Urinalysis: Microscopic Examination of Urine
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
Macroscopic
large enough to be visible to the naked eye
Standard amount of urine centrifuged for examination:
10-15mL
Relative centrifugal force (RCF)
Force required to separate two phases in a centrifuge
revolutions per minute (rpm)
Revolutions per minute, a unit of velocity.
Decanting
Pouring liquid off the top when sediment has settled to the bottom of the container
How much urine and sediment should remain in the tube after decantation?
0.5-1.0mL
Microscopic examination of urine should include observation of a minimum of:
10 fields under both low (10x) and high (40x) power
bright field microscopy
generates a dark image of an object over a light background
Semiquantitative terms:
rare, few, moderate, and many or as 1+, 2+, 3+, 4+
Routine urinalysis correlations of microscopic elements: RBCs
-physical= turbidity
-chemical= positive blood
-exceptions= number
or
-physical= red color
-chemical= positive protein
-exceptions= hemolysis
Routine urinalysis correlations of microscopic elements: WBCs
-physical= turbidity
-chemical= positive protein, positive nitrite, and positive LE
-exceptions= number and lysis
Routine urinalysis correlations of microscopic elements: Epithelial cells
-physical= turbidity
-exception= number
Routine urinalysis correlations of microscopic elements: Casts
-chemical= positive protein
-exceptions= number
Routine urinalysis correlations of microscopic elements: Bacteria
-physical= turbidity
-chemical= increased pH, positive nitrite, and positive Leukocytes
-exceptions= number and type
Routine urinalysis correlations of microscopic elements: Crystals
-physical= turbidity
-chemical= pH
-exceptions= number and type
or
-physical= color
-chemical= positive bilirubin
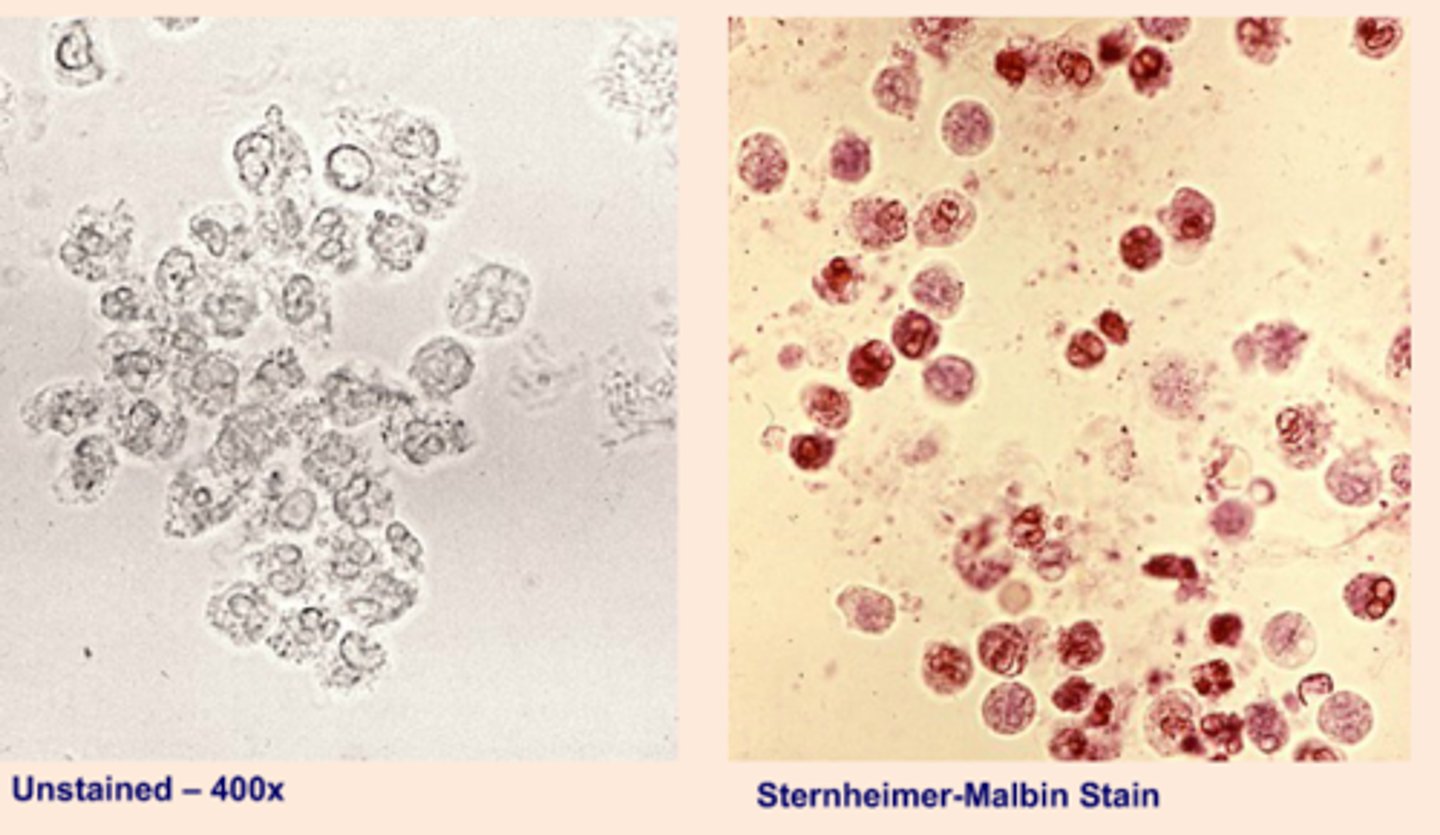
Sternheimer-Malbin stain
Delineates structure and contrasting colors of the nucleus and cytoplasm. (Identifies WBCs, epithelial cells, and casts)
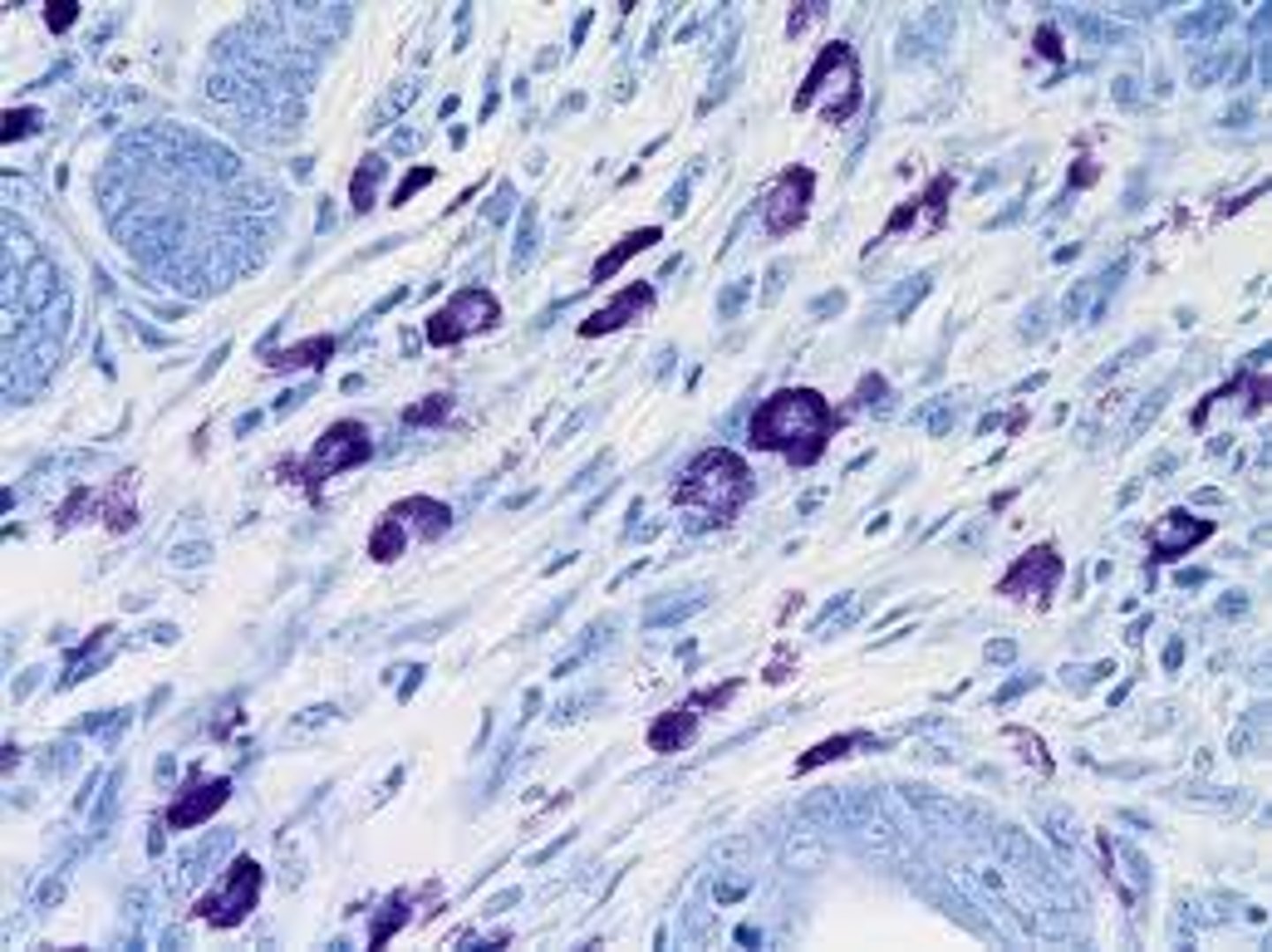
Toluidine blue stain
Enhances nuclear detail. (differentiates WBCs and renal tubular epithelial cells (RTE))
2% acetic acid stain
Lyses RBCs and enhances nuclei of WBCs. (distinguishes RBCs from WBCs, yeast, oil droplets, and crystals)
Lipid Stains: Oil Red O and Sudan III
Stain triglycerides and neutral fats orange-red. Do not stain cholesterol. (Identify free fat droplets and lipid-containing cells and casts)
Gram stain
