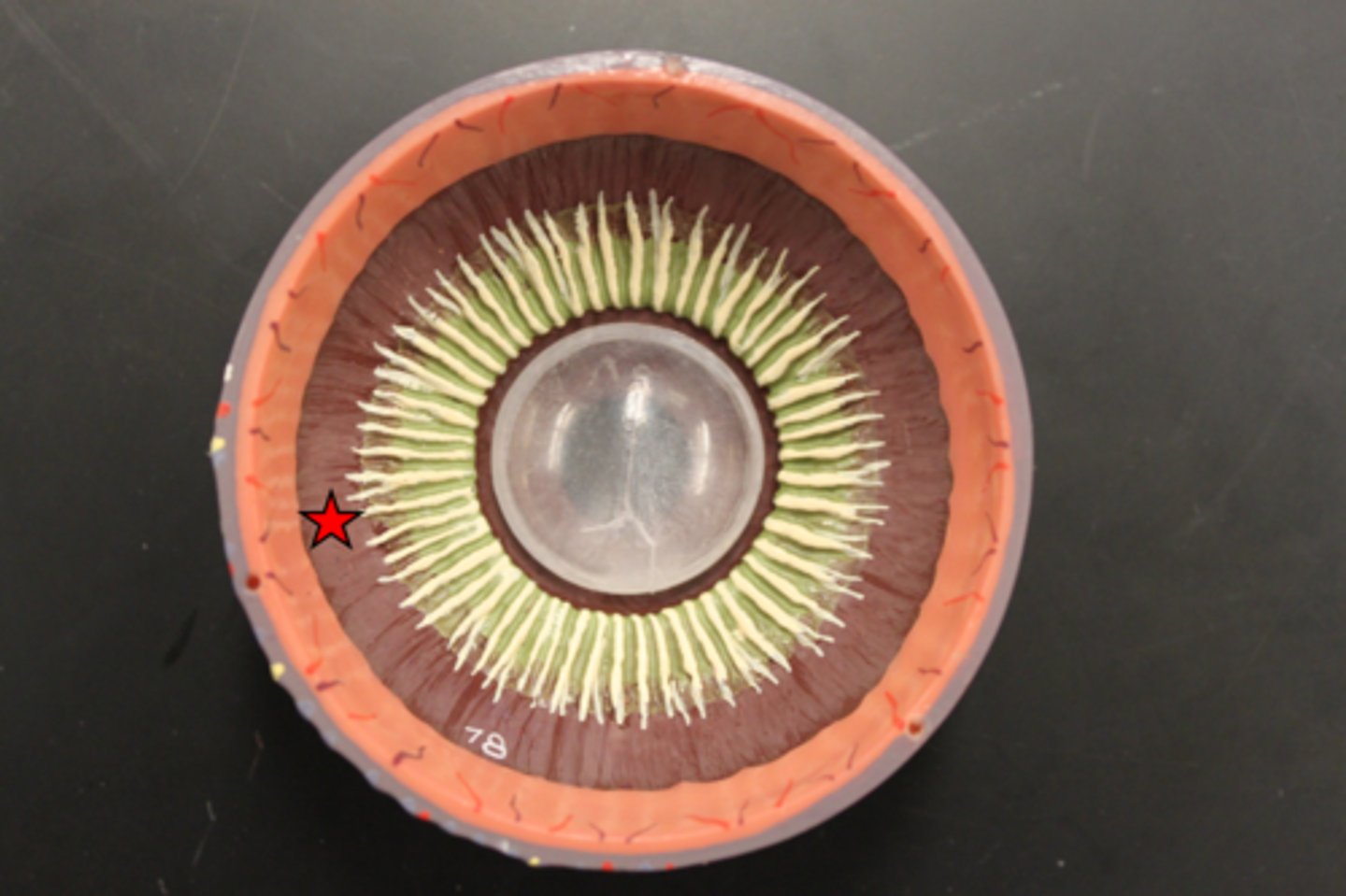
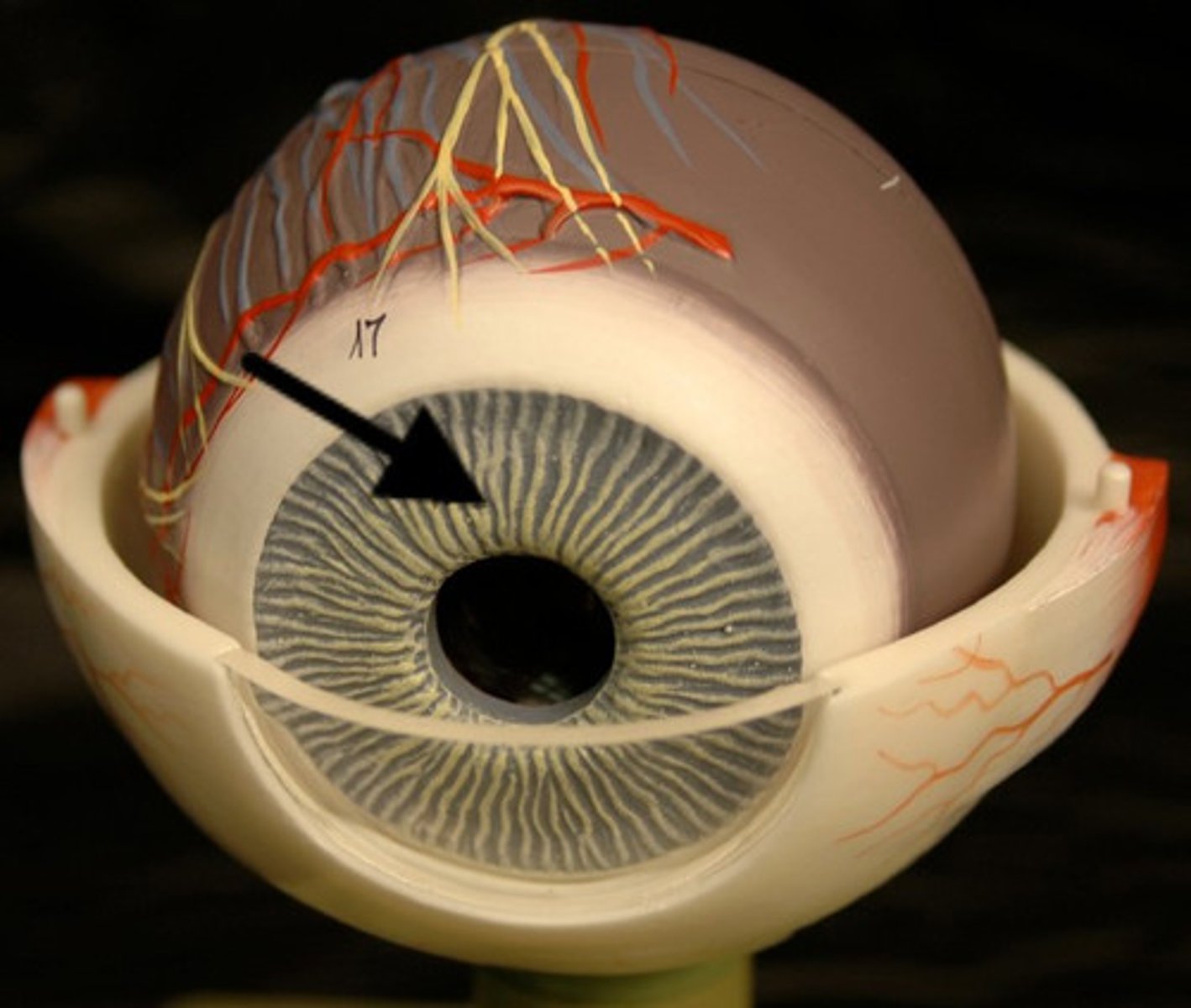
Iris
A ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening.
Pupil
The adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters.

Retina
Light sensitive layer of the eye; contains rods and cones.

Tapetum Lucidum
Iridescent layer found in nocturnal animals for maximizing vision under low intensity light
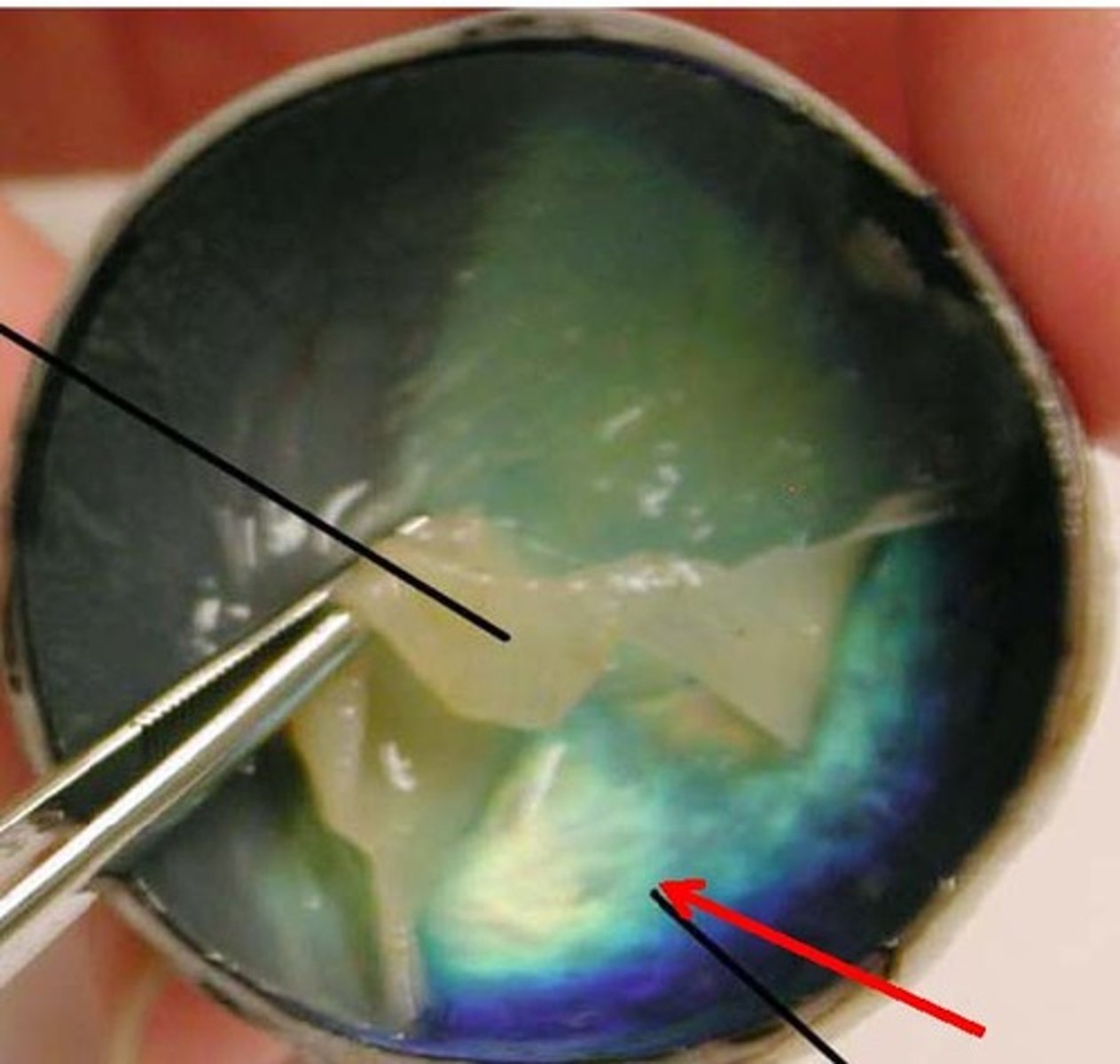
Vitreous Humor
The transparent jellylike tissue filling the eyeball behind the lens.
