All abnormalities ch 22
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
normal chest configuration
AP to Transverse - 1:2 ratio
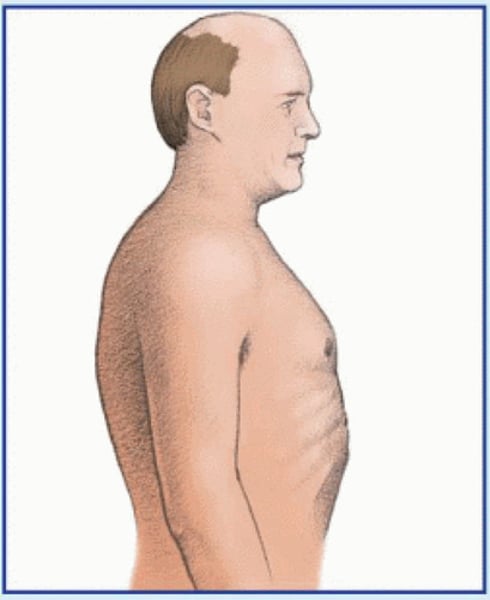
barrel chest
thorax is round shaped. ratio is 1:1
seen in aging adults, copd, and chronic asthma
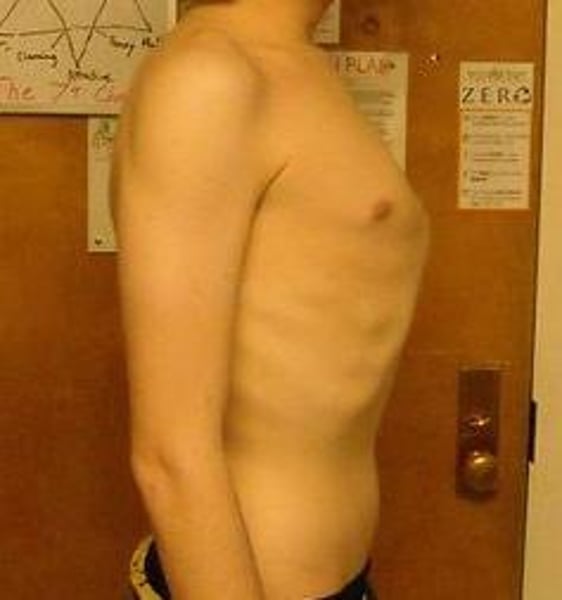
Funnel Chest (Pectus Excavatum)
depression in lower sternum
can cause murmurs or compress heart and vessels
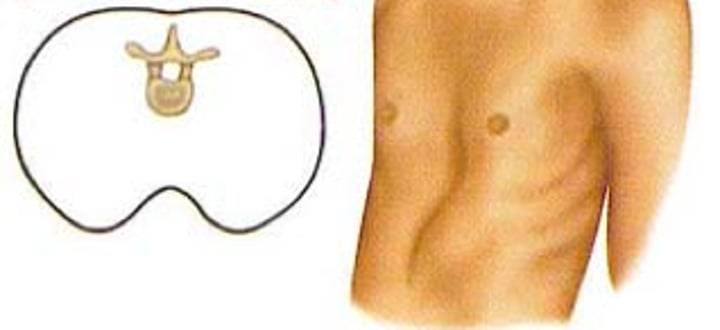
Pigeon Chest (Pectus Carinatum)
sternum protrudes forward
congenital
increased ap diameter
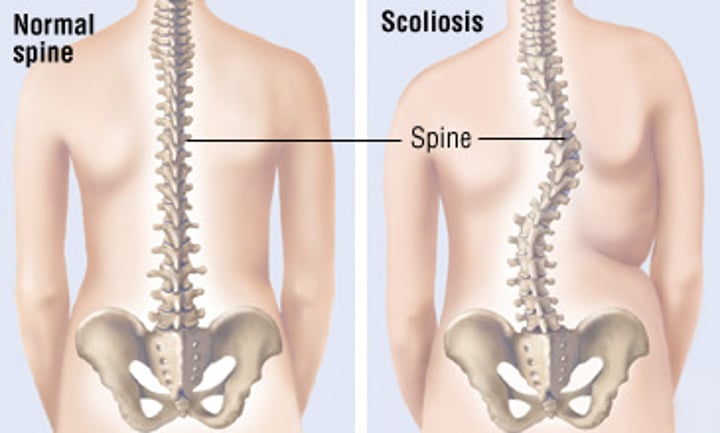
Scoliosis
abnormal lateral curvature of the spine
s shape
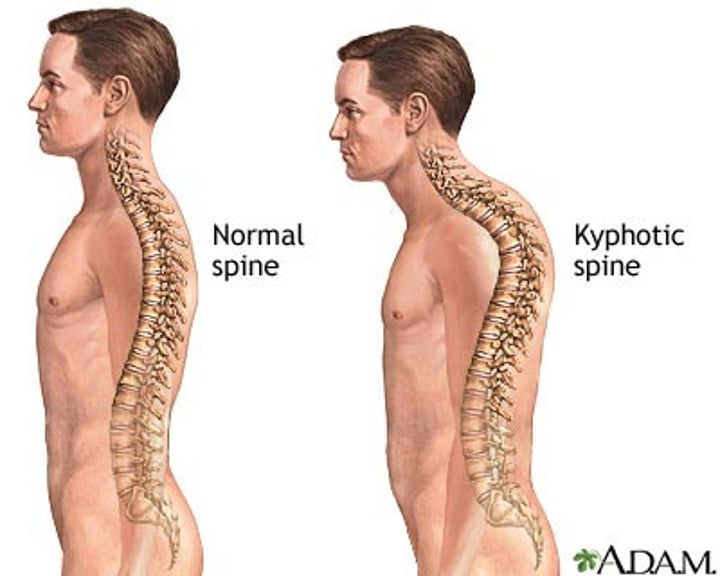
kyphosis
hunchback
athletes that use their arms in overhead positions
including swimmers
forward translated head and internally rotated shoulders
pluses bisferiens
Each pulse has 2 strong systolic peaks, with a dip in between
Bigeminal pulse
2 rapid beats followed by a long interval

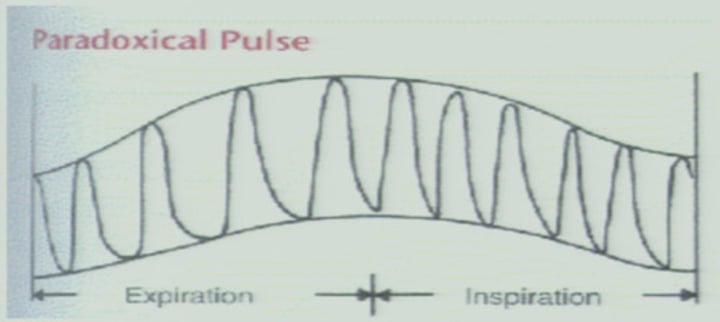
paradoxical pulse
Large difference in pulse pressure between inhalation and exhalation.
Lift (Heart)
sustained thrust during systole
thrill (heart)
vibratory sensation felt on the skin overlying an area of turbulence and indicates a loud heart murmur usually caused by an incompetent heart valve
Accentuated Apical Impulse
A sign of pressure overload
Increased force and duration
Laterally Displaced Apical Impulse
A sign of volume overload
Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC)
irregular heart rhythm characterized by atrial contractions occurring before the expected time
premature ventricular contraction (PVC)
a ventricular contraction preceding the normal impulse initiated by the SA node (pacemaker)
Sinus Arrhythmia
A sinus rhythm in which the rate varies with respiration, causing an irregular rhythm.
a fib
Atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat)
Atrial Flutter
irregular beating of the atria
often described as "a-flutter with 2 to 1 block or 3 to 1 block"
Aortic ejection click
heard at the 2nd right interspace and apex. intensity does not change with respiration
Pulmonic ejection click
Best heard at the second left ICS during early systole, the pulmonic ejection click often becomes softer with inspiration.
midsystolic click
mitral valve prolapse
can be heard over the mitral valve
late systolic murmur
Opening snap
A sharp, high-pitched click heard in early diastole related to opening of the abnormal valve in cases of mitral stenosis
S3 heart sound
in early diastole during rapid ventricular
filling phase.