Differentiates gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. (identifies bacterial casts)
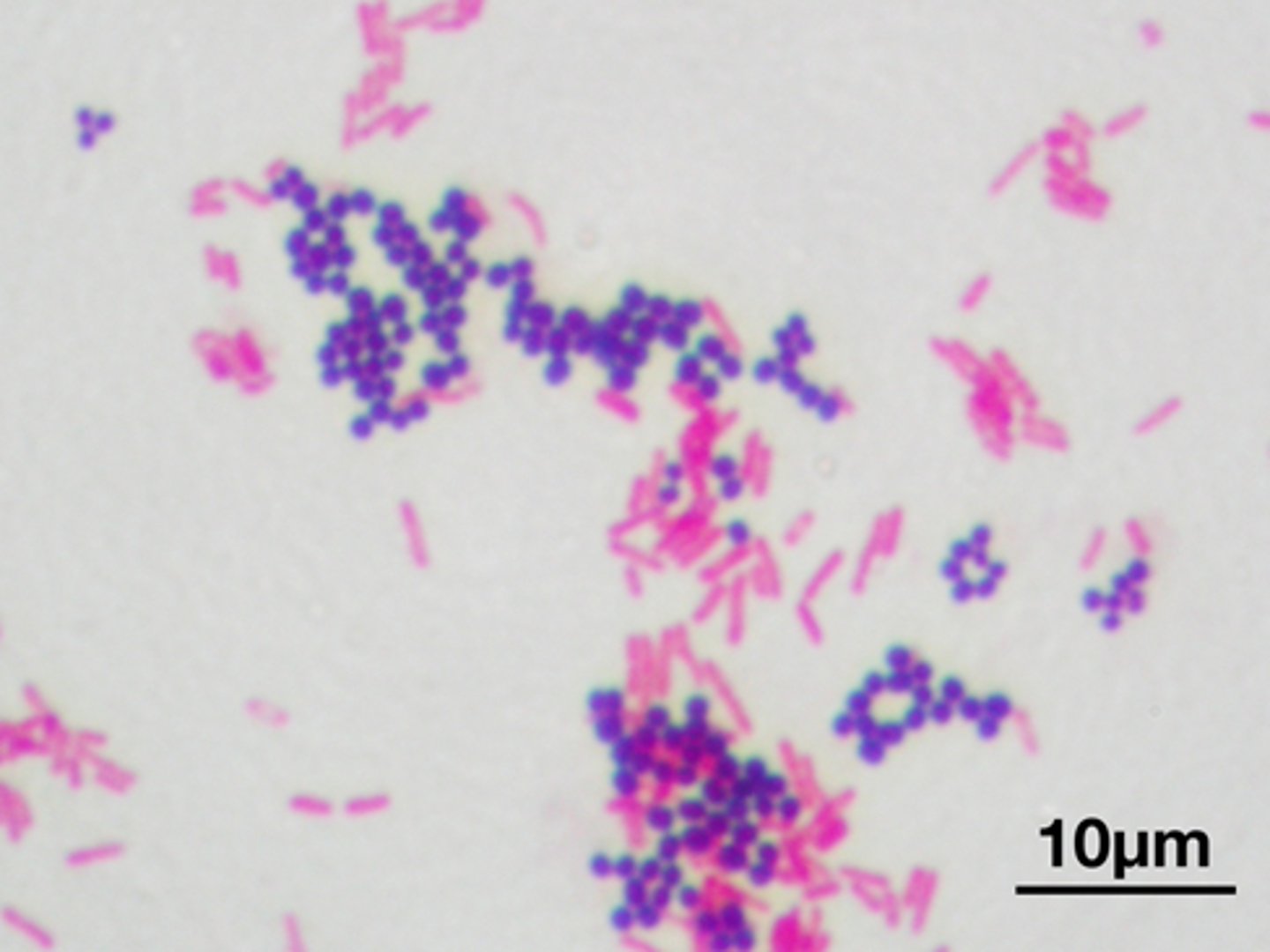
Hansel stain
Methylene blue & eosin Y stains eosinophilic granules. (identifies urinary eosinophils)
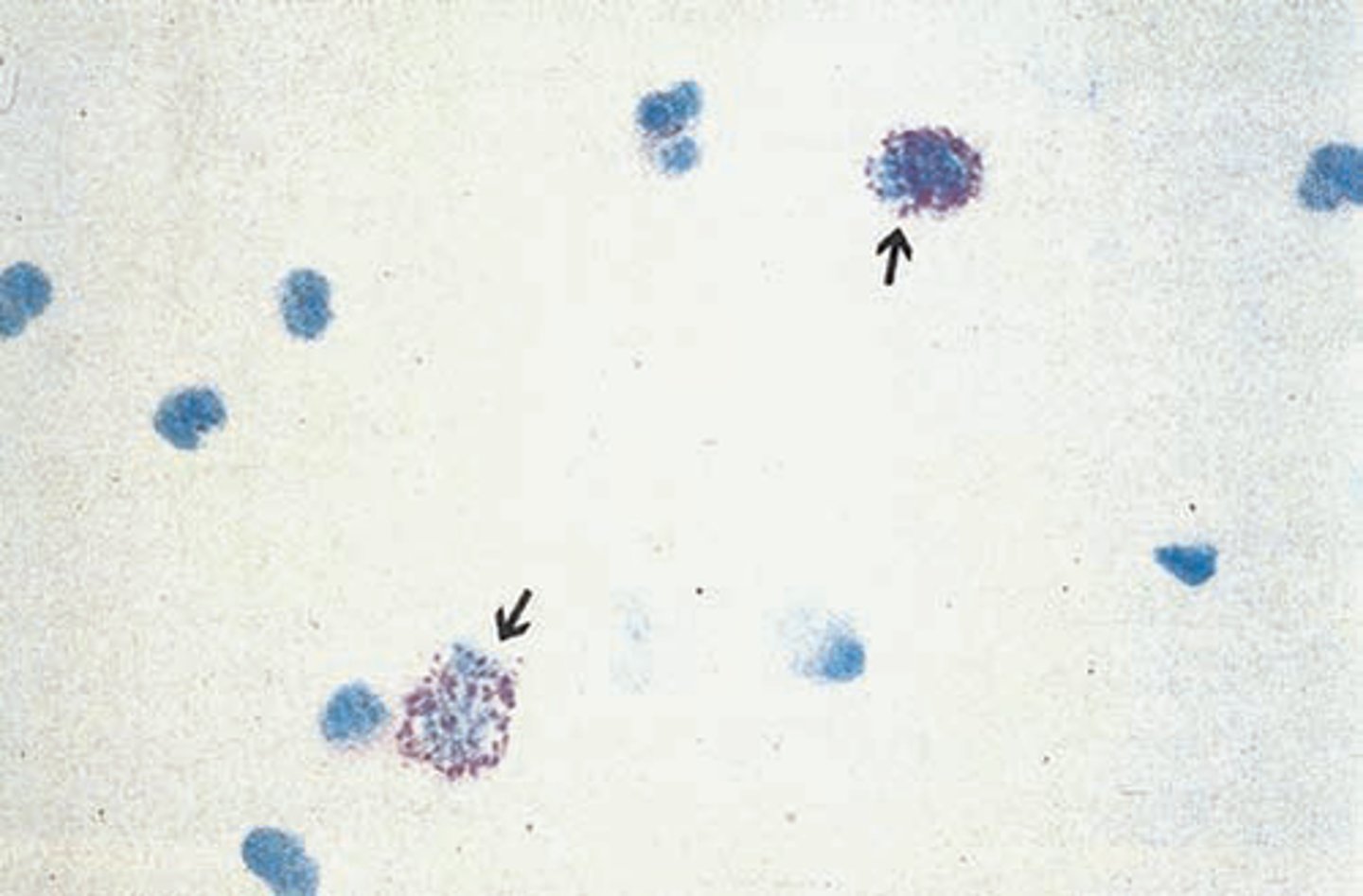
Prussian blue stain
Stains structures containing iron. (Identifies yellow-brown granules of hemo-siderin in cells and casts)
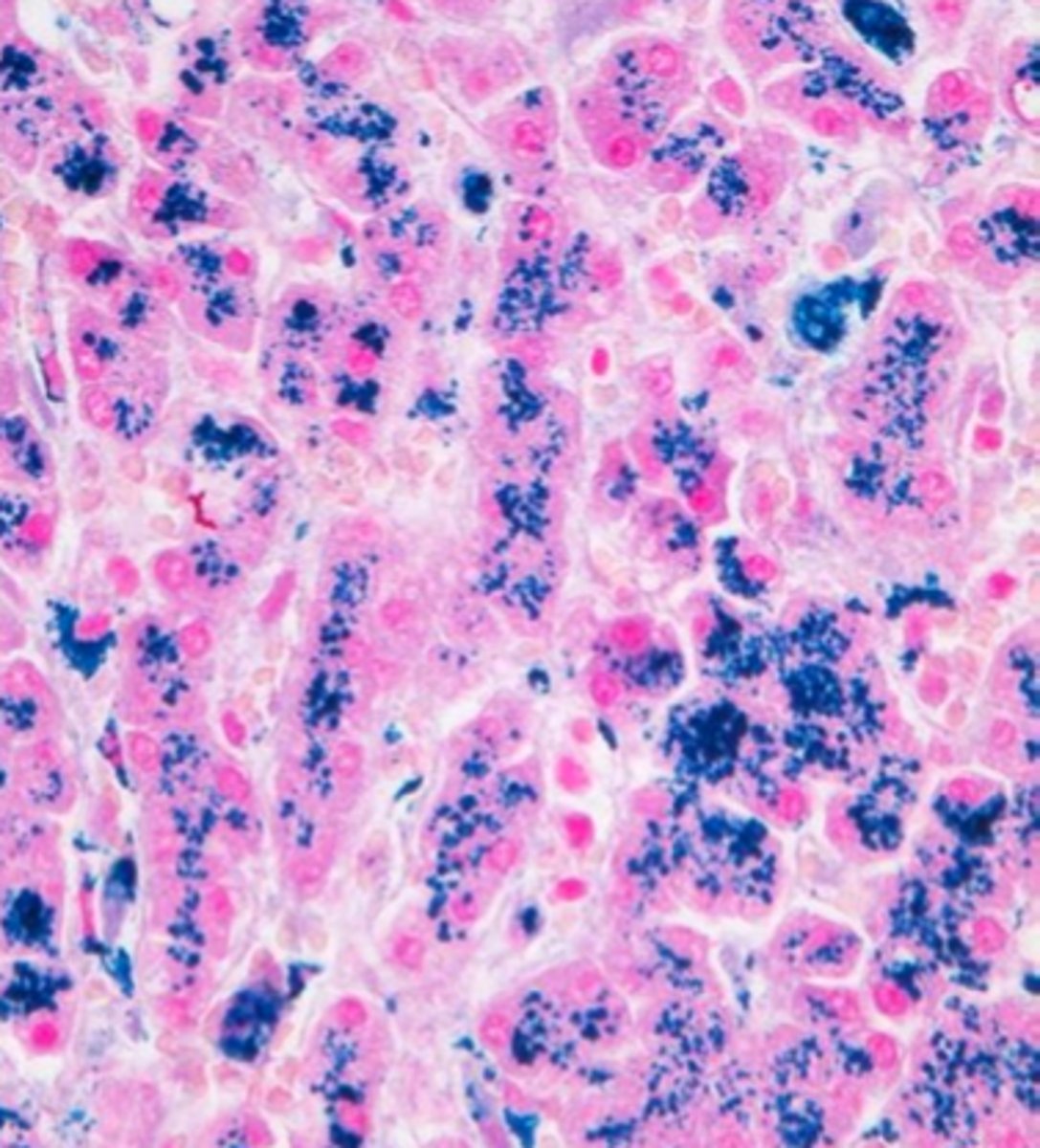
Phase-contrast microscopy
- enhances visualization of the elements with low refractive indices, such as hyaline casts, mixed cellular casts, mucous threads, and Trichomonas
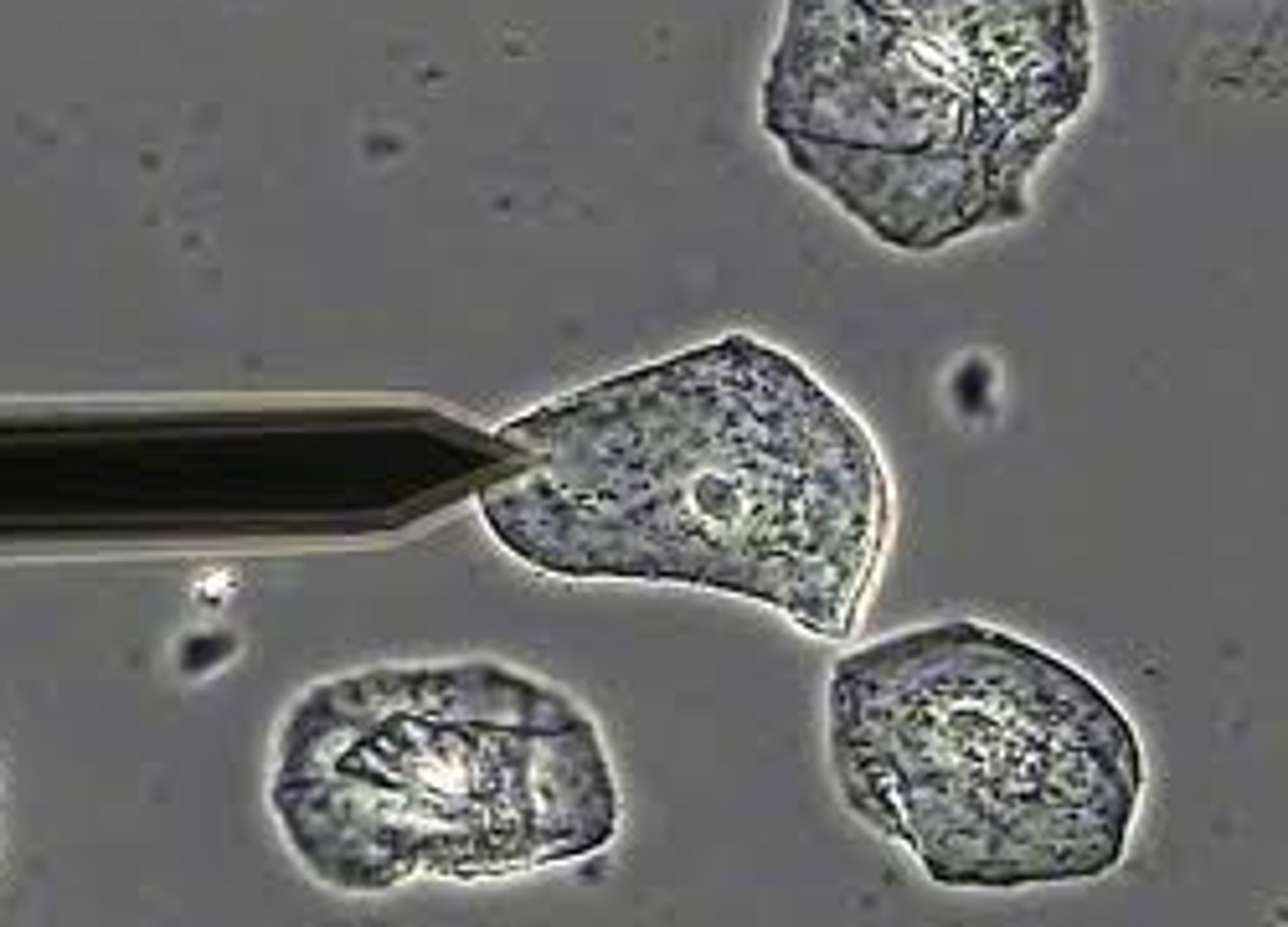
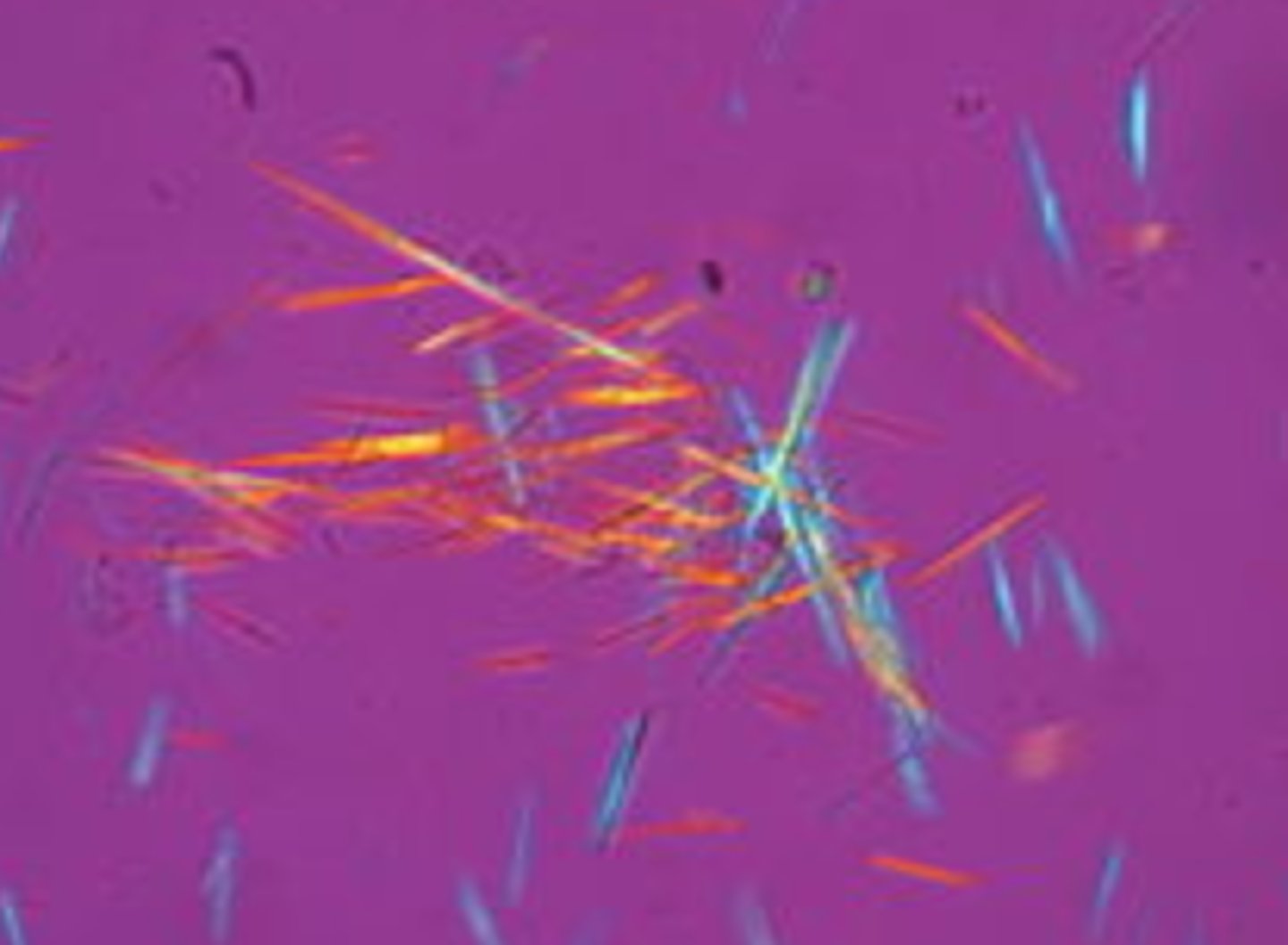
Polarizing microscopy
aids in identification of cholesterol in oval fat bodies, fatty casts, and crystals

dark field microscopy
Aids in identification of Treponema pallidum
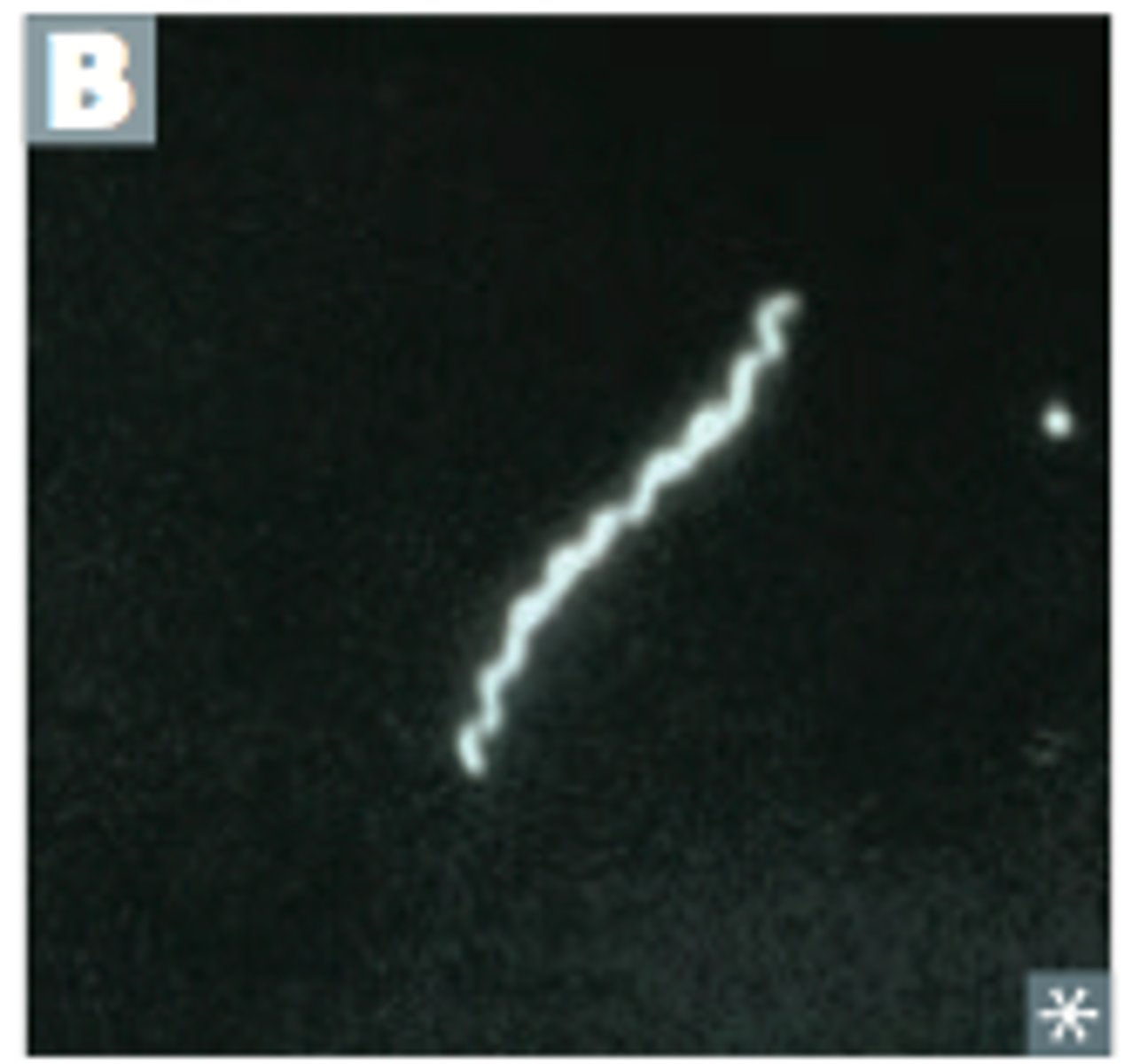
fluorescence microscopy
Allows visualization of naturally fluorescent microorganisms or those stained by a fluorescent dye including labeled antigens and antibodies
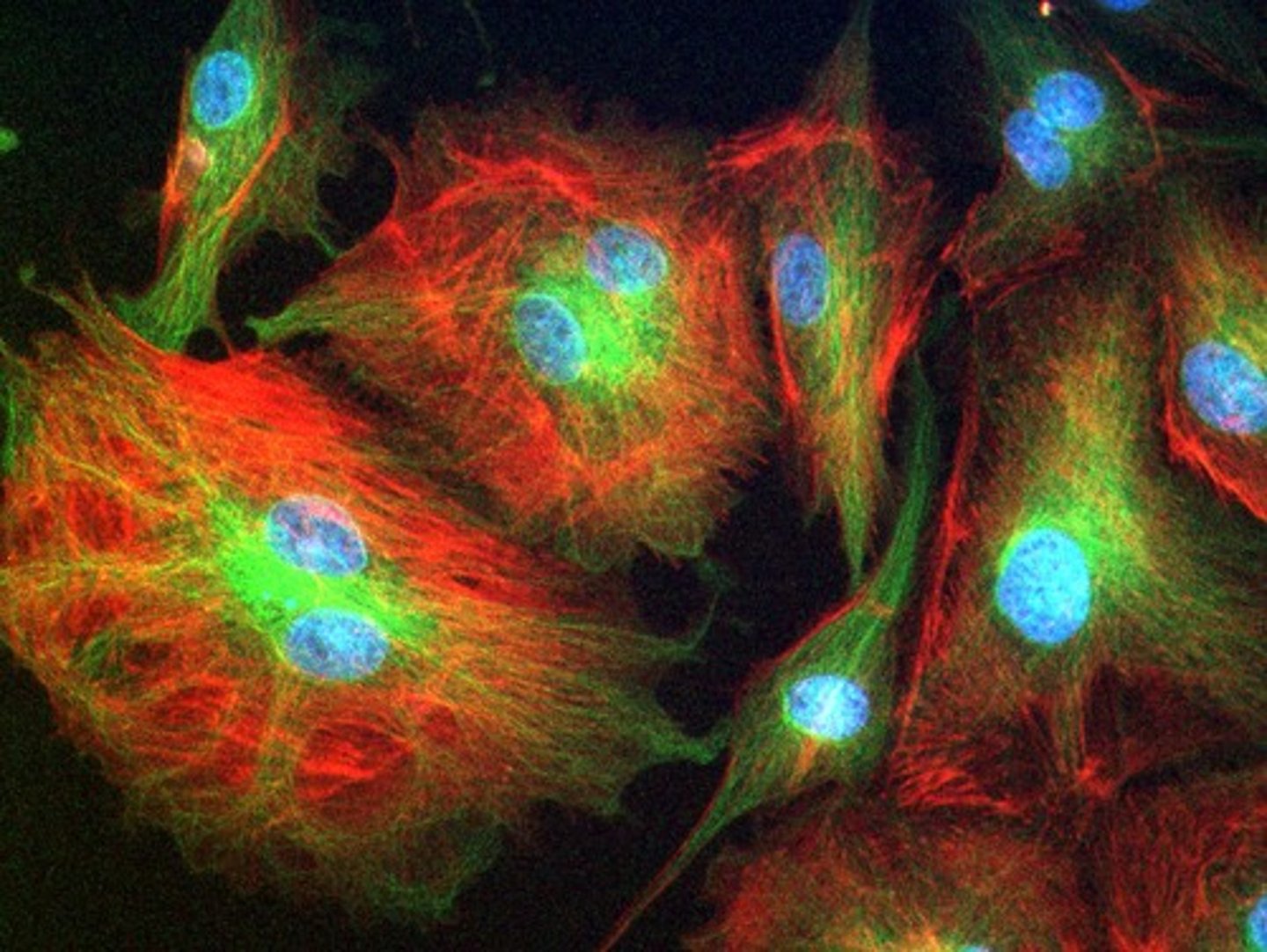
Interference-contrast microscopy
-produces 3D image and layer by layer imaging of specimen
Care of Microscope
1. always carry with two hands
2. always hold in vertical position
3. clean optical surfaces only with a good quality lens tissue and commercial lens cleaner
4. do not use oil on 10x and 40x objects (only for 100x)
5. clean the oil immersion lens after use
6. always remove slides with the low-power objective raised
7. store microscope with the low-power objective in position and stage centered
Kohler illumination
alignment of illuminating light for microscopy; double diaphragm illumination
To center the condenser and obtain Kohler illumination, take the following steps:
1. place a slide on stage and focus the object using the low-power objective w/ the condenser raised
2. close the field diaphragm
3. lower the condenser until the edges of the field diaphragm are sharply focused
4. center the image of the field diaphragm w/ the condenser centering screws
5. open the field diaphragm until its image is at the edge of the field
6. remove an eyepiece and look down through the eyepiece
7. adjust the aperture diaphragm until approx. 75% of the field is visible
8. replace the eyepiece
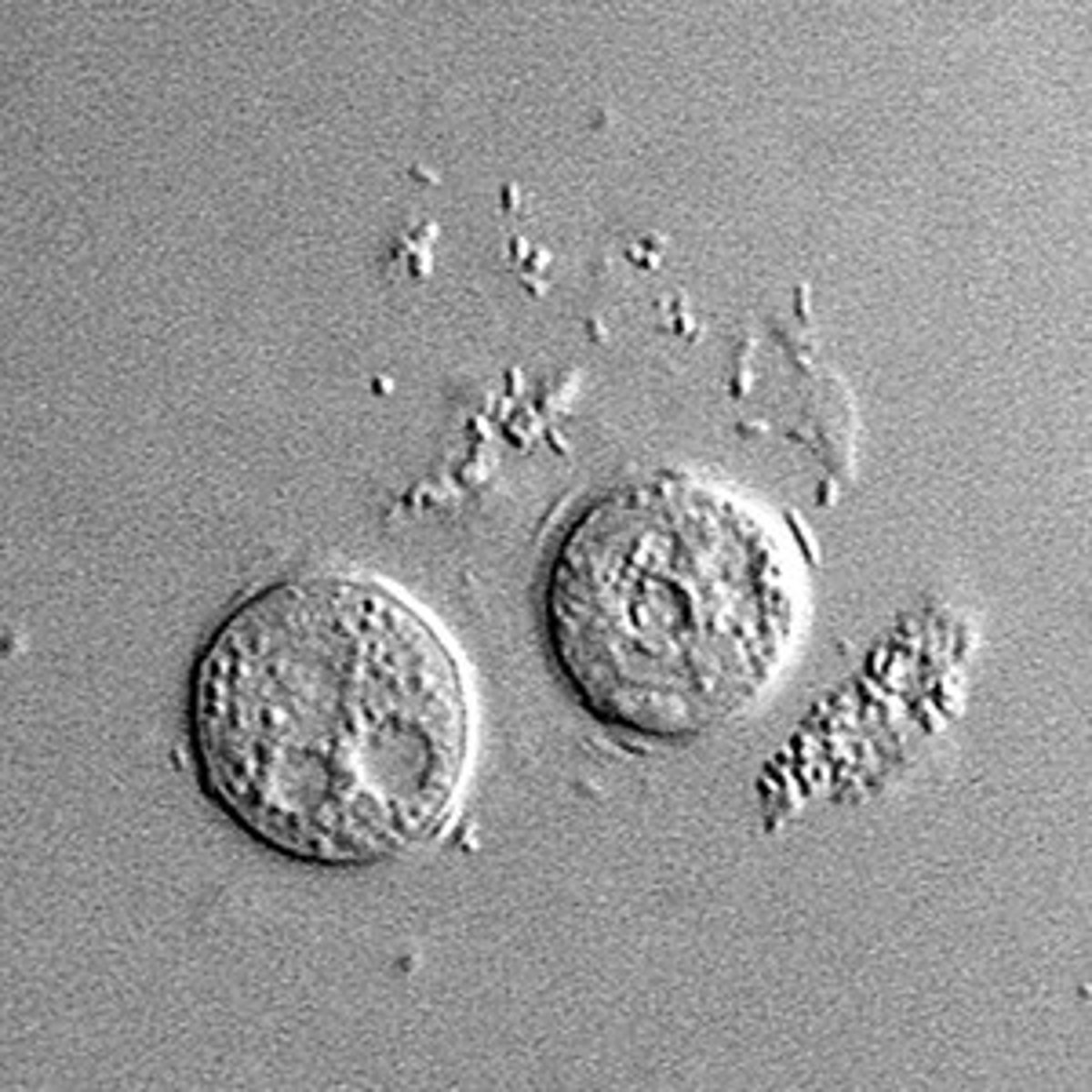
Microscopic RBCs in urine:
Non-nucleated biconcave disks, crenated in hypertonic urine, ghost cells in hypotonic urine, dysmorphic with glomerular membrane damage
Normal RBCs in urine