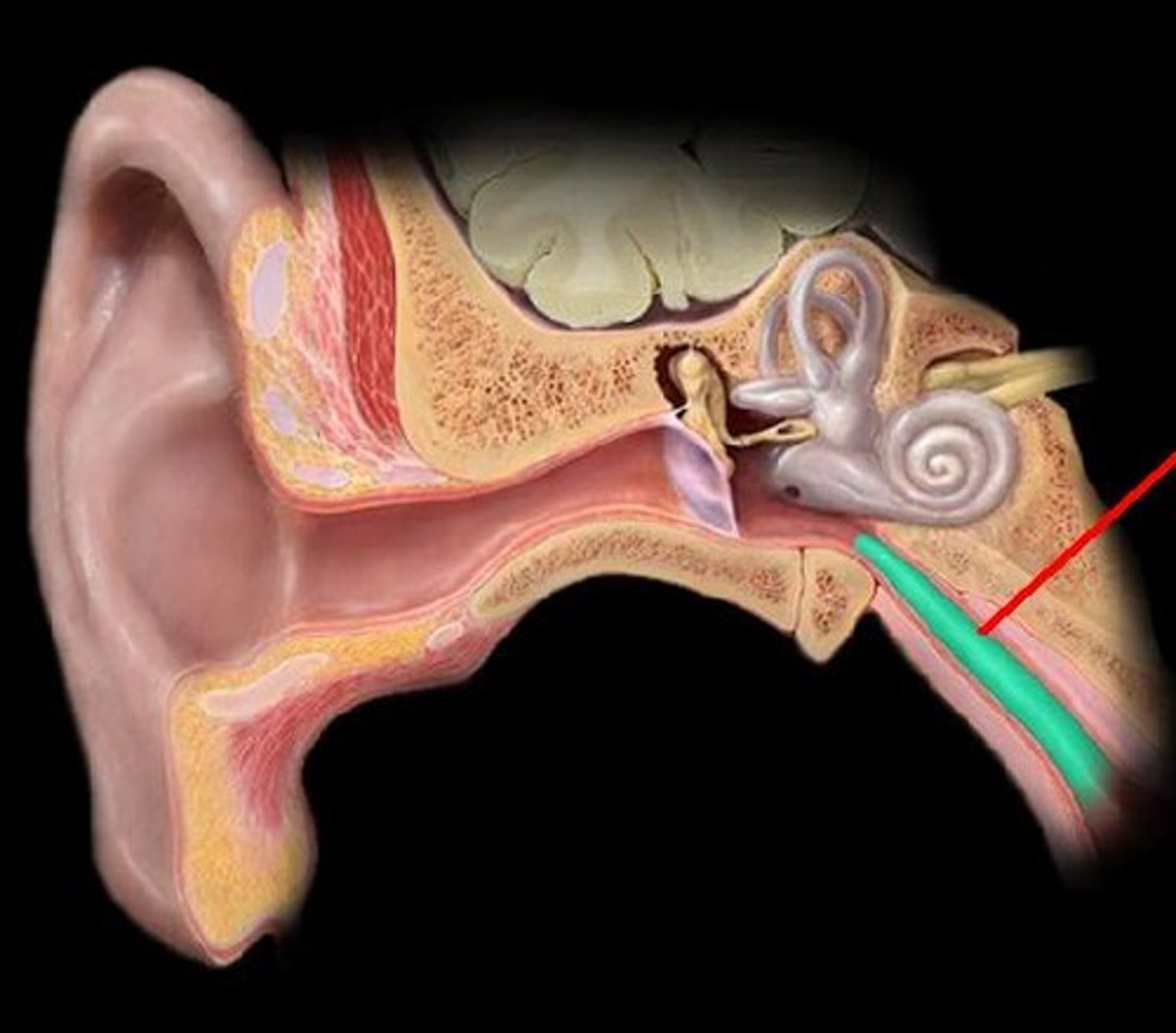
Pinna
The visible part of the ear.
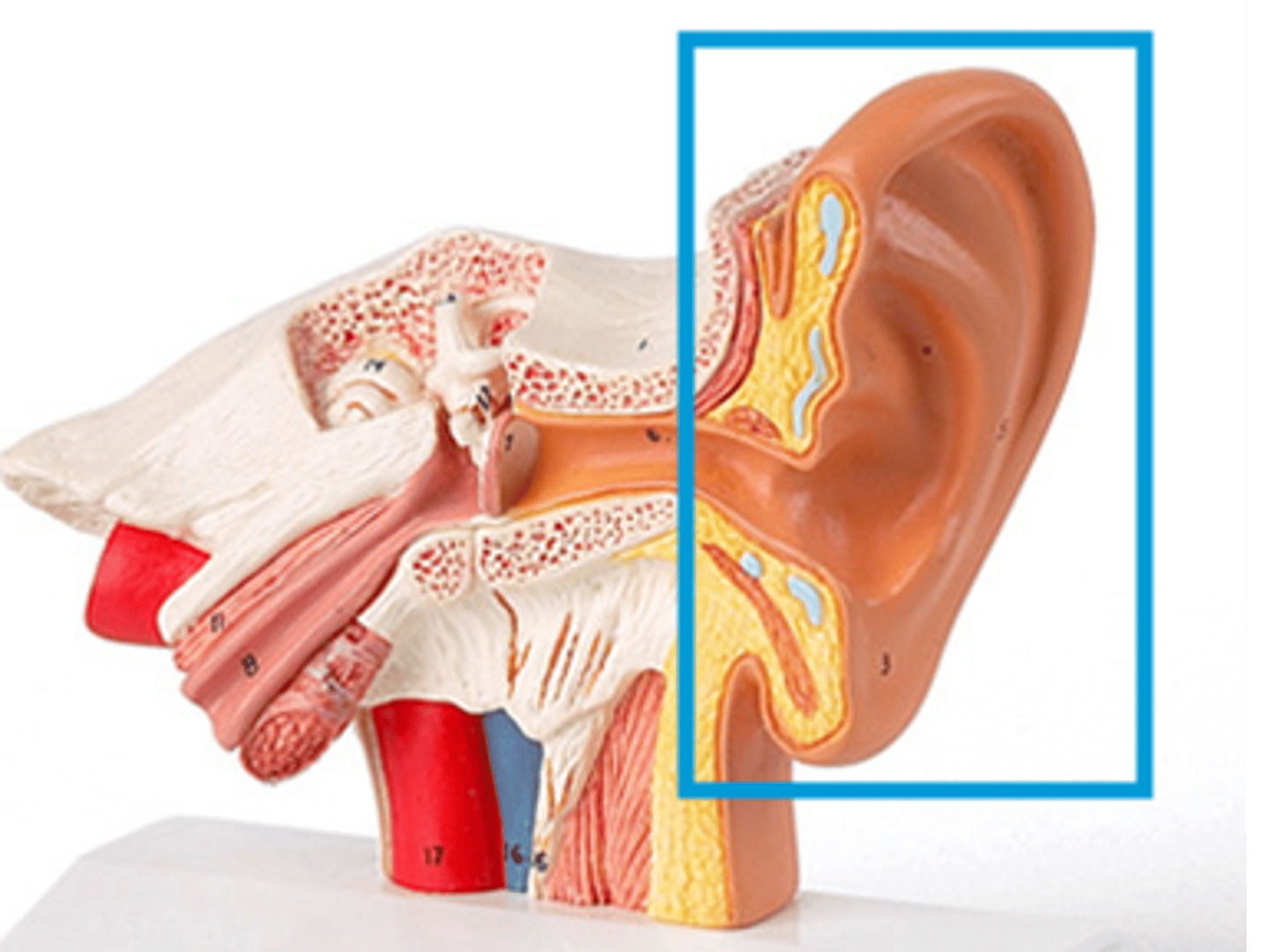
External Auditory Canal
The ear canal; leads to the tympanic membrane.
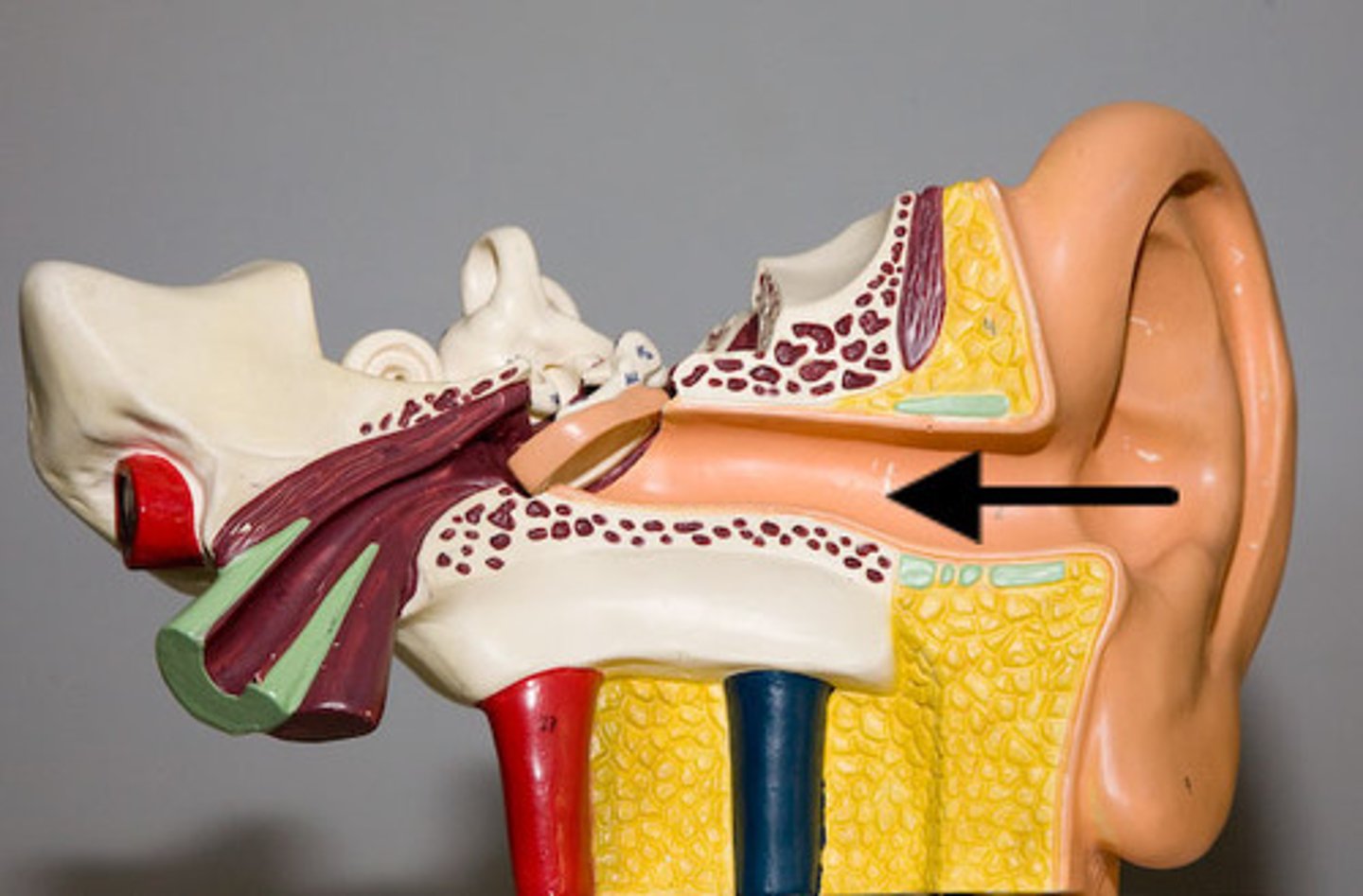
Tymphanic Membrane
Eardrum; consists of ossicles (malleus, incus and stapes).