Associated with increased filling pressures (e.g., mitral regurgitation, HF) and more common in dilated ventricles
normal in children and pregnant women
S4 heart sound
coincides with atrial contraction in late diastole and "a" wave in jugular venous pressure curve
due to increased resistance to ventricular filling following vigorous atrial contraction
summation gallop
abnormal mid-diastolic heart sound heard when both the pathologic S3 and S4 are present
pericardial friction rub
scraping or grating noise heard on auscultation of the heart; suggestive of pericarditis
patent ductus arteriosus
passageway between the aorta and the pulmonary artery remains open after birth
venous hum
A continuous murmur heard on auscultation over the major veins at the base of the neck or around the umbilicus
not normally heard
heard best with the diaphragm of the stethoscope
mid systolic murmur
begins after S1 and stops before S2
innocent murmur
no valvular or other pathologic cause, generally soft
vibratory or musical quality
Heard, at 2nd/3rd left ICS and disappears w/ sitting
physiological murmur
caused by temporary increase in blood flow
can occur in anemia, pregnancy, fever, and hyperthyroidism
murmur of pulmonic stenosis
Loud harsh systolic murmur that radiates to the left shoulder and increases with inspiration
In mild-moderate stenosis a loud ejection click precedes the murmur -> decreases with inspiration
murmur of aortic stenosis
Systolic crescendo/decrescendo murmur that radiates to the neck; ↑ with ↑ preload (Valsalva maneuver).
murmur of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
only systolic murmur that increases during "strain phase" of valsalva maneuver due to increased outflow tract obstruction
Murmur—mitral regurgitation.
A HOLOSYSTOLIC MURMUR that RADIATES to the AXILLA; ↑ with ↑ afterload (HANDGRIP MANEUVER)
Murmur of Tricuspid Regurgitation
Pansystolic murmur
Increases in intensity with inspiration
ventricular septal defect
large hole between two ventricles lets venous blood pass from the right to the left ventricle and out to the aorta without oxygenation
murmur of aortic regurgitation
Occurring when the leaflets of the aortic valve fail to close completely
the murmur of aortic regurgitation is the result of blood flowing from the aorta back into the left ventricle.
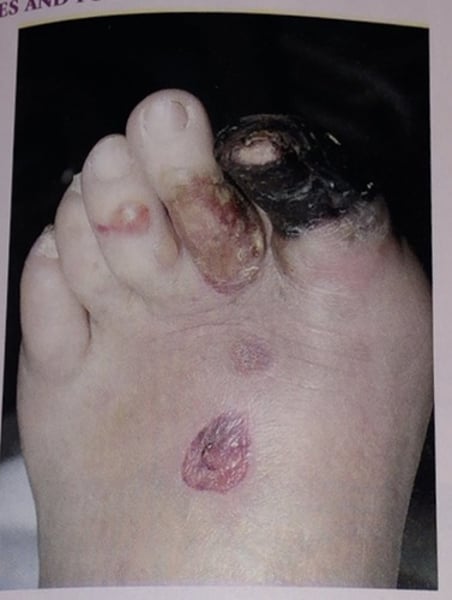
necrotic great toe with blisters on toes and foot
Arterial ulcer. Great toe is necrotic with blisters on the toes and foot seen in arterial insufficiency.
Raynaud disease, Raynaud syndrome
cyanosis of the fingers or toes due to vascular constriction, usually caused by cold temperatures or emotional stress
arterial insufficiency
inadequate blood flow through the arteries
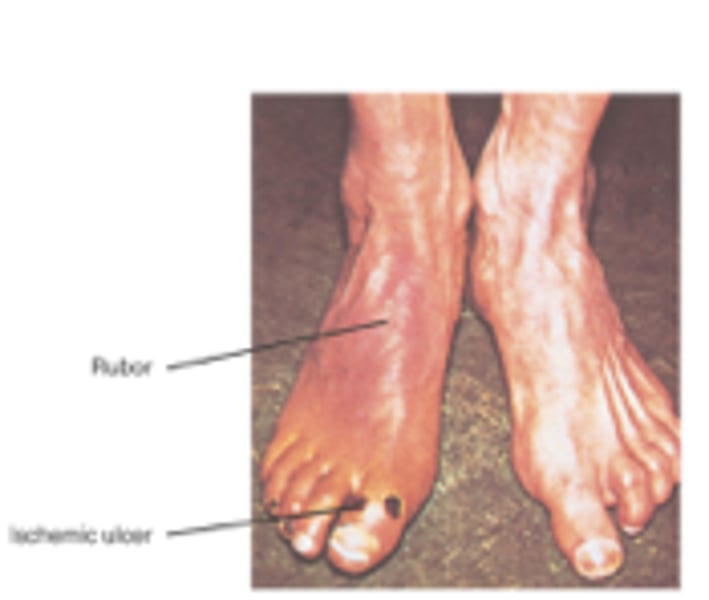
venous insufficiency
an abnormal circulatory condition characterized by decreased return of venous blood from the legs to the trunk of the body
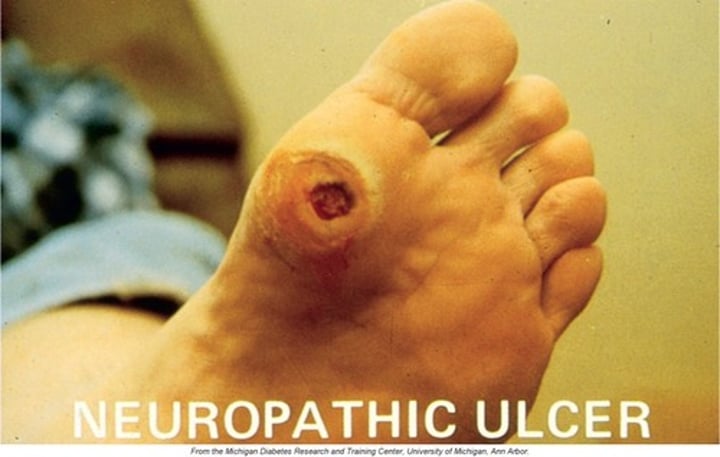
neuropathic ulcer
secondary complication usually associated with a combination of ischemia and neuropathy.
