57. Mastitides (lactational, ductus ectasia, fat necrosis, galactocele). Mastopathies (fibrocystic change). Fibroepthelial tumours.
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
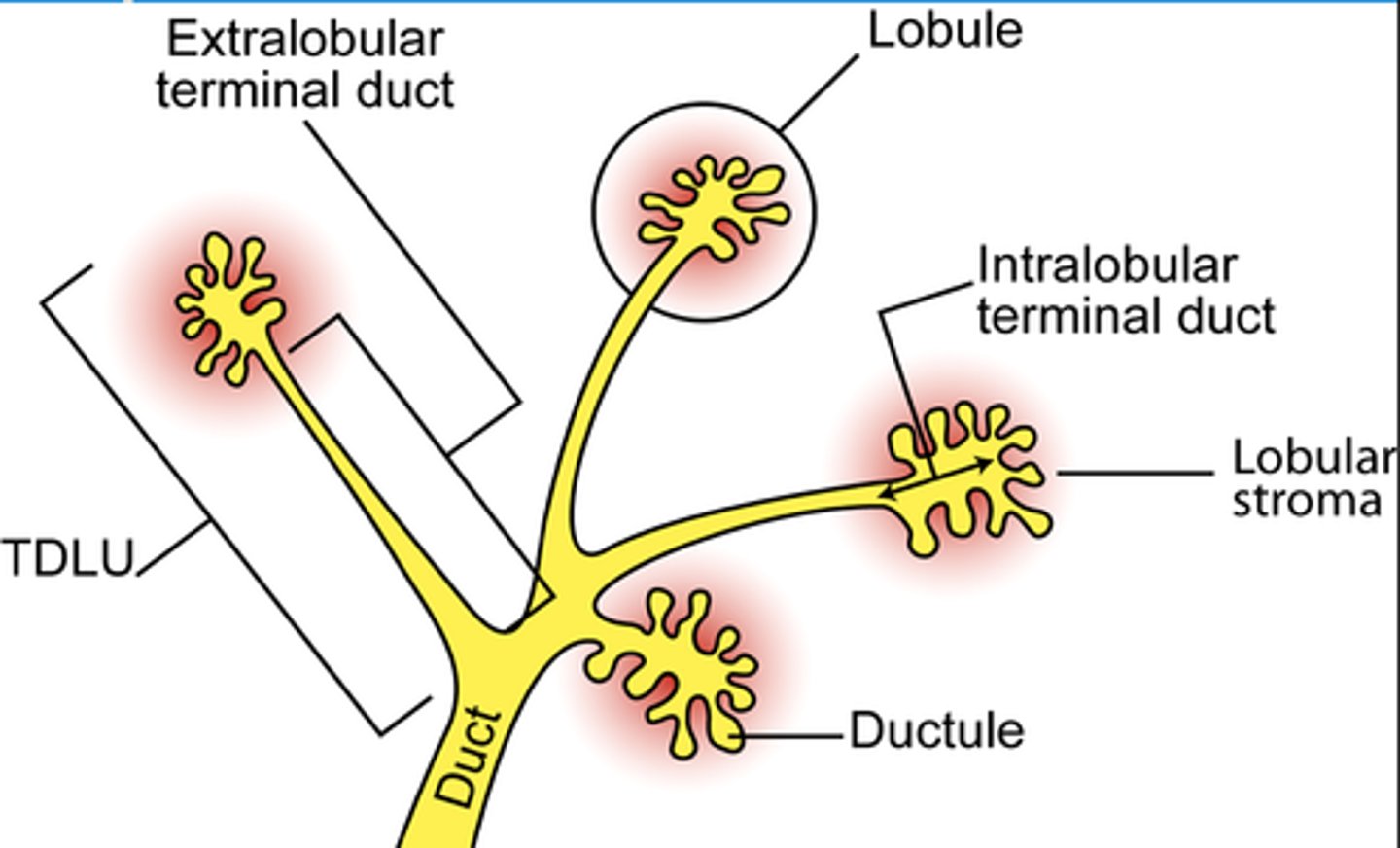
Functional unit of the breast?
Terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU)
Lobule + terminal duct that the lobule empties into
- Lobule produces milk
- Duct carries milk to nipple
Cell layers of ducts and lobules of the breast?
They all have two cell layers:
1. Luminal cell layer (faces lumen)
2. Myoepithelial layer
Why is TDLU significant?