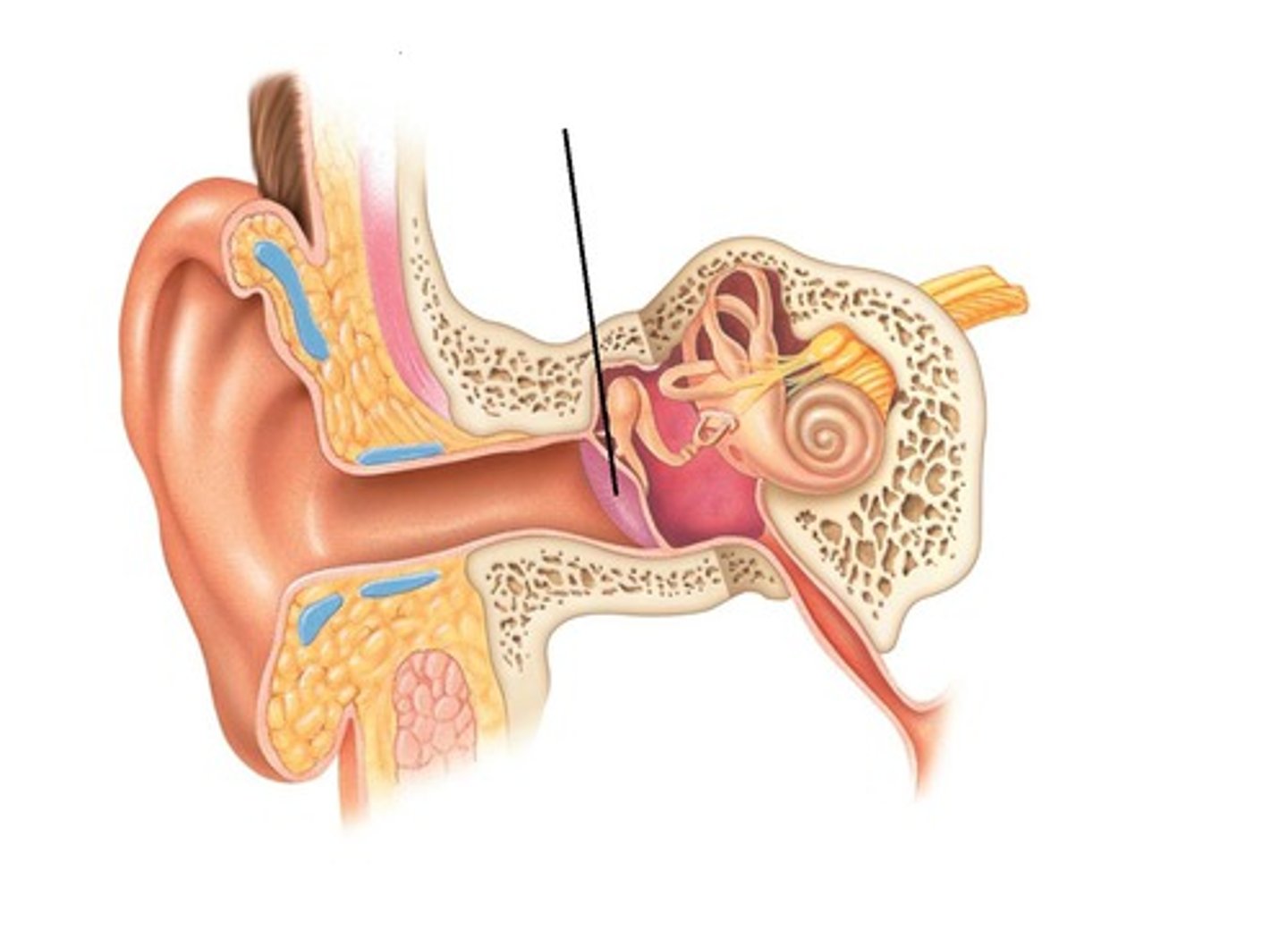
Malleus
Hammer; first of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear.
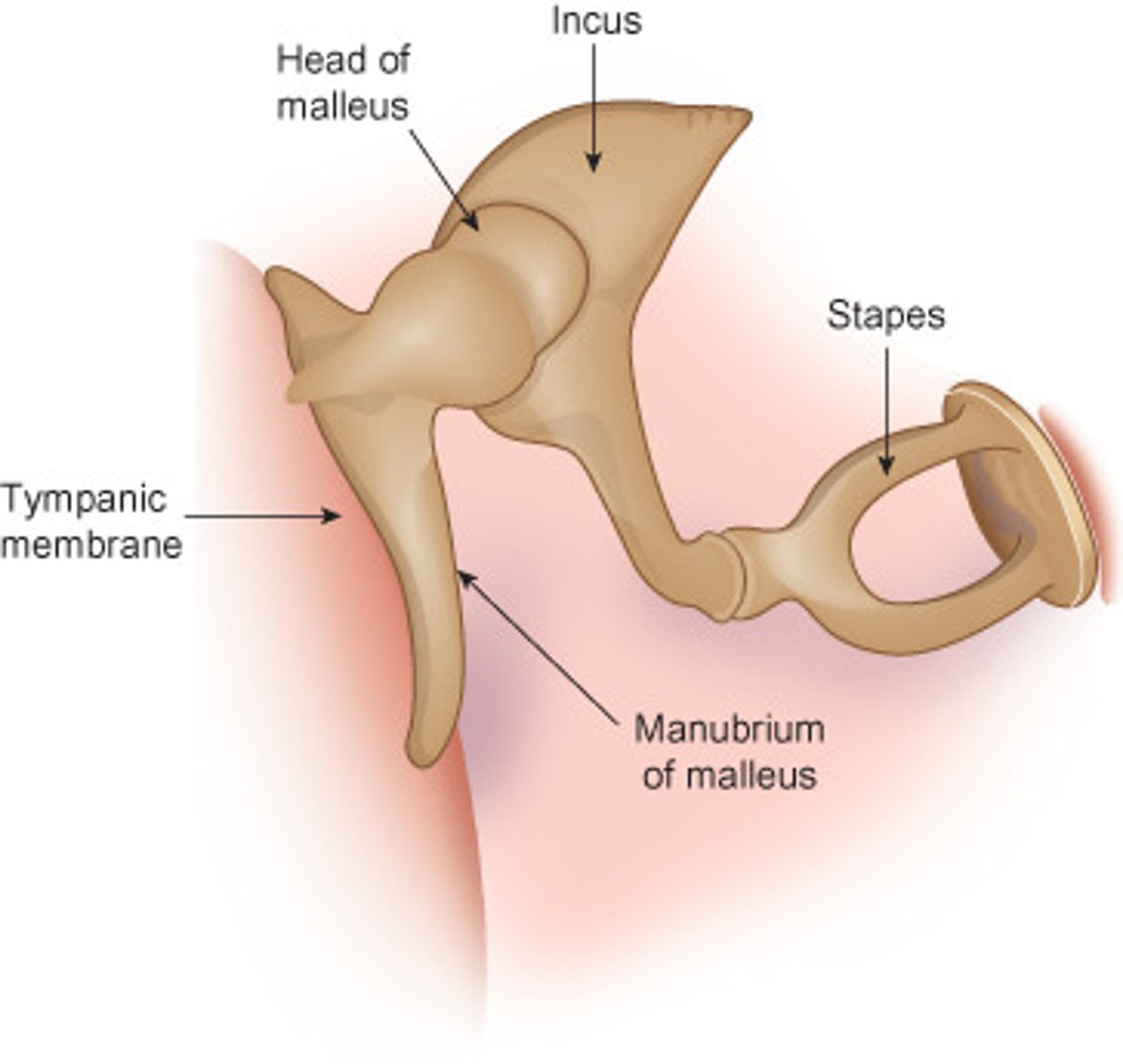
Incus
Anvil; middle of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear.
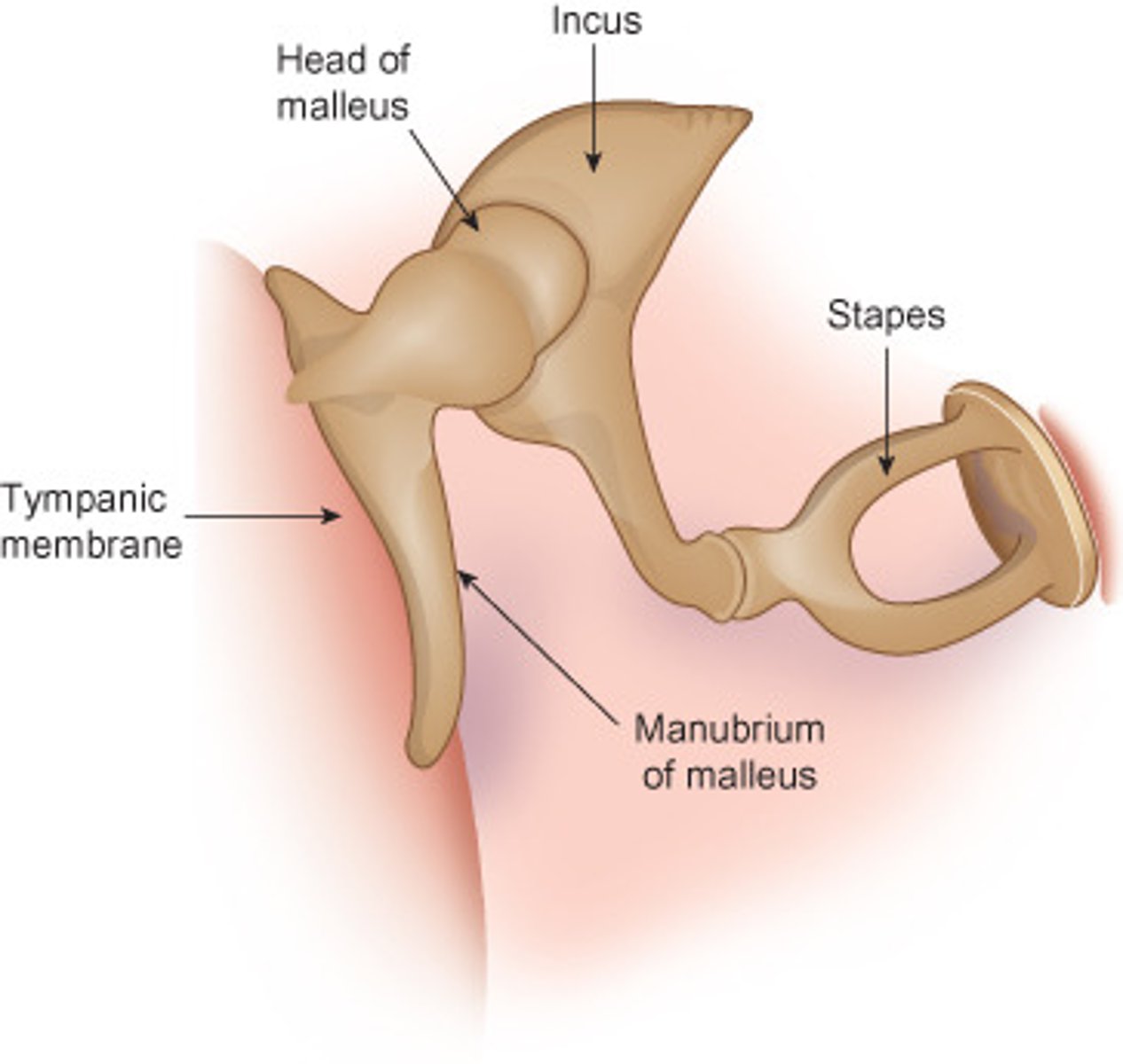
Stapes
Stirrup; last of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear.
