L18 Sleep (Imported from Quizlet)
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Change in behaviour, change in brain activity, structural changes, gene expression
What happens during sleep?
Non-REM, REM
Sleep consists of cycles of ____-_____ and ____ sleep
Rapid eye movement
What does REM stand for?
Reduced motor activity, reduced response to stimulation, stereotypic postures (eyes closed in humans), relatively easy reversibility
Sleep defined behaviourally as ...?
Electrical recordings
Physiological activity can be conveniently measured using __________ __________
Muscle
Which movements is measured using electromyography?
Eye
Which movements is measured using electro-oculography?
Brain
Which activity is measured using electroencephalography?
Synchronous, electrical, neurones, brain
Electroencephalogram measured the _________, __________ activity from large populations of ________ in the _______
Cellular, ionic movements
What creates an electric field that is then measured by electrodes placed on the surface of the scalp in electroencephalography?
An electrical amplifier (they are tiny electrical fields) and to a monitor
What are the electrodes placed on the scalp to detect electrical fields linked to?
Invasive, temporal, spatial
Electroencephalography is non-_______, easy to administer, data is easily gathered, has high _________ resolution (milliseconds) and low _______ resolution
Cortical activity
Electrical fields follow an inverse square law so only _________ __________ detectable
Many types of brain waves
What does this image show?
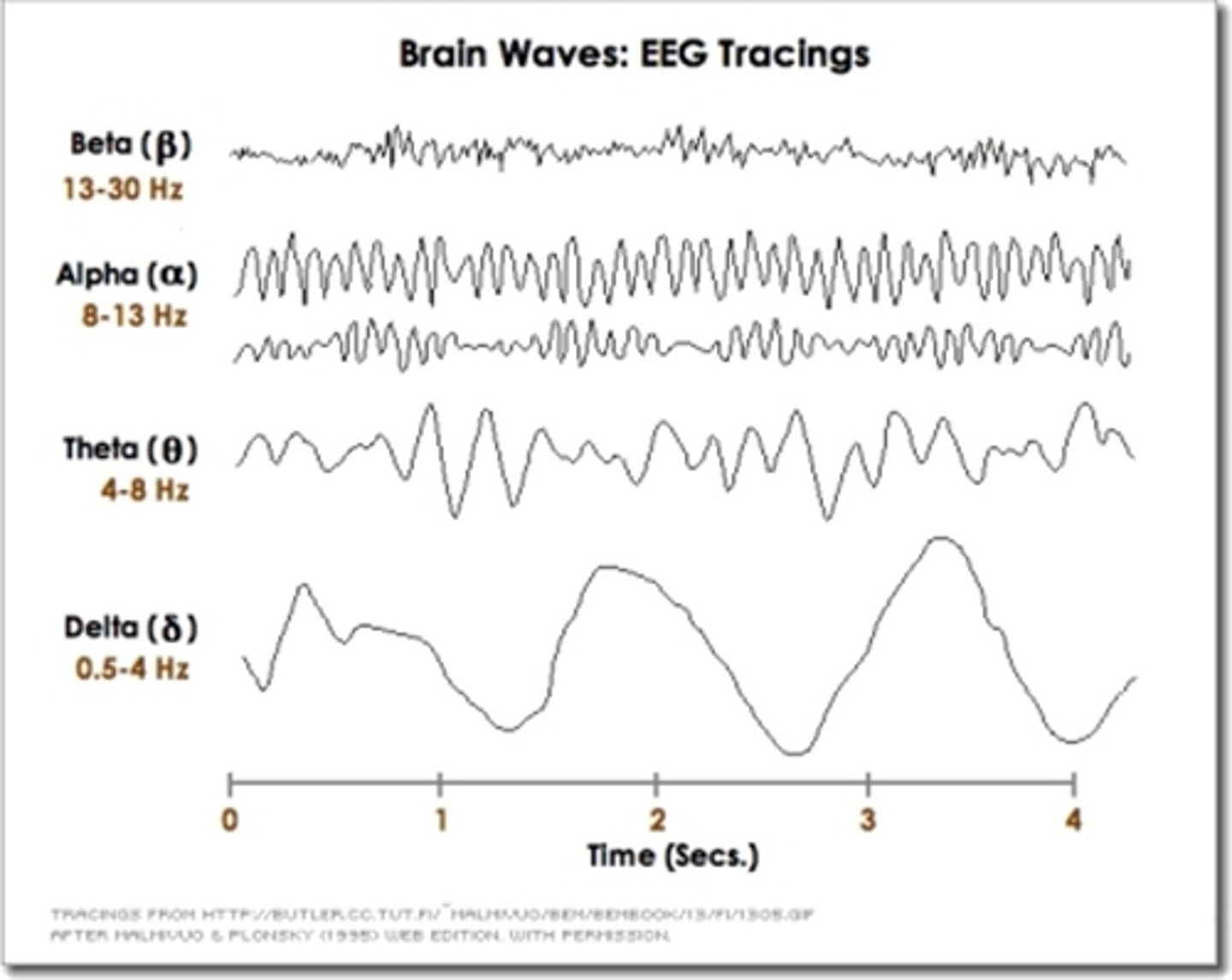
4
How many stages are there in non-REM sleep?
Not much action potential firing between neurones
Neuronal activity is low in non-REM sleep, what does this mean?
Lowest
Is metabolic rate and brain temperature at their lowest or highest during non-REM sleep?
Decreased sympathetic nervous system outflow
Heart rate and blood pressure decline during non-REM sleep, what does this mean?
Parasympathetic
In the stages of non-REM sleep there is an increase in _______________ nervous system
Muscle, reflexes
_________ tone and _______ are intact during non-REM sleep
Drowsiness
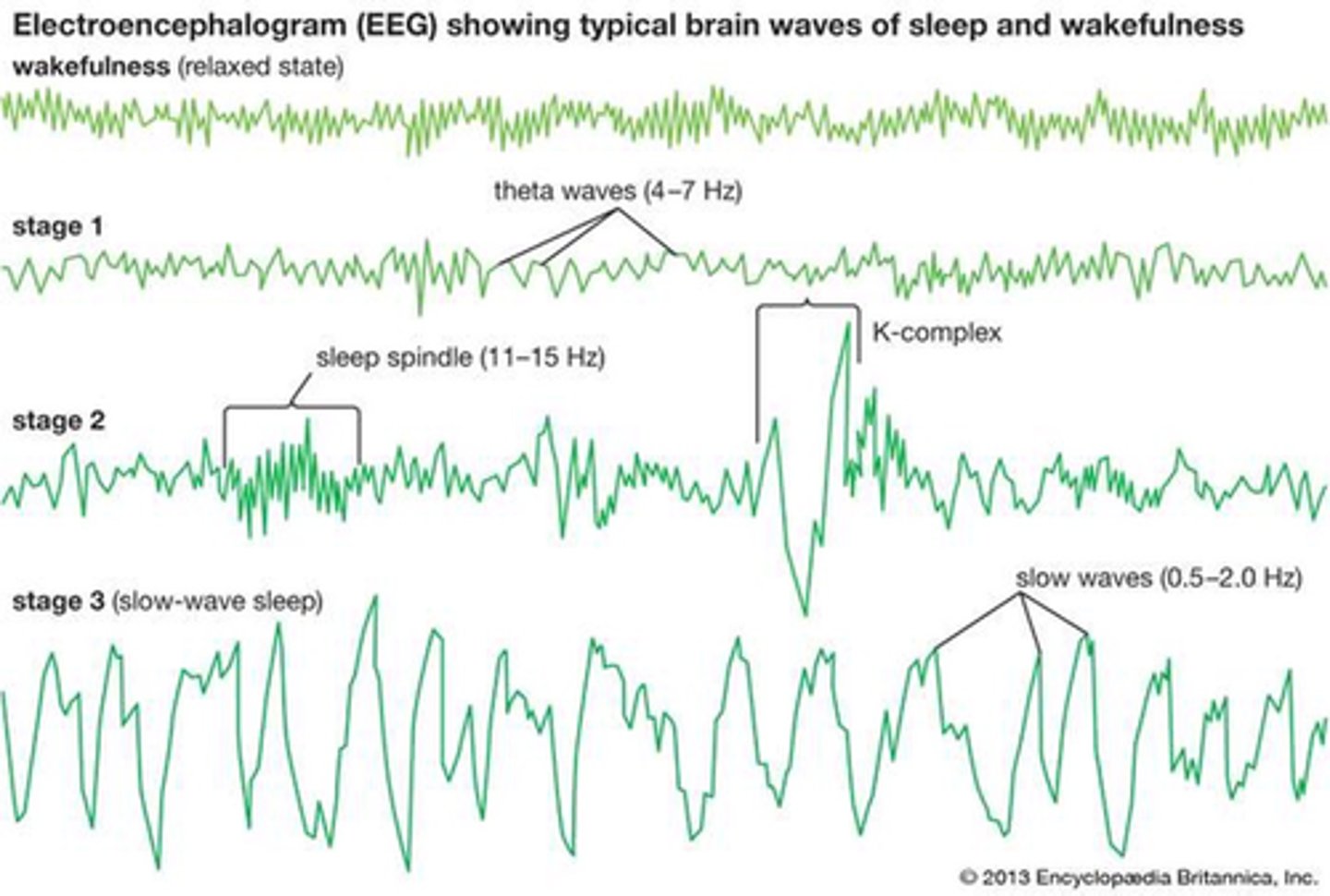
What is the first stage of non-REM sleep?