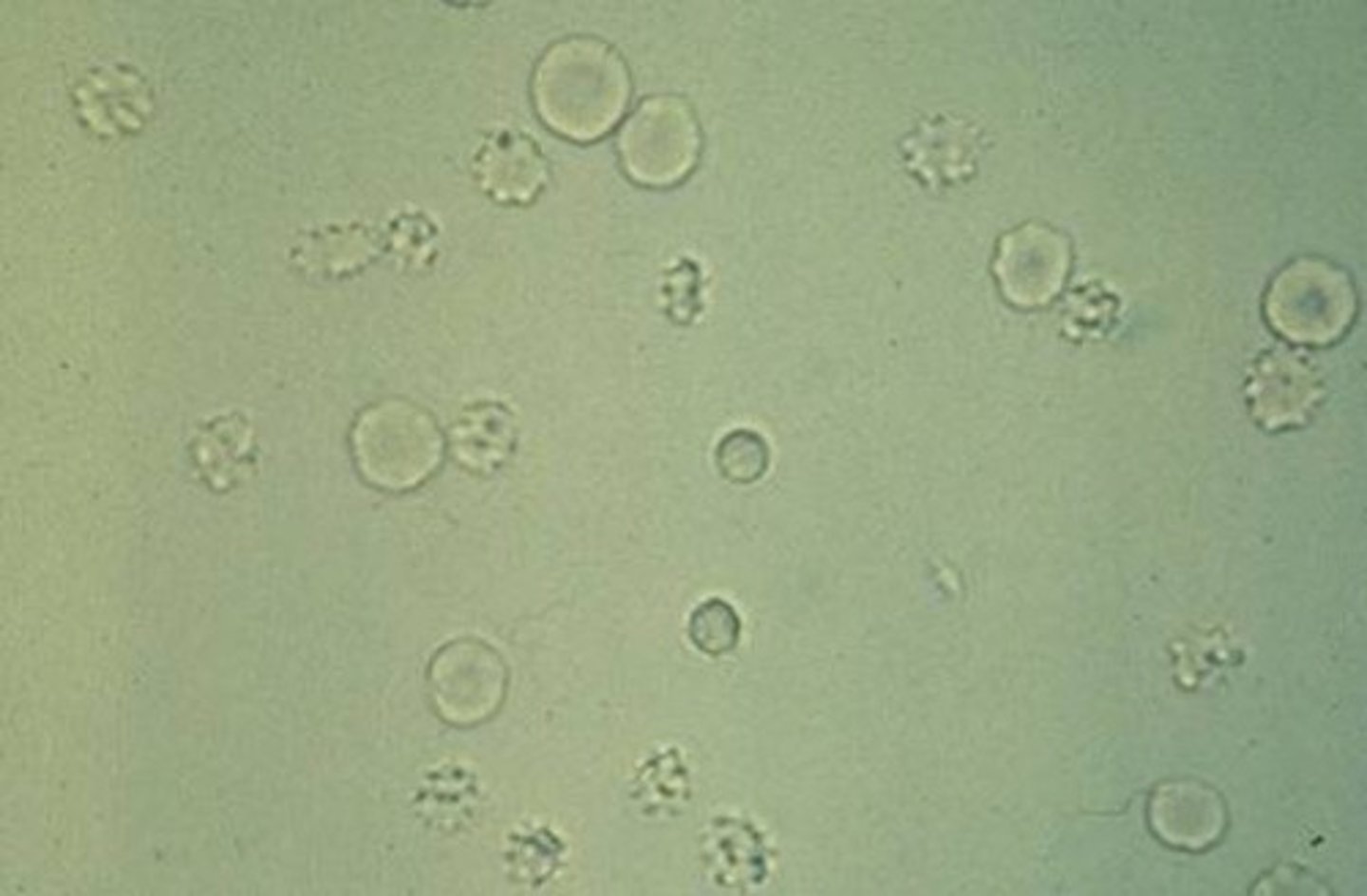
Microcytic/crenated RBCs in urine
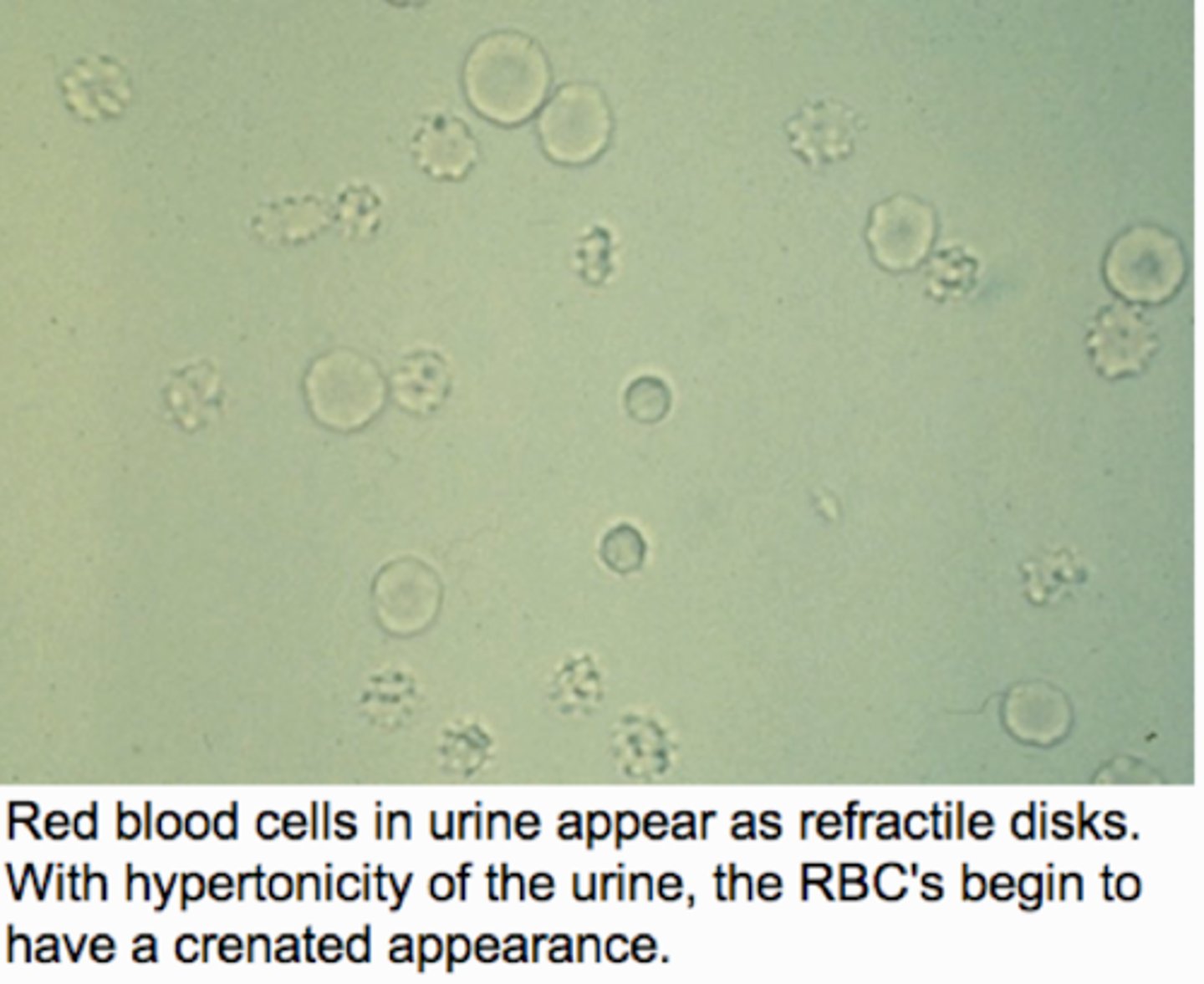
Sources of identification error: RBCs
Yeast cells, oil droplets, and air bubbles
ghost cells
RBCs in hypotonic urine
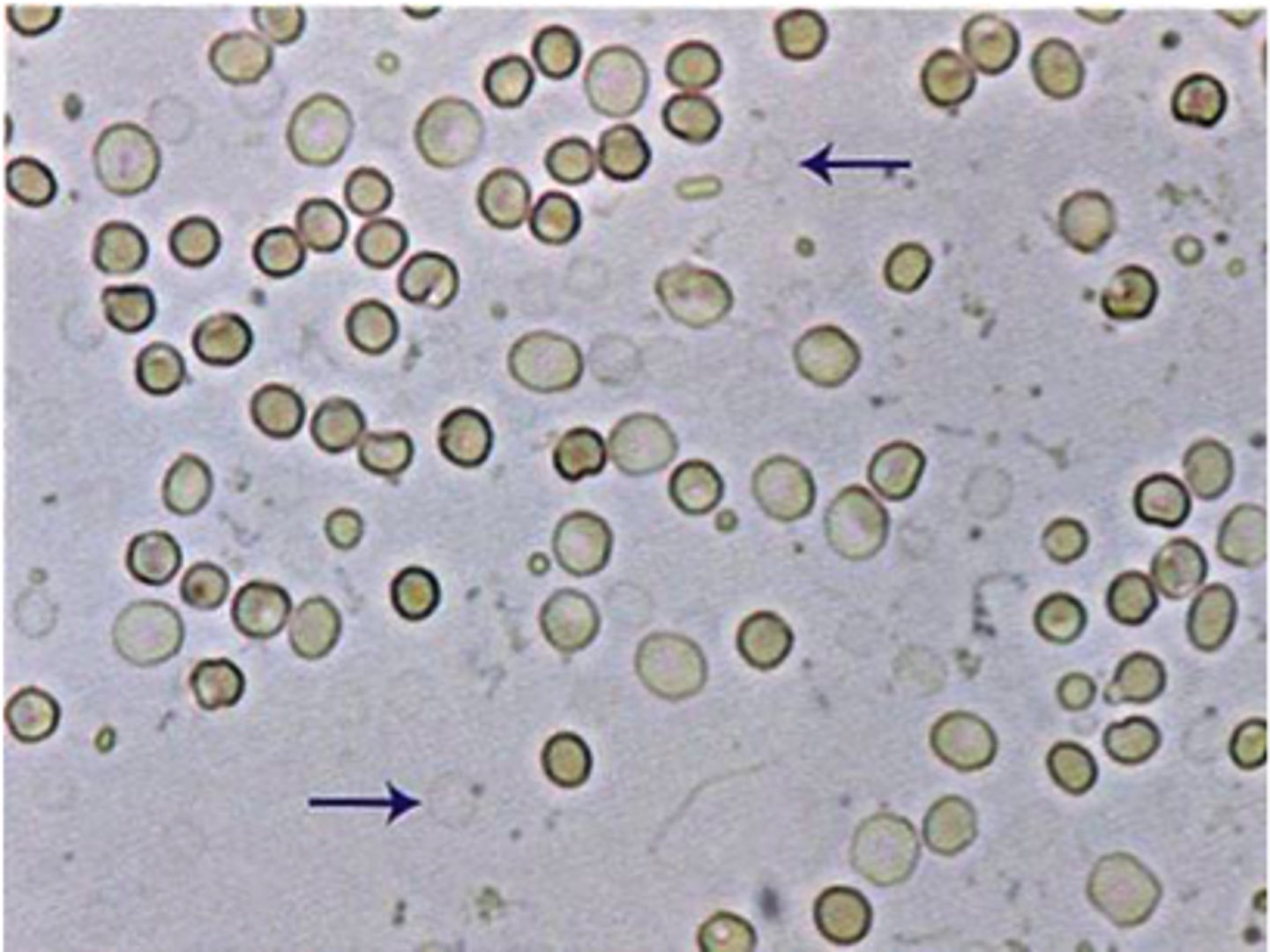
Microscopic RBCs in urine reported as:
Average number per 10 hpfs
Microscopic RBC urinalysis correlations:
Color and reagent strip blood reaction
Urinary microscopic WBCs appearance:
Larger than RBCs, Granulate/ neutrophils, glitter cells in hypotonic urine, mononuclear cells with abundant cytoplasm
WBCs in urine:
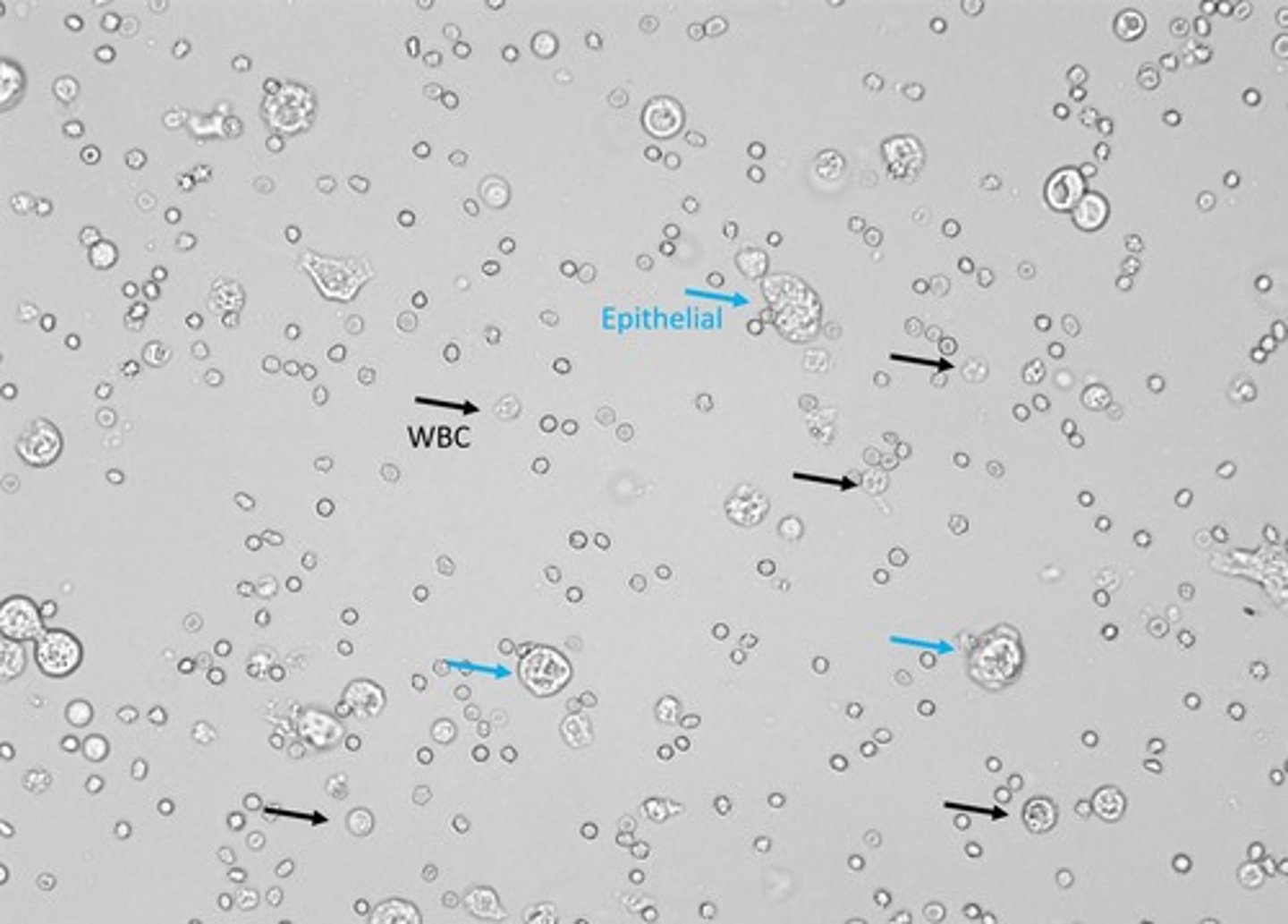
Sources of error (WBCs):
renal tubular epithelial cells
renal tubular epithelial cells
Line the tubules of the nephrons
Increased numbers associated with tubular necrosis
Reporting microscopic WBCs:
average number per 10 hpfs
Microscopic WBCs urinalysis correlations:
LE, Nitrite, Specific gravity, and pH
glitter cells
WBCs in hypotonic urine
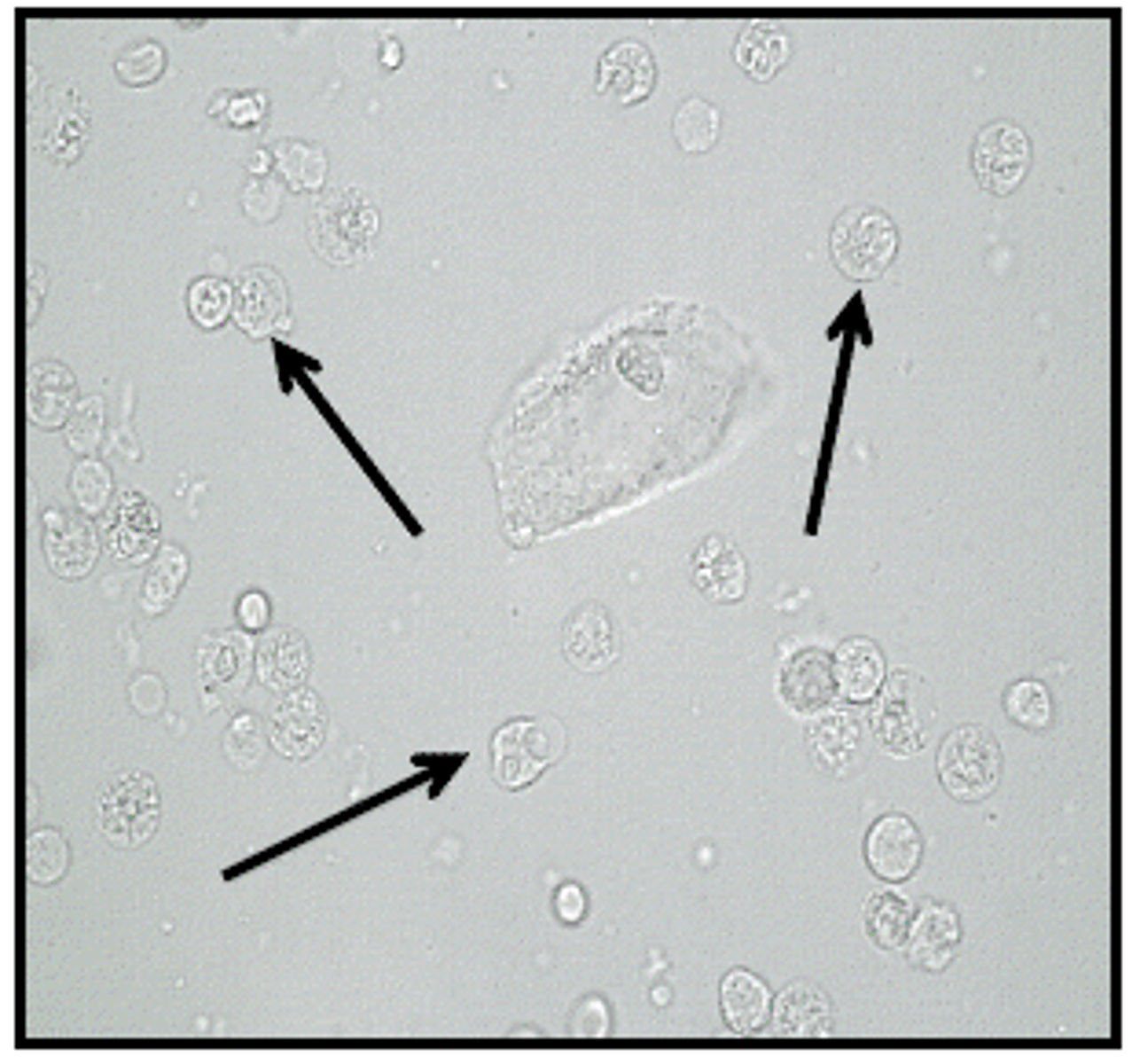
Squamous epithelial cells appearance in urine:
Largest cells in the sediment with abundant, irregular cytoplasm and prominent nuclei
(Reported as: rare, few, moderate, or many per lpf)
-correlations= clarity
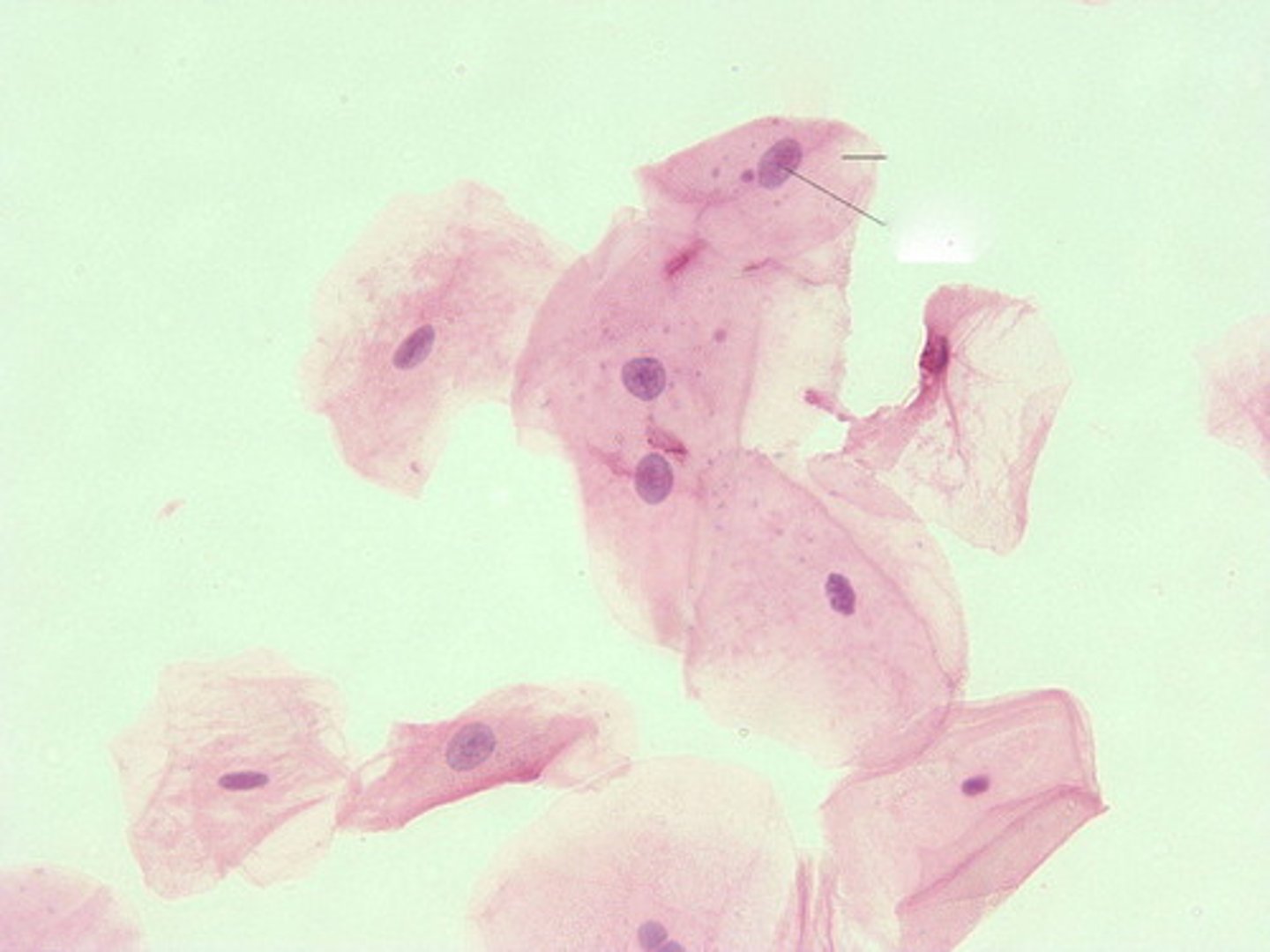
squamous epithelial cells
these are flat nucleated cells which slough off from the lining of the urethra/ vaginal opening
Transitional epithelial cells appearance in urine:
Spherical, polyhedral, or caudate with centrally located nucleus (reported as few, moderate, or many per hpf)
-correlations= clarity and blood
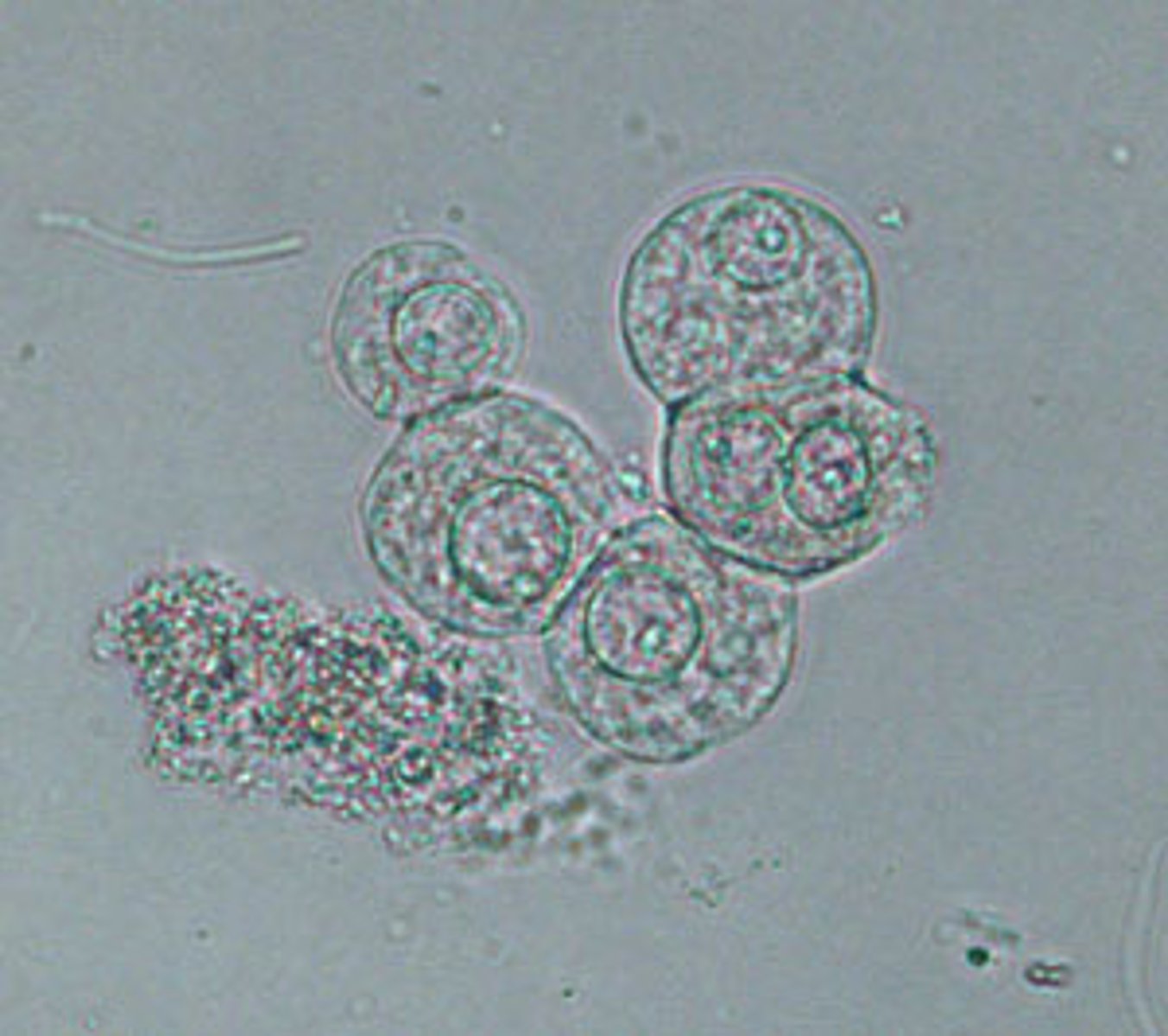
transitional epithelial (urothelial) cells
lines the organs of the urinary system
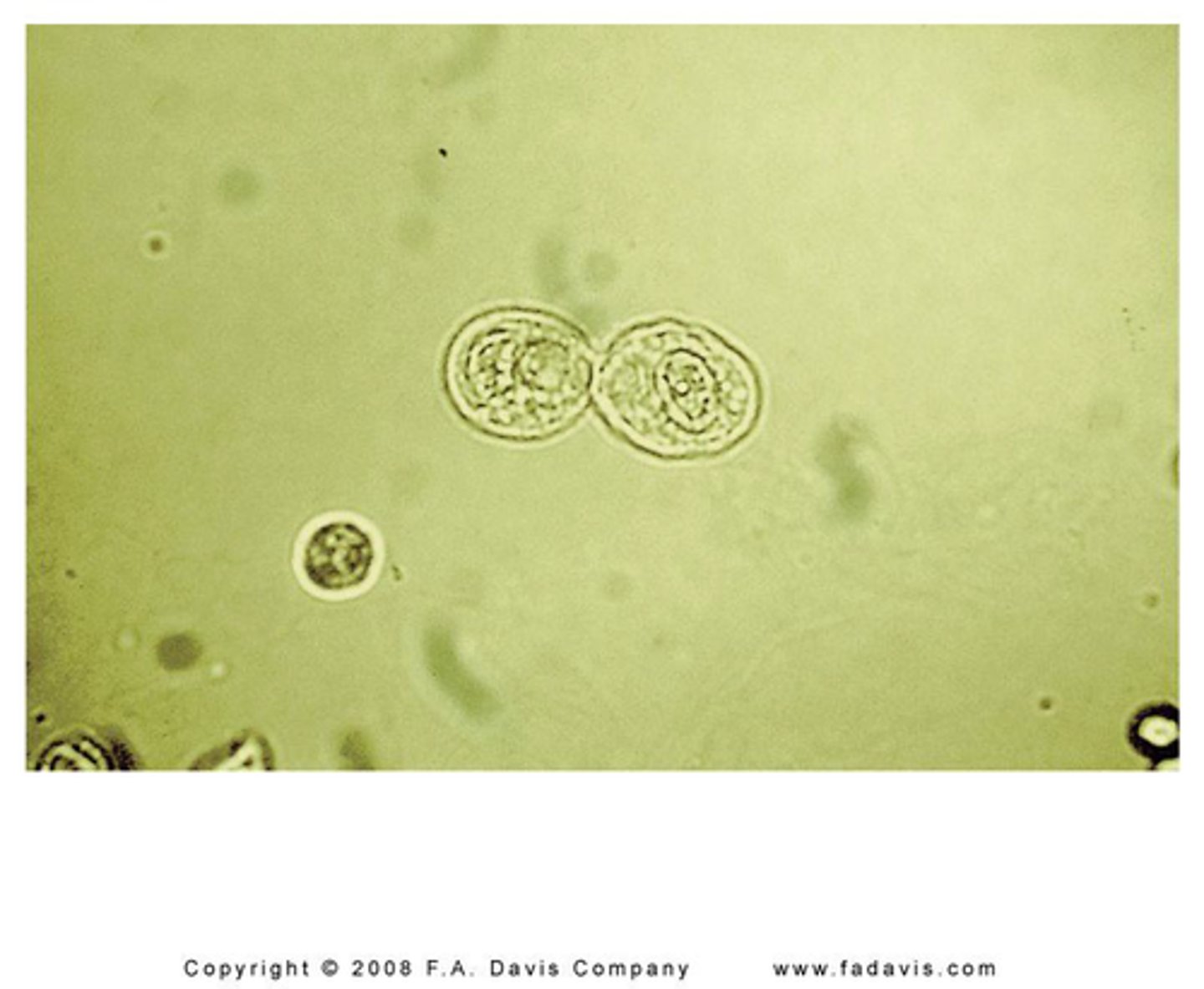
RTE appearance in urine:
Rectangular, columnar, round, oval or, cuboidal with an eccentric nucleus possinly bilirubin-stained or hemosiderin-laden
(reported as: average number per 10 hpfs)
-correlations= LE, nitrite, color, clarity, protein, bilirubin and blood
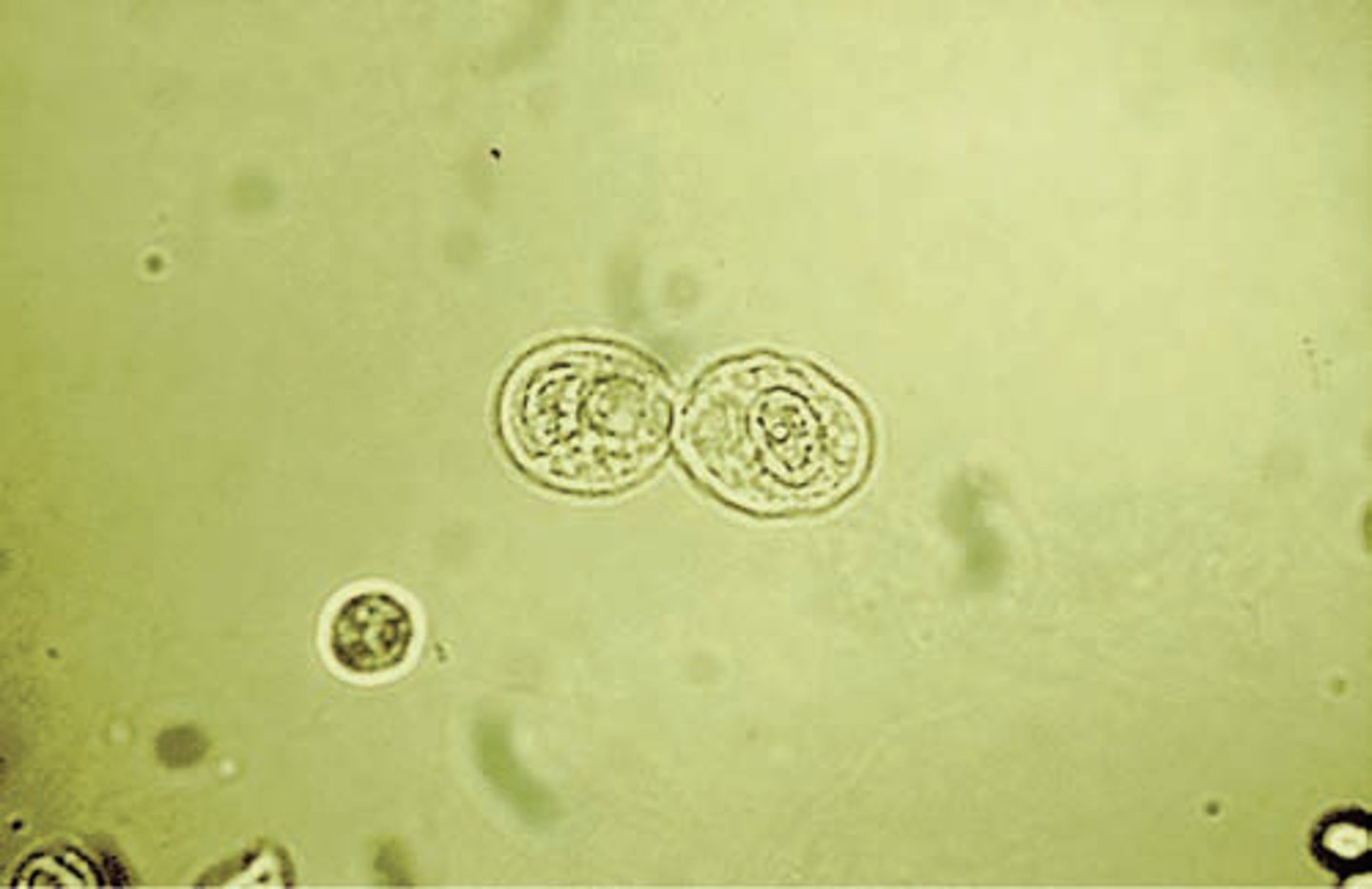
Renal tubular epithelial cells (RTE)
-line the renal tubules
-most clinical significant of all urinary epithelial cells
- small dense eccentrically placed nucleus
Caudate
having a tail
Caudate transitional epithelial cells
-originate from the renal pelvis
- seen in patients with pyelonephritis or calculi in the renal pelvis
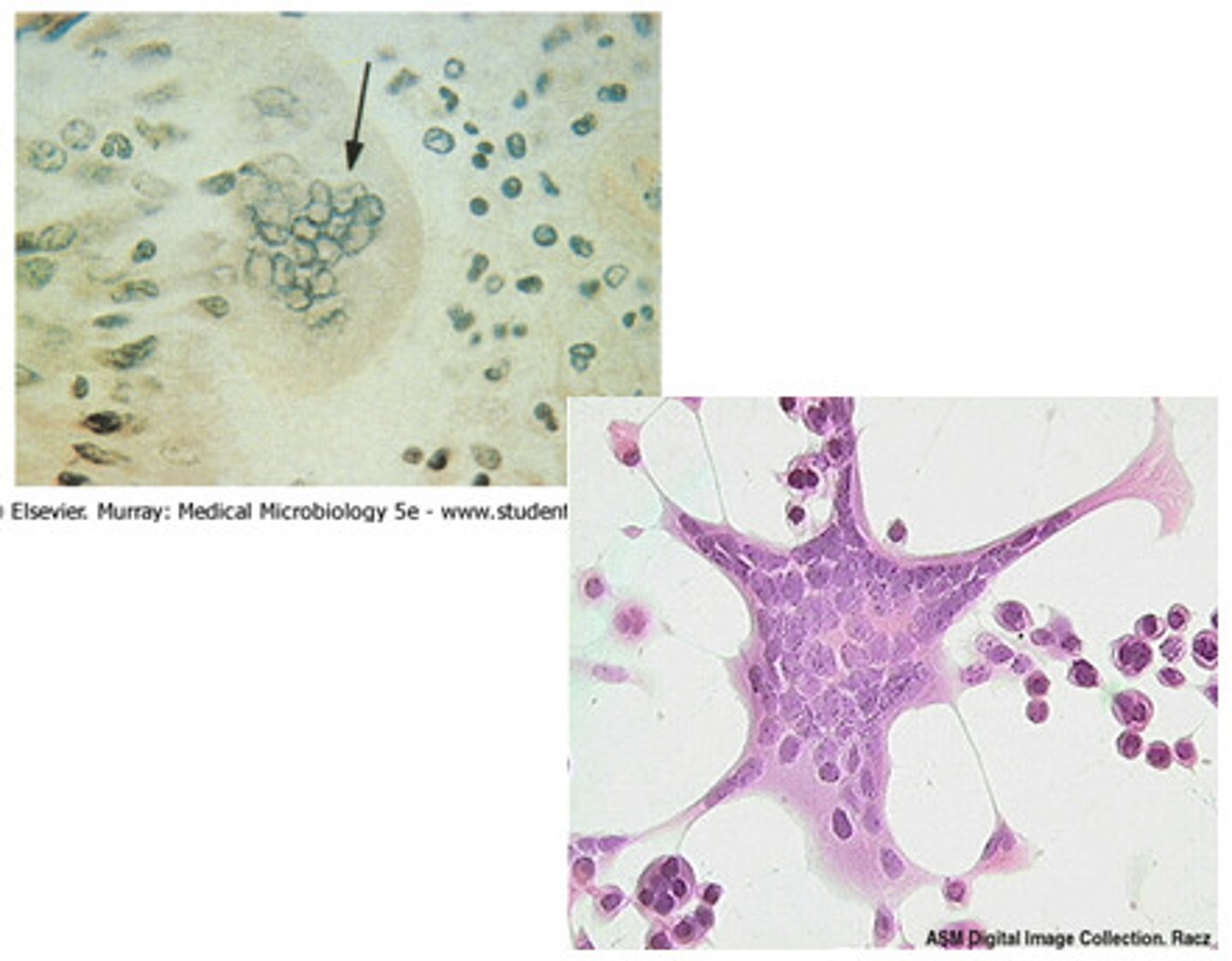
syncytia
Multinucleate cell which results from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells.