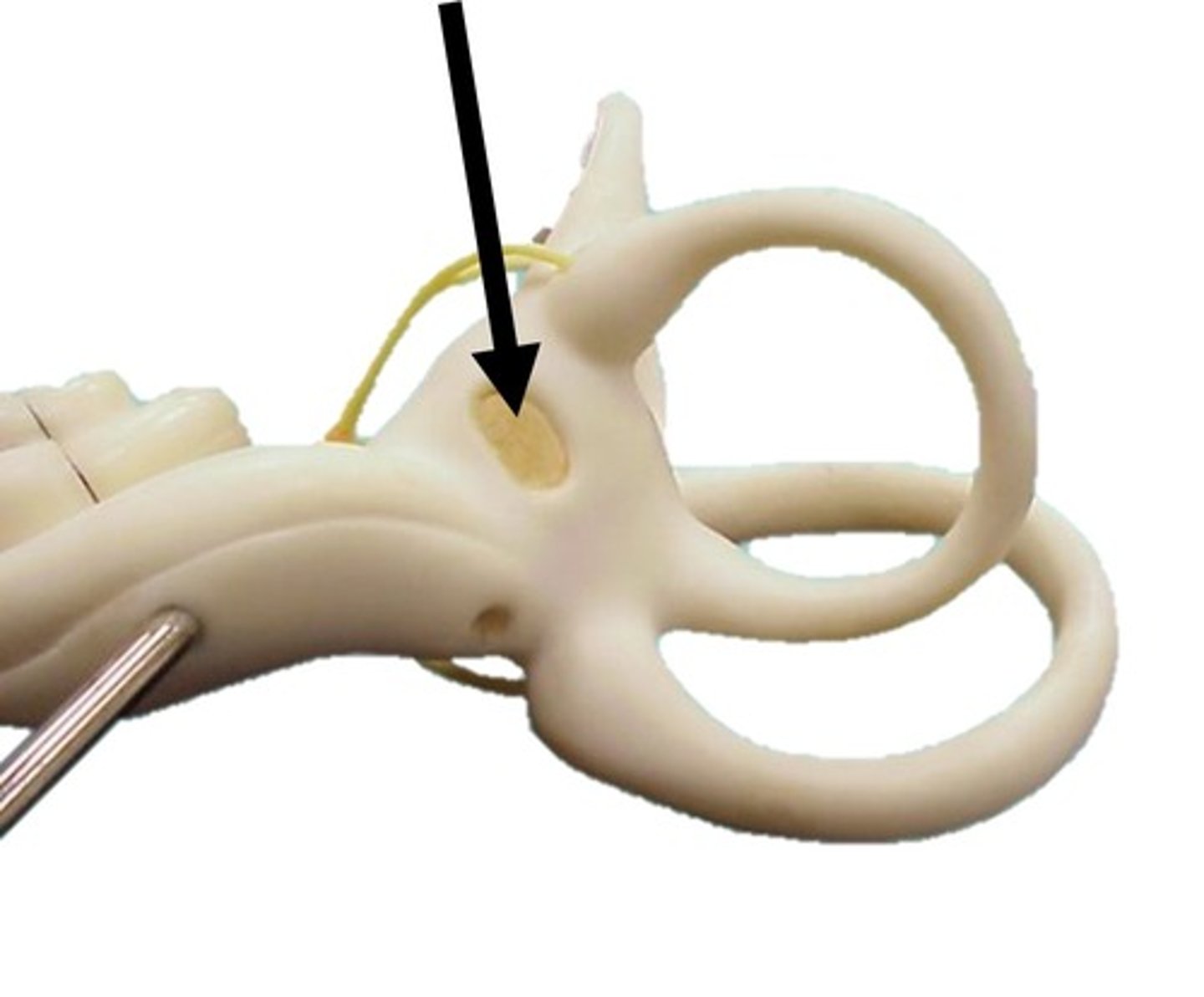
Oval Window
Membrane at the entrance to the cochlea through which the ossicles transmit vibrations.
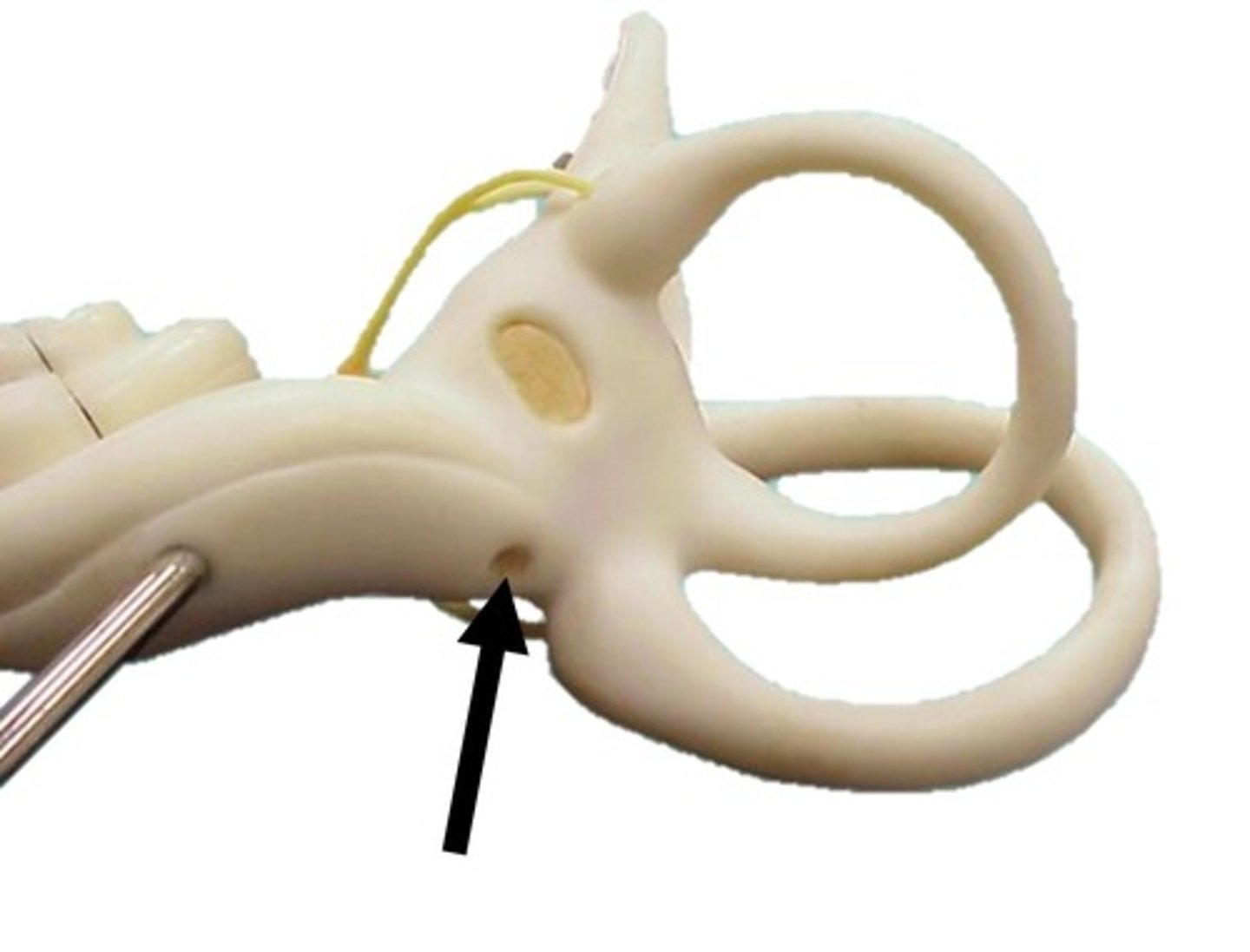
Round Window
Located just below the oval window; equalize pressure in the inner ear.
Eustachian Tube
Connects the middle ear with the nasopharynx and allows passage of air.
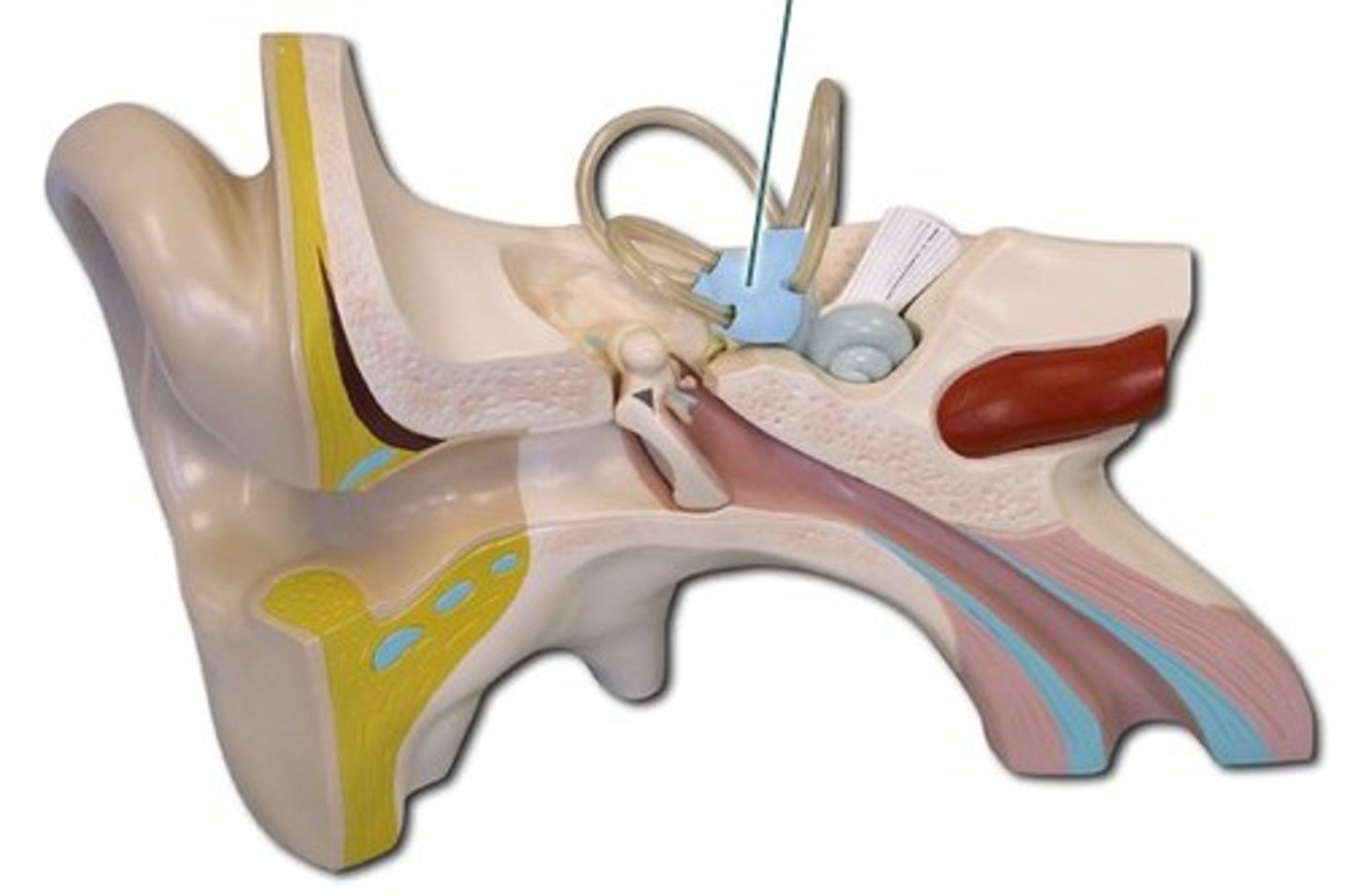
Bony Labyrinth
Passageways in temporal bone.
