Amino Acids
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Nonpolar NonAromatic
Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Ile, Met, Pro (Hydrophobic side chains that avoid water and stabilize structures by aligning towards center of the protein)
Nonpolar Aromatic
Phe, Trp (rings absorb UV)
Polar Aromatic
Trp
Polar Uncharged
Ser, Thr, Cys, Asn, Gln (side chains can form H bonds with water —> hydrophilic)
Polar Charged
Asp, Glu, Lys, Arg, His (can be acidic or basic, important for electrostatic interactions)
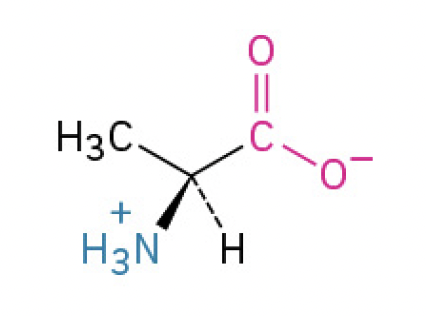
Glycine (Gly, G) (simplest, most flexible)
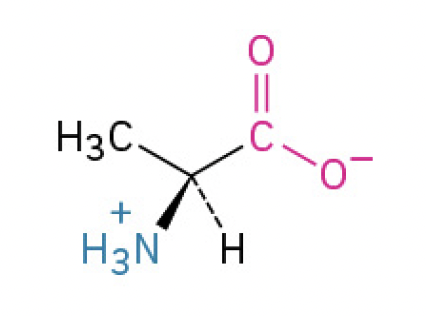
Alanine (Ala, A)
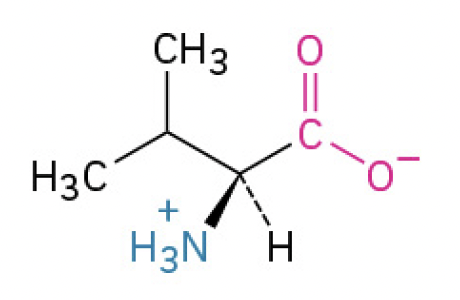
Valine (Val, V)
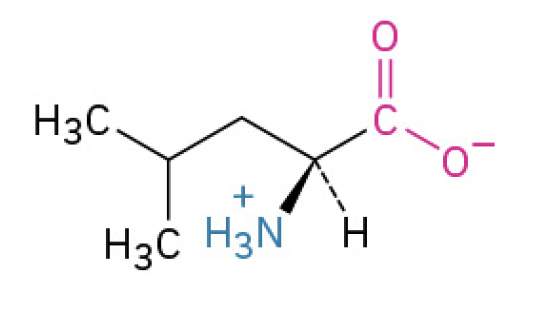
Leucine (Leu, L)
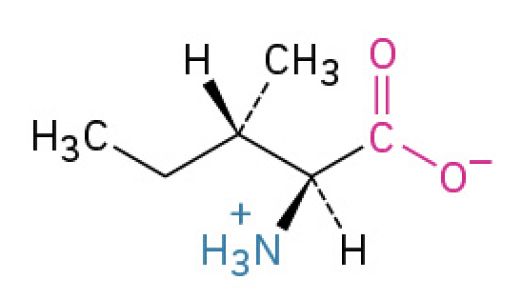
Isoleucine (Ille, I)
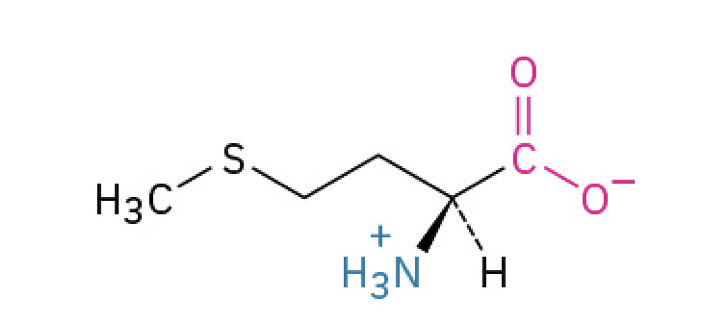
Methionine (Met, M) (involved in initiating protein synthesis)