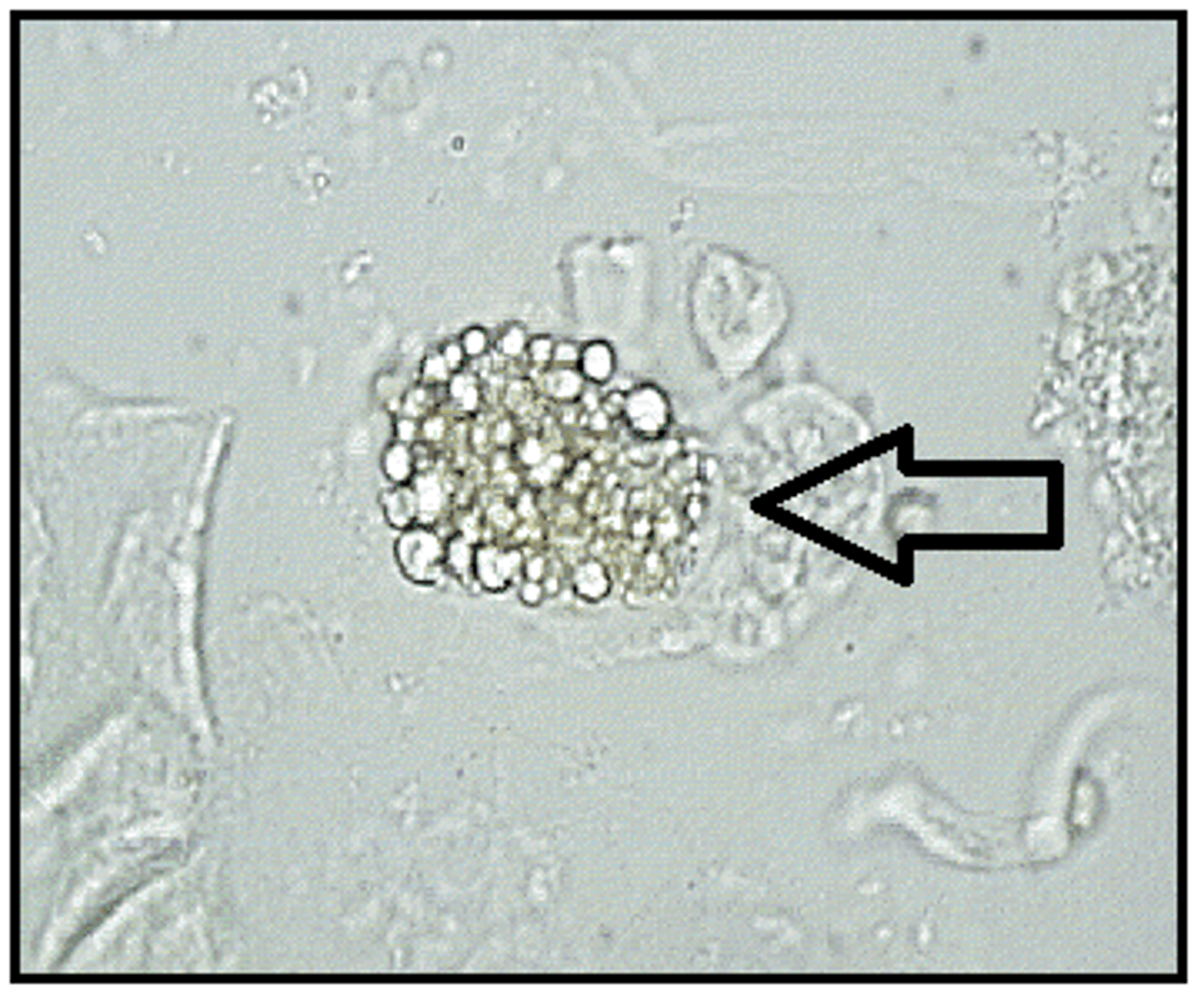
Oval fat bodies
-RTE cells that absorb lipids
-highly retractile RTE cells
-reported as average number per hpf
-correlation= clarity, blood, protein, and free fat droplets/ fatty casts
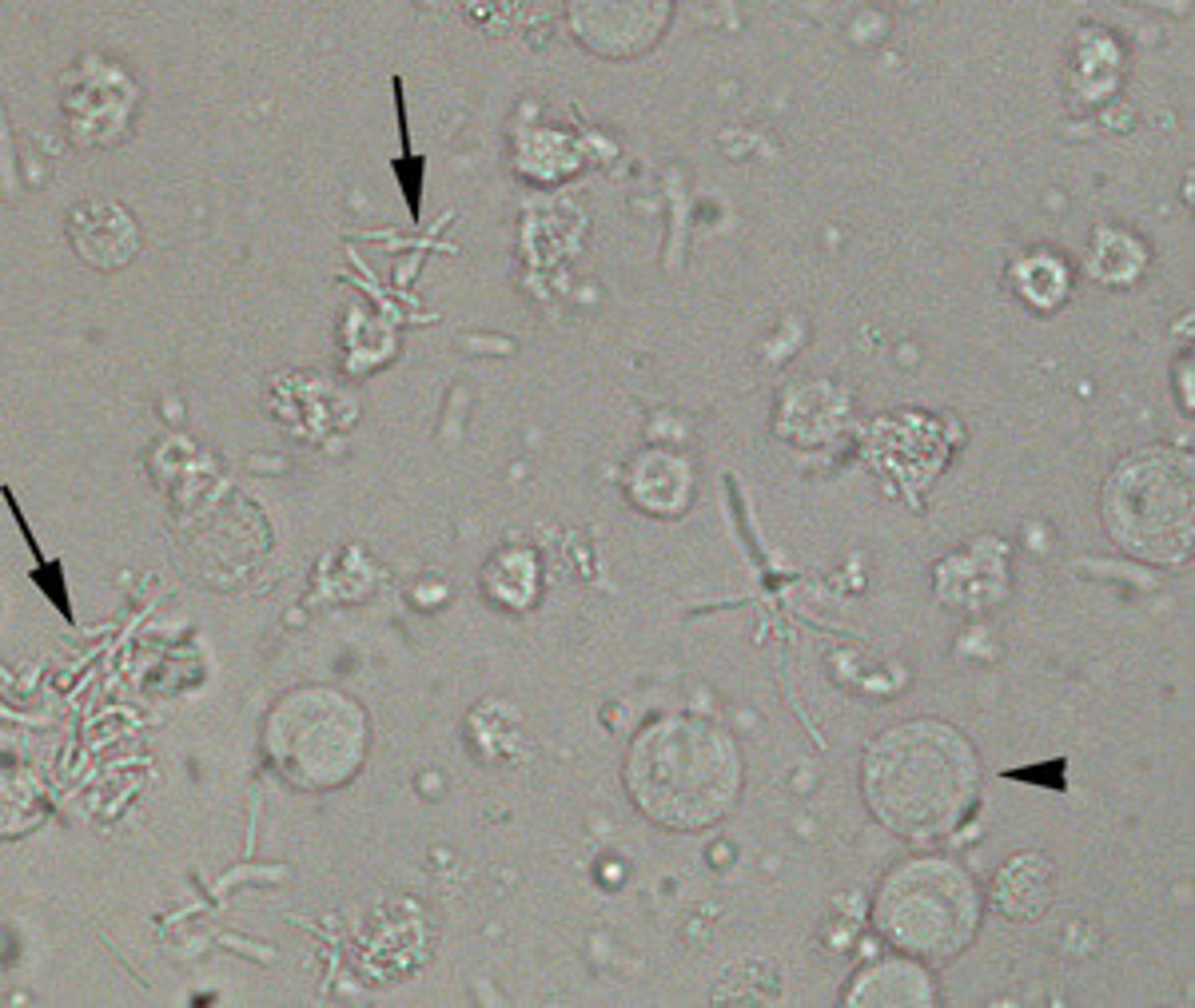
Bacteria in urine:
Small spherical and rod-shaped structures
-sources of error= amorphous phosphates/ urates
-reported= few, moderate, or many per hpf
-correlations= pH, nitrite, LE, and WBCs
Yeast in urine:
small, oval, refractile structures with buds or mycelia
-sources of error= rbc
-reported as= rare, few, moderate, or many per hpf
-correlations= LE, Glucose, WBCs
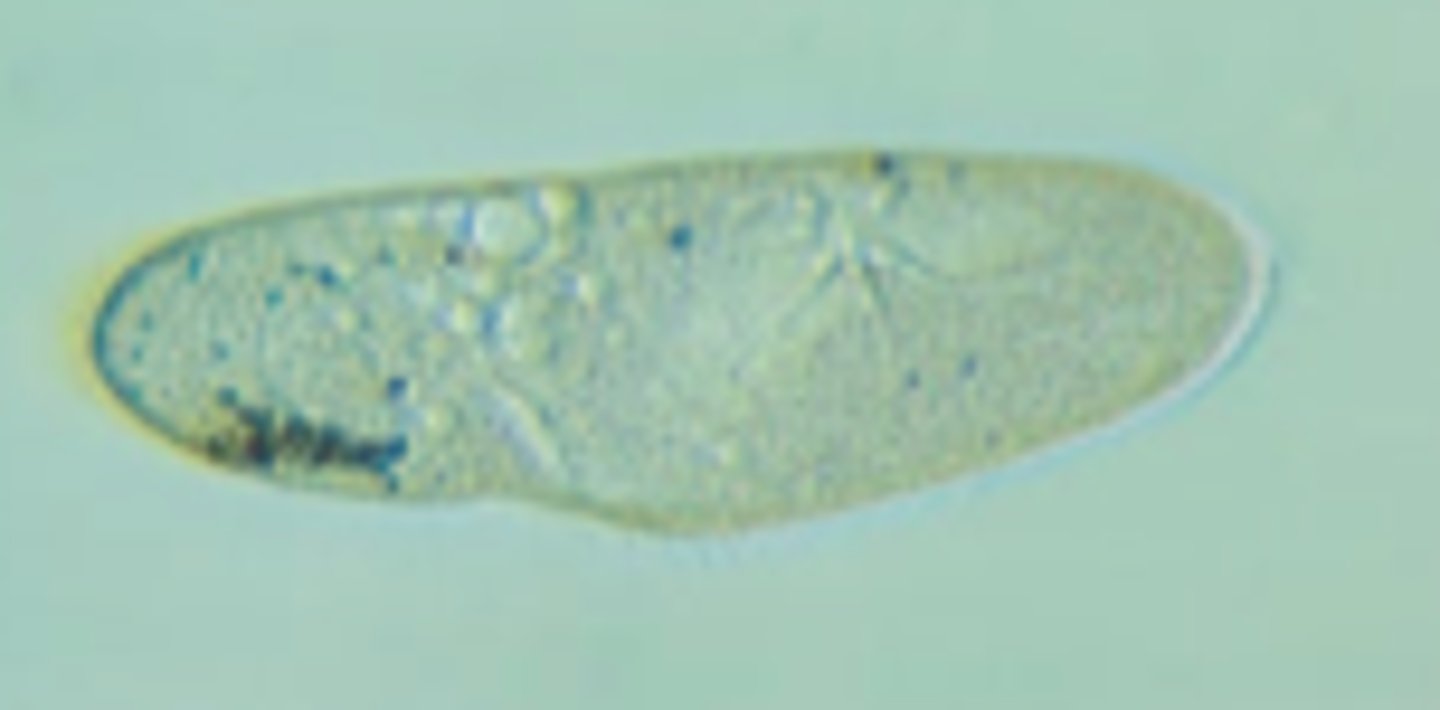
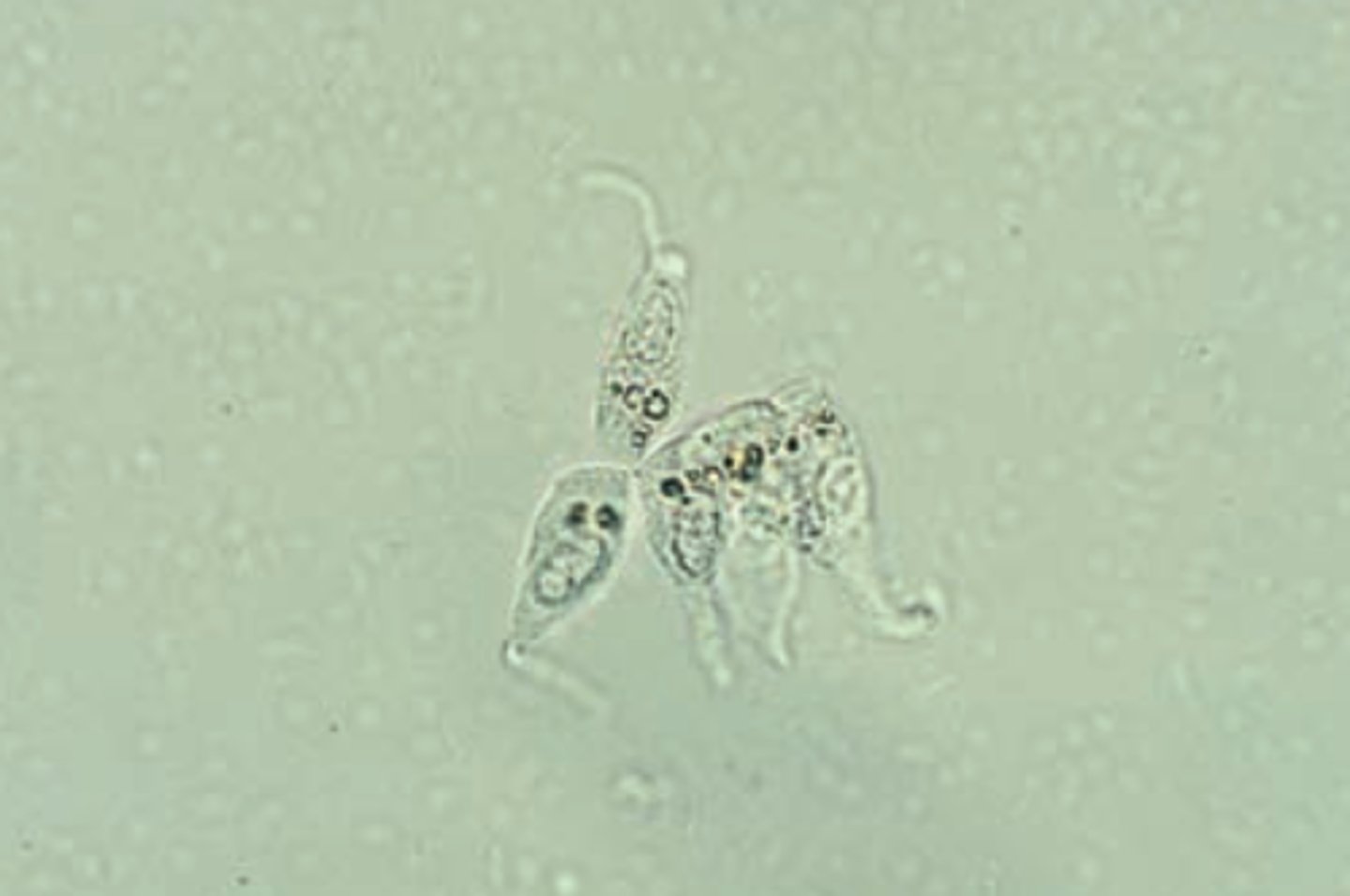
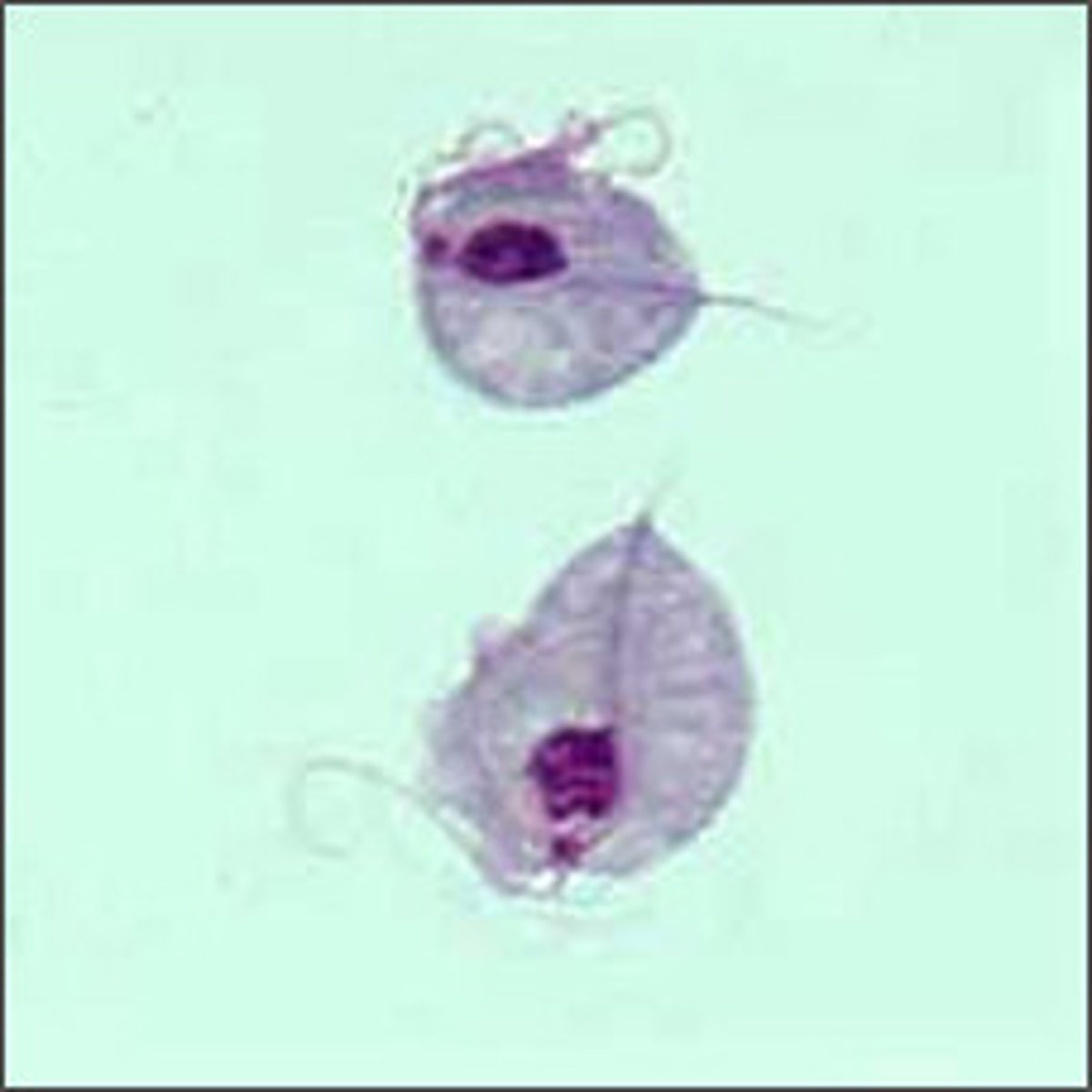
Trichonmonas in urine:
Parasite that is pear-shaped, motile, flagellated (a sexually transmitted pathogen)
-sources of error= WBCs, RTE cells
-reporting= rare, few, moderate, or many per hpf
-correlations= LE, WBCs
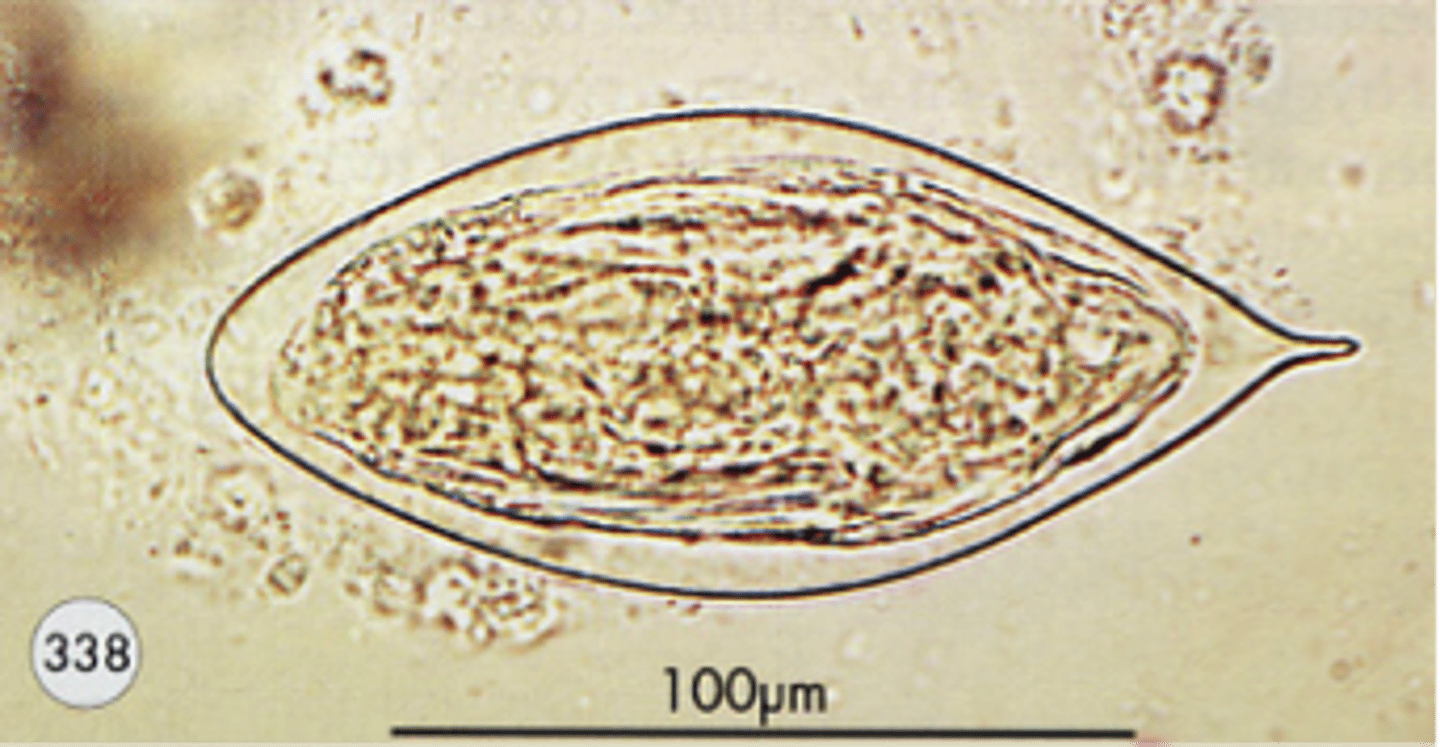
Schistosoma haematobium
Bladder cancer (squamous cell)
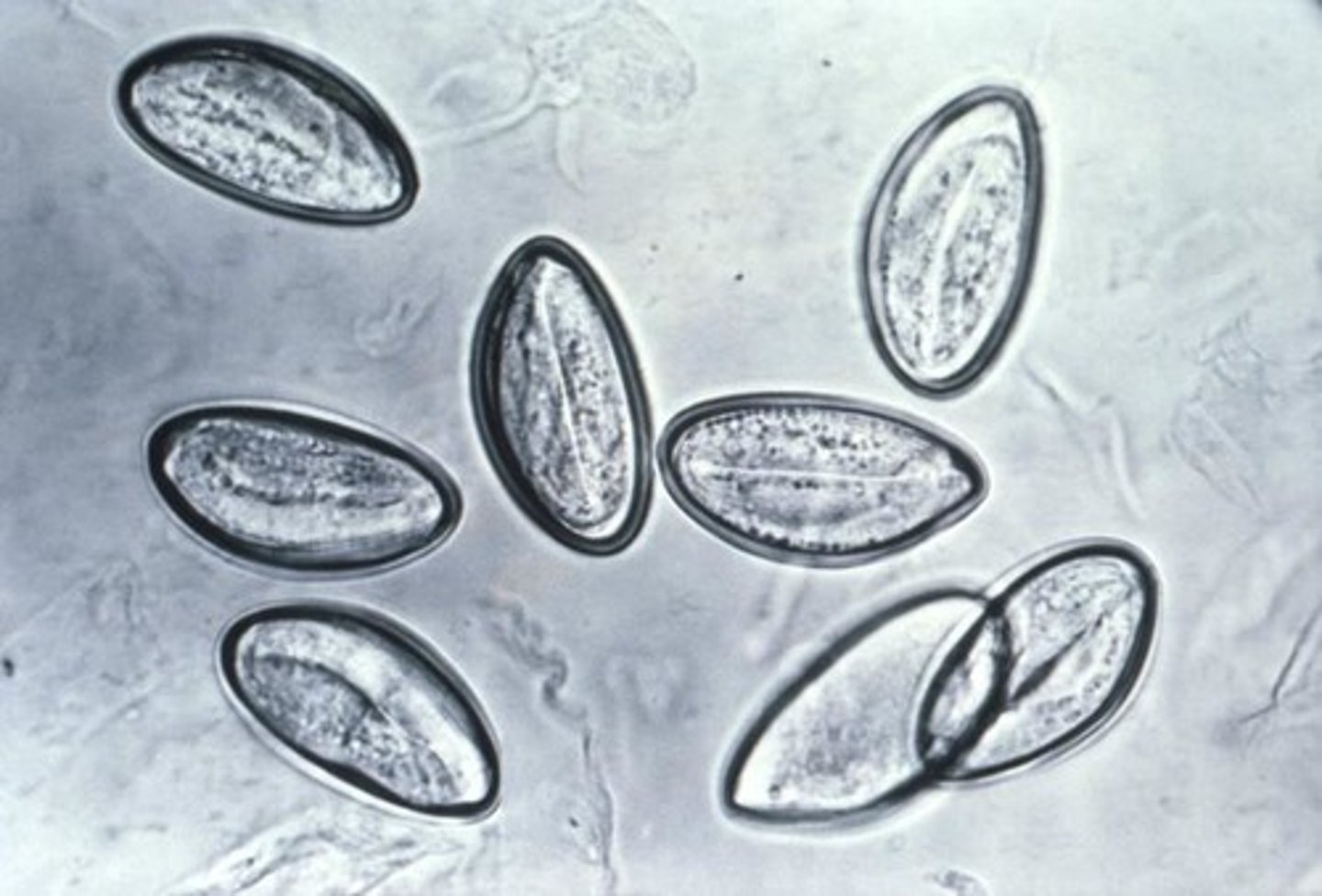
Enterobius vermicularis
pinworm
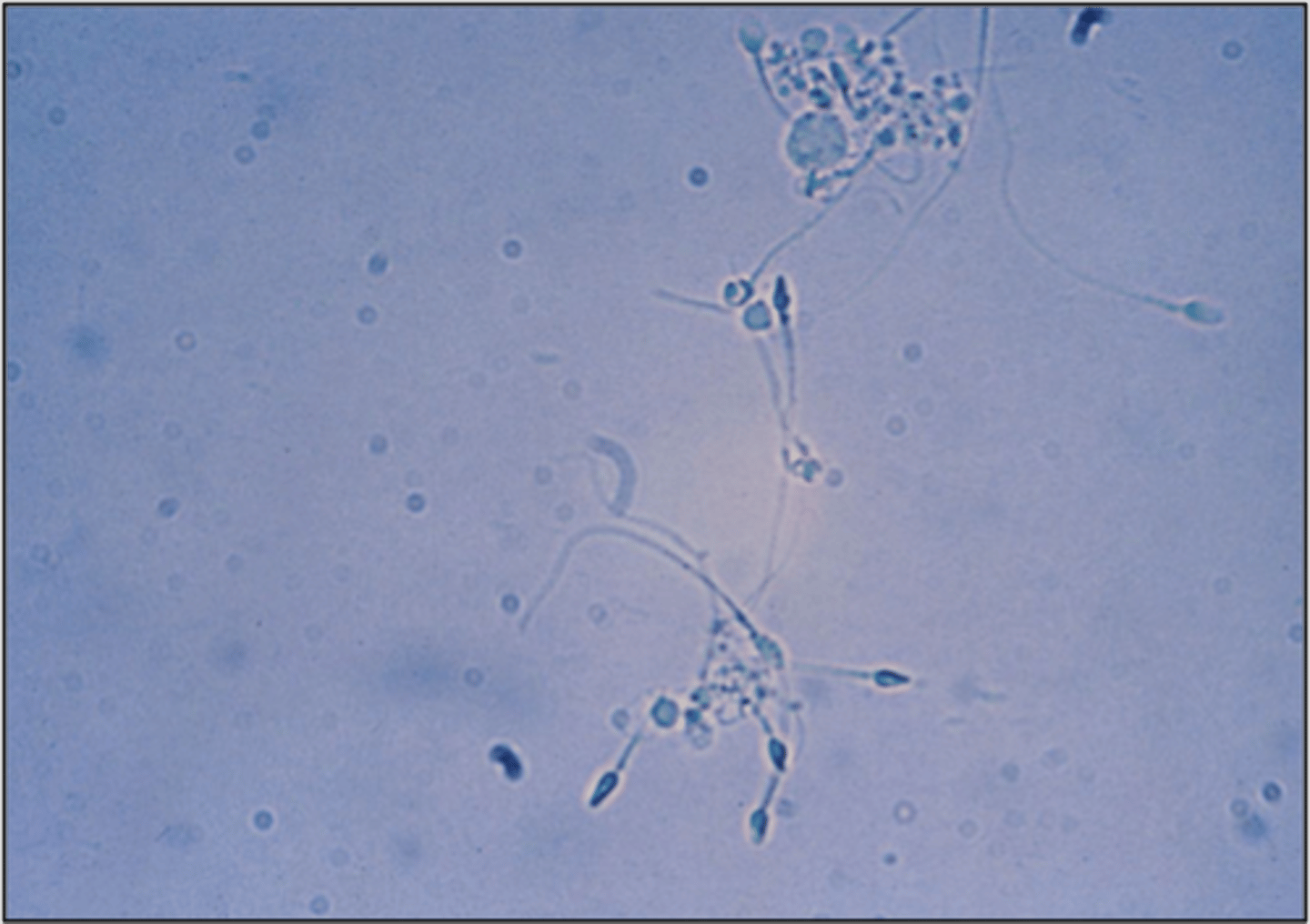
Spermatozoa in urine:
Tapered oval head with long thing tail
-reported as= present
-correlations= protein
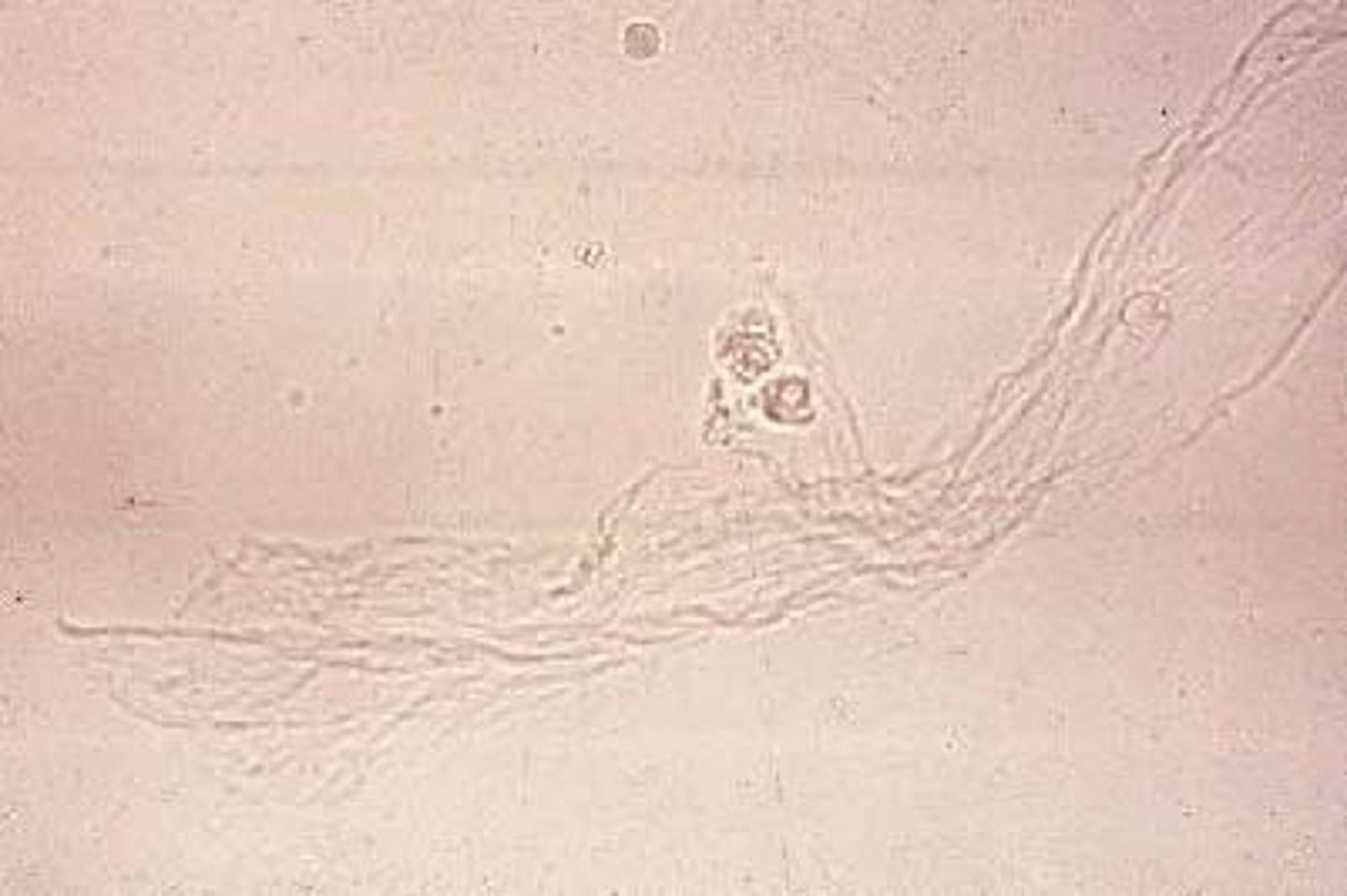
Mucus in urine:
single or clumped threads with a low refractive index
-source of error= hyaline cast