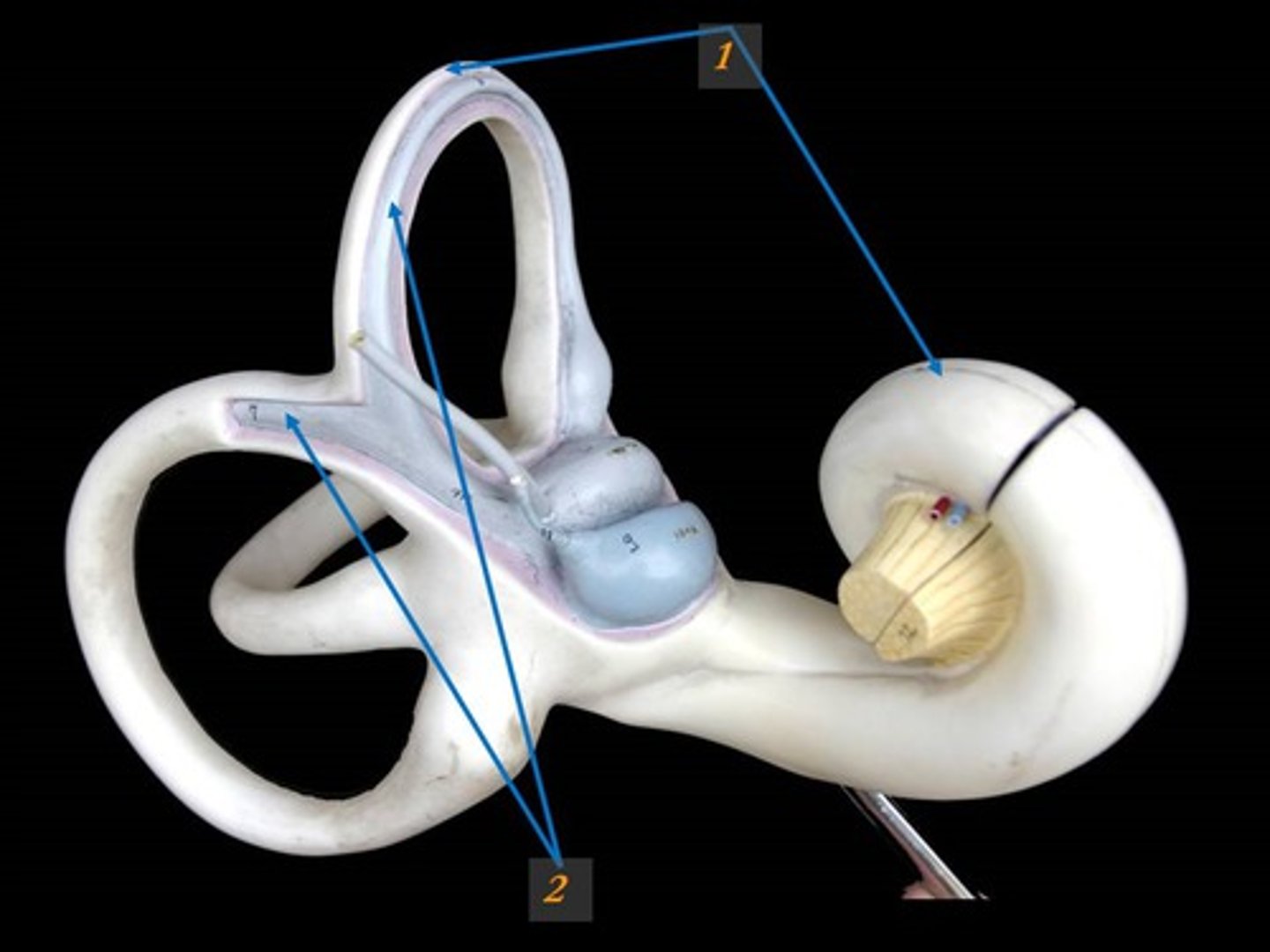
Membranous Labyrinth
Membrane-covered tubes inside the bony labyrinth.
Endolymph
Fluid within the labyrinth of the inner ear.
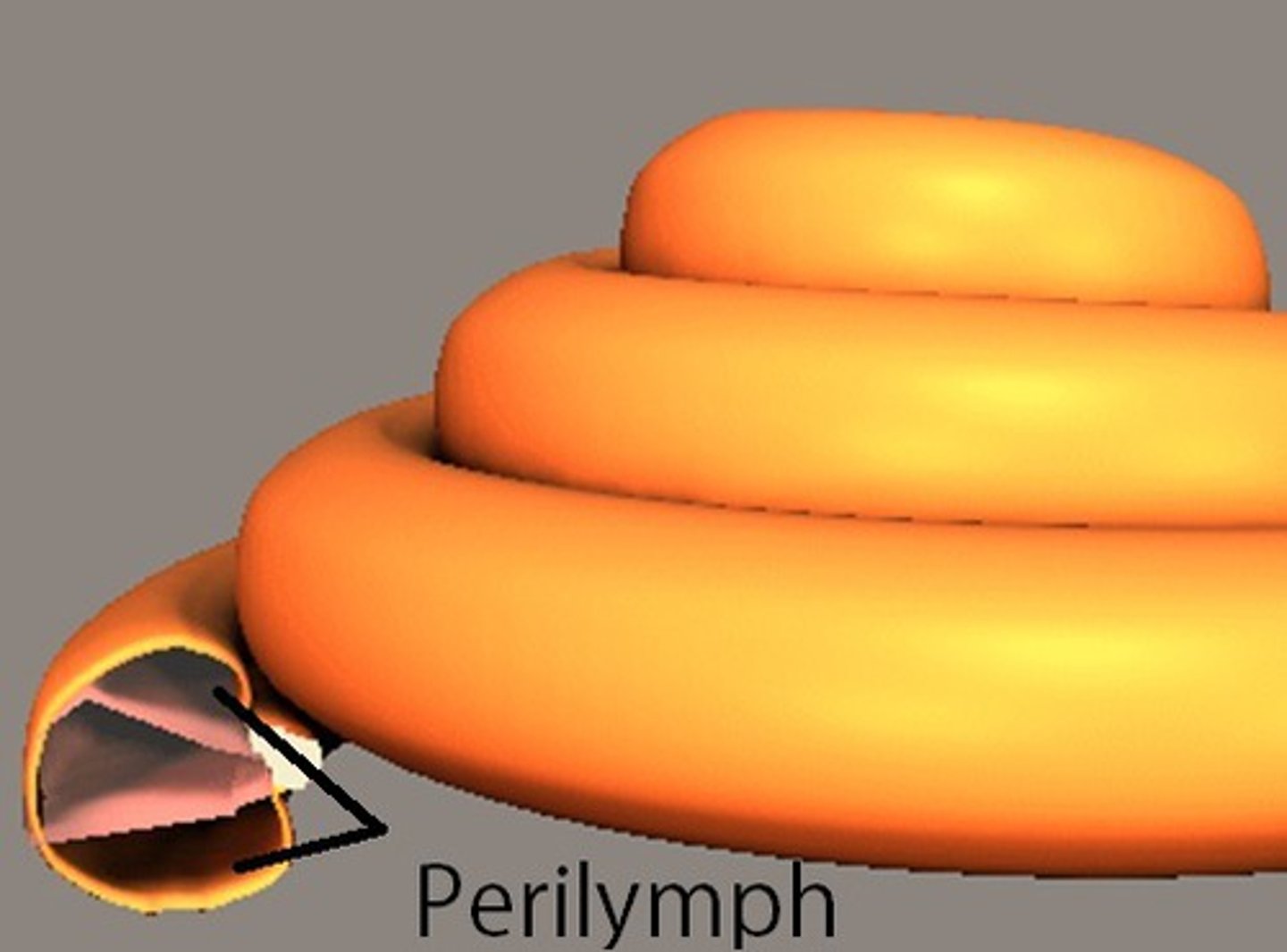
Perilymph
Fluid that very closely resembles spinal fluid but found in the cochlea.
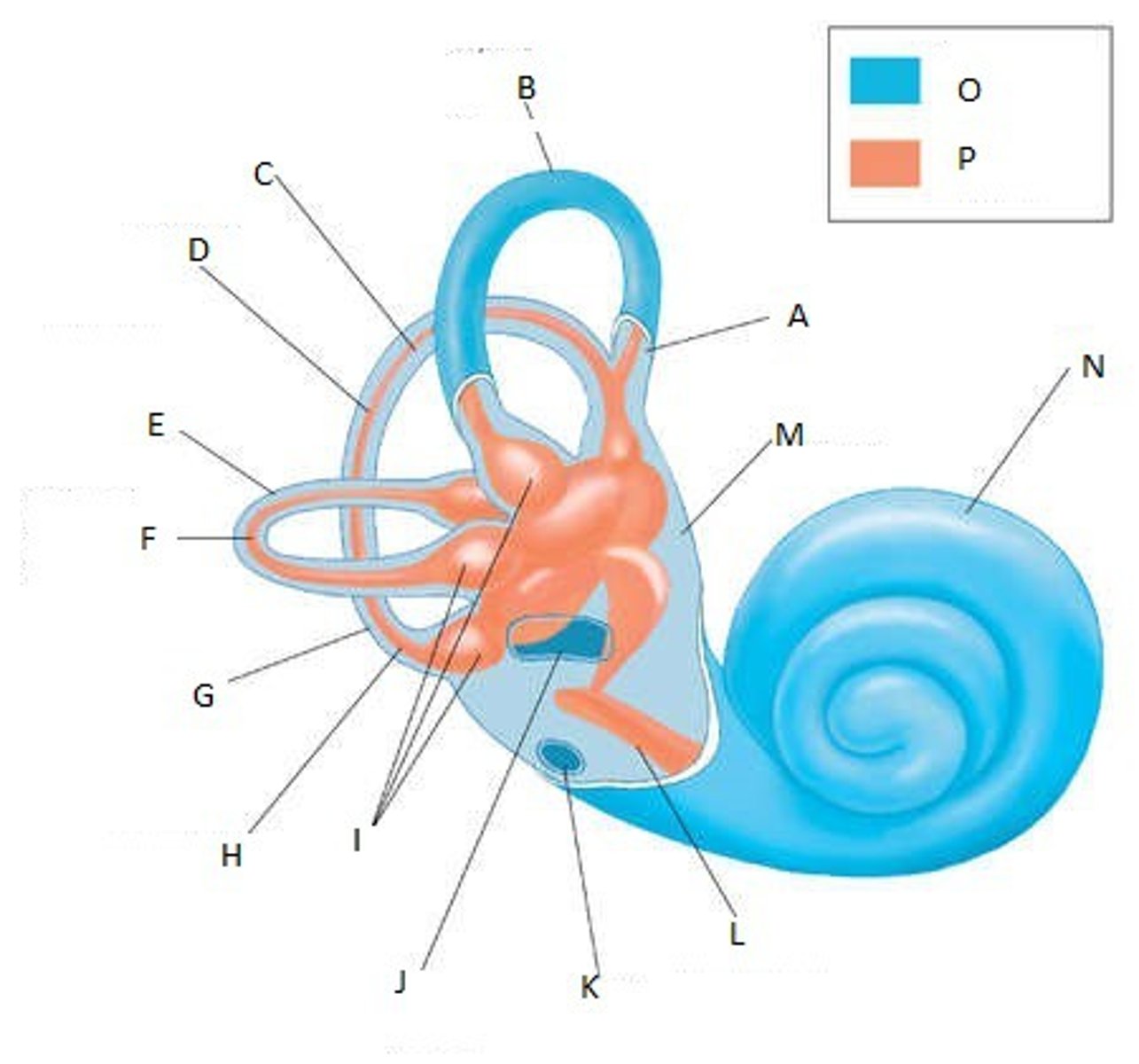
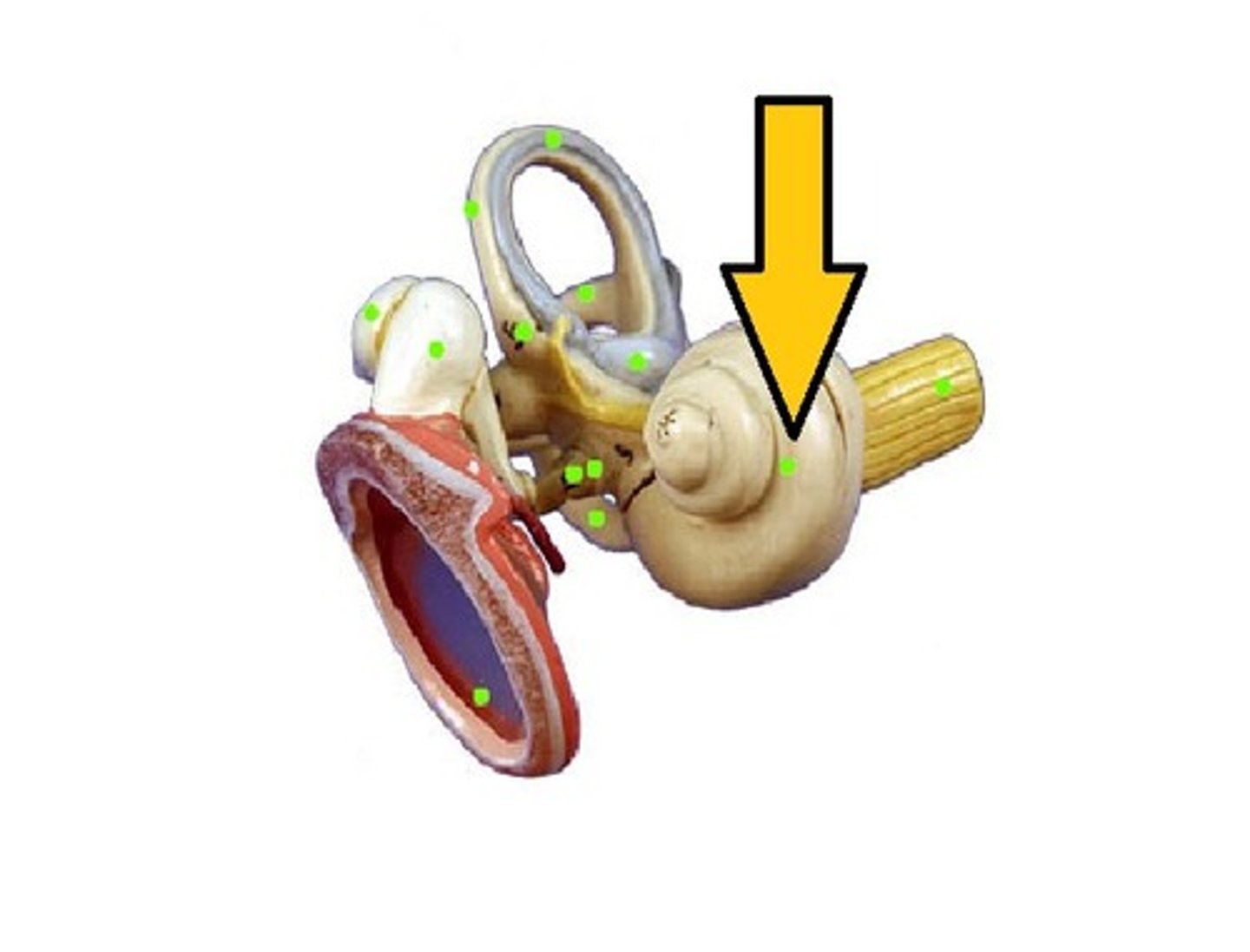
Vestibule