Awakened easily
Eyes move slowly and muscle activity slows
During this stage, many people experience sudden muscle contractions preceded by a sensation of falling
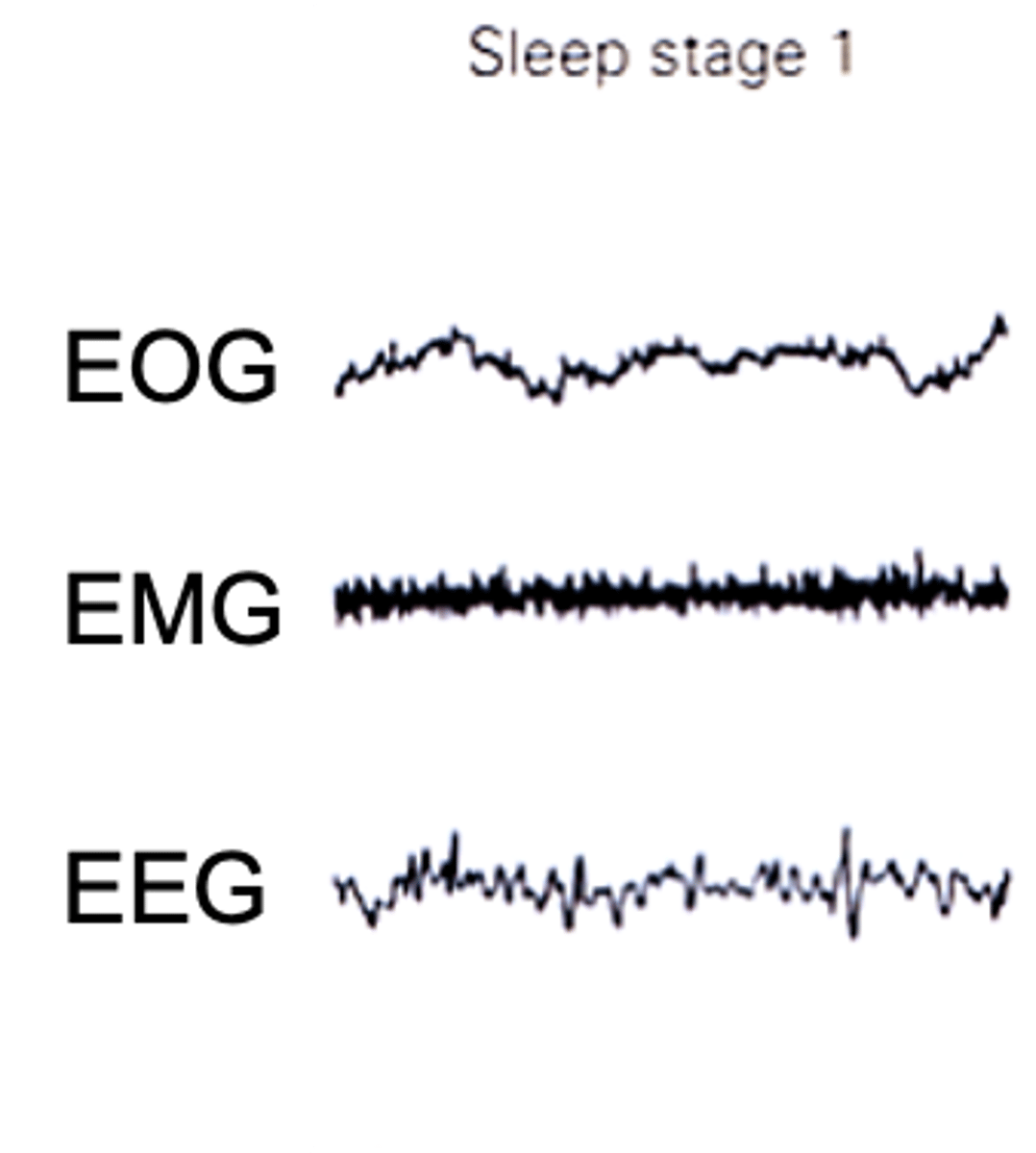
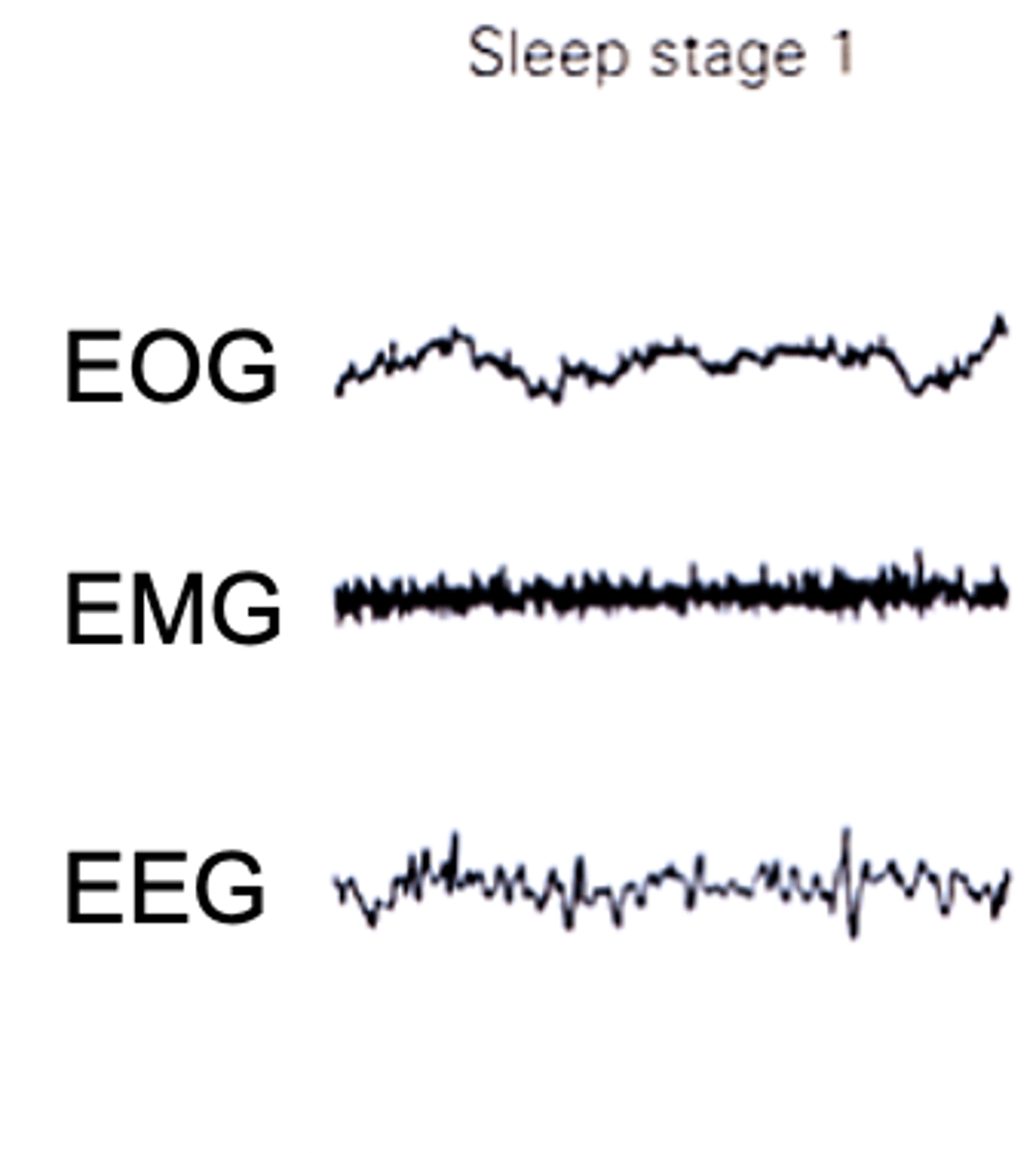
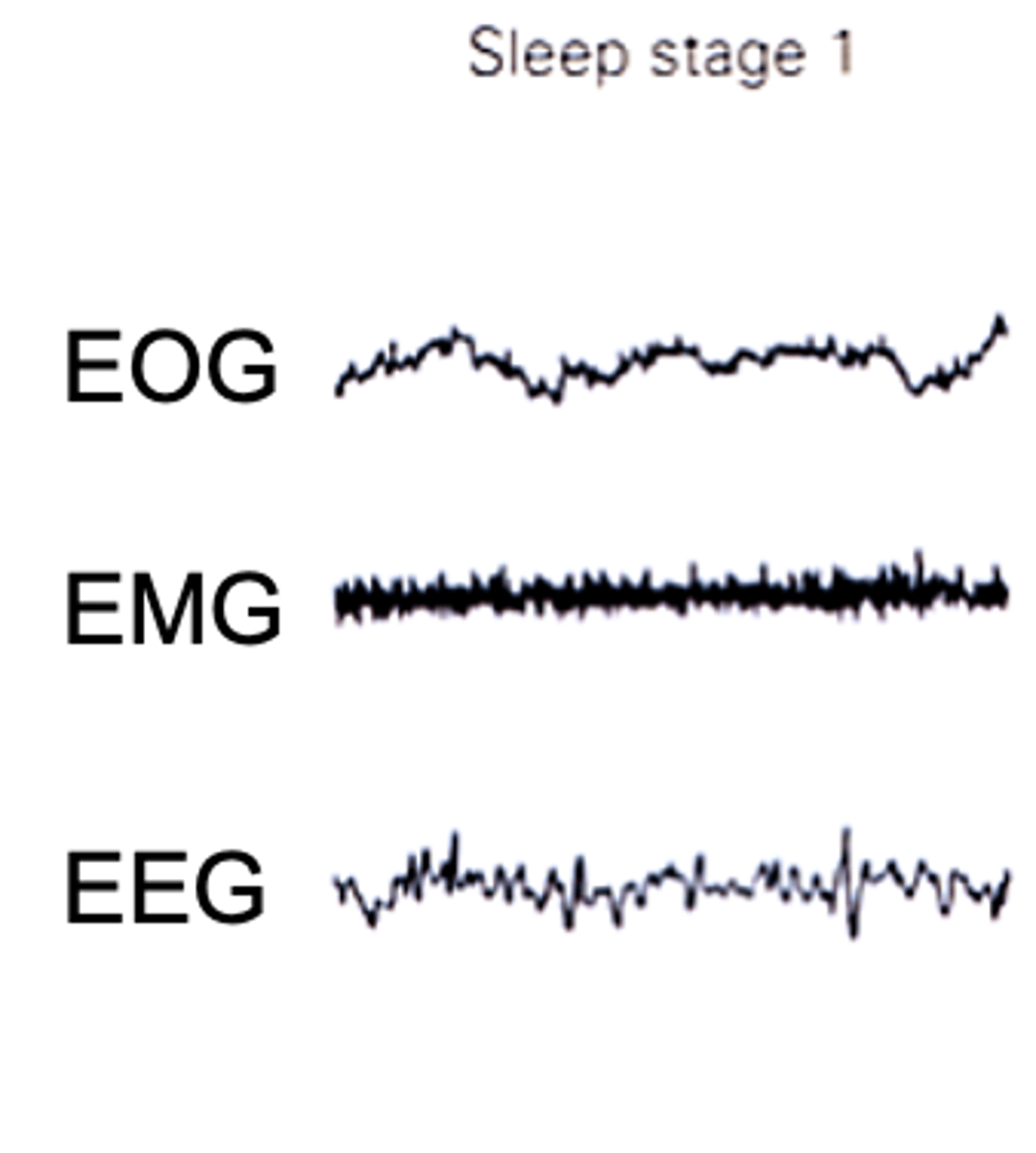
What are the properties of stage 1 of non-REM sleep?
Several minutes
Transition from wakefulness to onset of sleep lasts how long?
Low, sinusoidal
Awake people show ____ voltage EEG activity (10-30μV@16-25Hz)