It is from here the breast tumors originate from
Mastitis?
Inflammation of the breast
Associated with:
- Redness
- Edema
- Pain
- Tenderness
- Fever
May be infectious or non-infectious
Subtypes of mastitis?
- Lactational mastitis
- Mammary duct ectasia
- Fat necrosis
- Galactocoele
- Mastitis carcinomatosa
Lactational mastitis?
Milk stagnation in the breast -> due to lactating mothers cannot lactate enough; for various reasons
Allows for organisms to grow in the stagnated milk -> causing infection
- Staphylococcus aureus is the most common organism
How does bacteria enter the breast in lactational mastitis?
Bacteria enter the breast through fissures in the skin that develop during breastfeeding
Treatment lactational mastitis?
Symptomatic treatment:
- Painkillers
- Cold compresses
- Emptying of the breast regularly
- Antibiotics may be used
Mammary duct ectasia? "Plasma cell mastitis"
- Non-bacterial lymphoplasmacytic inflammation of the breast
- Occurs in older, non-breastfeeding women
Etiology&pathogenesis: unknown
- Ducts are dilated
How does mammary duct ectasia mimic cancer?
Breast secretions from the ducts into the periductal C.T. occurs -> a periareolar mass forms (mimics cancer)
This condition is harmless
There is green nipple discharge
Fat necrosis of the breast?
A non-bacterial, non-neoplastic condition that occurs after trauma to the breast
Firm mass is formed
- may mimic cancer
- The necrotic debris may calcify -> can be visualized on mammography
Galactocoele?
Milk-containing cyst in the breast
- Occurs in young, lactating women
Due to obstructed milk duct
- Importance: to distinguish it from cancer
Mastitis carcinomatosa?
Inflammatory breast carcinoma
- Type of breast cancer that manifests with an inflamed breast
Should be considered in patients with mastitis which does not resolve with antibiotic therapy
Fibrocystic changes of the breast?
Refers to multiple conditions where the TDLU is cystically dilated and fibrotic
- Happen in women in the reproductive age -> can be thought of as physiological aging (rarely cause problem)
Clinical relevance - fibrocystic changes of the breast?
They are not harmful themselves, but some may have increased risk for progressing into carcinoma
- If atypia is shown -> risk is even higher
Must be distinguished from cancer
Difference in fibrocystic changes of the breast and breast carcinoma?
Fibrocystic changes: myoepithelial cells are present -> these are not present in breast cancer
Types of fibrocystic changes of the breast?
• Non-proliferative pattern
• Proliferative pattern
- Epithelial hyperplasia
- Sclerosing adenosis
- Complex sclerosing lesion
are important...
Non-proliferative fibrocystic changes?
Most common of the two types
- Formation of cysts
- Increase in fibrous stroma
- No epithelial hyperplasia
Cysts range from <1cm to 5cm
They are typically blue -> "blue dome cysts"
Proliferative fibrocystic changes?
- Epithelial hyperplasia
- Sclerosing adenosis
- Complex sclerosing lesion
Epithelial hyperplasia - Proliferative fibrocystic changes?
Proliferative fibrocystic change, characterized by hyperplasia of the two epithelial layers of the TDLU
If there is atypia, it is called:
- Atypical ductal hyperplasia
or
- Atypical lobular hyperplasia
Depending whether the ducts of lobules are affected
What is epithelial hyperplasia of the breast a precursor for?
- DCIS
- LCIS
Sclerosing adenosis - Proliferative fibrocystic changes?
An increase in glands and stroma
- Glands will be compressed by the surrounding stroma
- May cause calcifications -> visualized on mammography
Complex sclerosing lesion - Proliferative fibrocystic changes?
Characterized by:
- A stellate architecture with prominent fibroelastosis and epithelial hyperplasia
Forms nodules that can cause skin retraction & palpable nodules
Should be removed - as they increase risk for malignancy
Fibroepithelial tumors?