Central cavity of the bony labyrinth that detects linear acceleration and connects the cochlea and semicircular canals
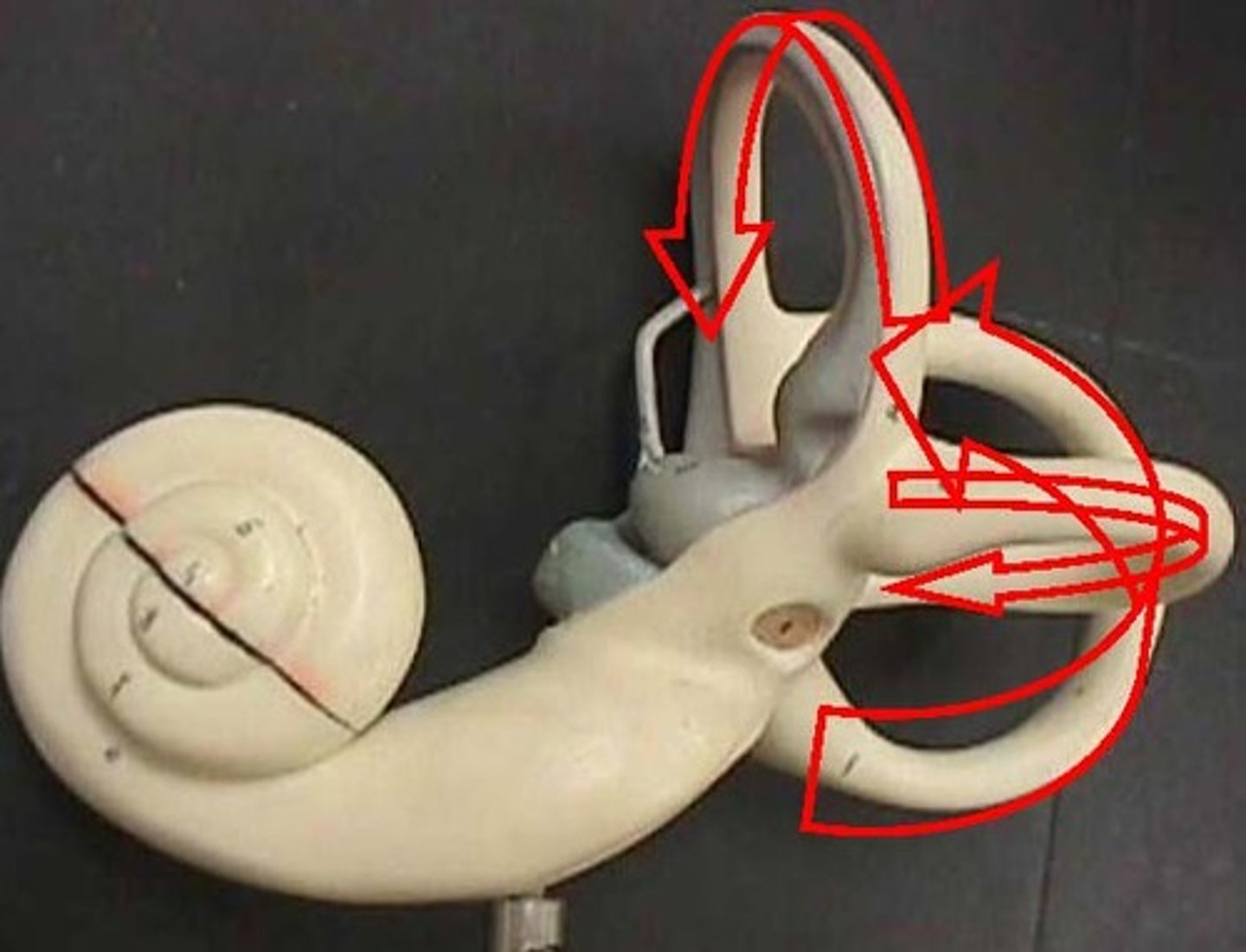
Semicircular Canals
Three fluid-filled canals in the inner ear responsible for our sense of balance.
Cochlea
A coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses.
Scala Vestibuli
The upper bony passage of the cochlea.
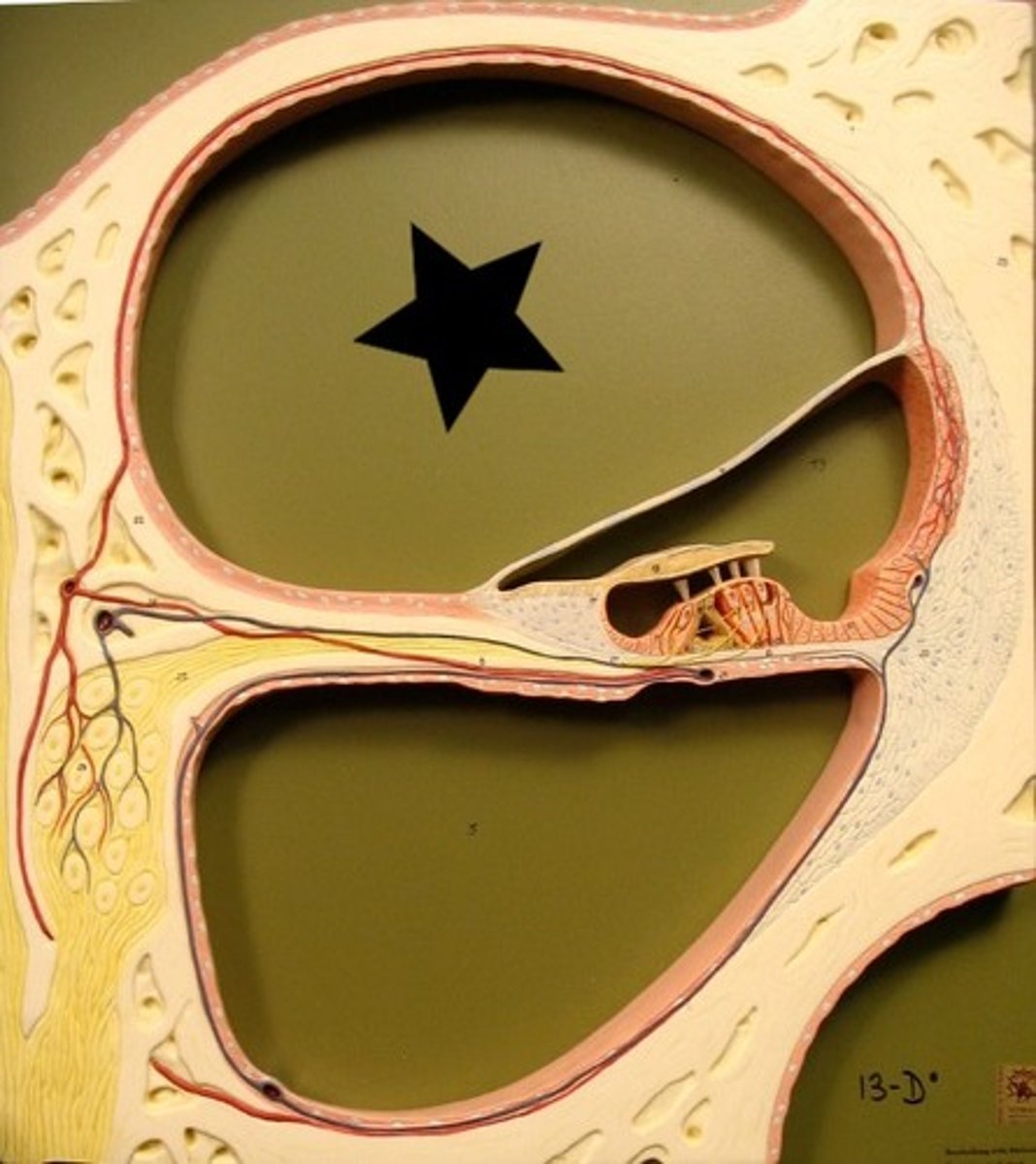
Scala Tympani
Extends from apex of cochlea to round window; lower portion.