As they relax - _____________ (alpha) activity 20-40μV@Hz
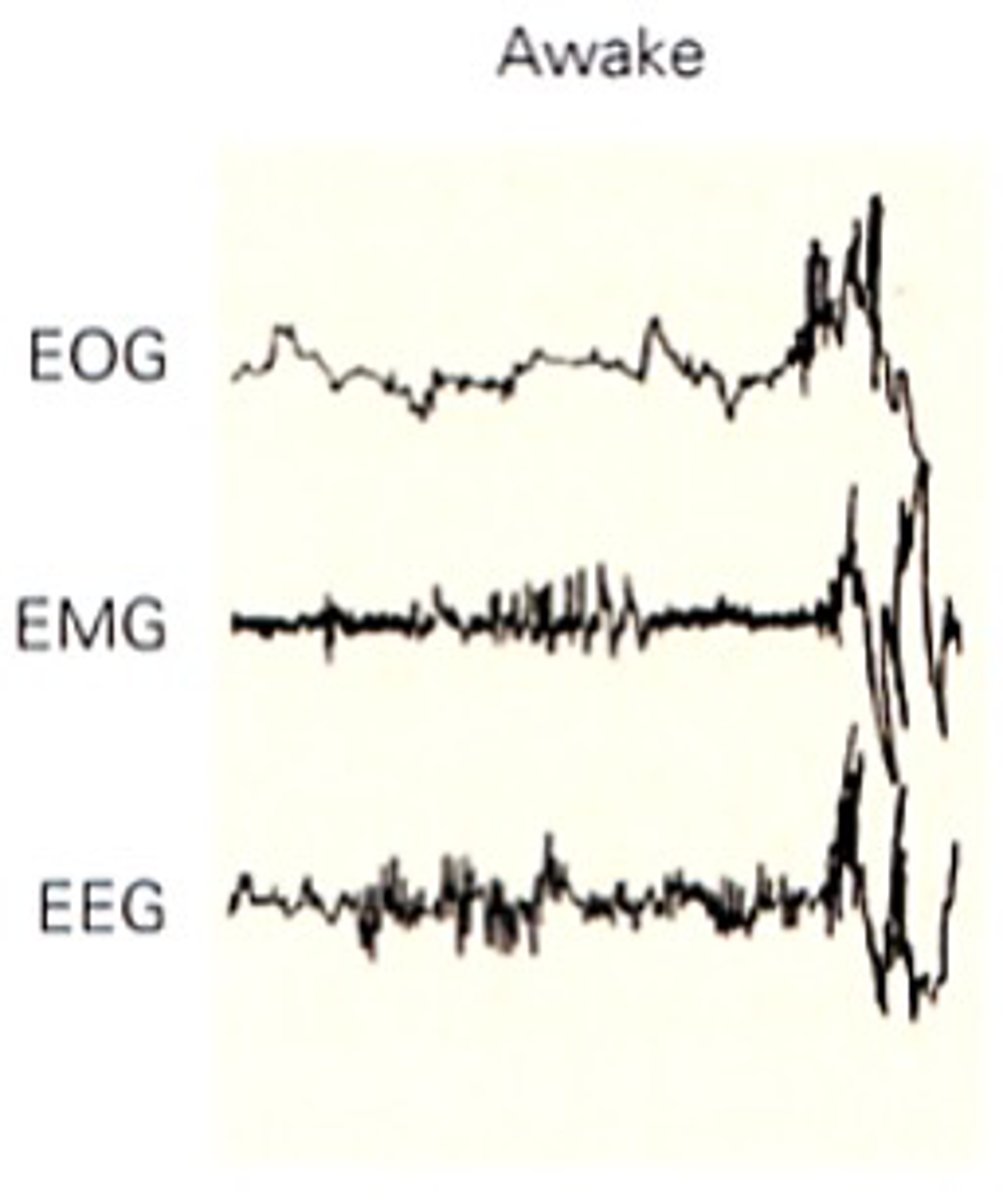
Eyes show slow, rolling movements
Describe what is happening in EOG
During Stage 1 and all non-REM - some muscular activity
Describe what is happening in EMG
Low-voltage, frequencies
EEG characterised by ____-_________ activity if mixed ____________ (mostly theta waves)
Light sleep
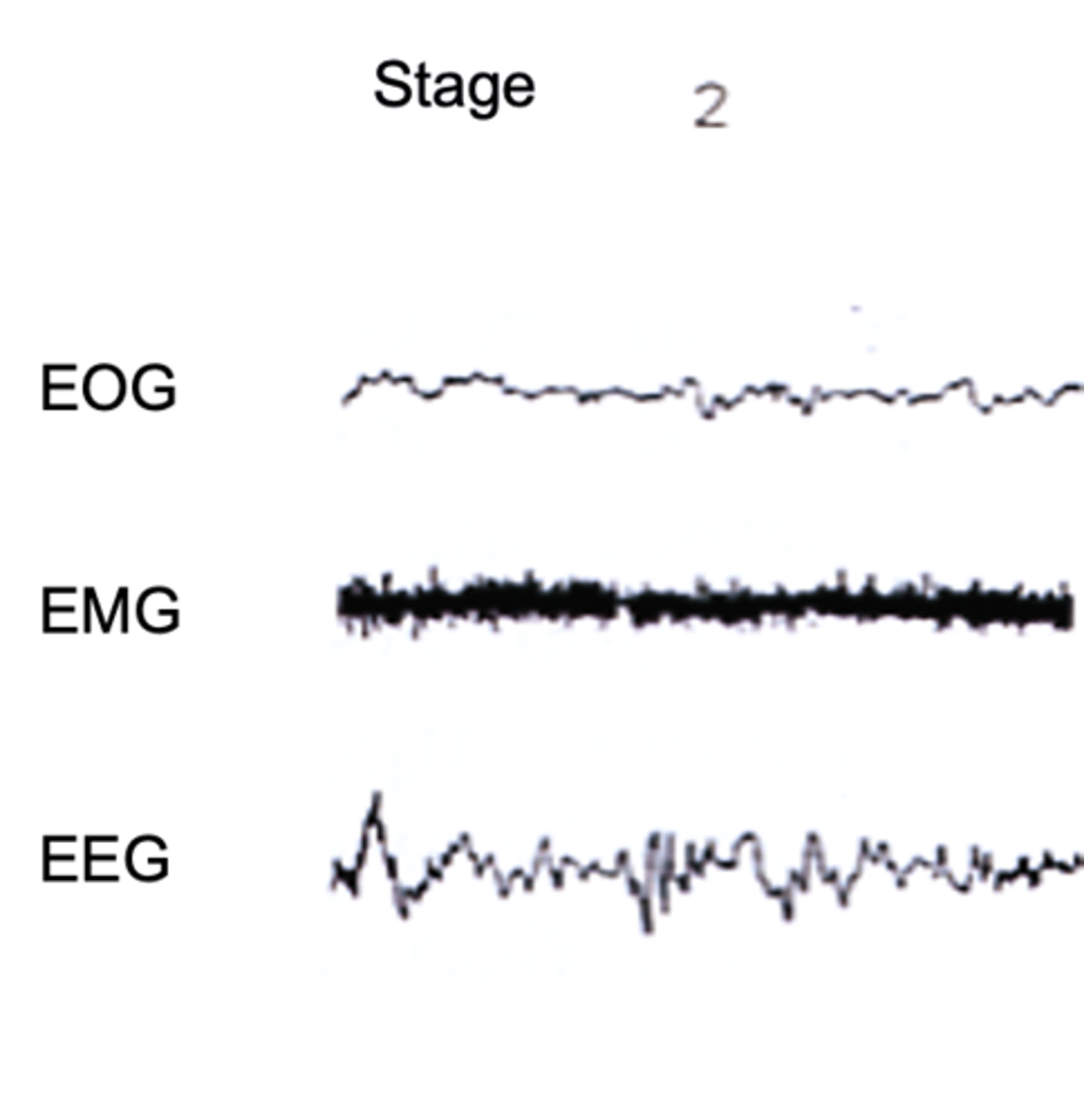
What is stage 2 of sleep?
Eye movement stops and brain waves become slower with only an occasional burst of rapid brain waves