-reported as= rare, few, moderate, or many per lpf
(no clinical significance)
urinary casts
only element found in urinary sediment that are unique to the kidney
Hyaline casts
-consist almost entirely of uromodulin
-usually caused by dehydration, exercise, or diuretic medicines
-correlations= blood, protein, color
-reported= average # per lpf
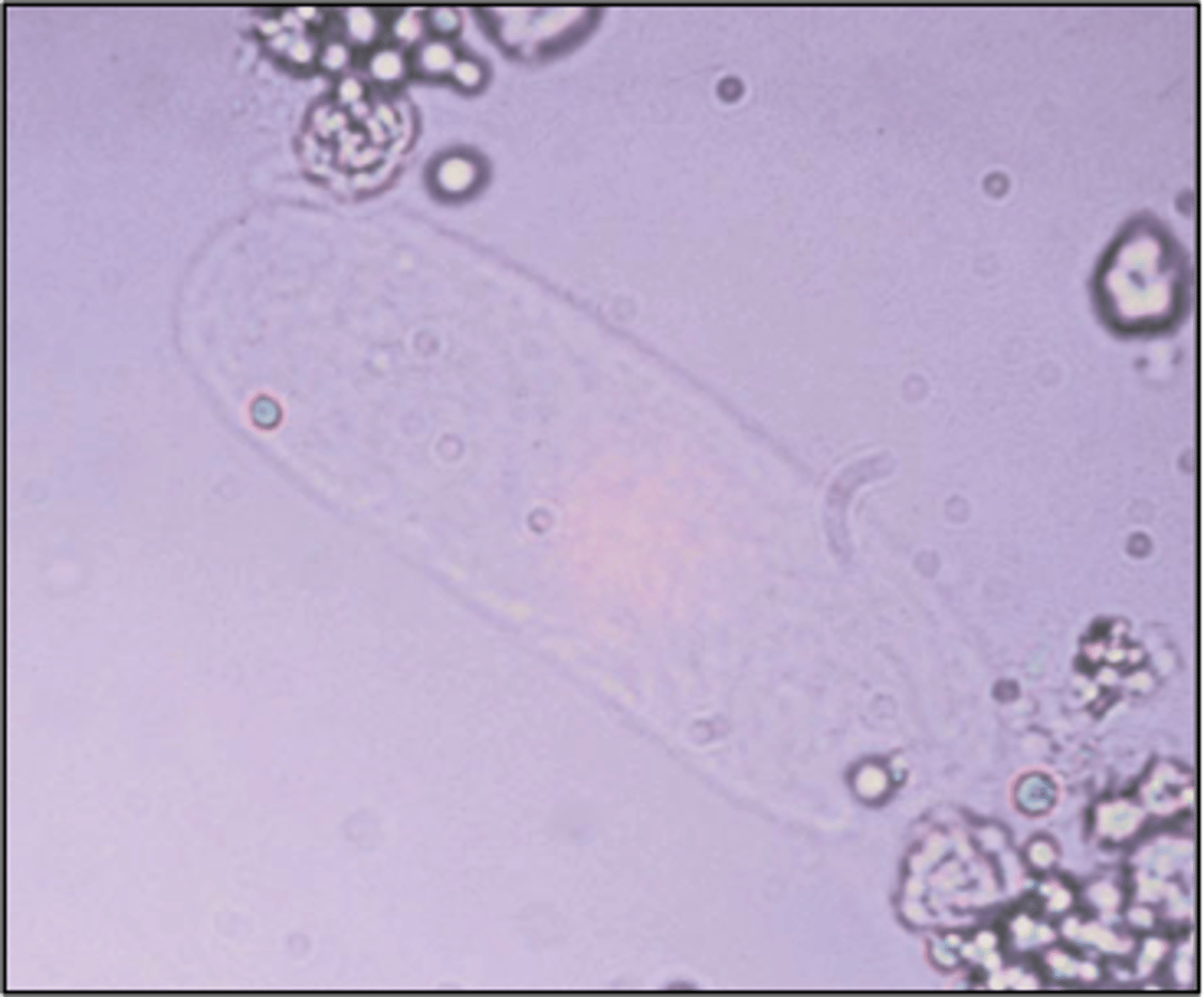
Hyaline cast clinical significance:
Glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, chronic renal disease, congestive heart failure, stress/exercise
RBC cast
Orange-red color, cast matrix, containing RBCs
-sources of error= rbc clumps
-reported= average number per lpf
-correlations= RBCs, blood, protein
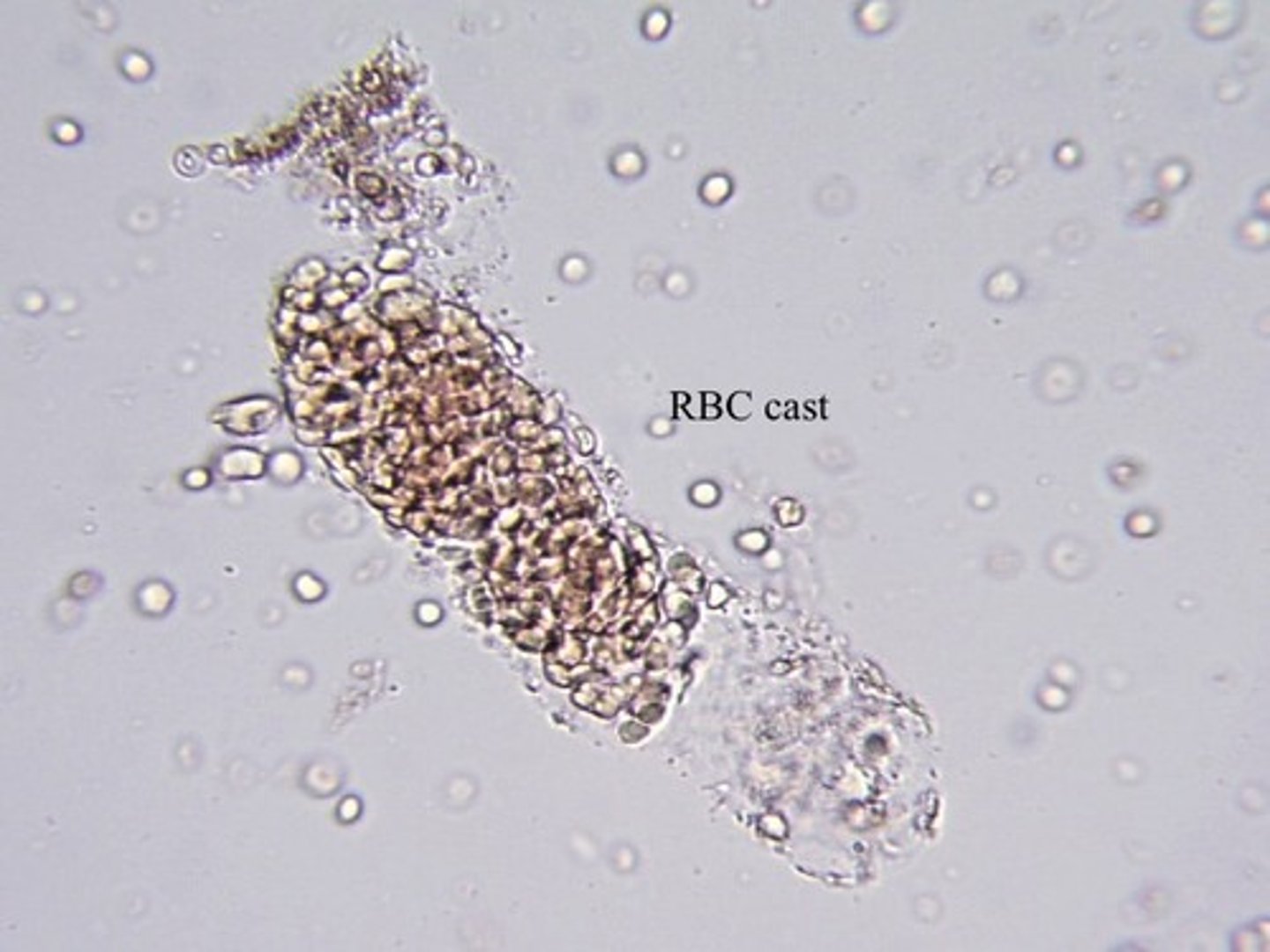
RBC cast clinical significance
Strenuous exercise or Glomerulonephritis
WBC cast
Cast matrix containing WBCs
-sources of error= WBC clumps
-reporting= average number per lpf
-correlations= WBCs, Protein, LE
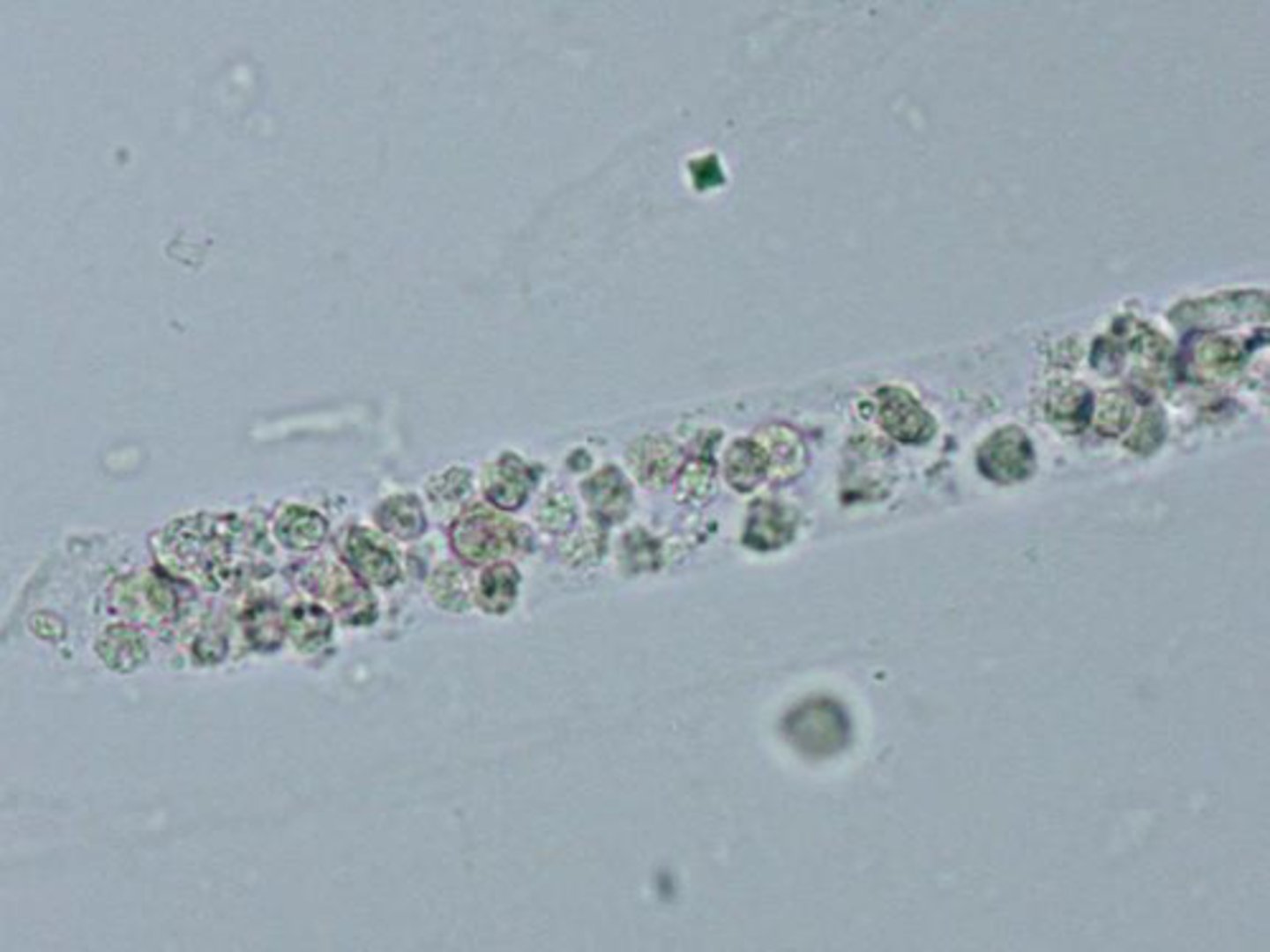
WBC cast clinical significance
pyelonephritis and acute interstitial nephritis
WBC clump
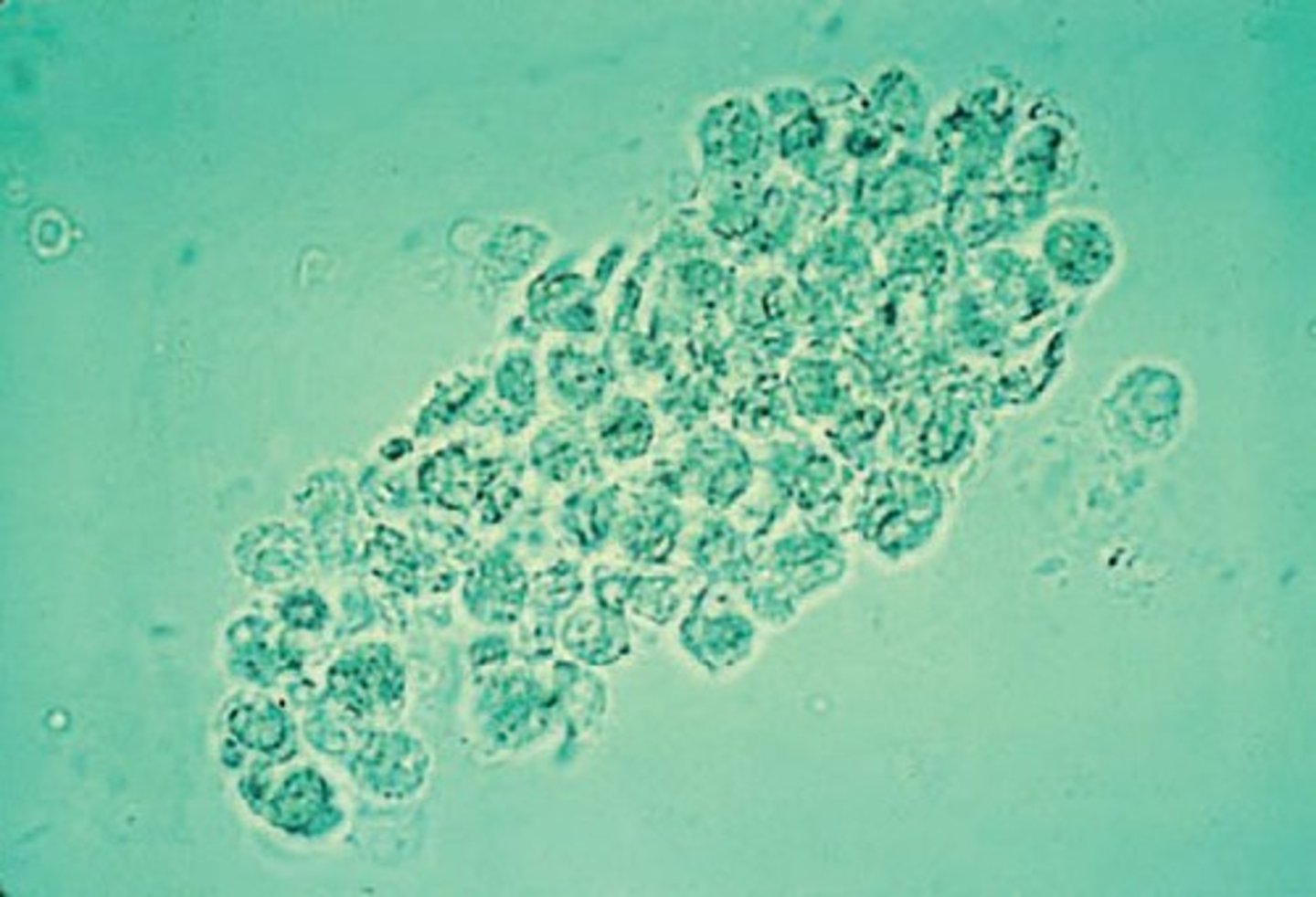
Bacterial cast
Bacilli bound to protein matrix
-sources of error= granular casts
-reported= avg. number per lpf
-correlations= WBCs, LE, nitrite, protein, bacteria
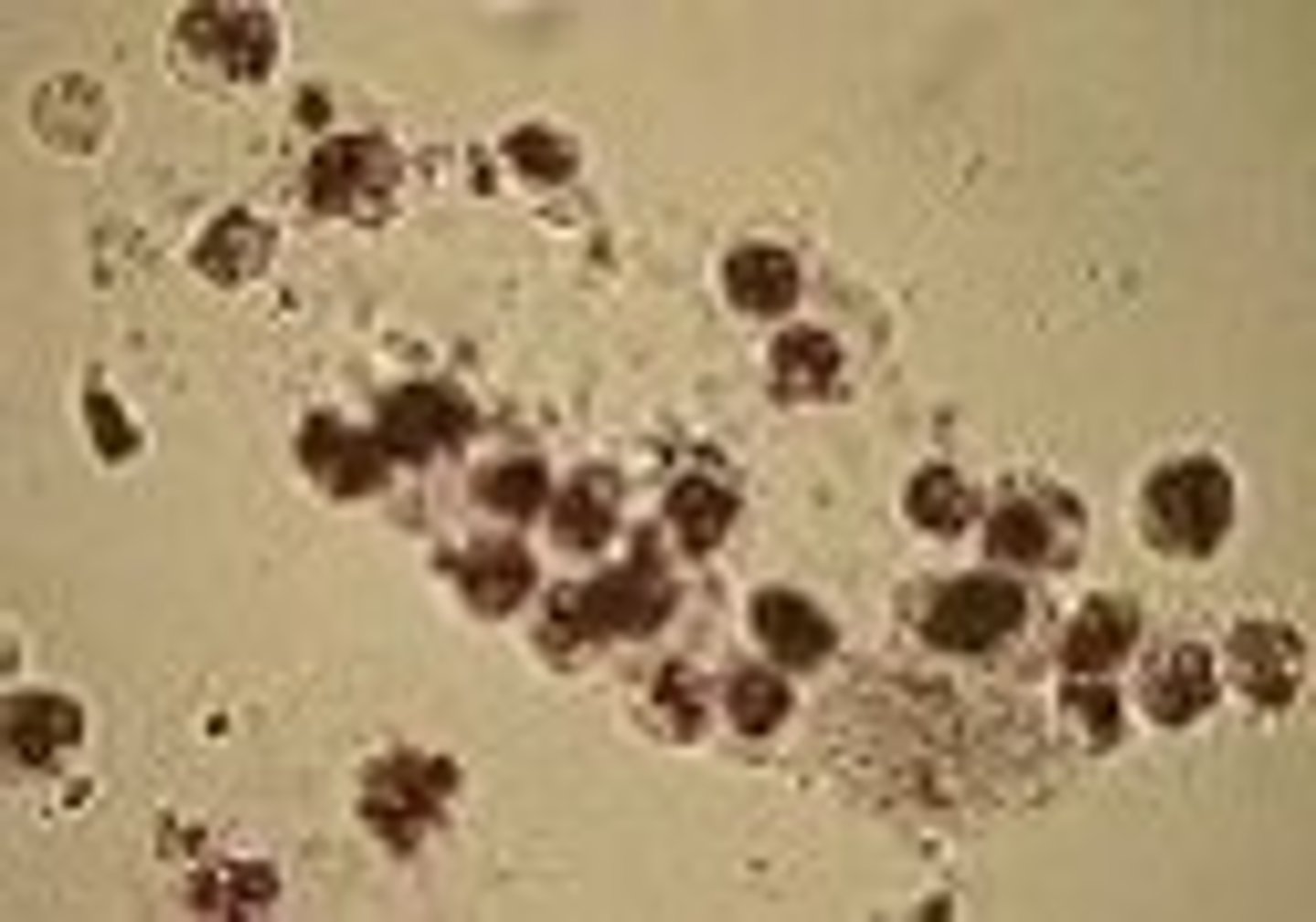
Bacteria casts clinical significance
pyelonephritis
Epithelial cell casts