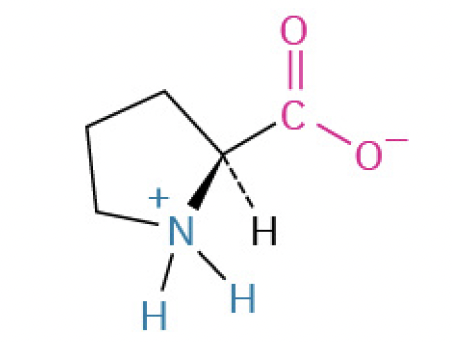
Proline (Pro, P) (amino nitrogen in the cyclic structure, restricts flexibility so found in twists and turns in protein)
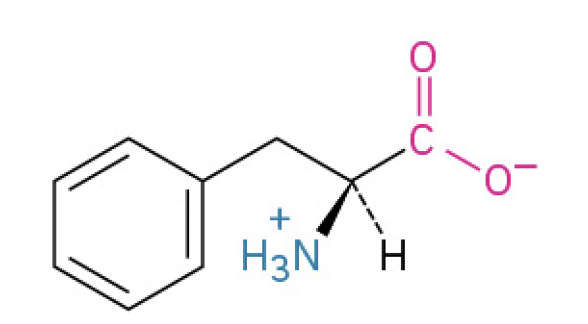
Phenylalanine (Phe, F) (benzyl chain is hydrophobic)
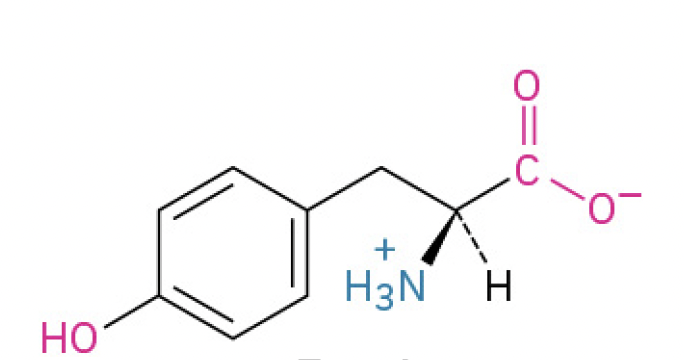
Tyrosine (Tyr, Y) (hydroxyl group makes it polar, vital to signaling pathways)
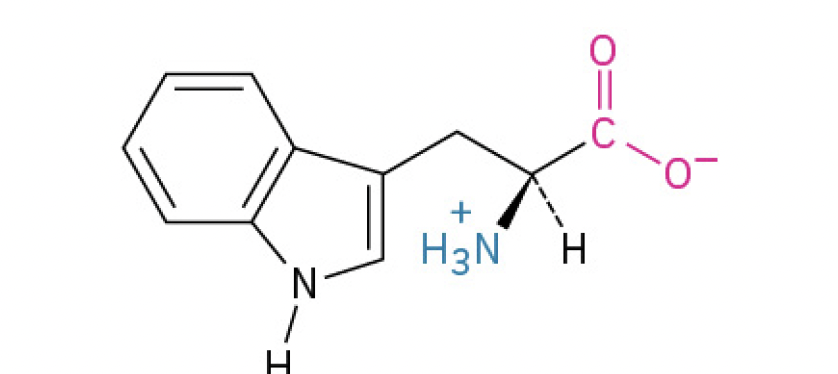
Tryptophan (Trp, W) (largest amino acid)
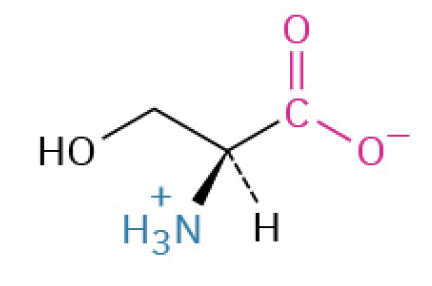
Serine (Ser, S) (used in phosphorylation)
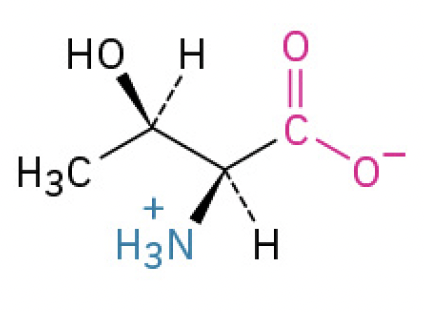
Theronine (Thr, T)
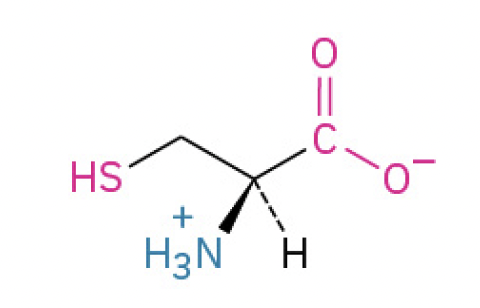
Cysteine (Cys, C) (thiol group, forms disulfide bonds, crucial for protein stability)
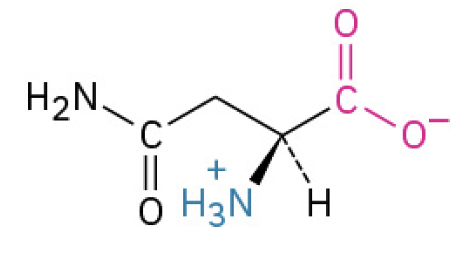
Asparagine (Asn, N) (neutral charge)
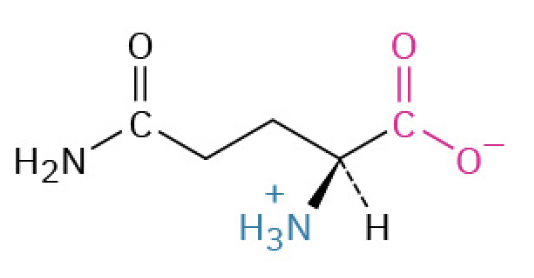
Glutamine (Gln, Q) (neutral in charge)
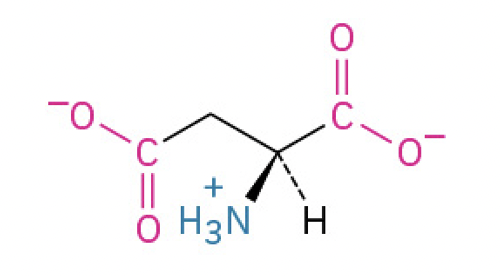