The body begins to prepare for deep sleep
Body temperature drops, heart rate slows
Describe the properties of Stage 2 of non-REM sleep
Sinusoidal, sleep spindles, biphasic, K complexes
Stage 2 of non-REM sleep is characterised by bursts of ____________ waves called '_______ ___________' (12-14Hz) and ___________ waves called _ ________
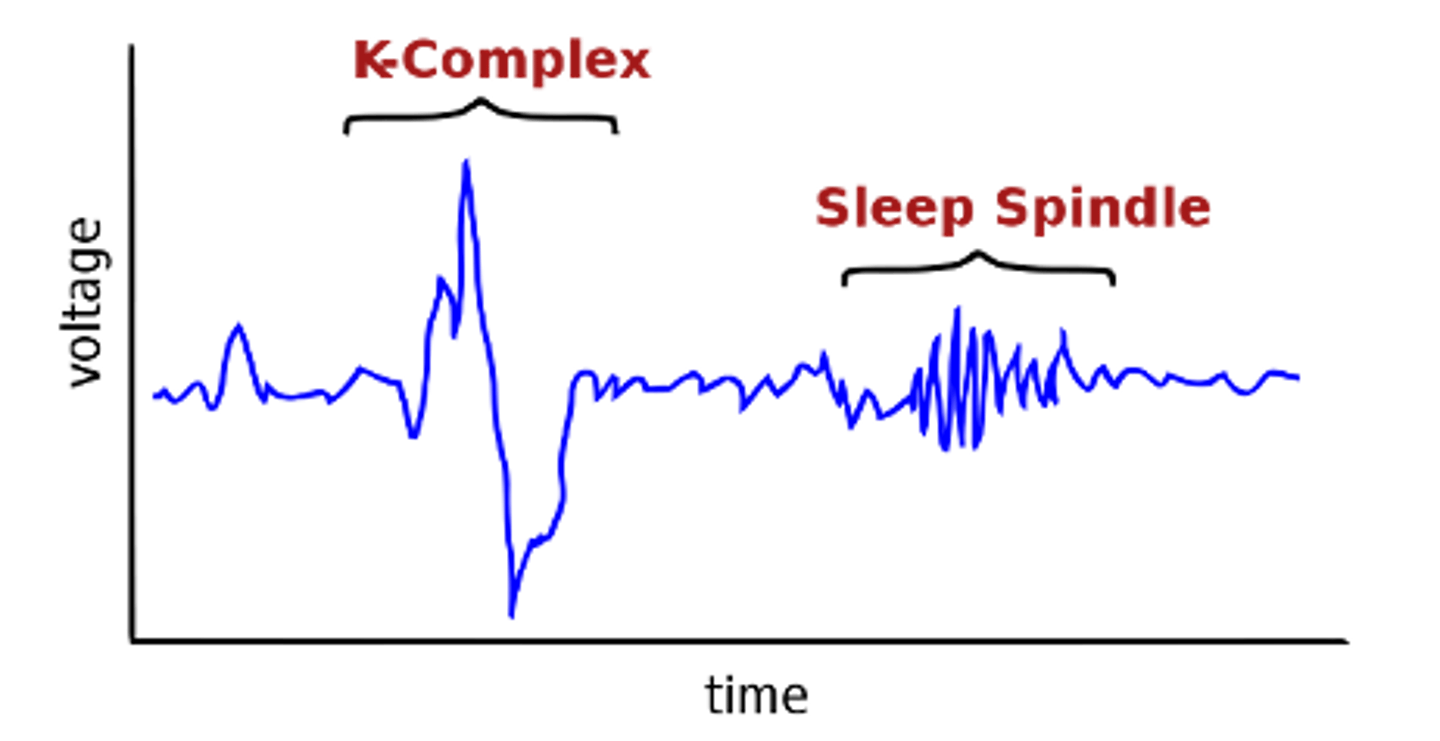
Episodically, low
K complexes occur ___________ against background of continuing ___-voltage EEG activity
Deep sleep
What is stage 3 of non-REM sleep?