- Fibroadenoma
- Phyllodes tumor
- Intraductal papilloma
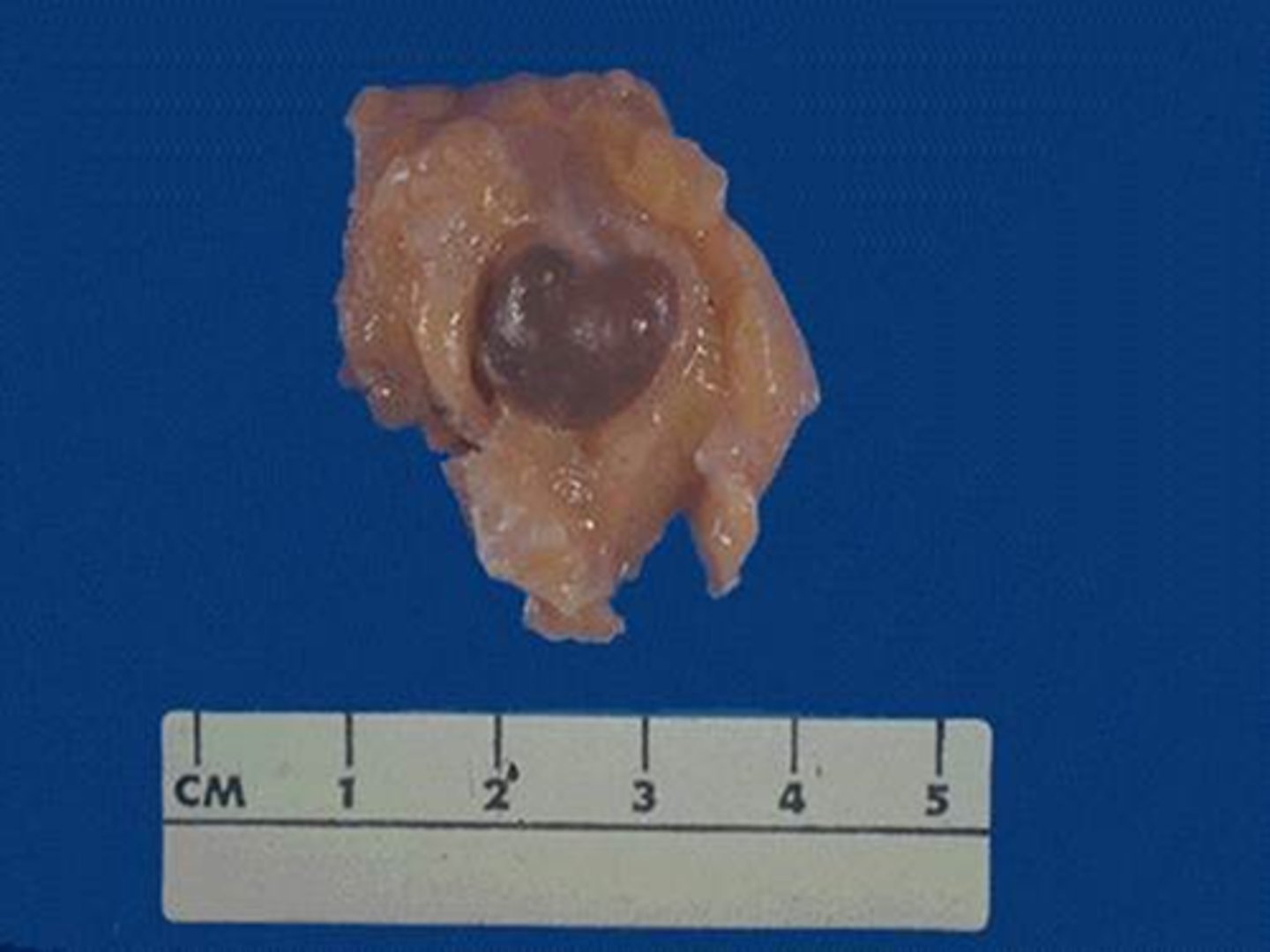
Fibroadenoma?
Most common benign neoplasm of the breast
Comprised of:
- Neoplastic fibroblastic stroma and normal glands
Most frequent in 20-30y/age
Morphology fibroadenoma?
Firm, solitary, mobile, off-white well-circumscribed masses
Are not necessary to remove, as they are benign
Phyllodes tumor?
Similar to fibroadenoma
- However: their stromal component is more cellular
Phyllodes = "leaf-like" -> stroma often form leaflike projections
- Less common than fibroadenoma
- 75% are benign, rest is malignant
- Should be surgically removed
Intraductal papilloma?
Papillary growth that occurs inside dilated ducts
- More frequent in premenopausal women
- Lesions are less than 1cm, usually solitary
- Can cause bloody nipple discharge
Should be removed, as they can have malignant potential