RTE cells attached to protein matrix
-sources of error= wbc cast
-reported= avg.# per lpf
-correlations= protein, RTE cells
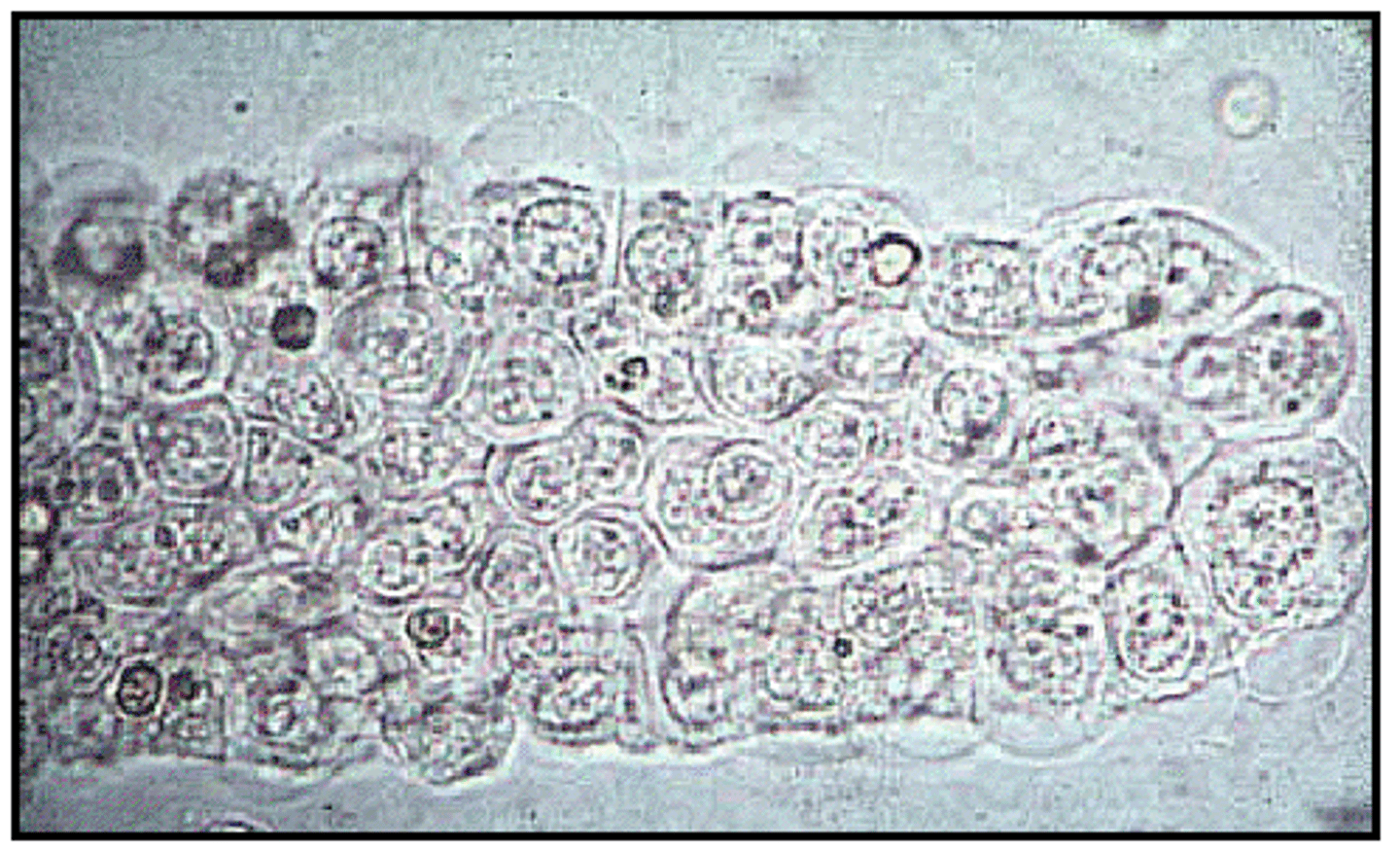
Epithelial cell cast clinical significance
Renal tubular damage
Granular cast
coarse/fine granules in a cast matrix
-reported= avg. # per lpf
-correlation= Protein, cellular casts, rbcs, wbcs
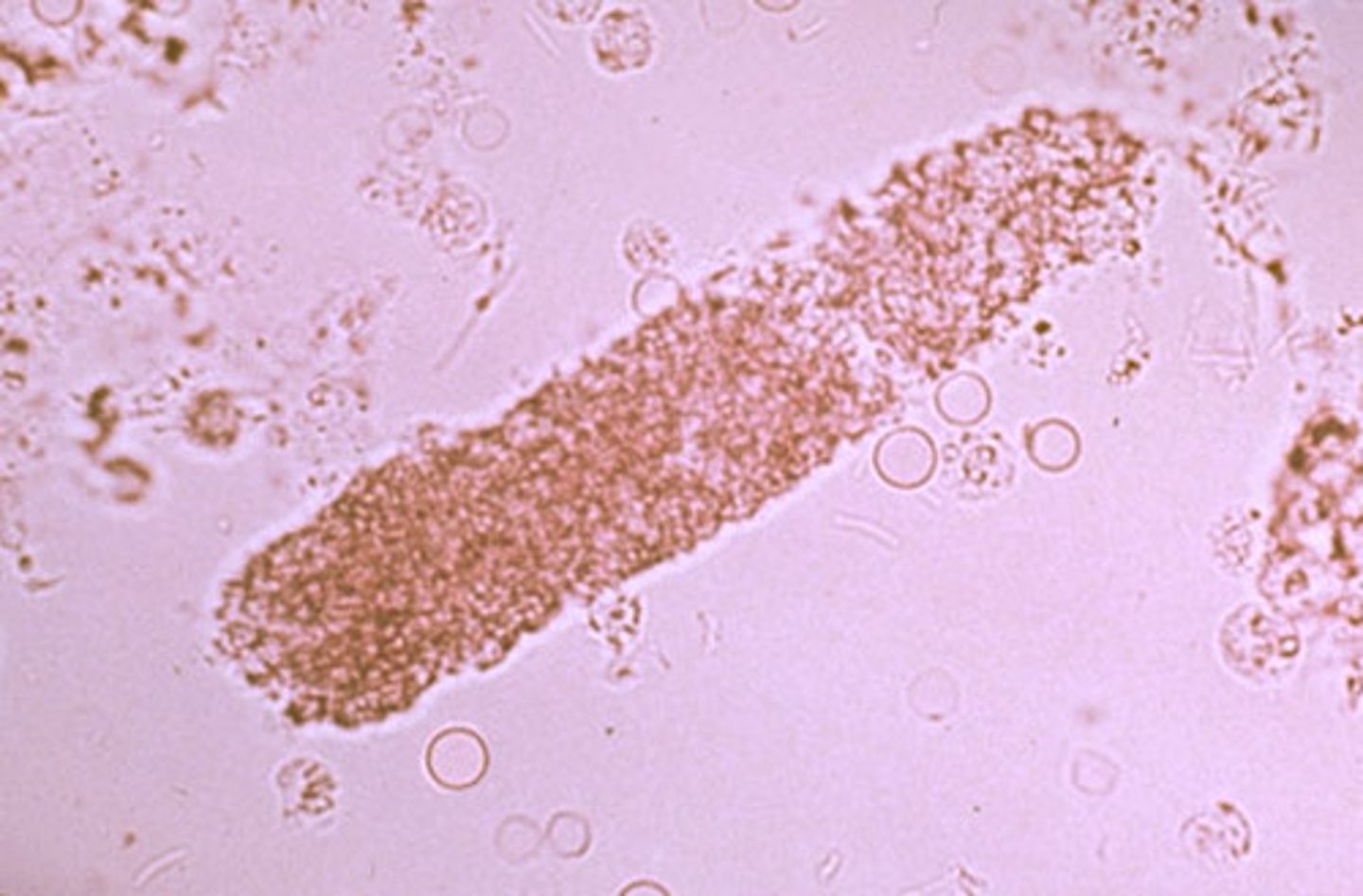
Granular cast clinical significance
Glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, stress/exercise
Waxy cast
highly refractile cast with jagged ends and notches
- sources of error= fibers and fecal material
-reported= avg. # per lpf
-correlations= protein, cellular casts, granular casts, WBCs, RBCs
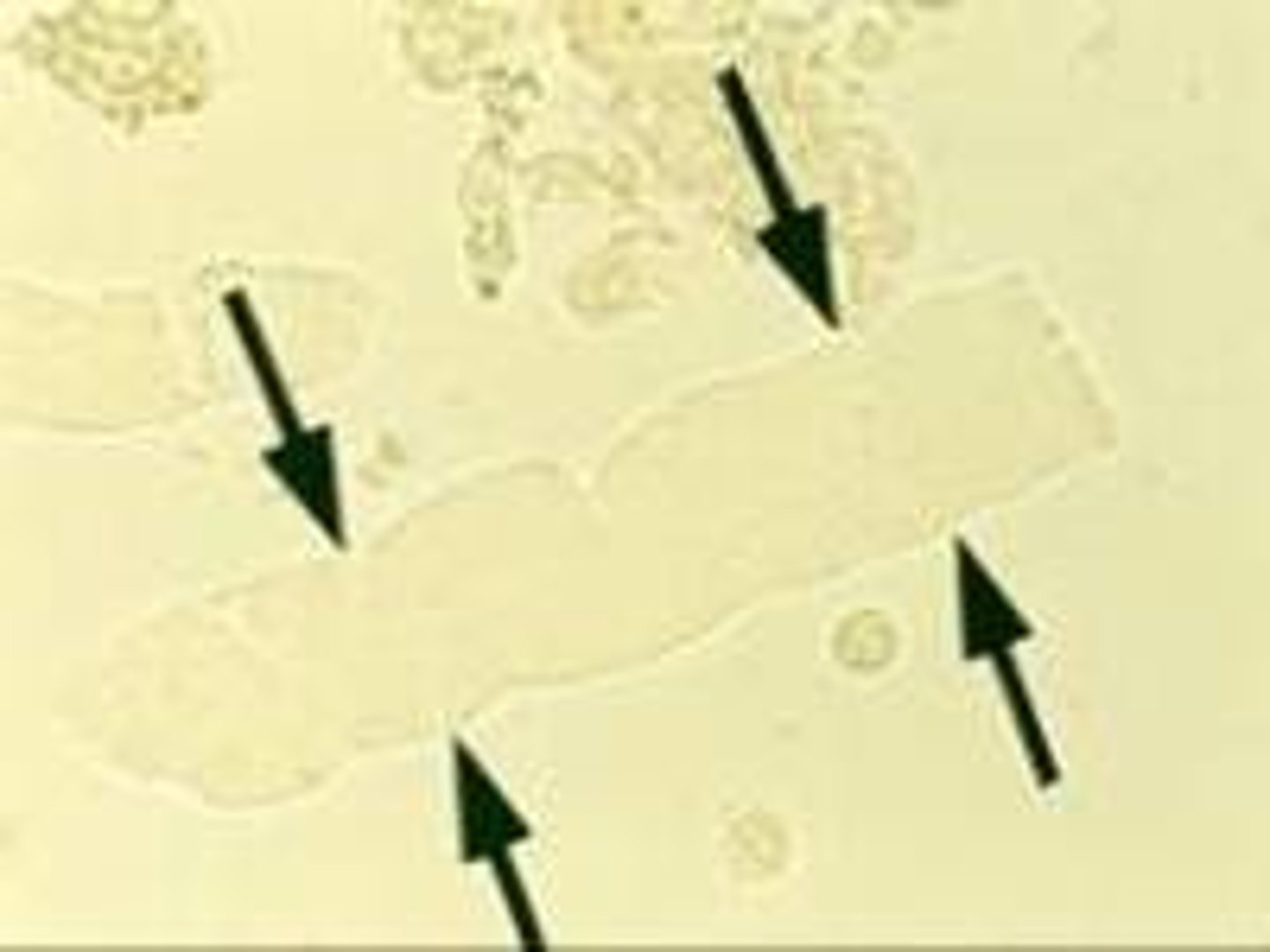
clinical significance of waxy cast
stasis of urine flow, chronic renal failure
Fatty cast
fat droplets and oval fat bodies attached to protein matrix
-sources of error= fecal debris
-reported= avg. # per lpf
-correlations= protein, free fat droplets, oval fat bodies
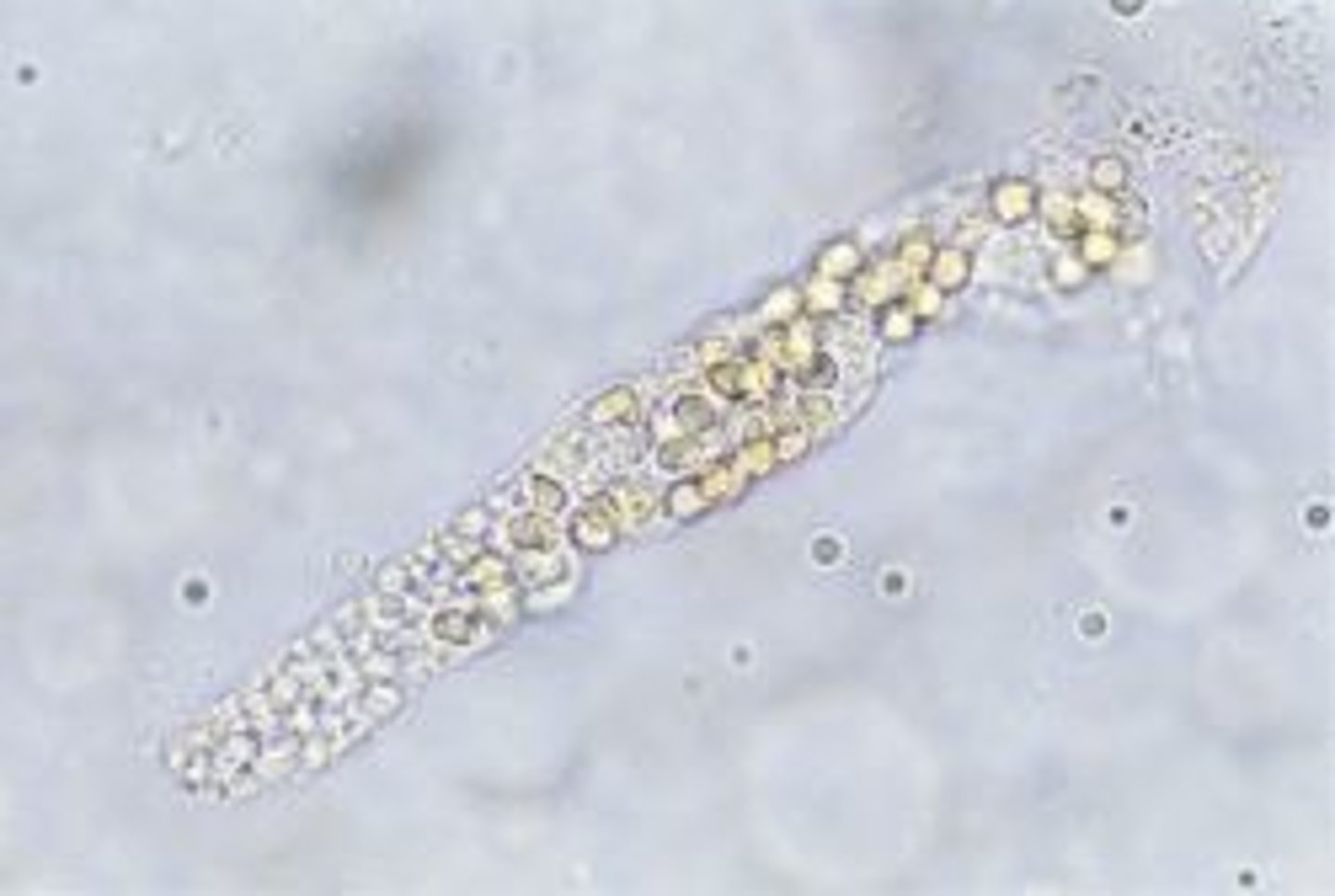
clinical significance of fatty cast
nephrotic syndrome, toxic tubular necrosis, diabetes mellitus, crush injuries
Broad cast
wider than normal cast matrix
-sources of error= fecal material, fibers
-reporting= avg. # per lpf
-correlations= protein, WBCs, RBCs, granular casts, waxy casts
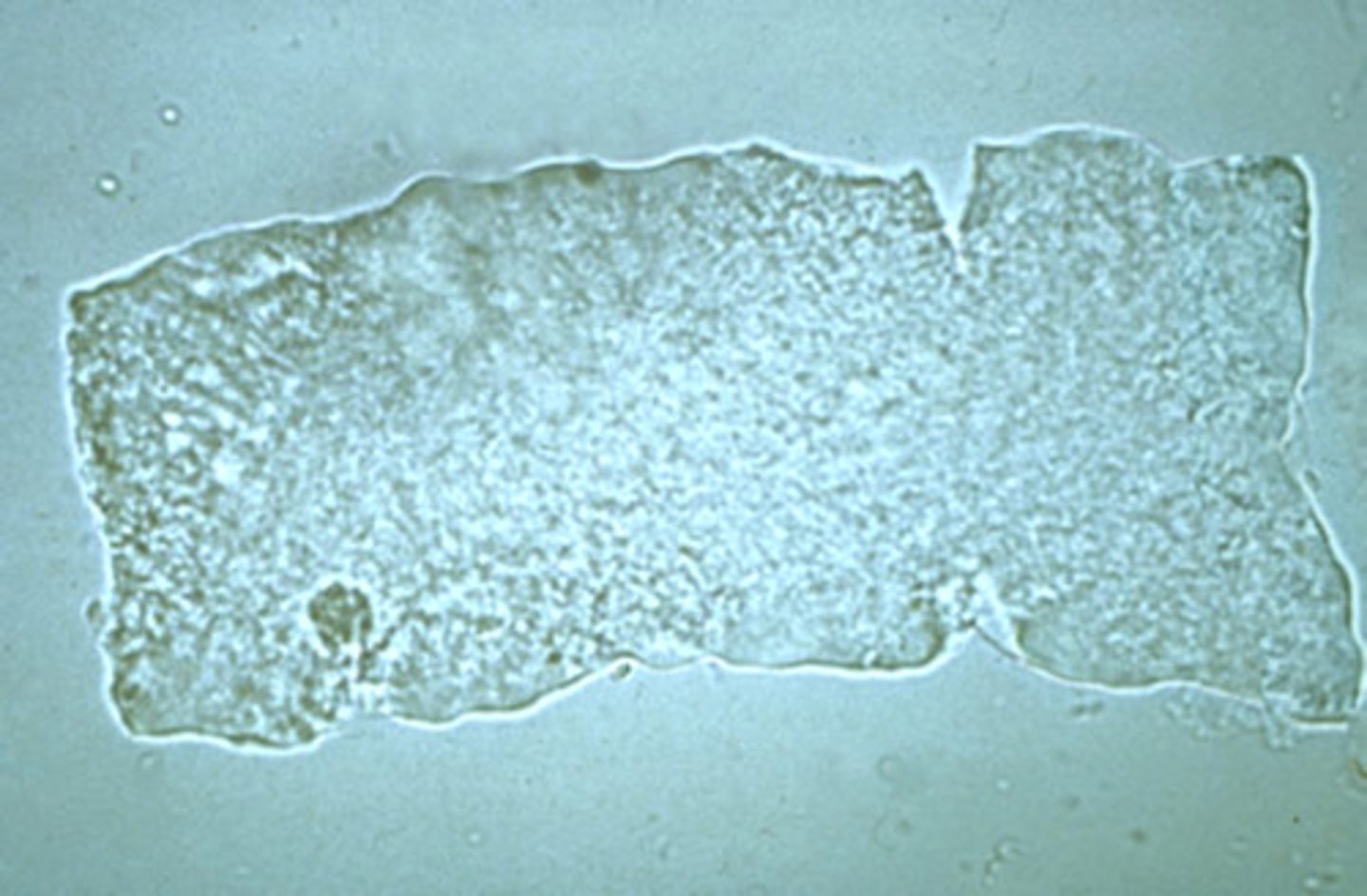
clinical significance of broad cast