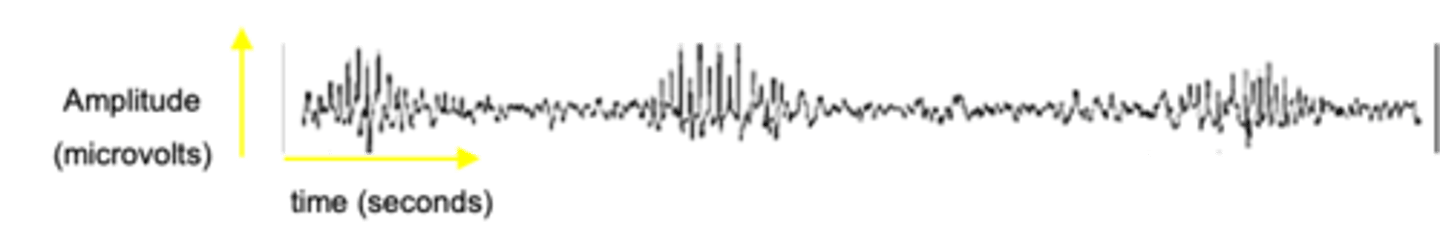
Extremely slow delta waves are interspersed with smaller, faster waves
Describe the properties of Stage 3 of non-REM sleep
Sleepwalking, night terrors, talking during one's sleep and bedwetting 'parasomnia'
What occurs during the transitions between non-REM and REM sleep?
High amplitude, slow delta waves (0.5-2Hz)
Describe the EEG of Stage 3 of non-REM sleep
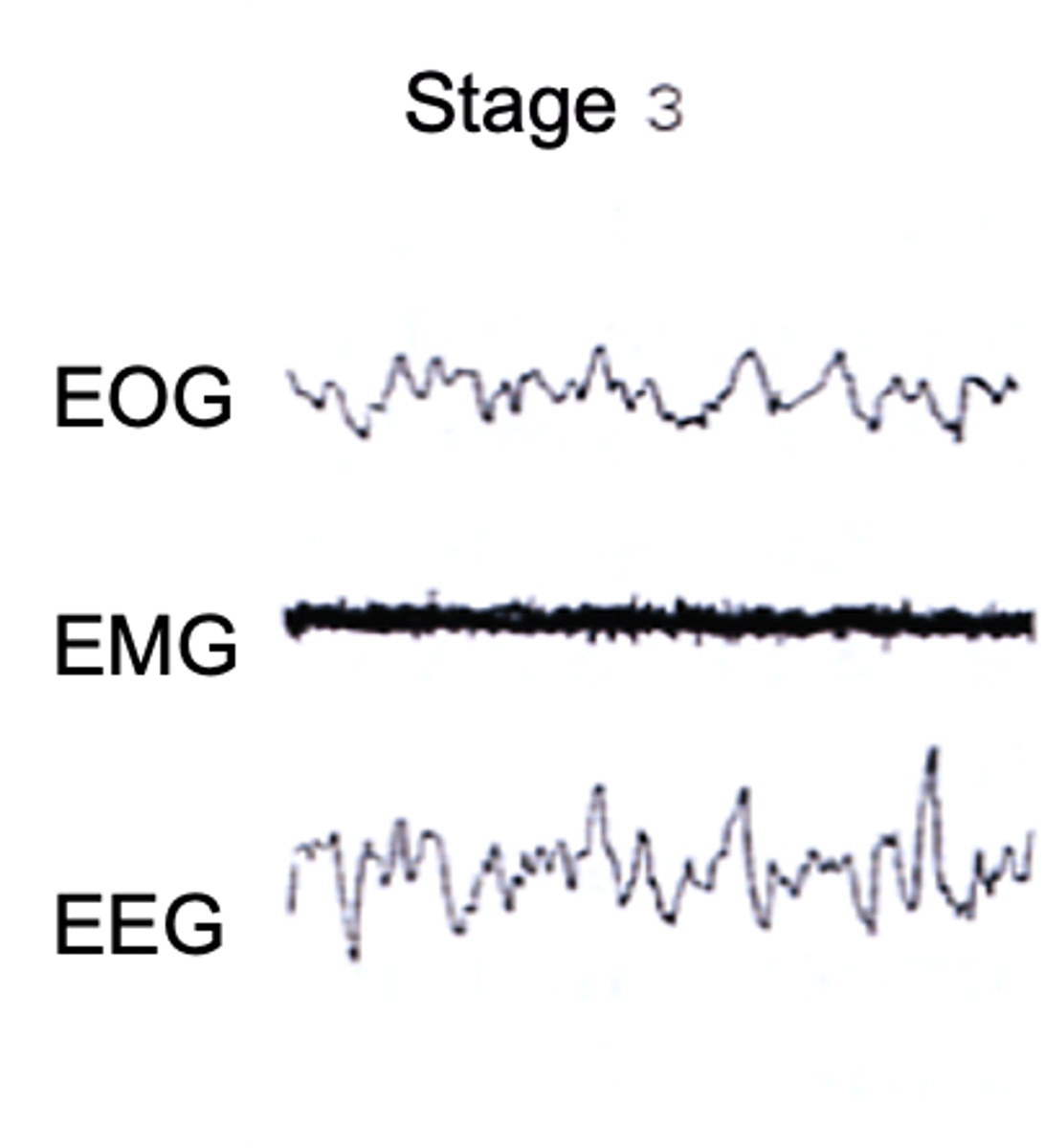
Very deep sleep
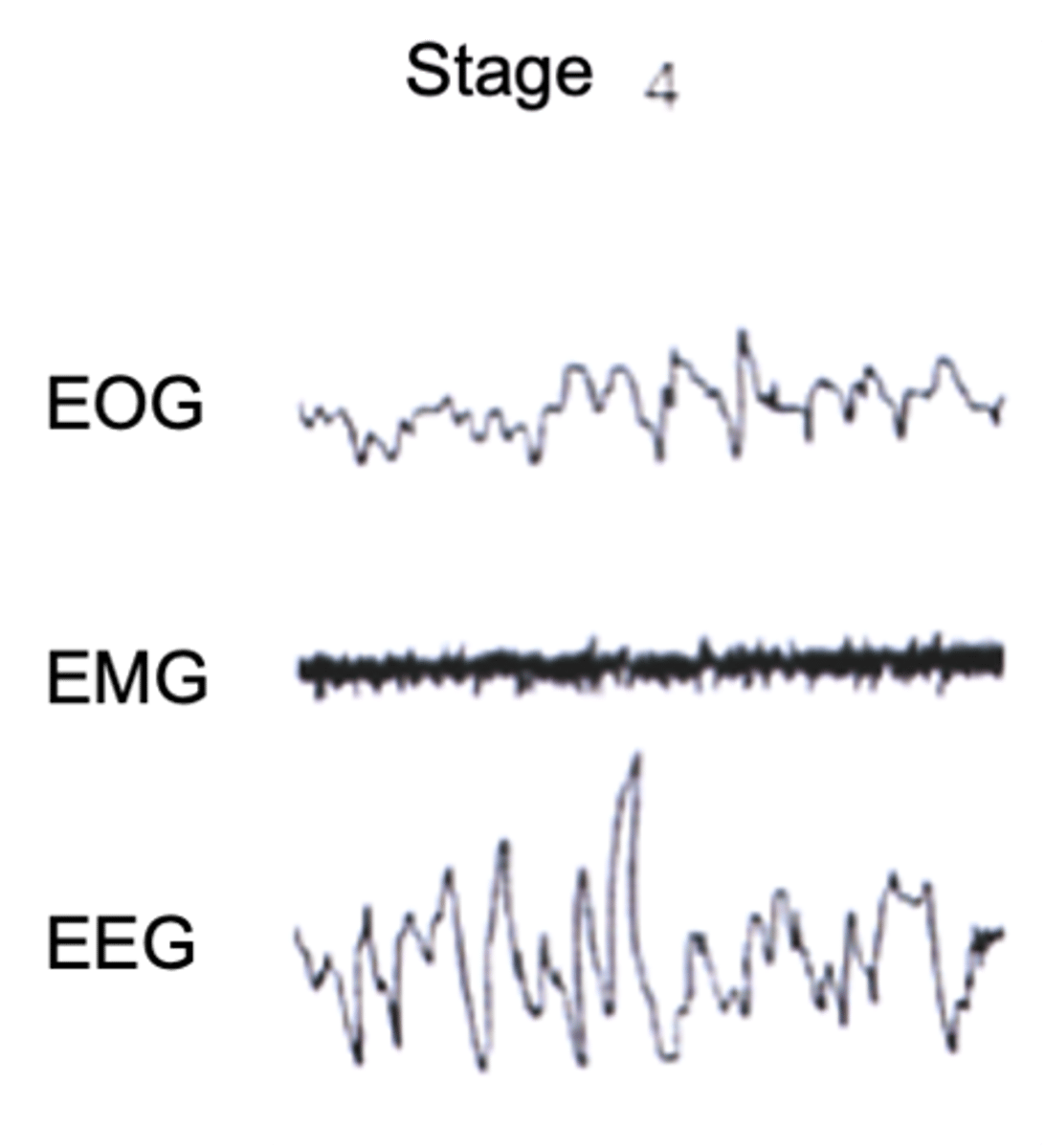
What is Stage 4 of non-REM sleep?