most often associated with diabetes.
frequently found on foot
wound has good granulation tissue and little or no drainage.
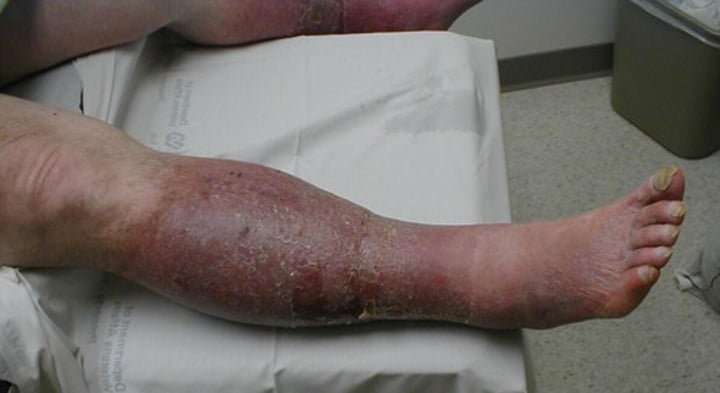
superficial thrombophlebitis
inflammation of a vein near the surface due to the presence of a blood clot
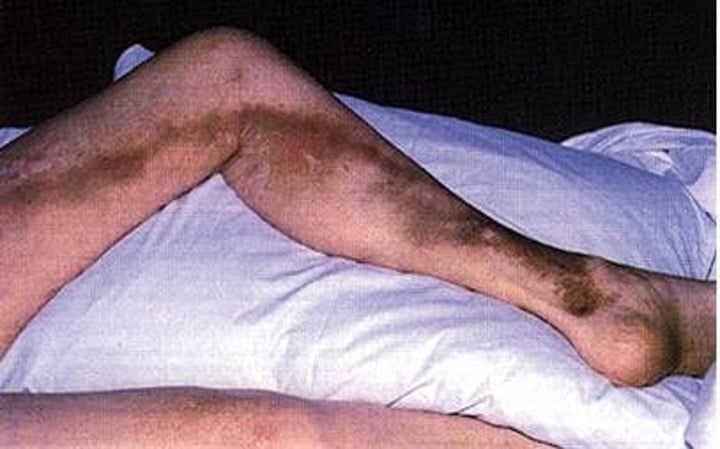
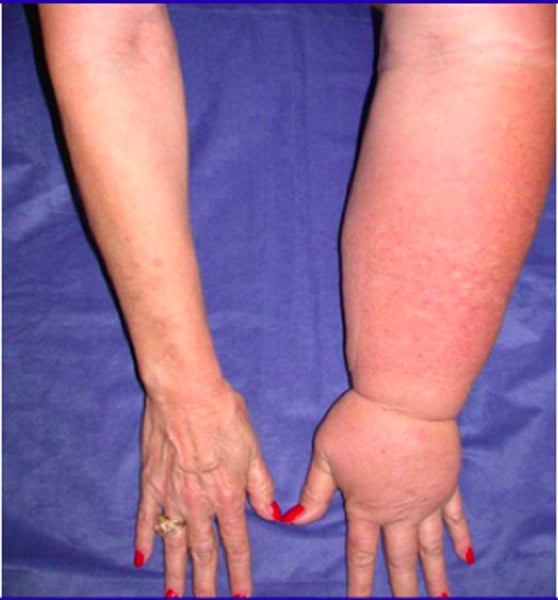
lymphedema
swelling due to an abnormal accumulation of lymph fluid within the tissues
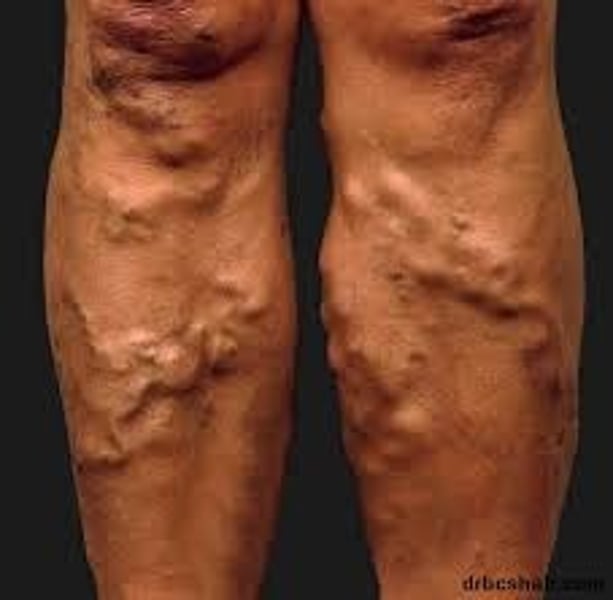
varicose veins