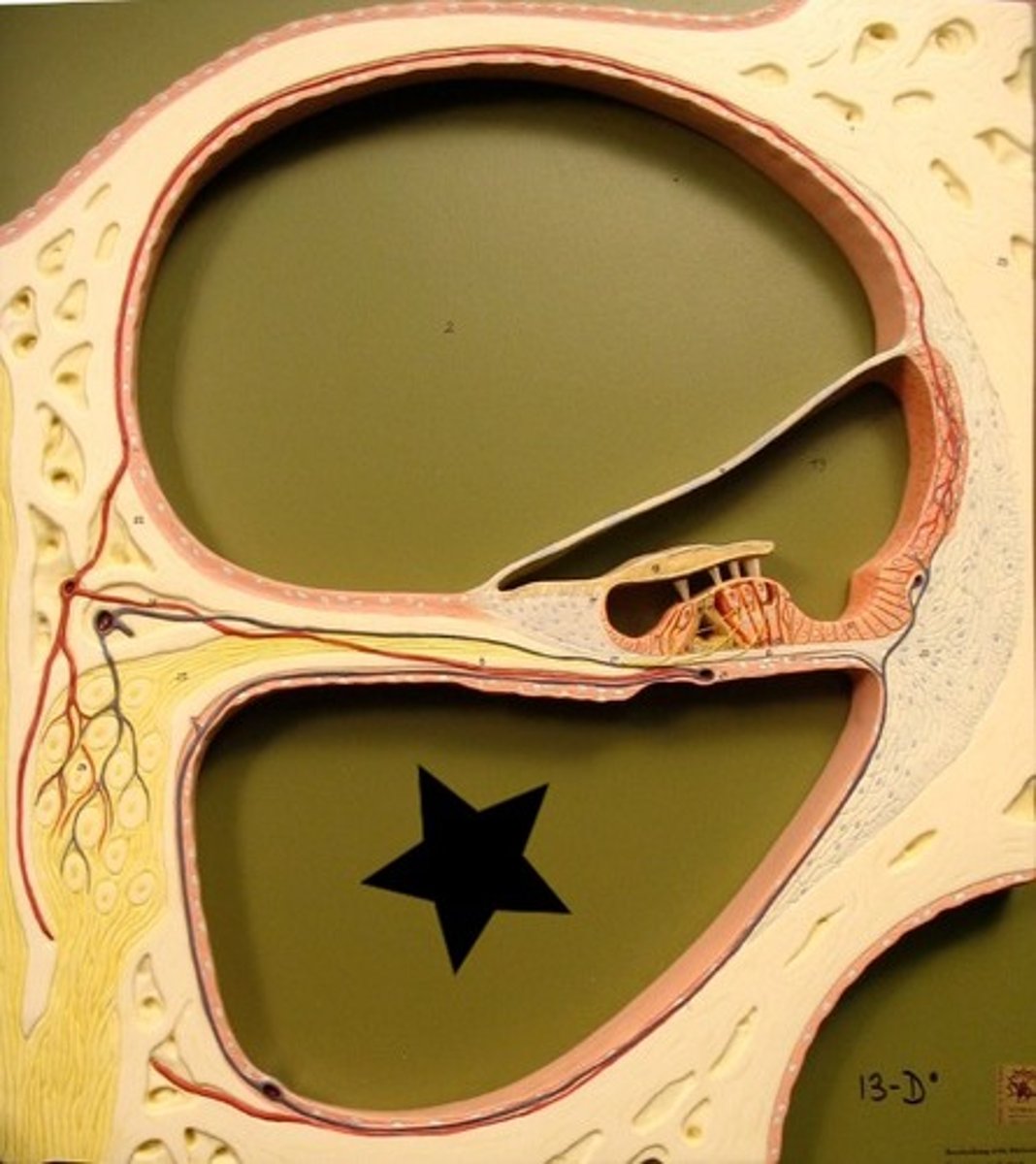
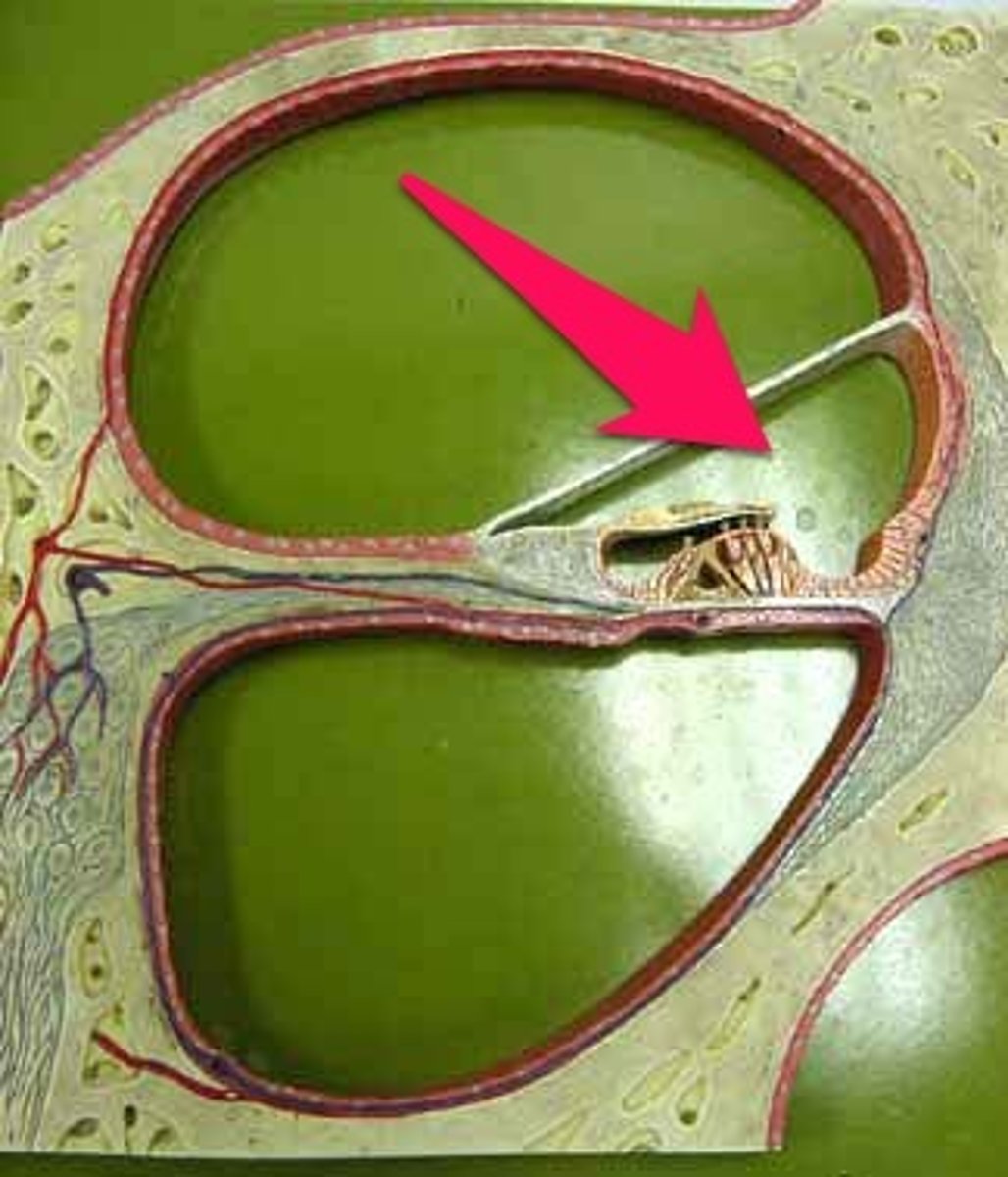
Cochlear Duct
Fluid filled cavity within the cochlea that vibrates when sound waves strike it.
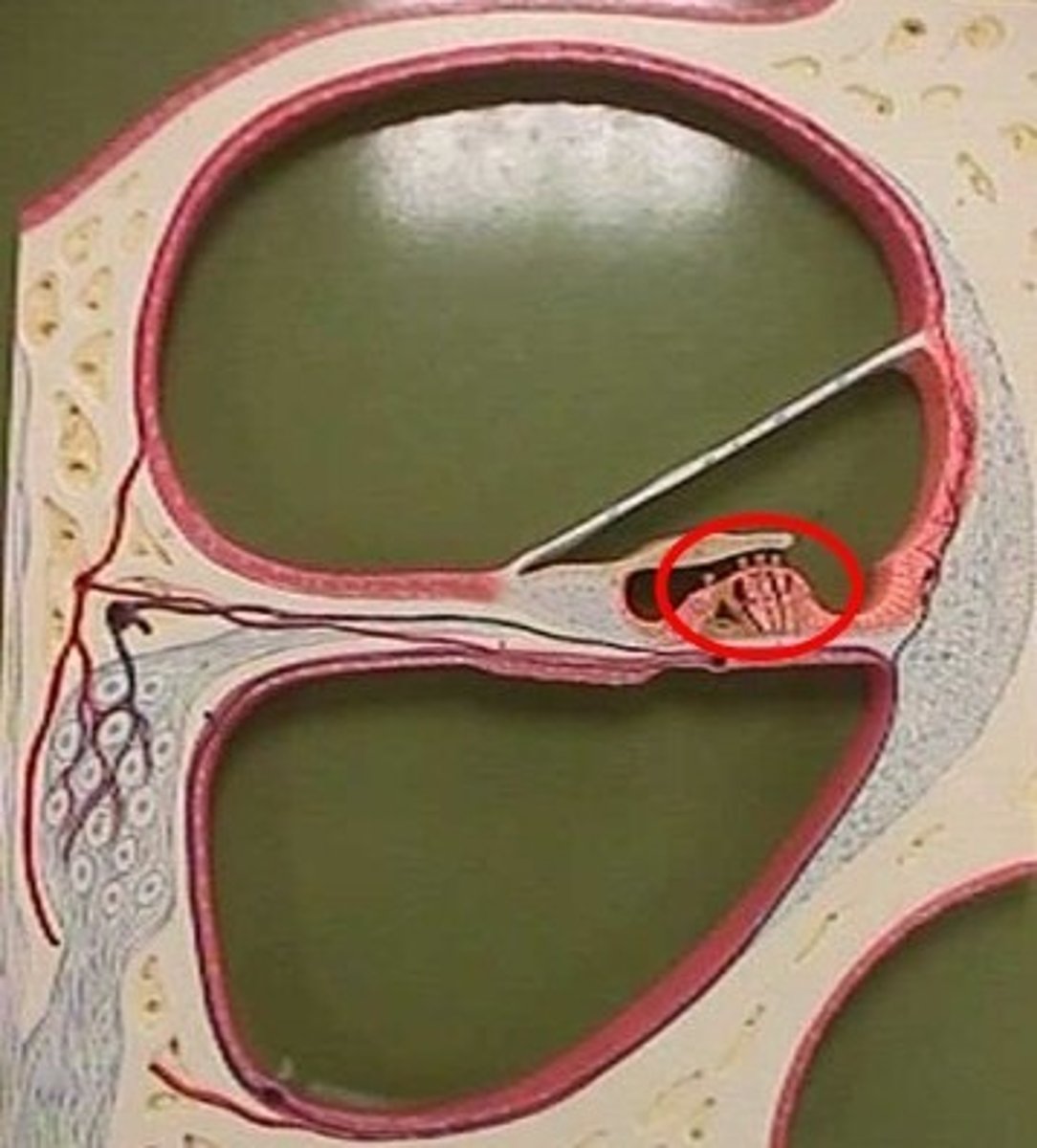
Organ of Corti
Tissue containing the hair cells necessary for hearing.
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
Primarily focuses on hearing and balance (sensory).