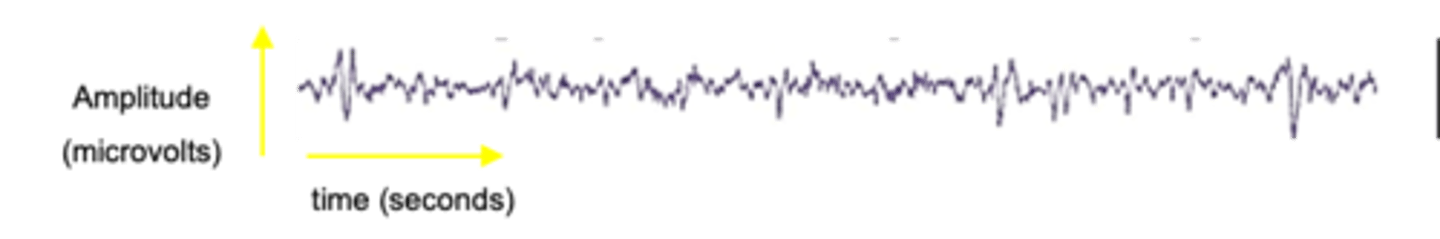
Brain produces delta waves almost exclusively
Disorientation for several minutes following arousal from stage 4
Describe the properties of Stage 4 of non-REM sleep
Slow, increases
______ wave activity _________ and dominates the EEG record
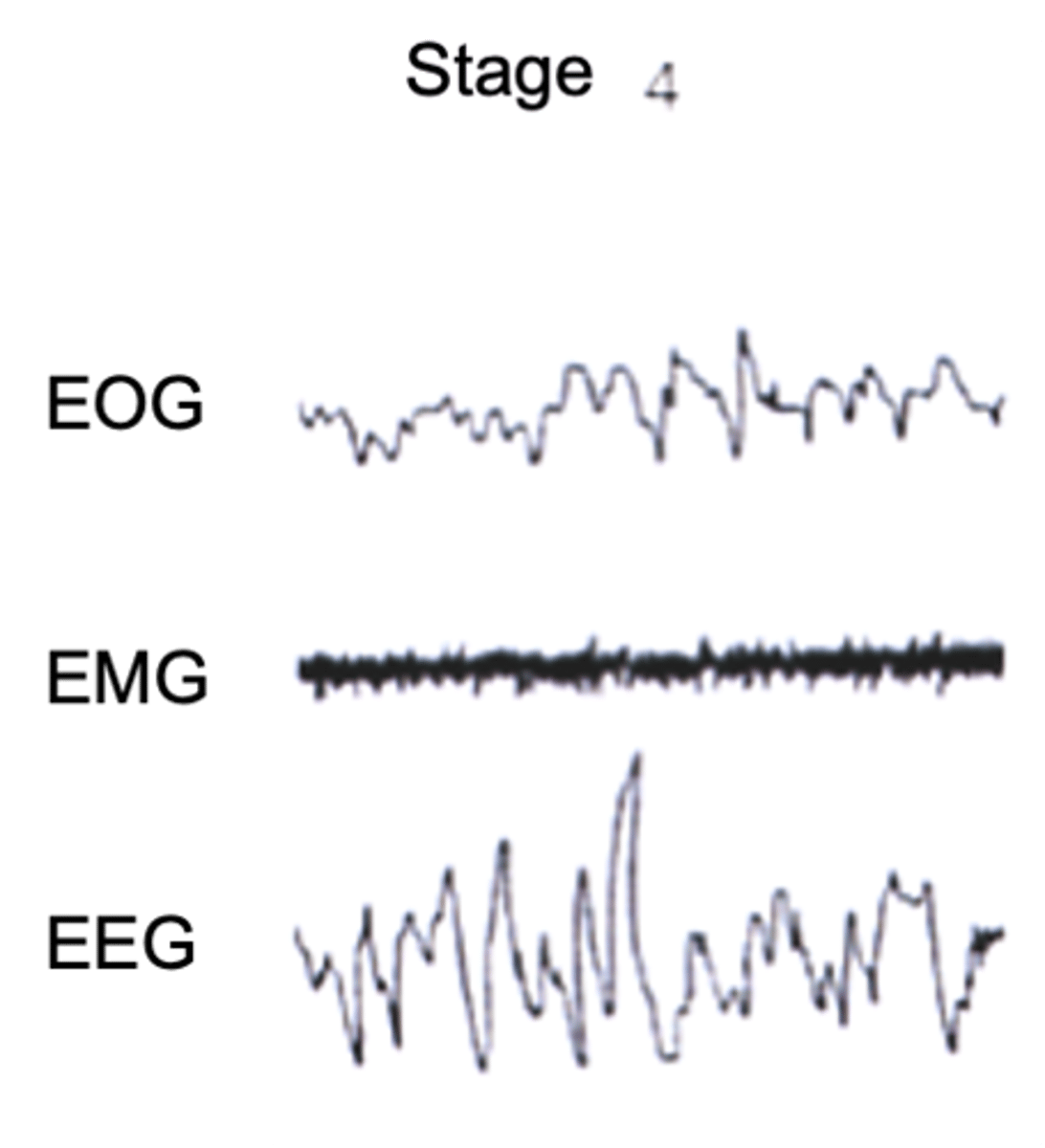
Slow wave sleep
Stages 3 and 4 in humans called ______ ______ _________
Stages of non-REM sleep compared
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep
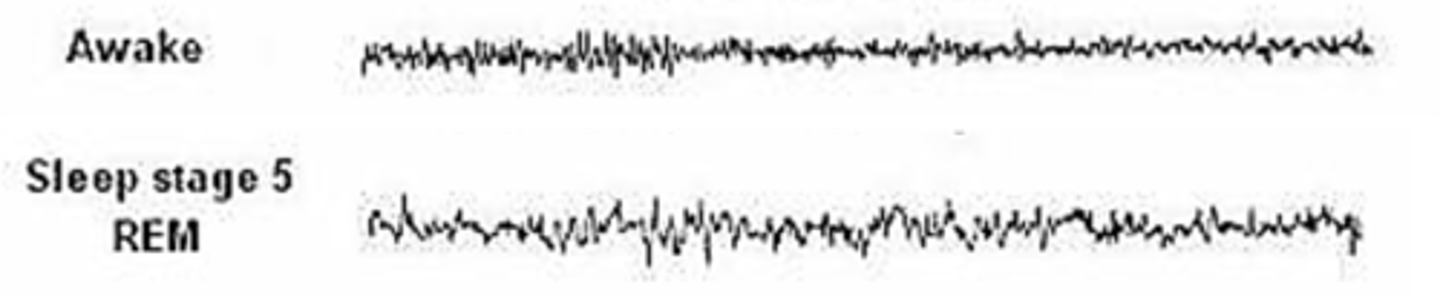
What is Stage 5 of sleep?