extreme urine stasis, renal failure
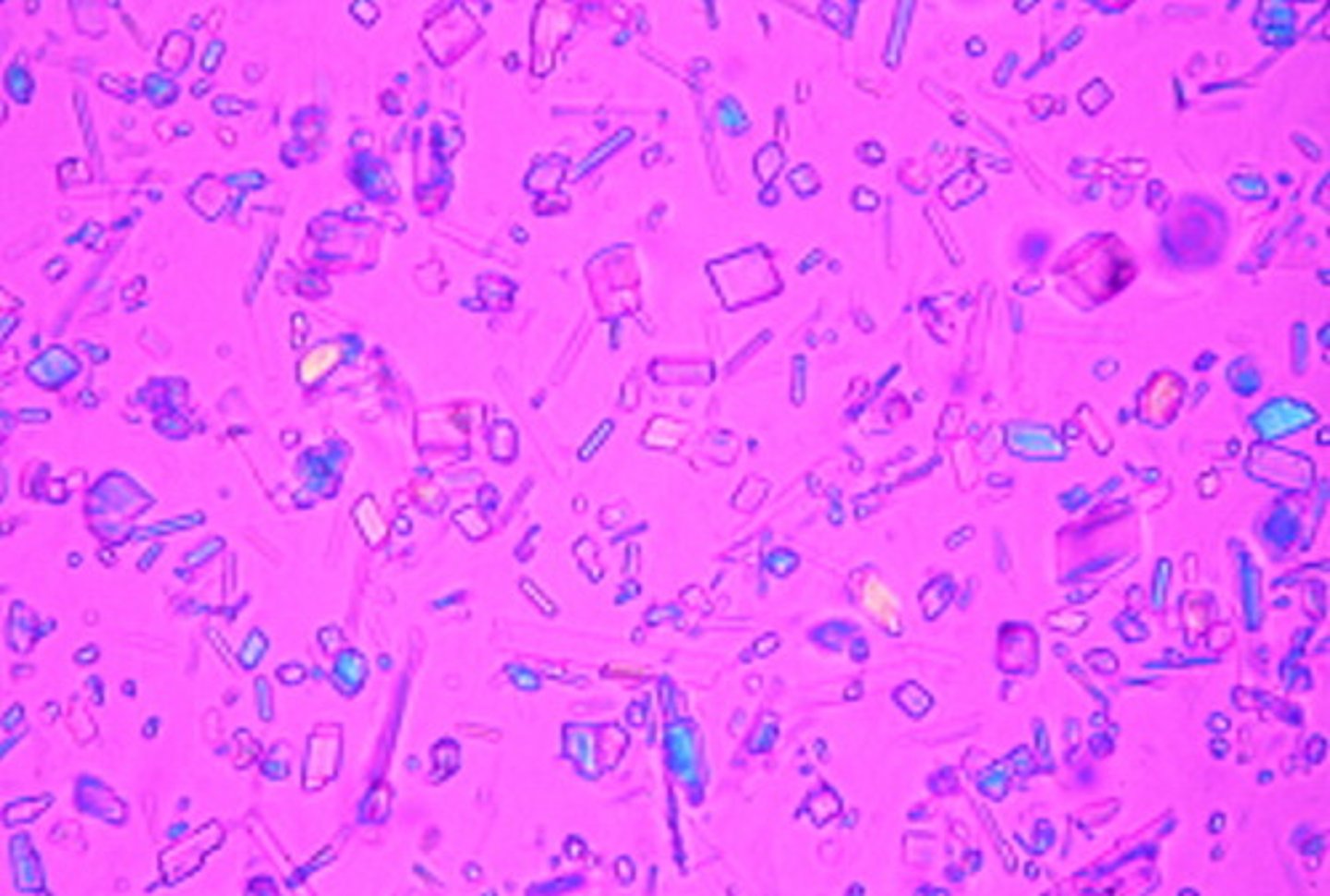
Crystals: uric acid
-Normal=seen in variety of shapes, and highly birefringent under polarized light
-pH= acid
-color= yellow-brown (rosettes, wedges)
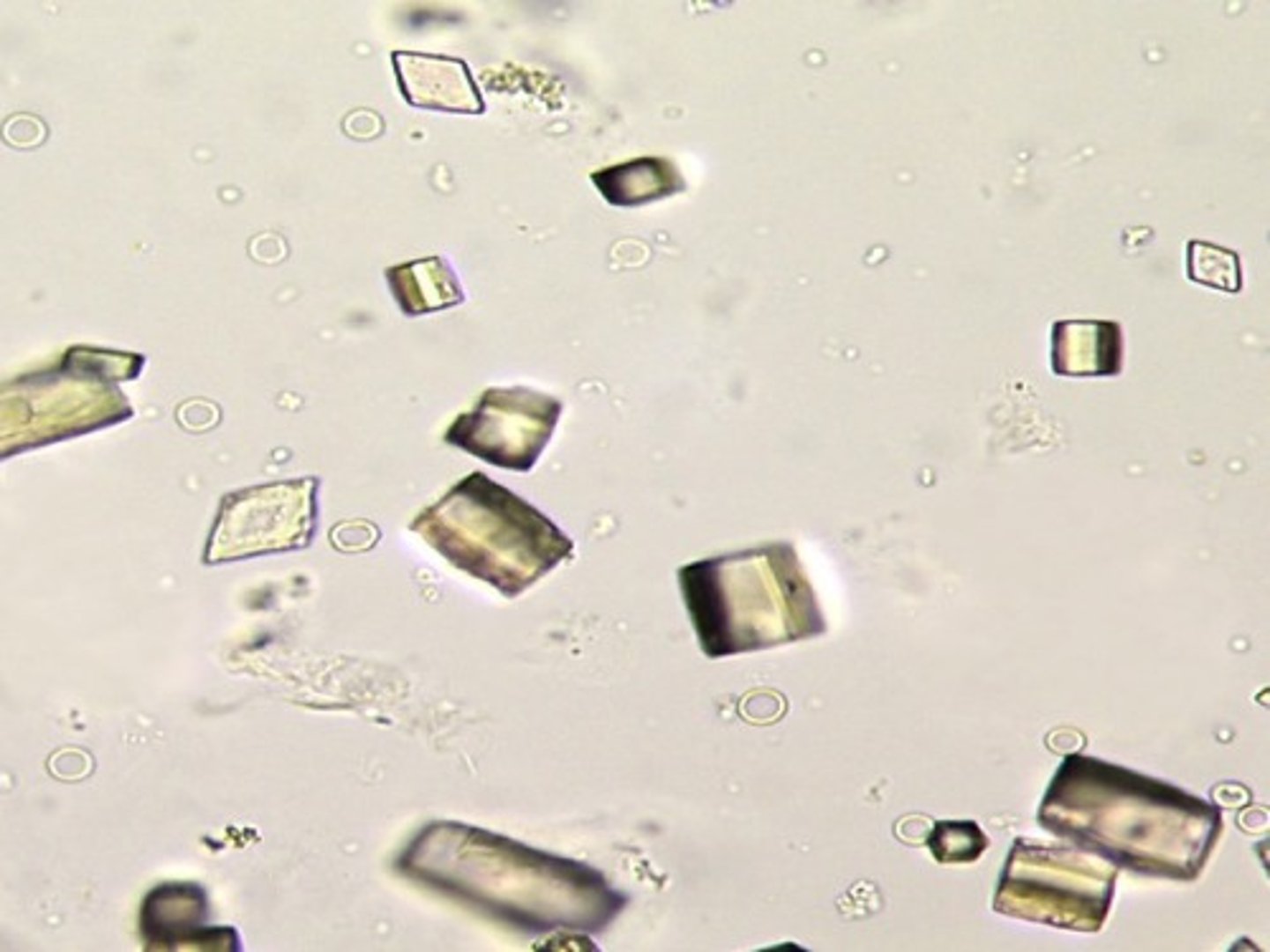

Birefringent
the ability to refract light in two directions
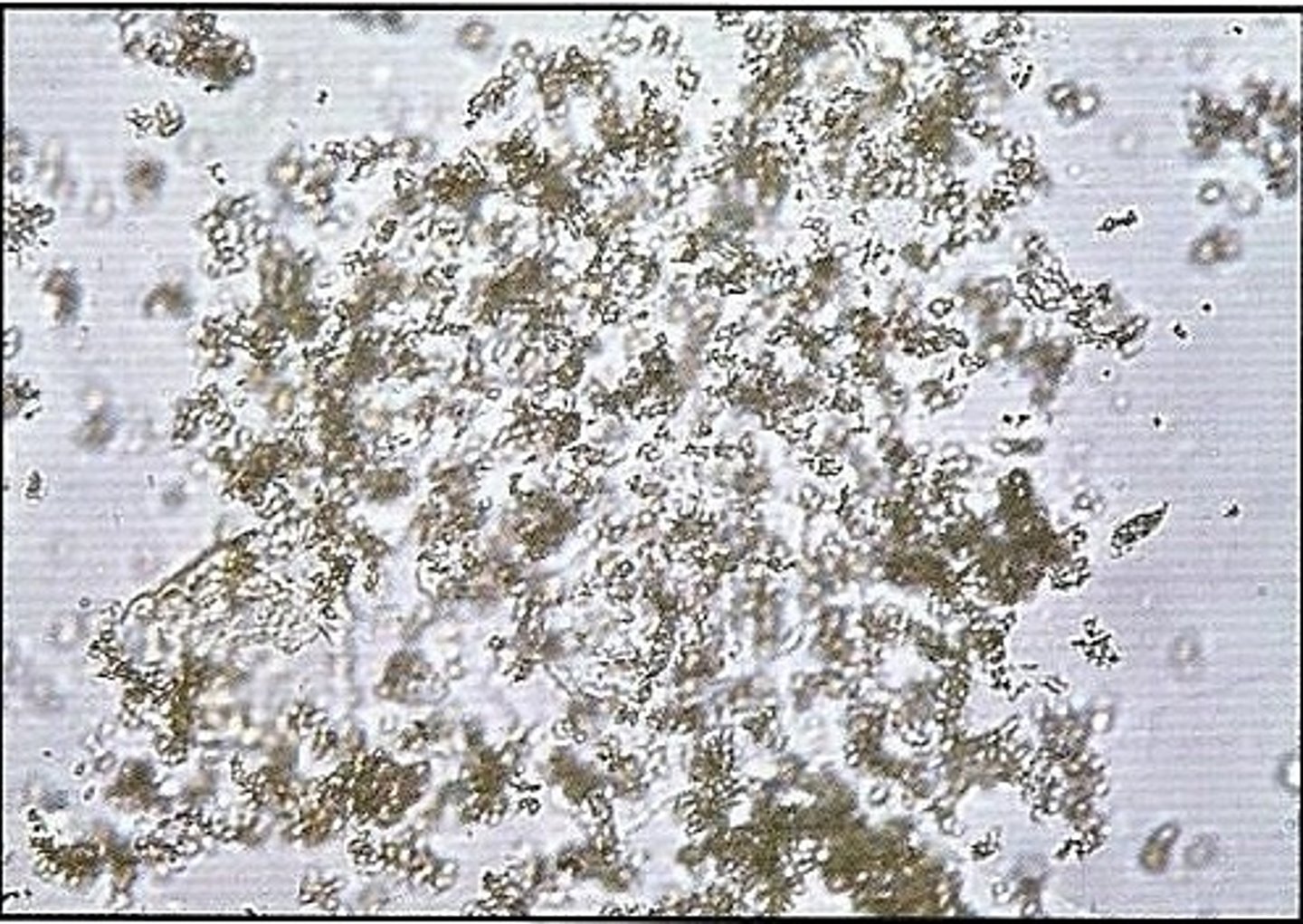
Crystals: Amorphous urates
-normal= in specimens that have been refrigerated and produce a pink sediment (caused by uroetythrin)
-pH= Acid
-Brick dust or yellow brown
Uroerythrin
red pigment present in urine
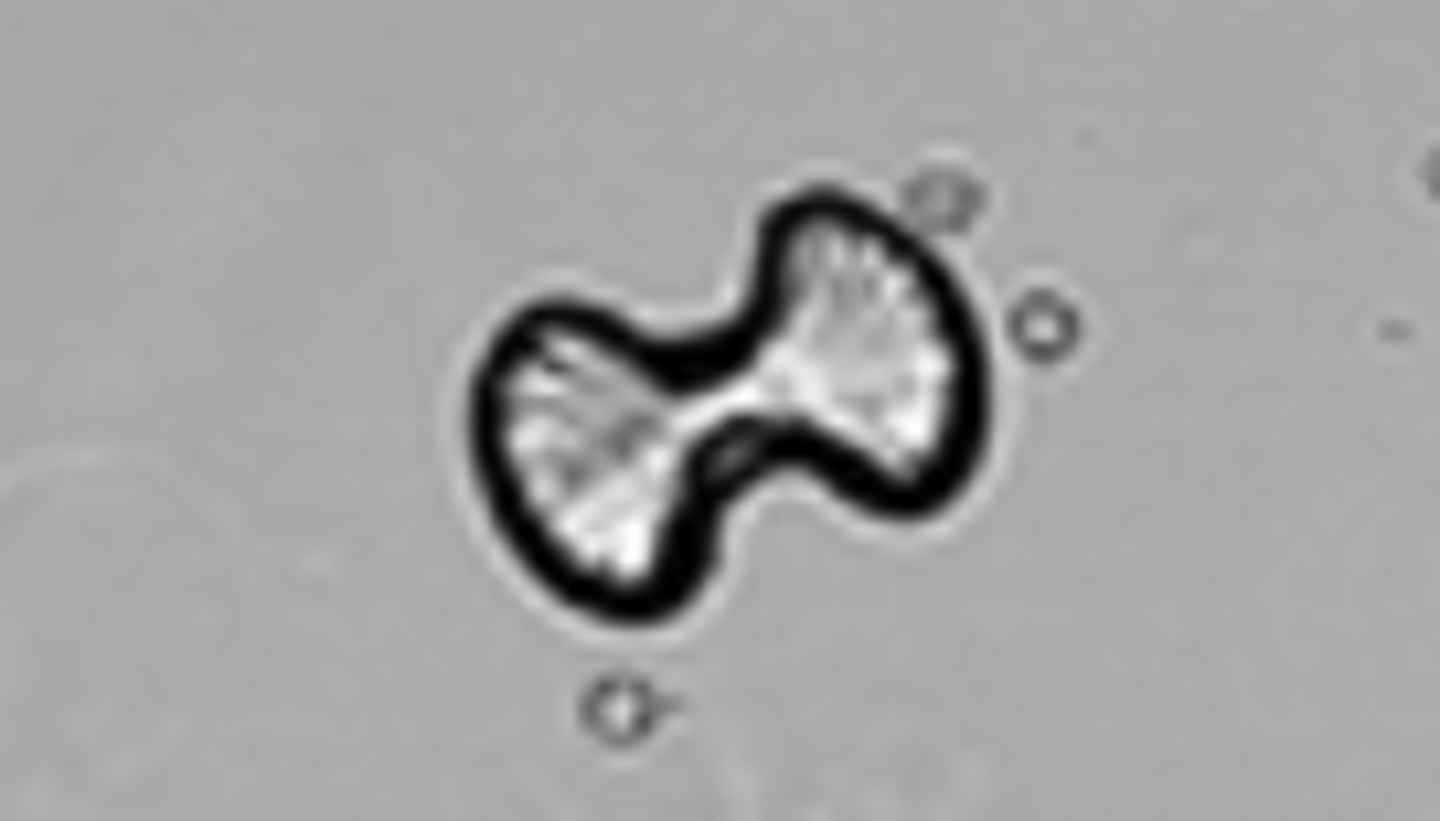
Crystals: Calcium oxalate
-Normal= unless clumped. Clumped cystals in fresh urine indicate formation of renal calculi. also associated with foods high in oxalic acid (tomatoes/ asparagus)
-pH= Acid/neutral (alkaline)
-colorless
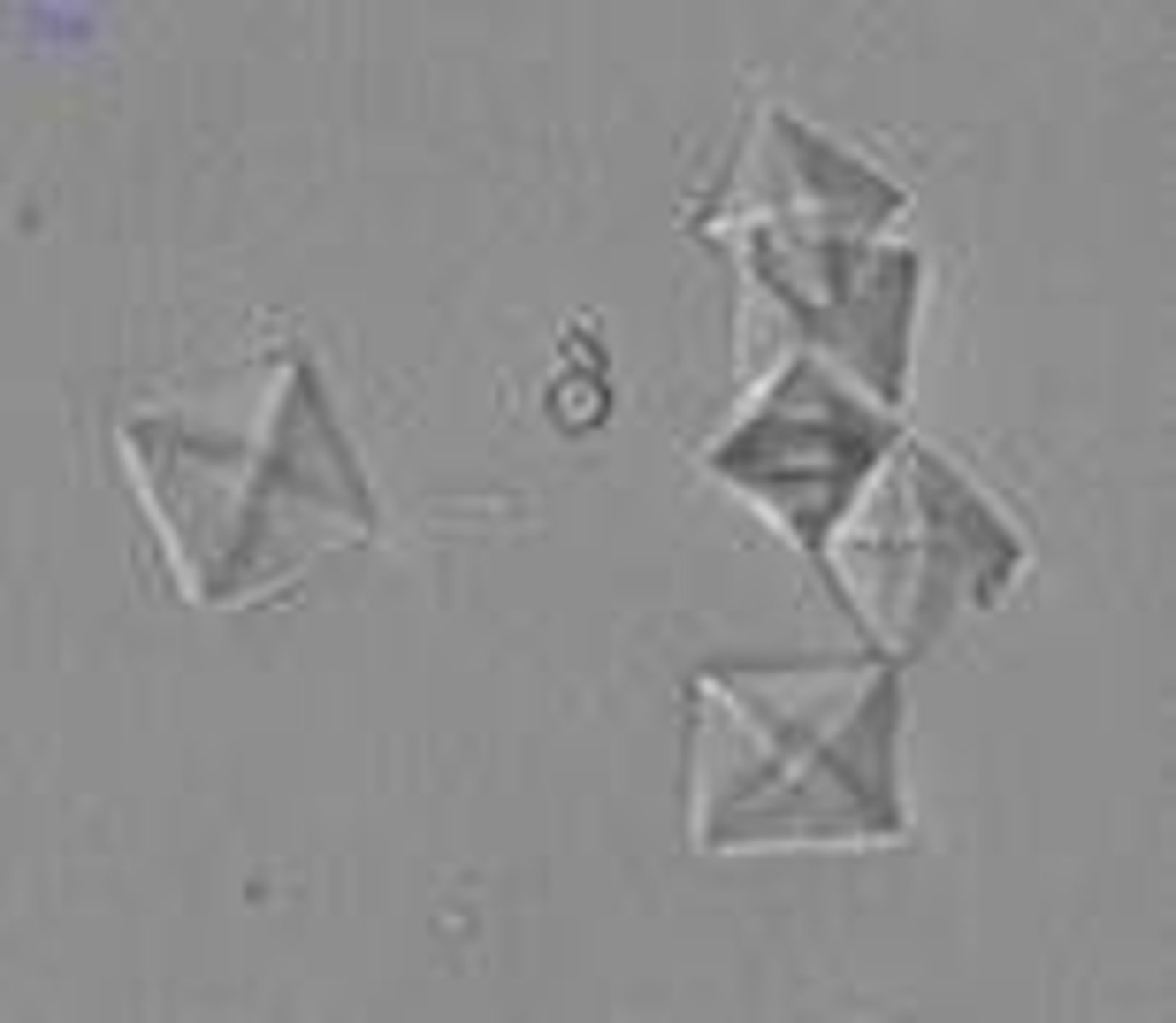

Monohydrate calcium oxalate crystals clinical significance:
ethylene glycol (antifreeze) poisoning
calcium oxalate
dumbbell shape
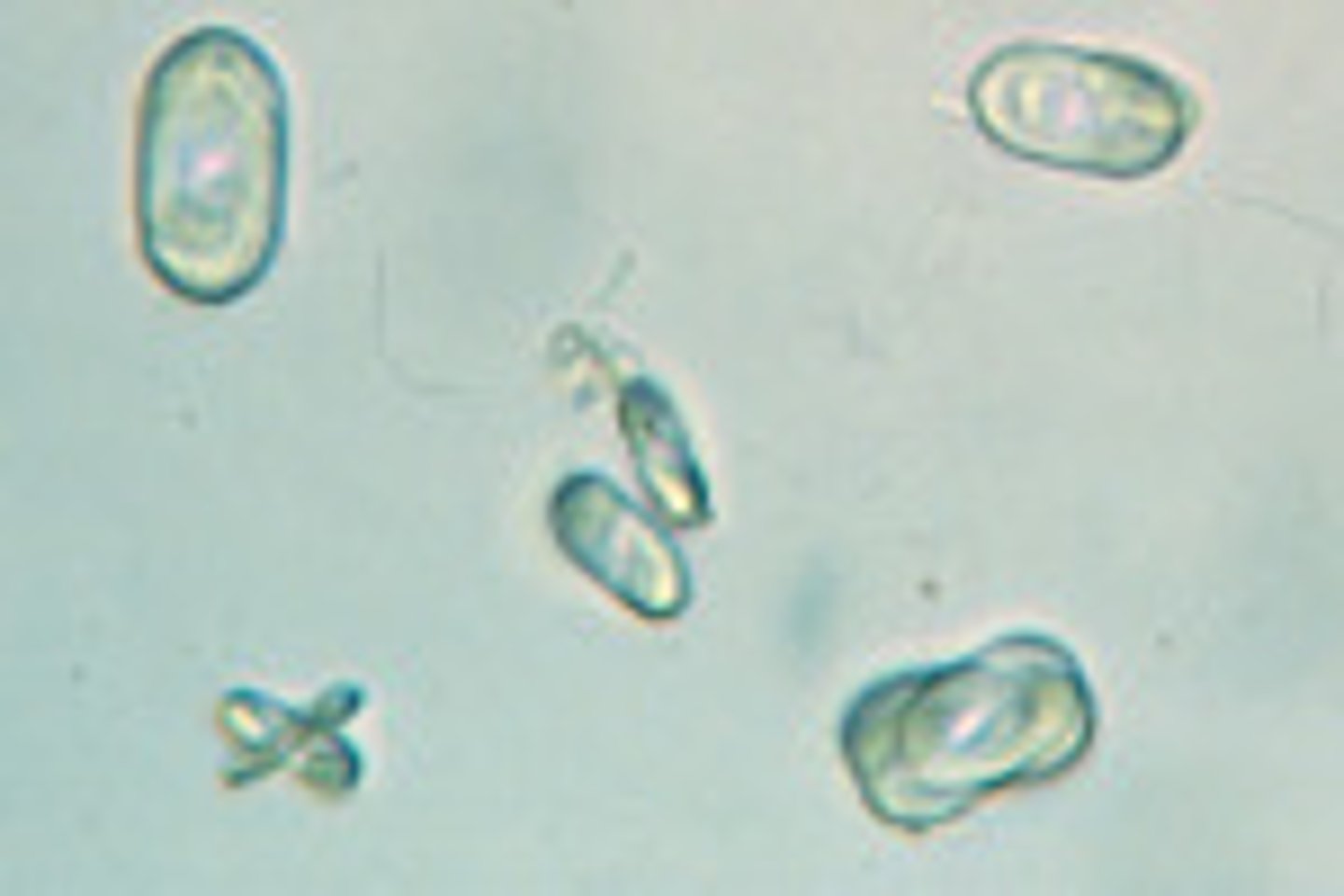
Crystals: Amorphous phosphates
-Normal= granular precipitate containing calcium and phosphate
-pH= Alkaline/ neutral
-color= white-colorless
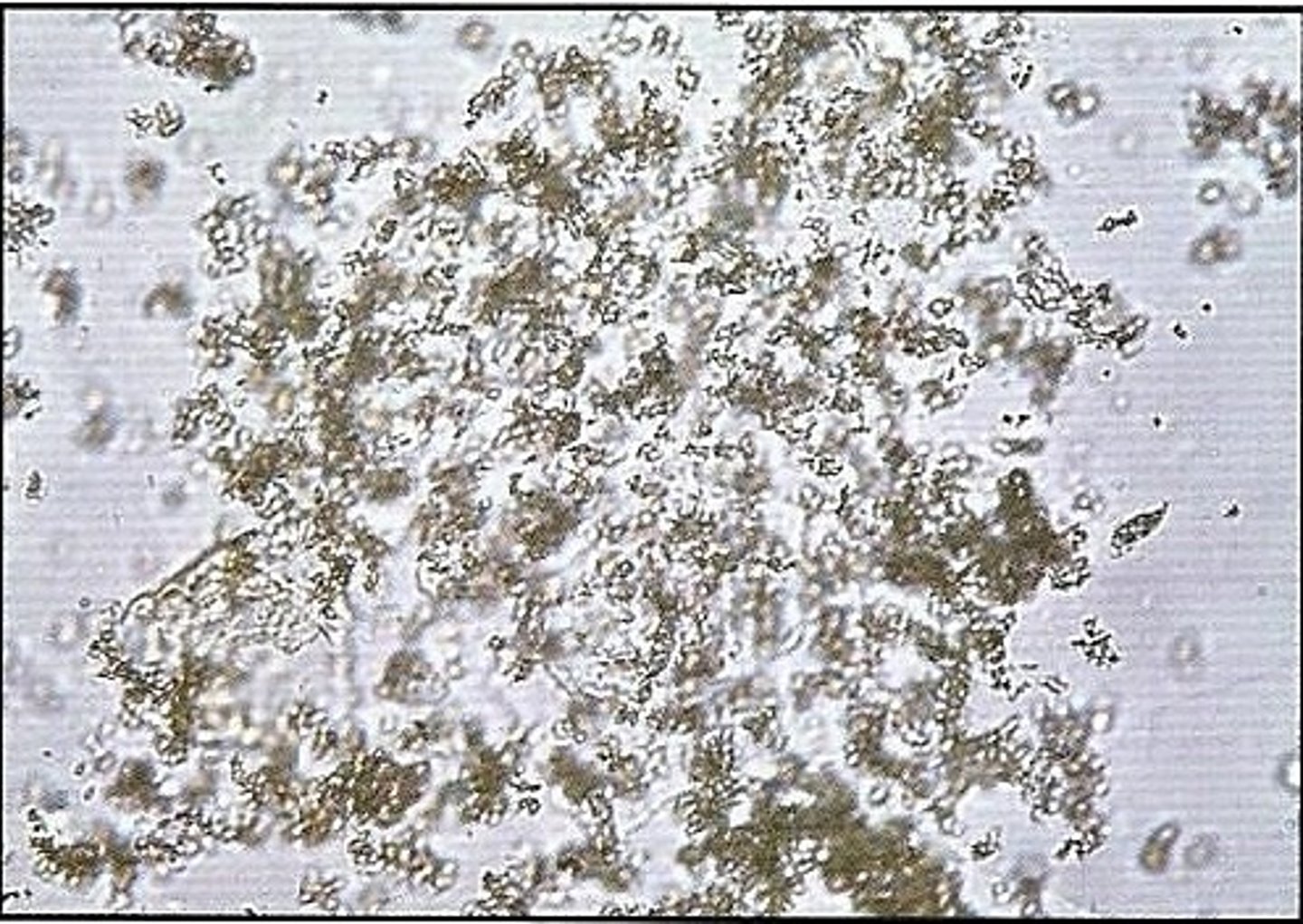
Crystals: Calcium phosphate
-Normal= flat rectangular plates or thin prisms often in rosette formations.
-pH= alkaline/ neutral
-color= colorless
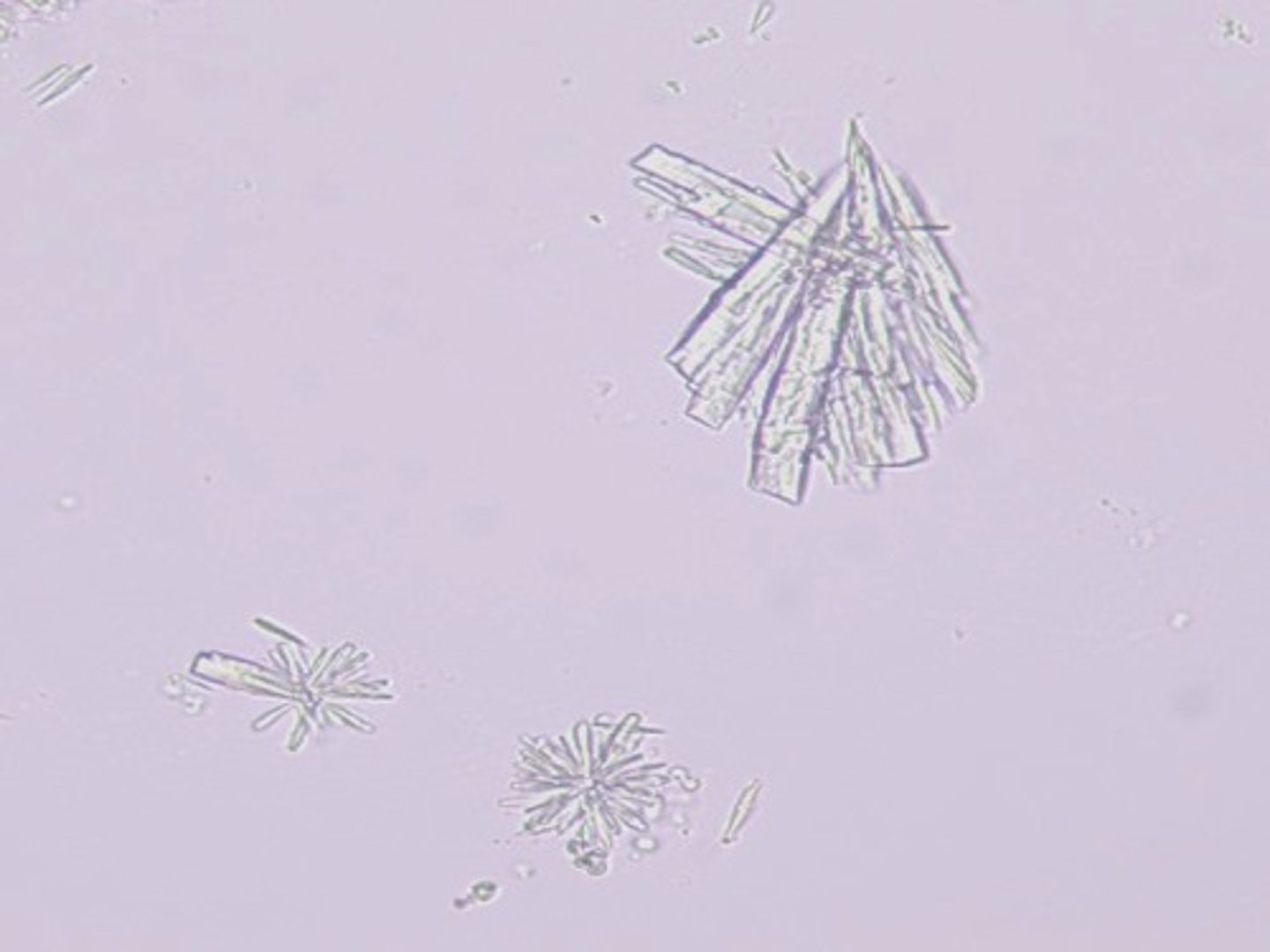