Aspartic Acid (Asp, D) (carboxyl group makes it acidic, loses protons and gains negative charge)
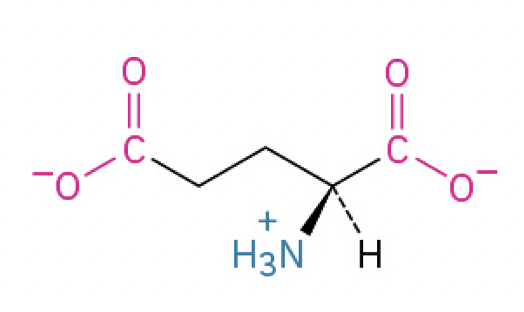
Glutamic Acid (Glu, E) (negatively charged, loses proton)
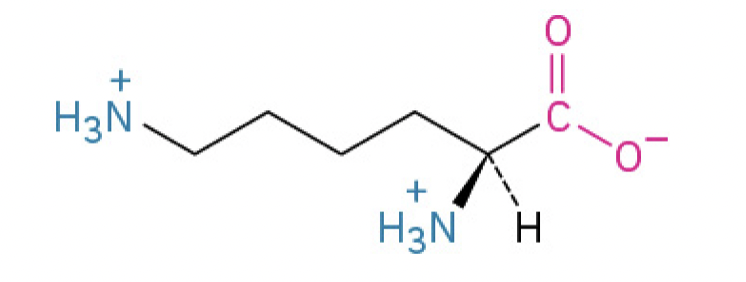
Lysine (Lys, K) (terminal primary amino group, binds to negatively charged molecules)
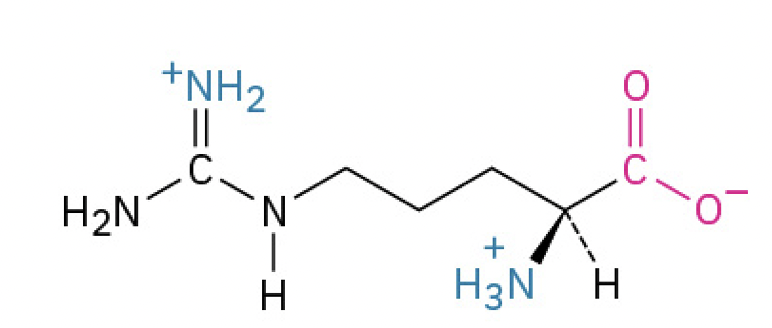
Arginine (Arg, R) (has a guanidium group and is HIGHLY basic)
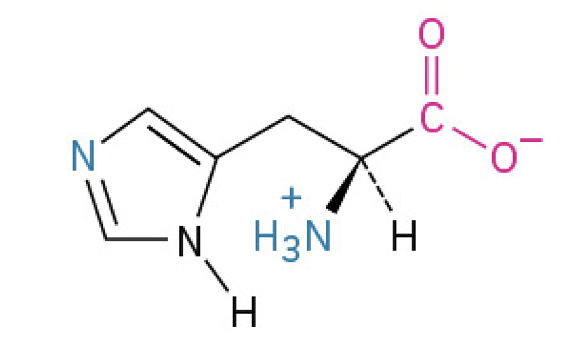
Histidine (His, H) (contains imidazole ring which can shuttle protons. plays role in active sites and buffering)
Essential Amino Acids
Cannot be synthesized by body (His, Ile, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Thr, Trp)
Non-Essential Amino Acids
Can be synthesized by body (Ala, Asp, Asn, Glu, Ser, Arg, Cys, Gln, Gly, Pro, Tyr)
Phosphorylation
Addition of phosphate group
Glycosylation
Attachment of carbohydrate groups
Ubiquitination
Attachment of ubiquitin to lysine residues to tag protein for degredation