Wakefulness
In Stage 5, what does EEG mimic?
Birds
REM is also found where?
Closed eyes move rapidly from side to side (perhaps related to the intense dream and brain activity)
What happens during Stage 5?
Stage 1/awake, low, frequency
EEG during human REM is similar to ________ _/______ -> ____ voltage mixed ____________
REM-neuronal firing very like in wakefulness
Stage 5 is paradoxical, what does this mean?
Rise, increased, greater
During REM sleep, brain temperature and metabolic rate ______, this is consistent with ___________ neural activity in some areas - _________ than in waking
Skeletal
During REM sleep, all _________ muscles are atonic
Flaccid and paralysed
What is atonic?
Muscles controlling movements of eye, middle ear ossicles and diaphragm (so you can breathe and hear any impending danger)
During REM sleep, which muscles remain active?
Cyclically
REM and non-REM sleep alternate __________
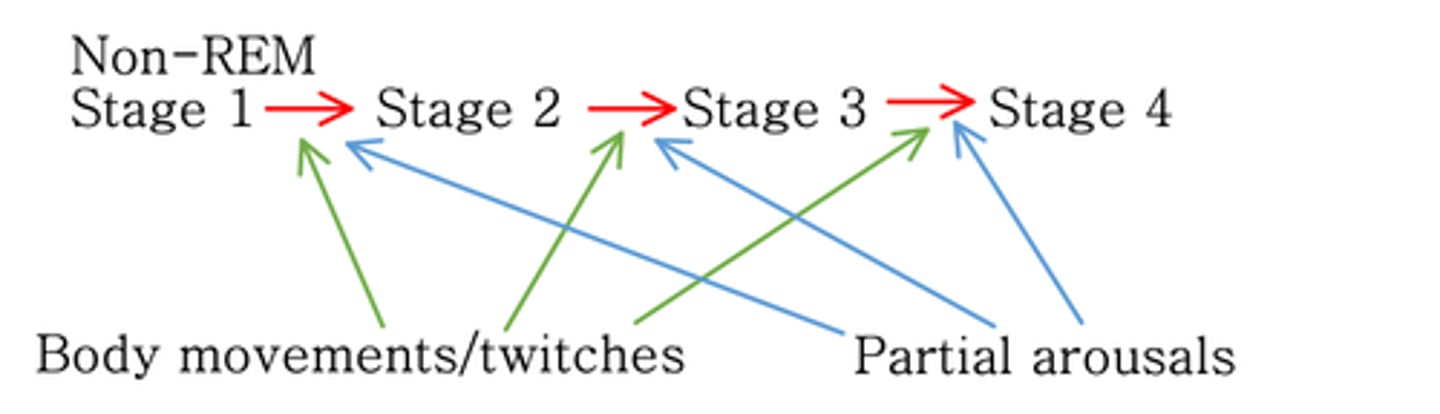
Non-REM sleep pattern
70-80, 8-10
After __-___ minutes sleep returns to stages 3 or even 2 before entering the first REM phase of the night which lasts _-__ minutes
90-110
Time from first stage to the end of REM = __-___ minutes
Decrease, increases
Repeated four or five times during the night - during each repetition, stages 3 and 4 __________ in duration and REM __________
5
In young adults, only _% of sleep time spent in Stage 1
50-60
In young adults, largest amount of sleep time is spent in Stage 2 - __-__% in Stage 2
15-20
In young adults, Stages 3 and 4 only constitute __-__%
20-25
In young adults, REM phases constitute only __-__%
Diffuse modulatory neurotransmission system
NE and 5-HT neurons in the brains stem
Diffuse modulatory system controls rhythmic behaviour in the Thalamus
Inhibition of motor neurons
Regulation of sleep
Sleep and coma
Lesions in the brain stem can cause ...?
Precedes, causes