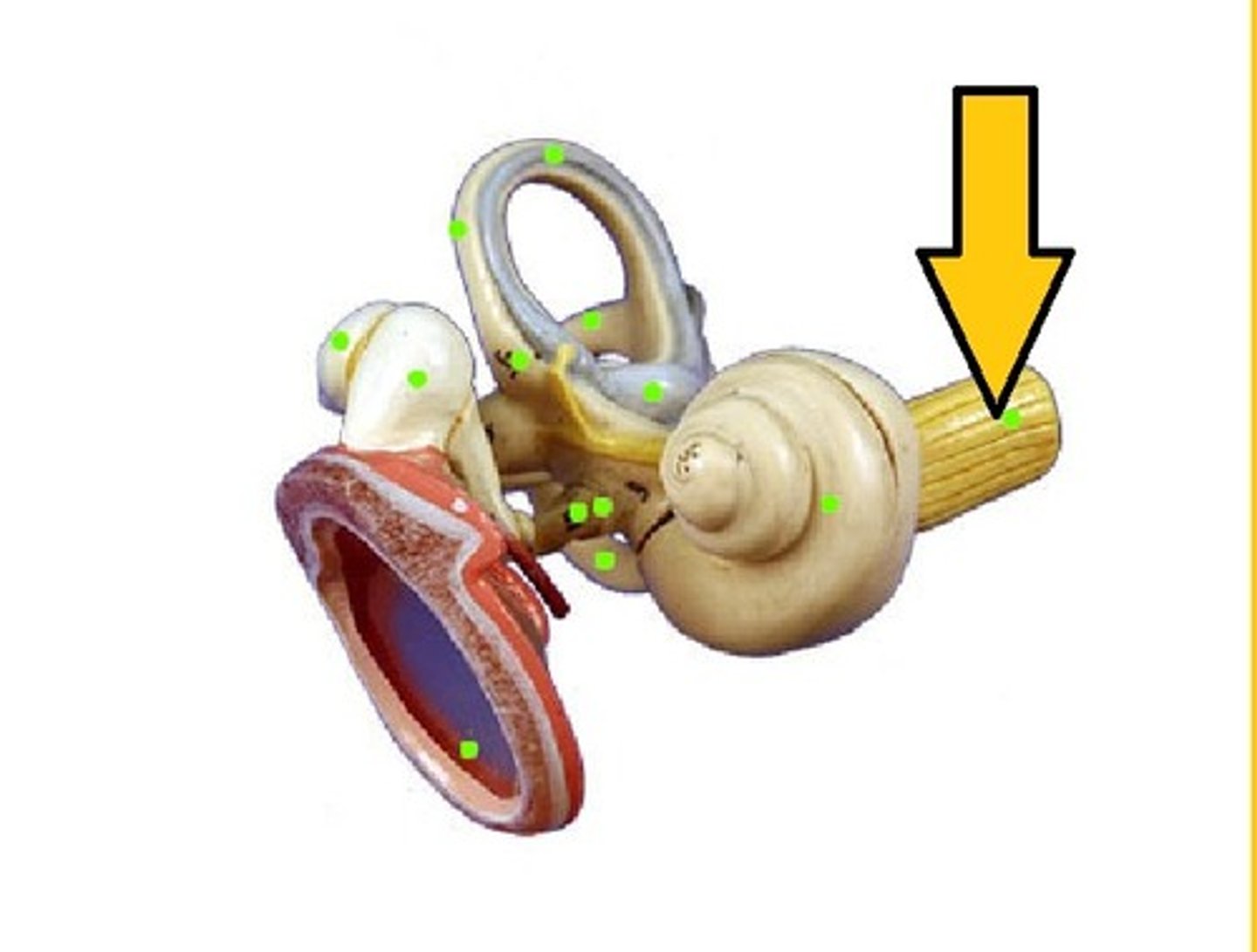
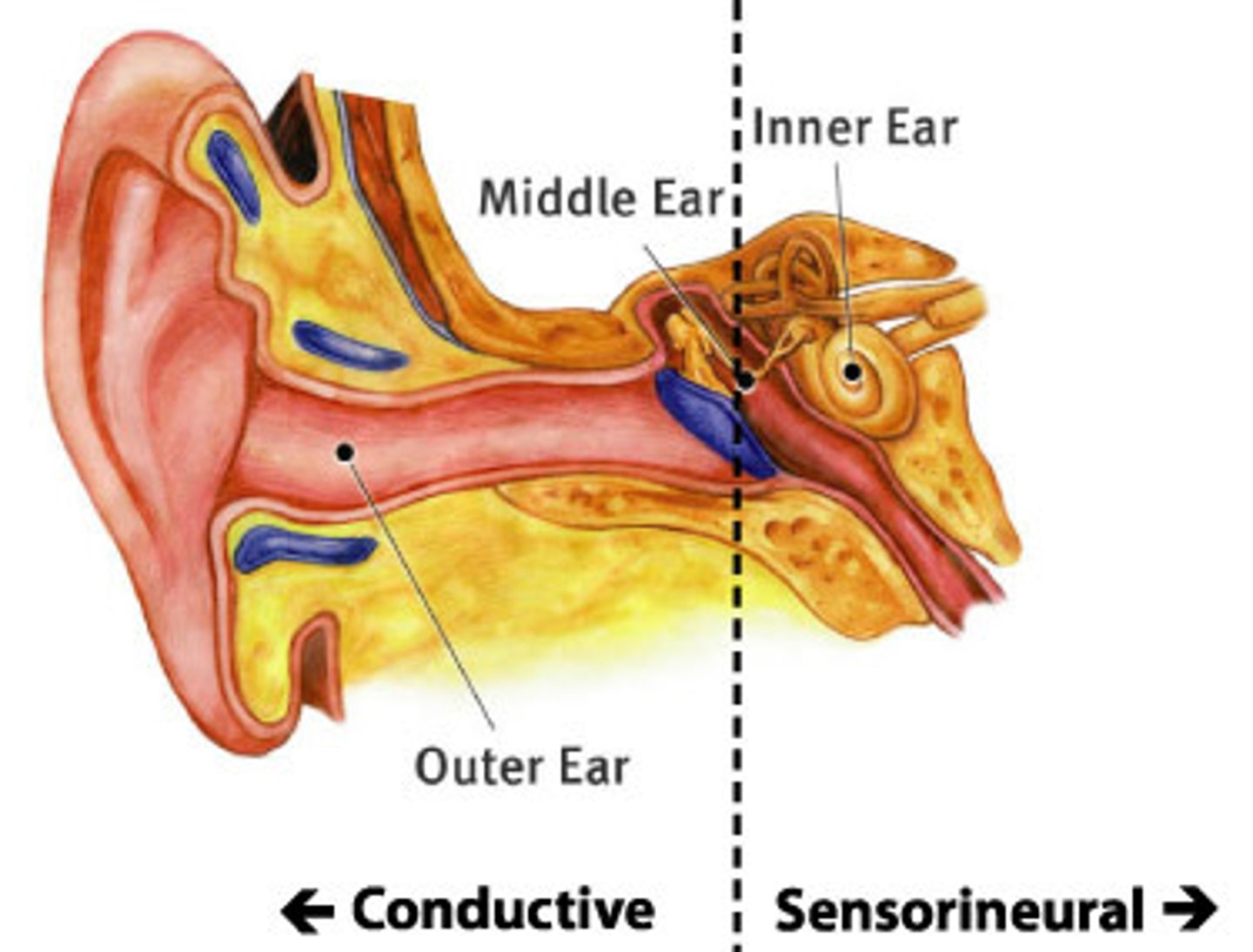
Conductive Hearing Loss
Hearing impairment caused by interference with sound or vibratory energy in the external canal, middle ear, or ossicles.
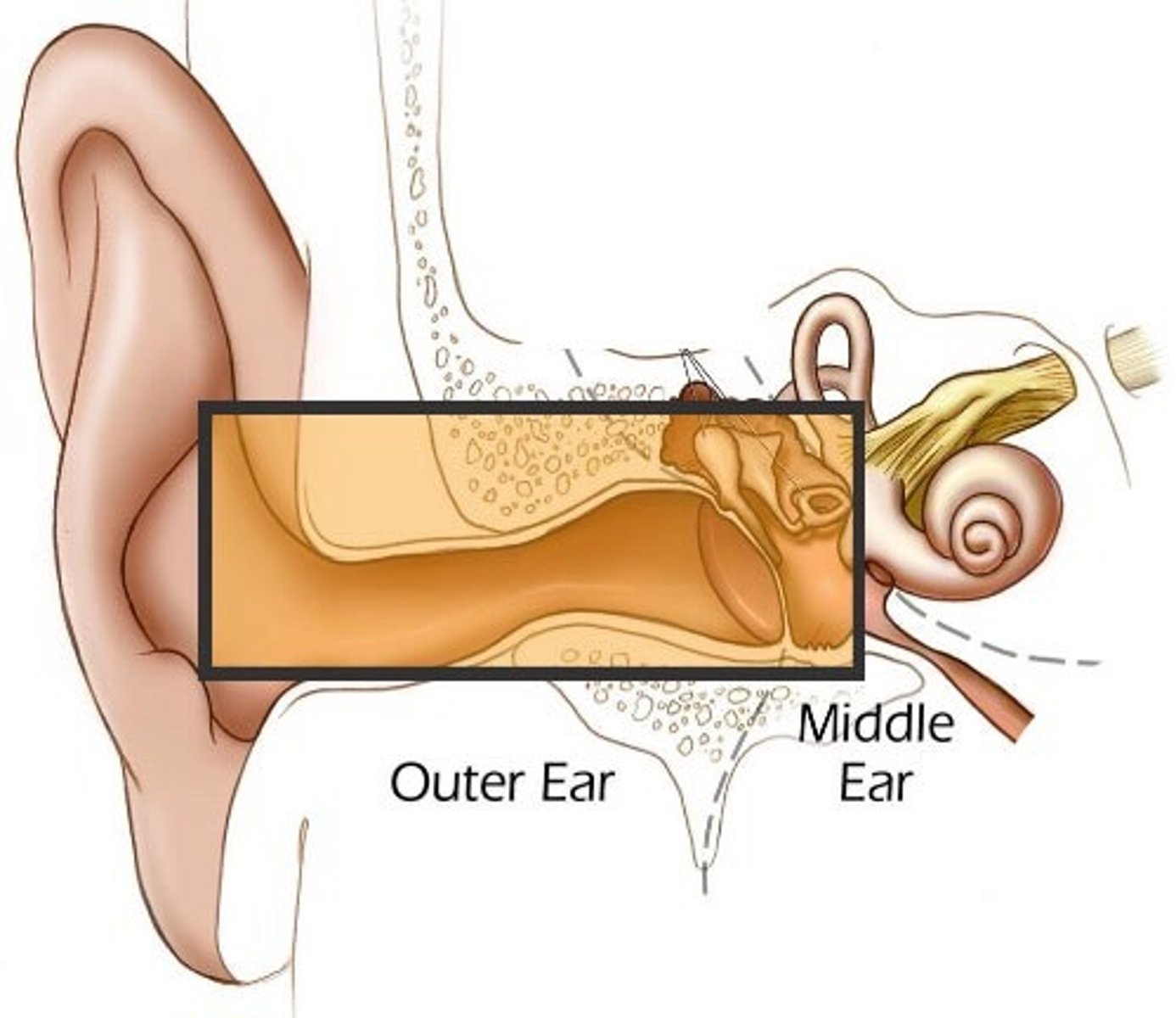
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
The most common form of hearing loss, also called nerve deafness; caused by damage to the cochlea's receptor cells or to the auditory nerves.
Static Equilibrium
A condition where there are no net external forces acting upon a particle or rigid body and the body remains at rest or continues at a constant velocity.
Dynamic Equilibrium
Result of diffusion where there is continuous movement of particles but no overall change in concentration.

Vertigo
Condition of dizziness, "room spinning".

Nystagmus
Involuntary rapid eye movements.