calcium phosphate

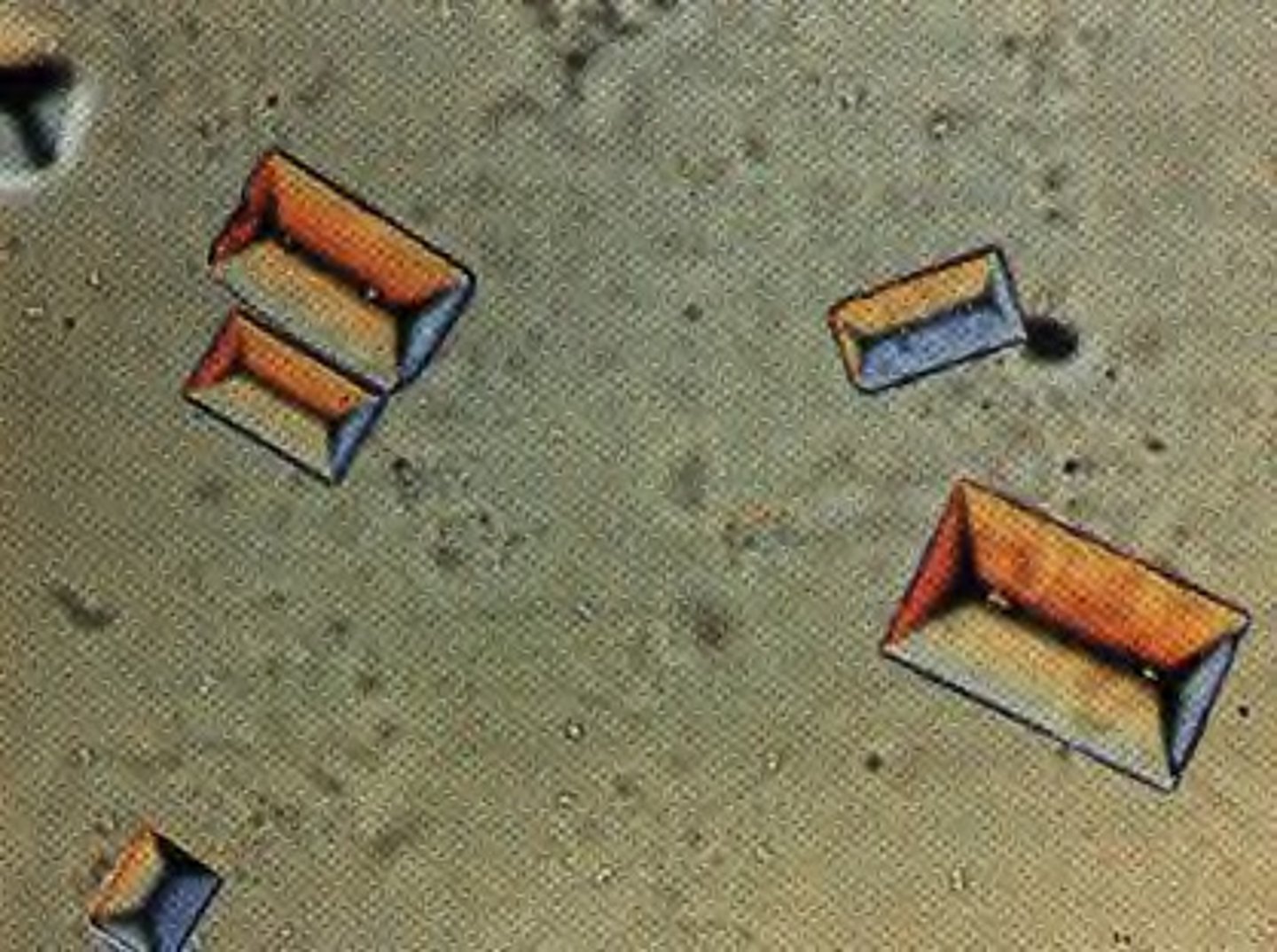
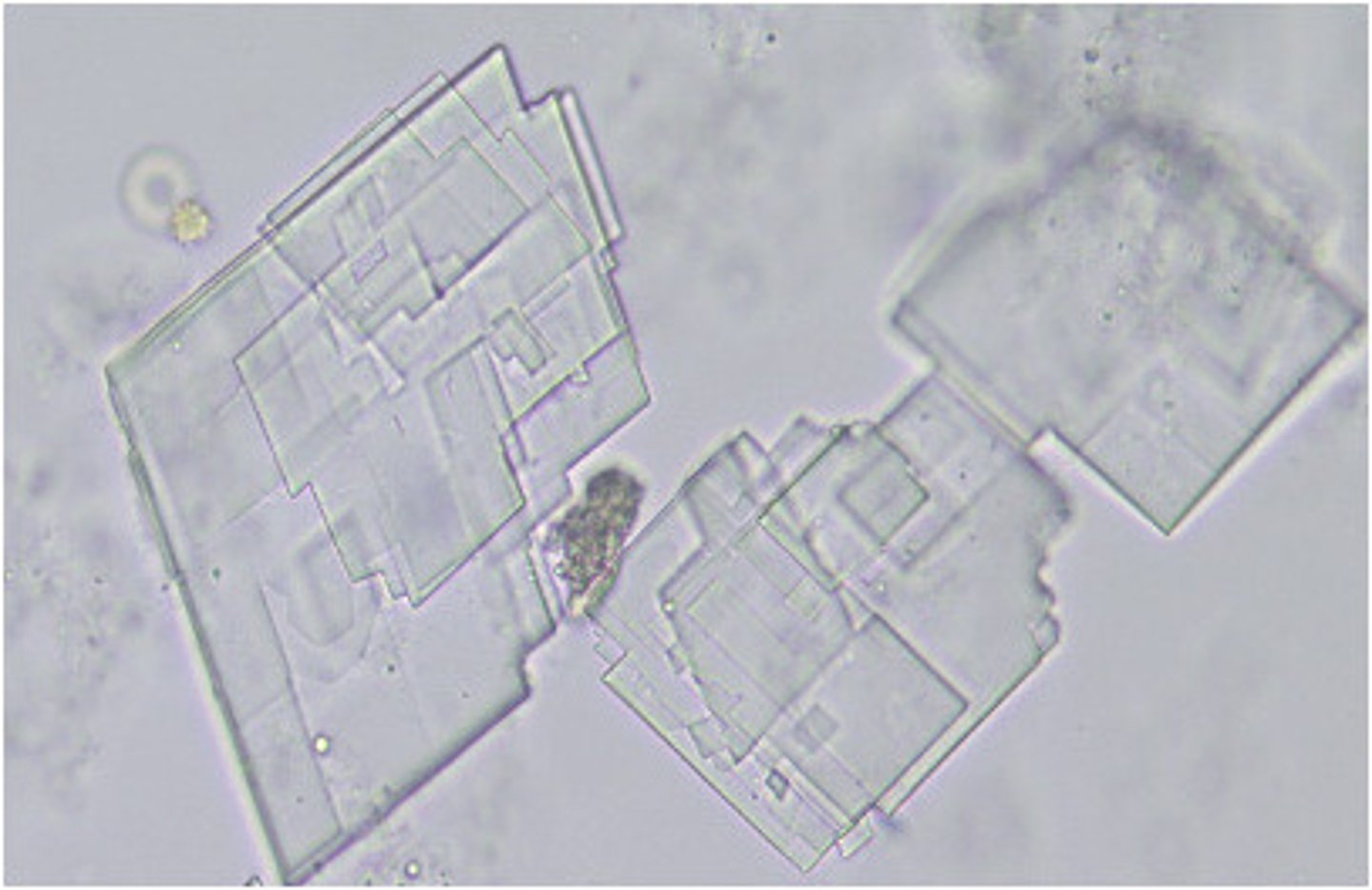
Crystals: Triple phosphate
-Normal= "coffin lid"
-pH= Alkaline
-color= colorless
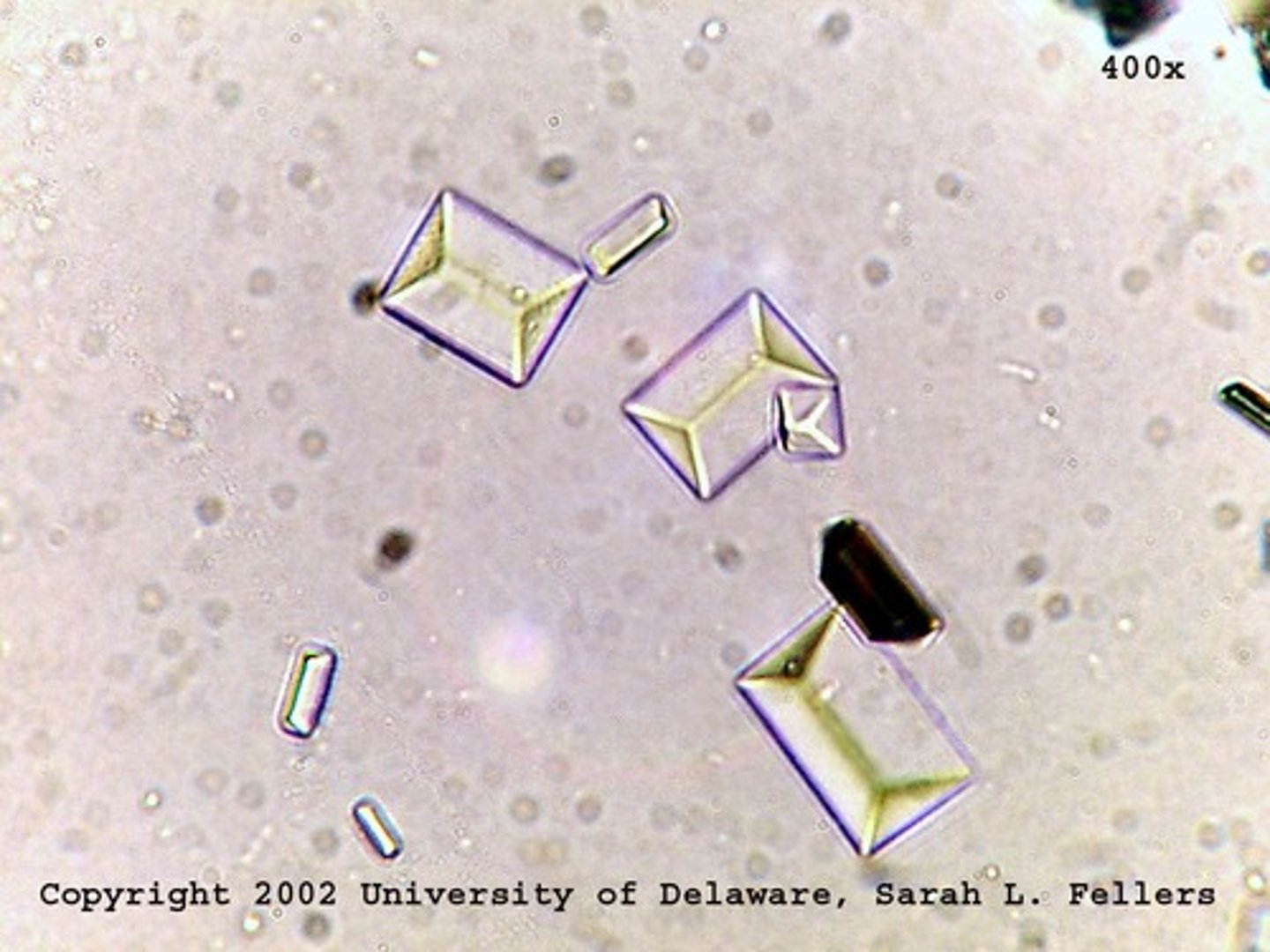
triple phosphate crystals
Crystals: Ammonium biurate
-Normal= "thorny apples". Encountered in OLD specimens
-pH= Alkaline
-color= yellow-brown
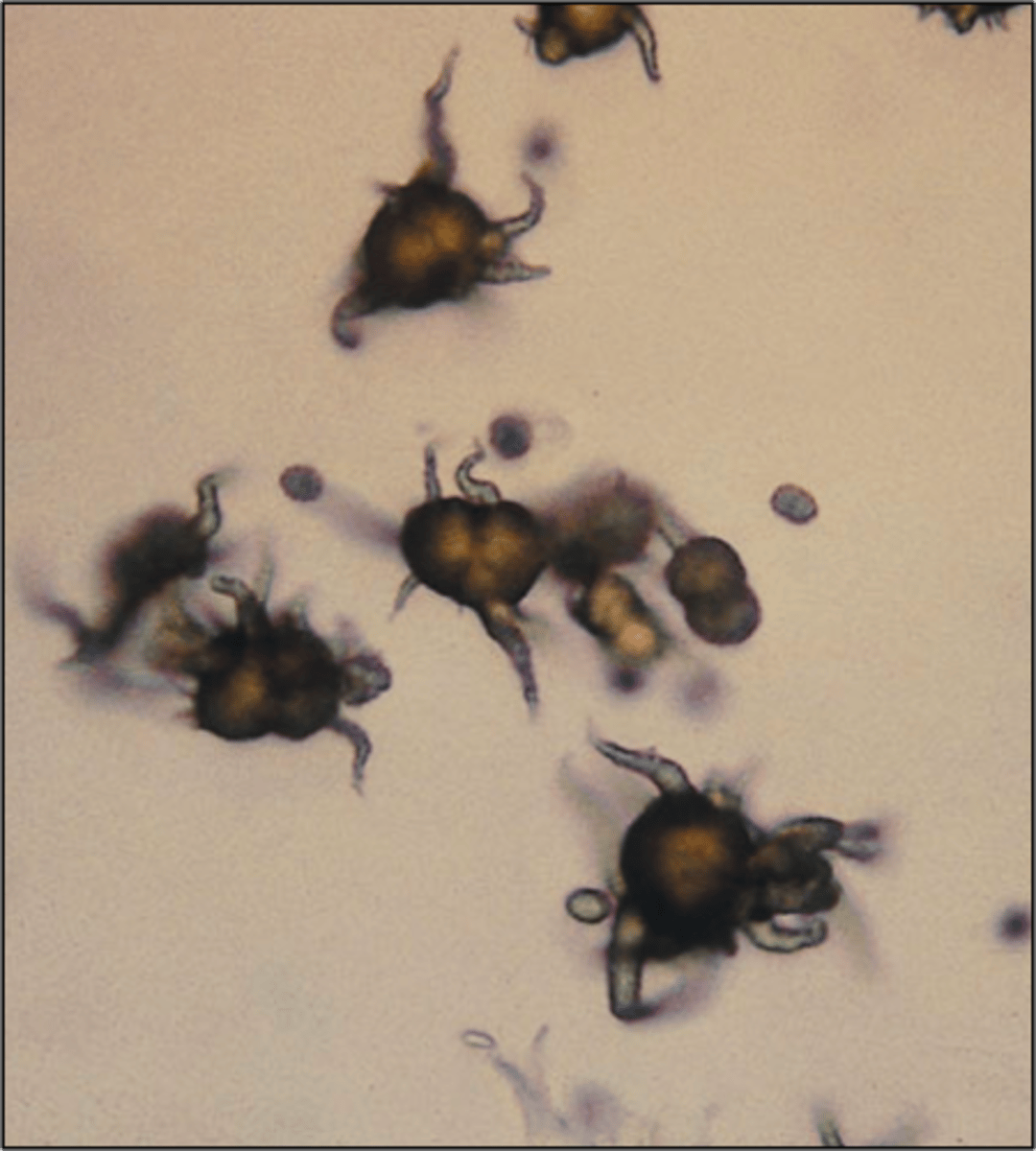
Ammonium biurate
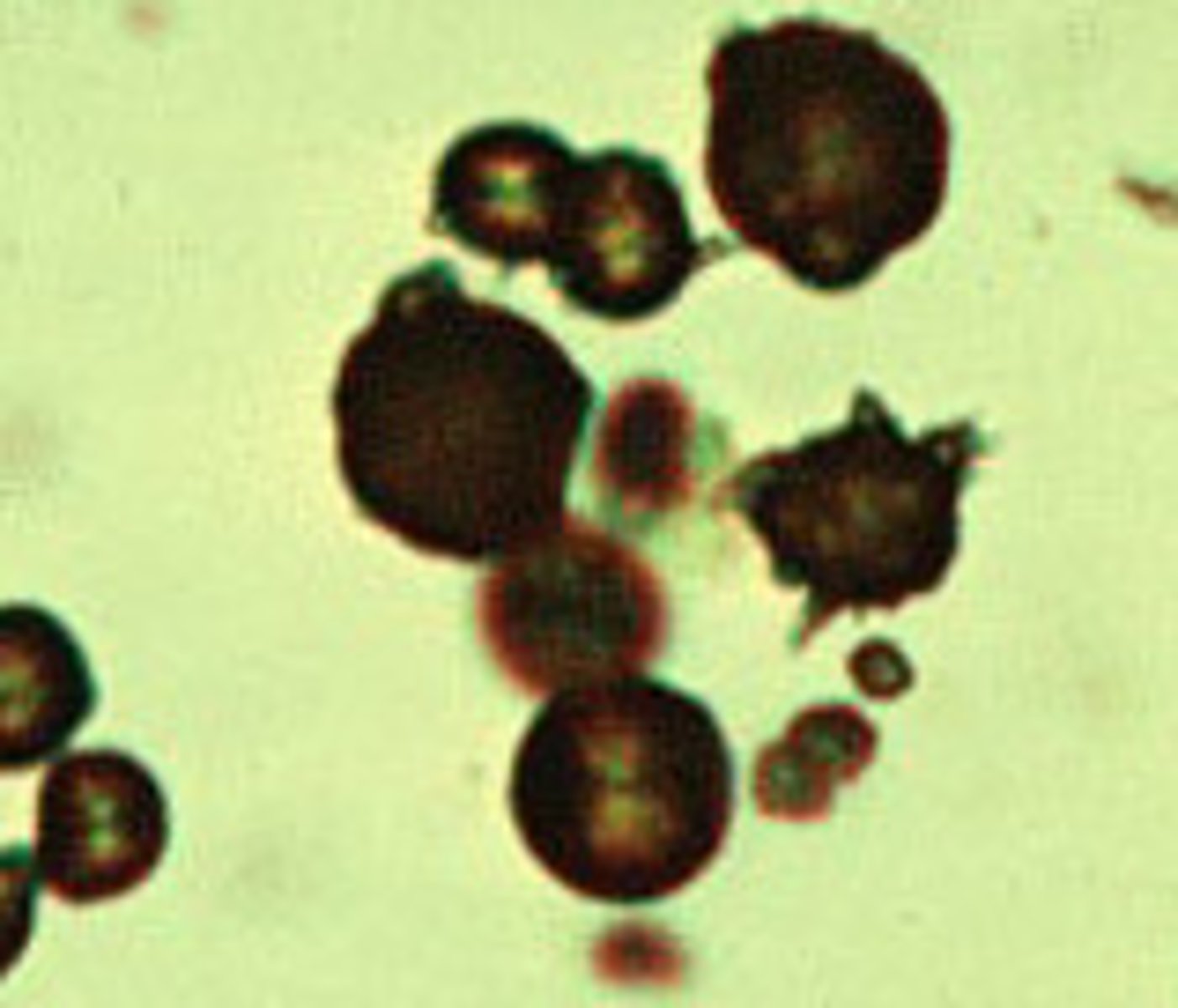
Crystals: Calcium carbonate
-Normal= dumbbell shaped and birefringent
-pH= alkaline
-color= colorless
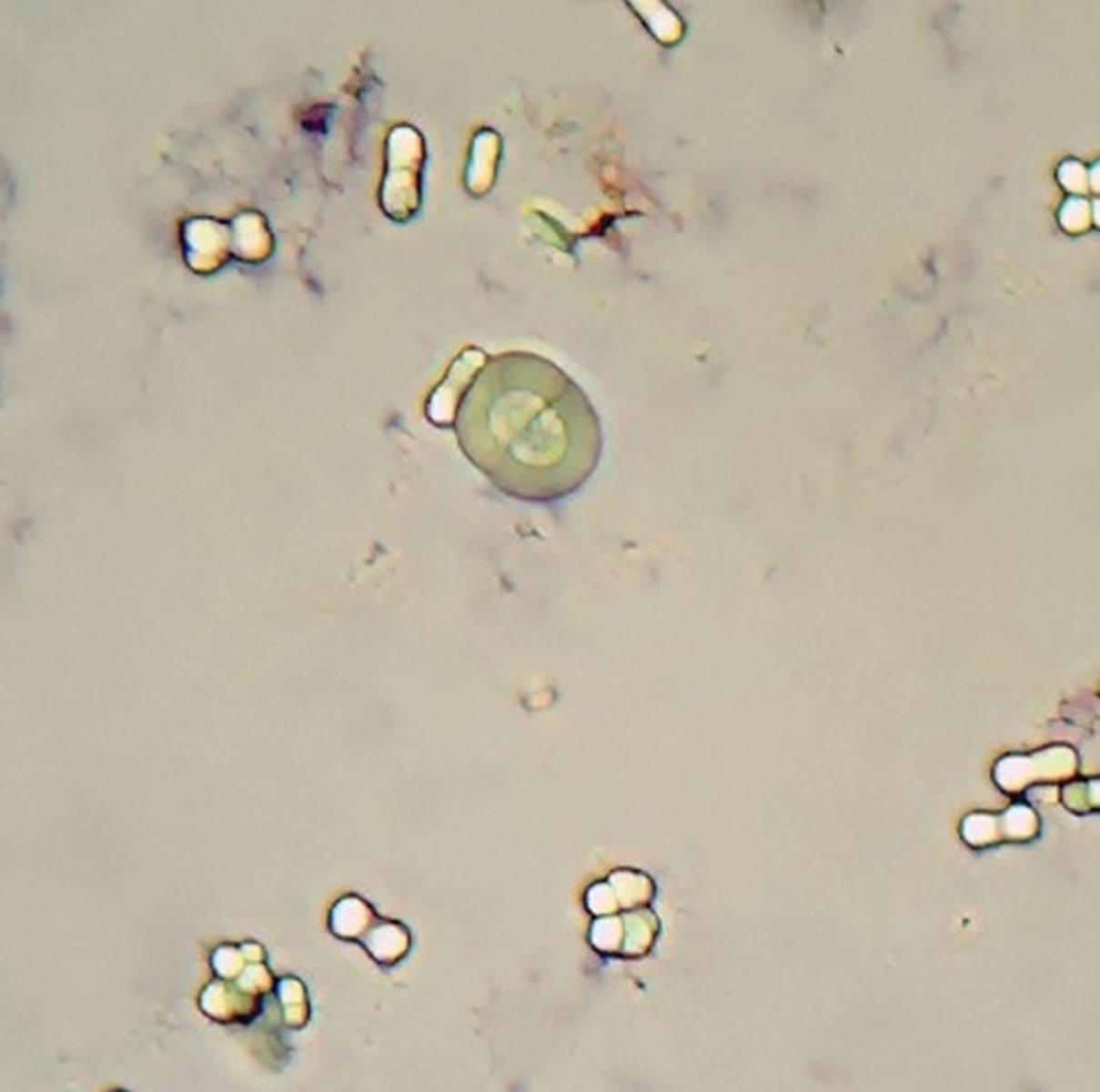
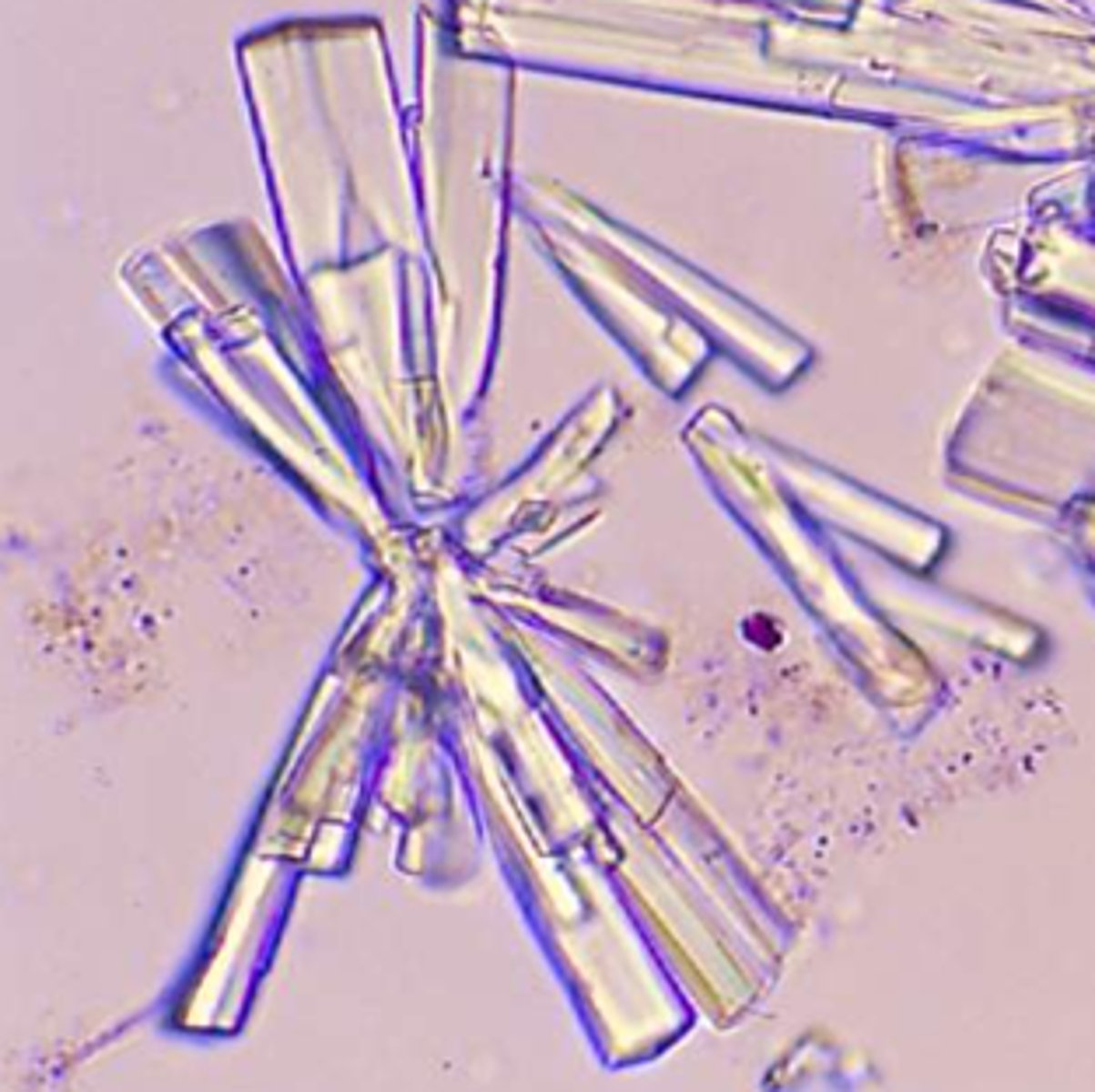
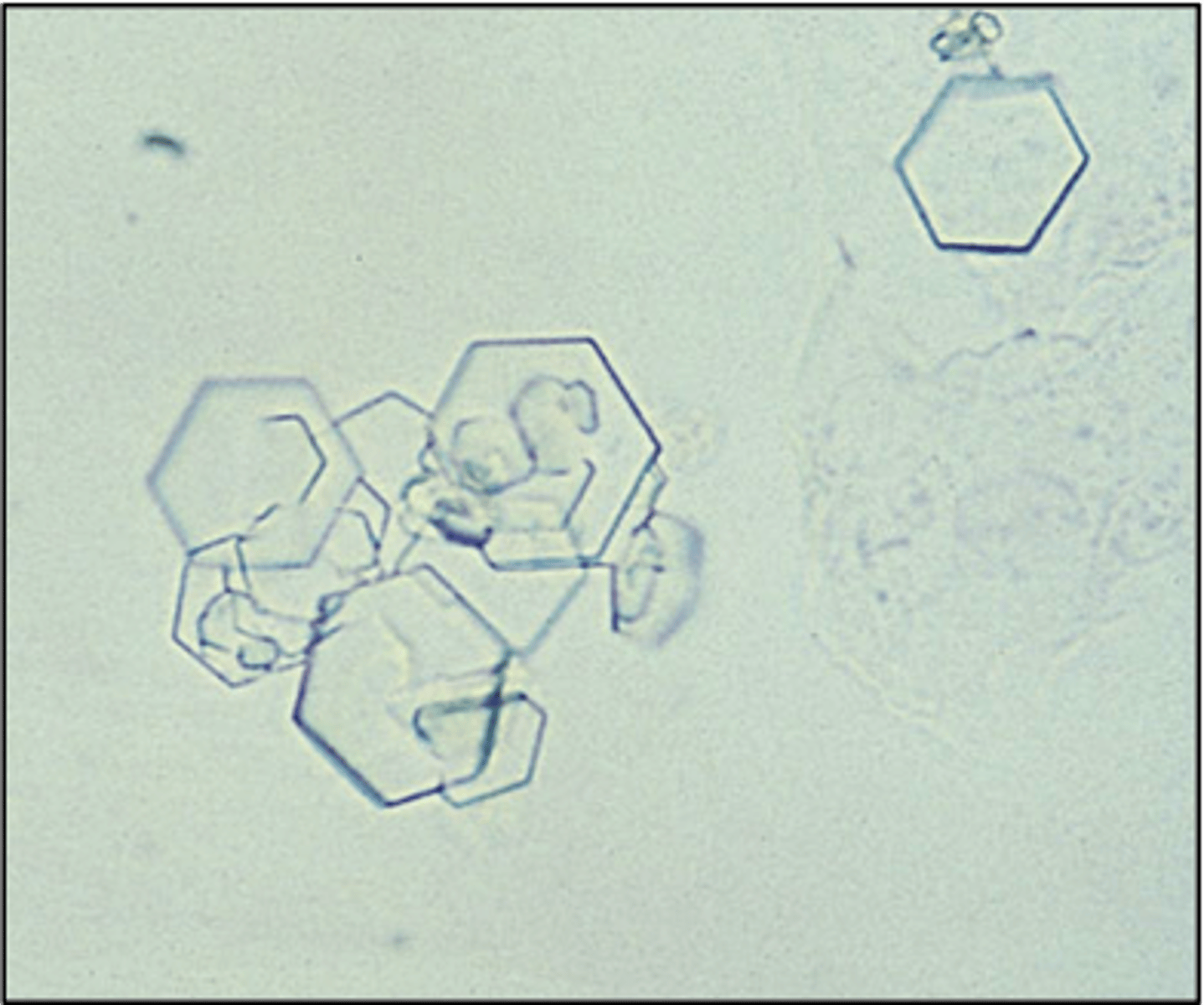
Crystals: Cystine
-Abnormal= due to metabolic disorder that prevents reabsorption of cystine by the renal tubules.
-Confirmatory test= cyanide-nitroprusside test
-pH= Acid
-Color/Form= Colorless (hexagonal plates)
-disorders= inherited cystinuria
Crystals: Cholesterol
-Abnormal= rarely seen unless specimen is refrigerated. Seen with fatty casts and oval fat bodies. Highly birefringent
-pH= Acid
-color/form= colorless (notched plates)
-Disorders= Nephrotic syndrome
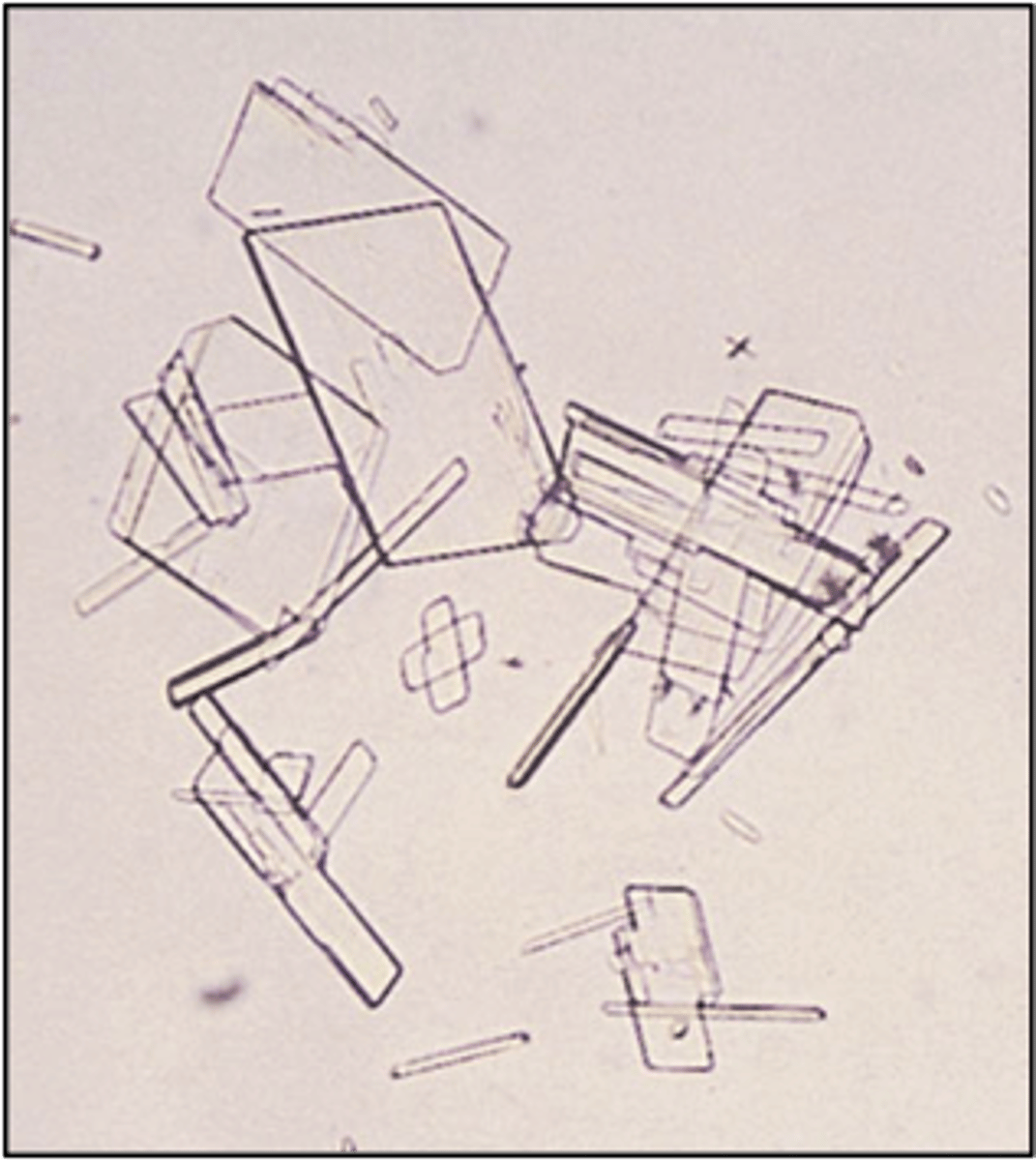
cholesterol crystals

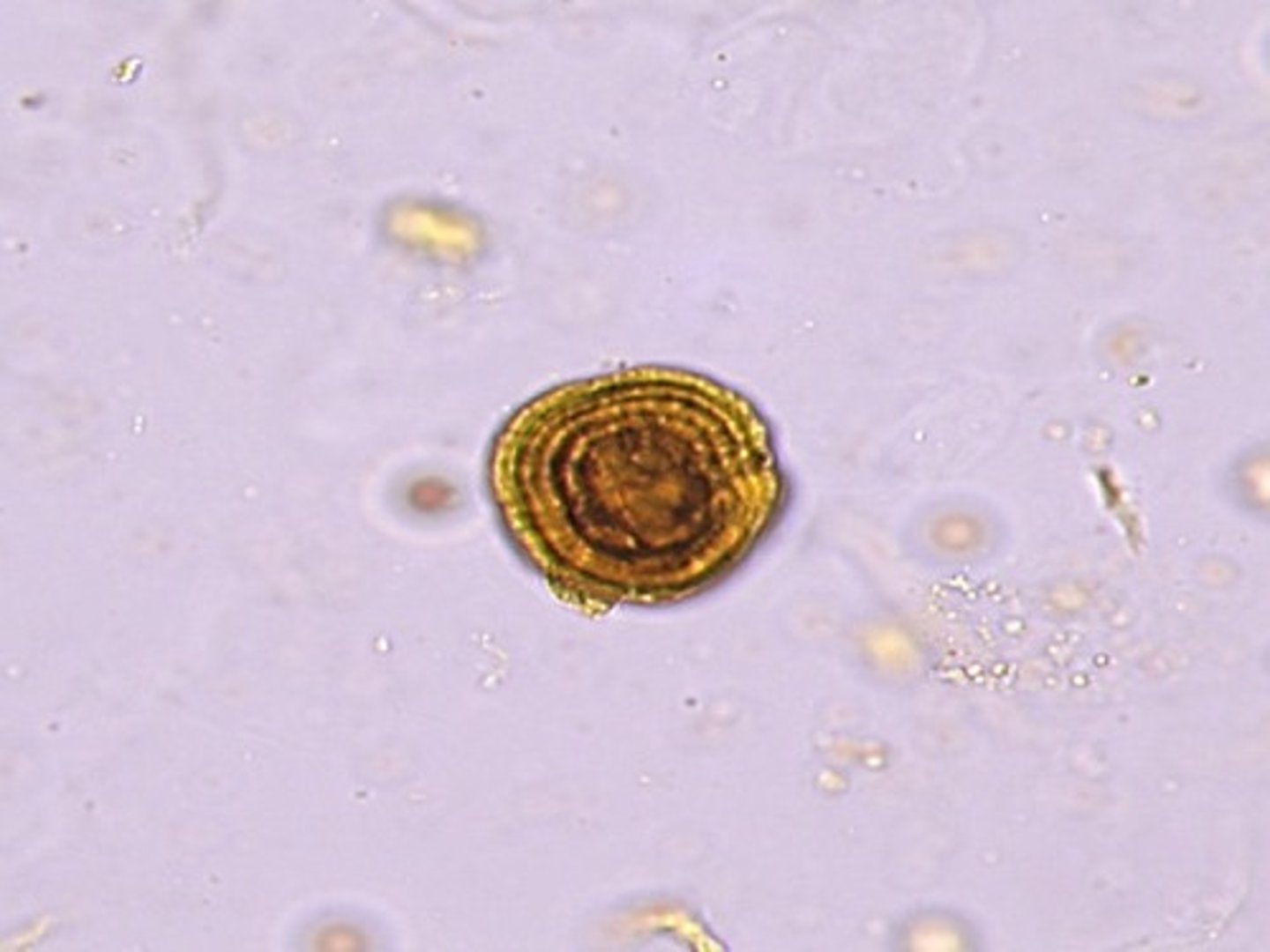
Crystals: Leucine
-Abnormal= when present should be accompanied by tyrosine crystals
-pH= Acid/neutral
-color/form= yellow (concentric circles)
-disorders= Liver disease