Activation of neurons in the brain stem __________ awakening - stimulation of brain stem ________ awakening
Depolarising
What kind of effect is there in wakefulness?
Decrease
In the non-REM stage, there is a __________ of firing in the brain stem
Spindles
In non-REM stage, what result from correlated activity in the thalamus?
Activity in the thalamus
In non-REM stage, delta rhythms result from what?
Awake
REM stage has fairly similar firing in an ______ state (but not early sensory systems)
Frontal lobe, raphe nuclei, locus coeruleus
In REM stage, there is no activity in the _________ _____ and no activity in ______ _______ and _____ ___________
Motor neurons
In REM stage, there is inhibition of what?
Strange imagery - brain not fully functioning
Exercises synapses when no external activity
'Memory consolidation'
'Circuit testing'
What are the theories of dreaming?
Circadian rhythm, 24
Sleep and wakefulness follow ___________ __________ with periodicity of about ___ hours
Endogenous, environmental
Circadian rhythms are ____________ and persist without ________________ cues
External timing cues
Circadian rhythms are modulated by what?
External timing cues that adapt the rhythm to the environment
What are 'Zeitgebers'?
Sensory stimulation
Circadian clocks require _________ _____________ but works without them as well
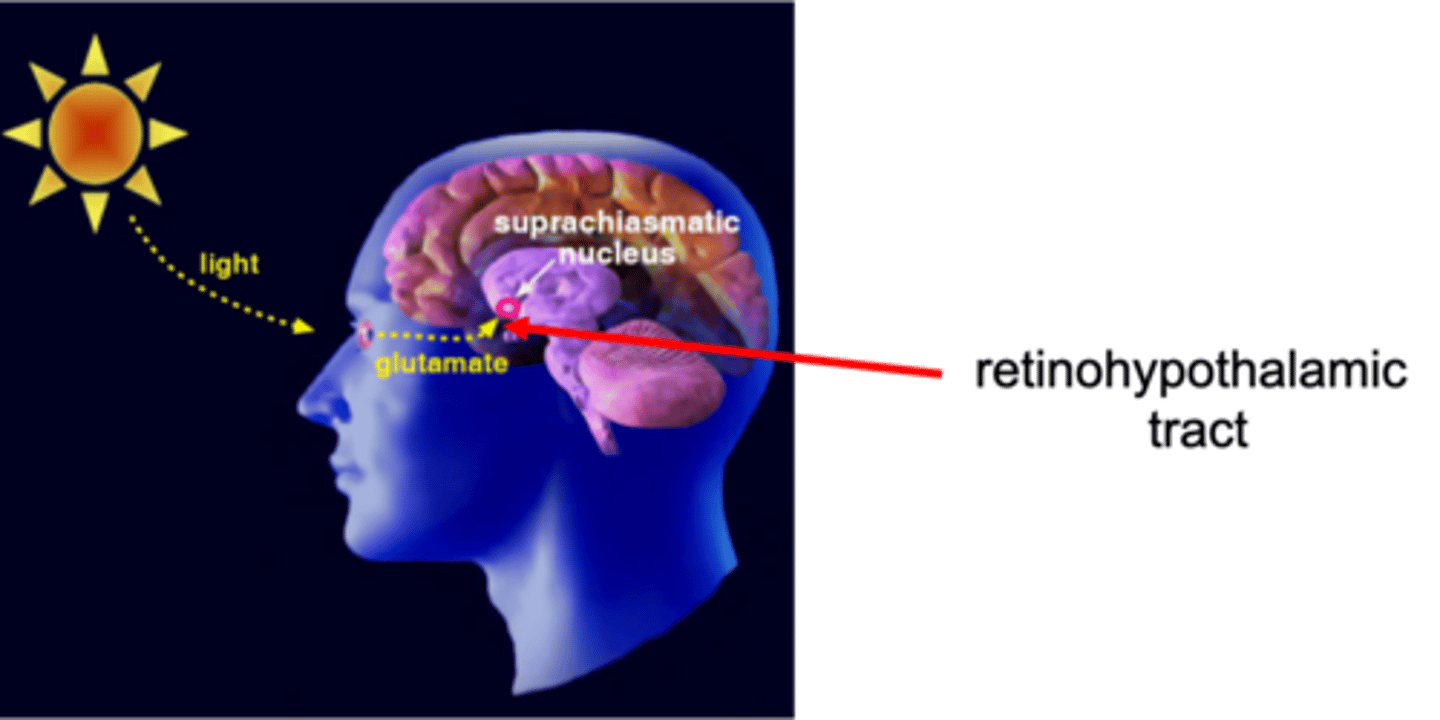
Suprachiasmatic nucleus, anterior hypothalamus
Major internal clock is ___________________ _______ of ___________ _______________
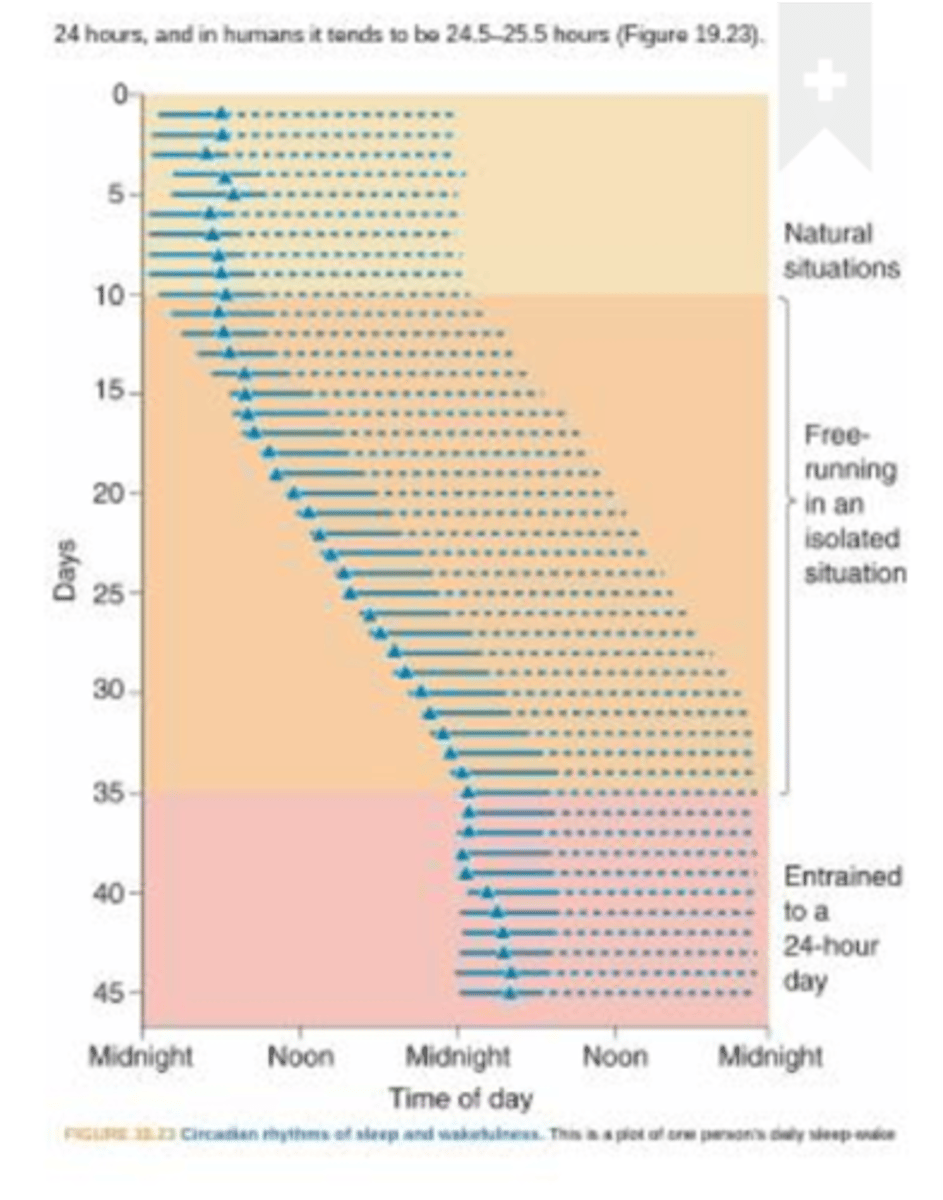
The circadian rhythm of sleep
Lesioning of the suprachiasmatic tract dampens down what?
Timing of sleep, sleep itself
Suprachiasmatic nucleus regulates _________ ___ ______ - it is not responsible for _______ __________
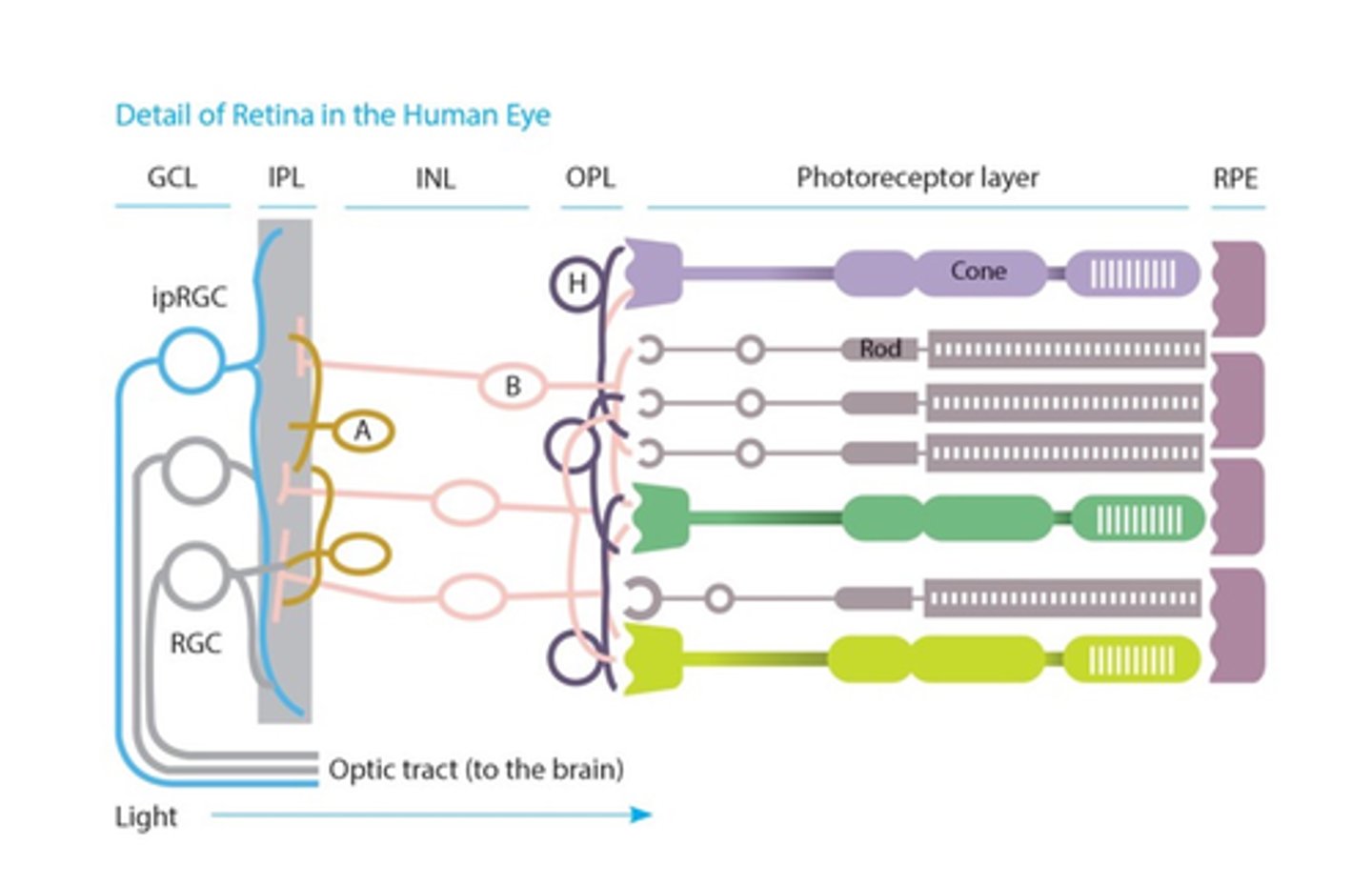
Intrinsically photosensitive ganglion cells
What provides input to the suprachiasmatic nucleus?
Lesioning of the suprachiasmatic tract dampens down what?