2.1 molecules to metabolism
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
1
New cards
define "molecular biology"
a branch of biology focused on structures and functions at the molecular level
2
New cards
what is the number and type of bond carbon can form with other atoms?
carbon can form four covalent bonds with other atoms Non-polar covalent
3
New cards
list the four major classes of carbon compounds used by living organisms.
1. Carbohydrates (CHO)-
1. monosaccharides (glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose)
2. disaccharides (maltose, lactose, sucrose)
3. polysaccharides starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin)
2. proteins (CHON)
1. amino acids, dipeptides, polypeptides
3. lipids (CHO)
1. fatty acides, sterols, triglycerides, phospholipids
4. nucleic acids (CHONP)
1. nucleotides, RNA, DNA
4
New cards
define metabolism and catalysis.
metabolism: chemical reactions that occur w/i an organism to maintain life
* break down of molecules to release energy
* synthesis of new molecules to support cellular functions
catalysis: process by which substance (catalyst) increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being consumed or undergoing any permanent chemical change
→ lowers activation energy needed for a chemical reaction to occur
often enzymes in biology:
* break down food
* w/o them, chem reactions would occur too slowly to support life
* break down of molecules to release energy
* synthesis of new molecules to support cellular functions
catalysis: process by which substance (catalyst) increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being consumed or undergoing any permanent chemical change
→ lowers activation energy needed for a chemical reaction to occur
often enzymes in biology:
* break down food
* w/o them, chem reactions would occur too slowly to support life
5
New cards
state the role of enzymes in metabolism
act as the catalyst to speed up metabolism
6
New cards
define anabolism, monomer + polymer
anabolism
* constructing large molecules from smaller monomer subunits
monomer
* small molecule that can bind w/ other molecules of same type to form large polymer
polymer
* large molecule composed of many repeating monomer subunits
* constructing large molecules from smaller monomer subunits
monomer
* small molecule that can bind w/ other molecules of same type to form large polymer
polymer
* large molecule composed of many repeating monomer subunits
7
New cards
describe condensation (dehydration synthesis) reactions
chemical reaction in which two molecules (monomers) combine to form a larger molecule with the formation of water
8
New cards
define catabolism
the breaking down of large molecules into smaller subunits
9
New cards
contrast anabolism and catabolism
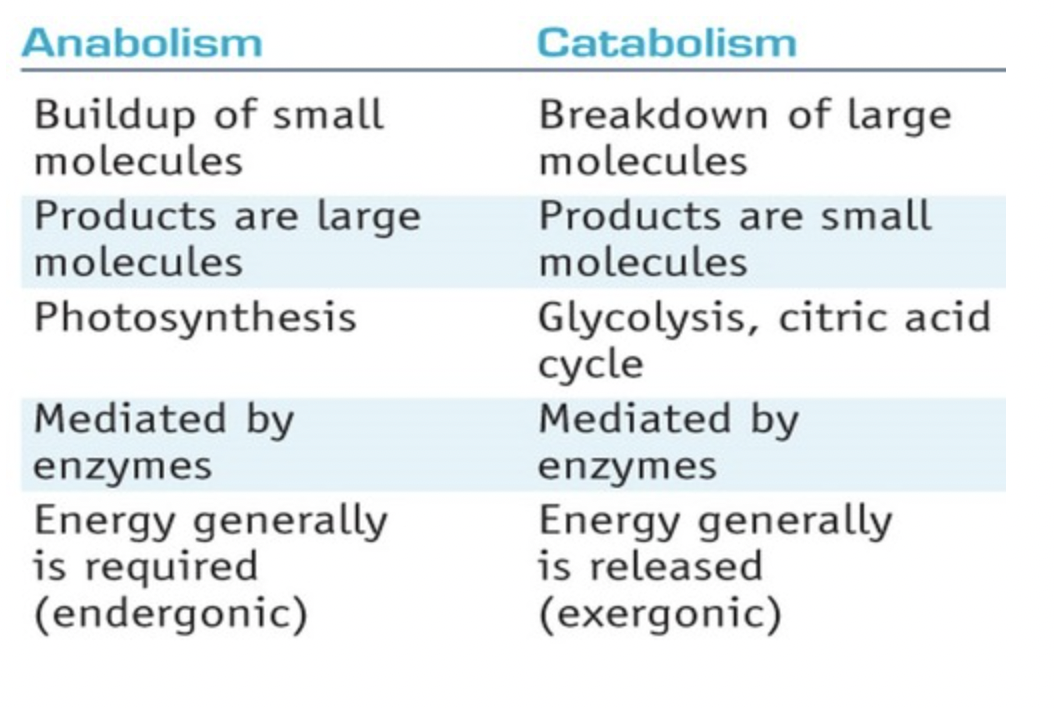
10
New cards
describe hydrolysis reactions
* chemical reaction in which a polymer breaks apart into smaller subunits
* addition of water is used to break bonds
* opposite of condensation reaction
* addition of water is used to break bonds
* opposite of condensation reaction