abnormally swollen, twisted veins with defective valves; most often seen in the legs
edema associated with lymphedema
Caused by abnormal or blocked lymph vessels
Nonpitting
Usually bilateral; may be unilateral
No skin ulceration or pigmentation
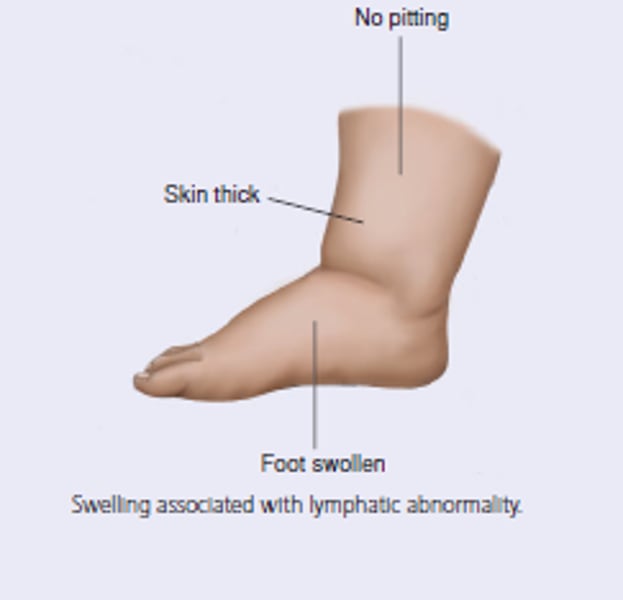
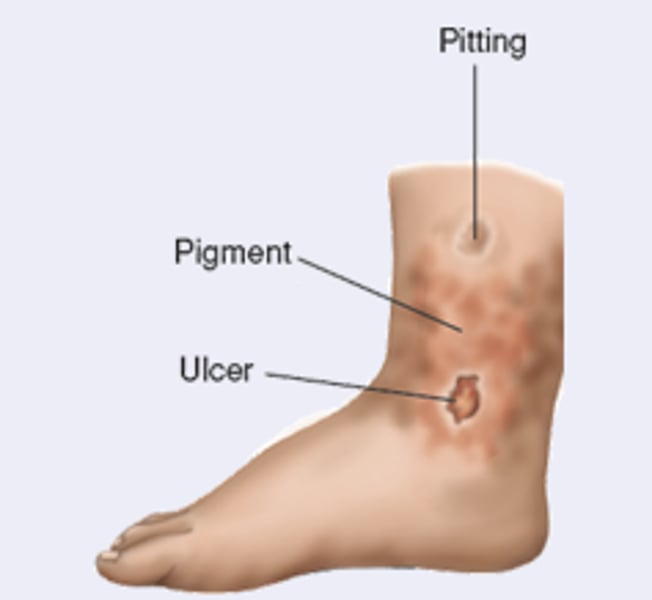
edema associated with chronic venous insufficiency
Caused by obstruction or insufficiency of deep veins
Usually unilateral; may be bilateral
Skin ulceration and pigmentation may be present