BIOL 1010 exam 4- peart
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
osmoregulation
secretion of hormones
filtration
functions of the urinary system
urinary bladder
store urine- have baroreceptors
short
urethra in women is ____
long
urethra in men is ____
osmoregulation
maintenance of the appropriate balance of water and salt in the blood
renal hilum
entrance and exit point of blood vessels and nerves in the kidneys
1 million
How many nephrons are in each kidney?
blood in renal artery-> nephron-> minor calyx->major calyx-> renal pelvis-> ureter
the very broad flow of filtration in kidneys
capsules
all organs have ____
renal pyramids
filter solutes through osmoregulation
180 liters
how many liters of blood do our kidneys filter a day
afferent arteriole
carries blood towards the glomerulus
efferent arteriole
carries blood away from the glomerulus
filtering
nephrons main function
bowmans capsule-> proximal convoluted tubule->loop of henle-> distal convoluted tubule->collecting duct
filtration process in a nephron
H2O and solutes
only ____ and ____ go into nephrons
tubular reabsorption
solutes are reabsorbed from the nephron into the peritubular capillary network
tubular secretion
process of substances being removed from blood
loop of henle
only part that dips into the medulla
visceral
internal urethral sphincter is _____
somatic
external urethral sphincter is ____
closed
mens internal urethral sphincter stays_____
stretch
womens internal urethral sphincter sense _____
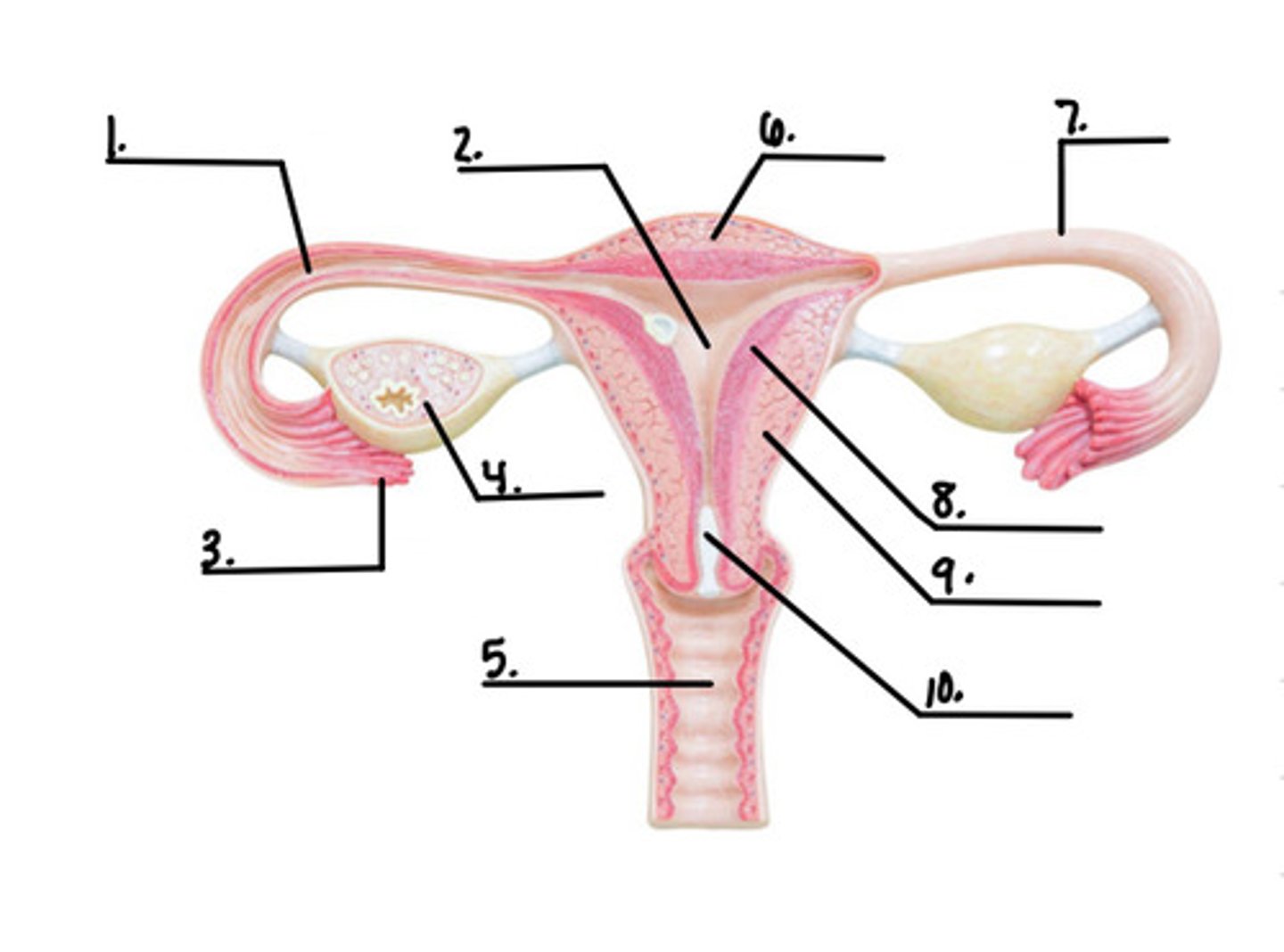
1. aorta
2. right kidney
3. ureter
4. urethra
5. inferior vena cava
6. left kidney
7. urinary bladder
label the diagram
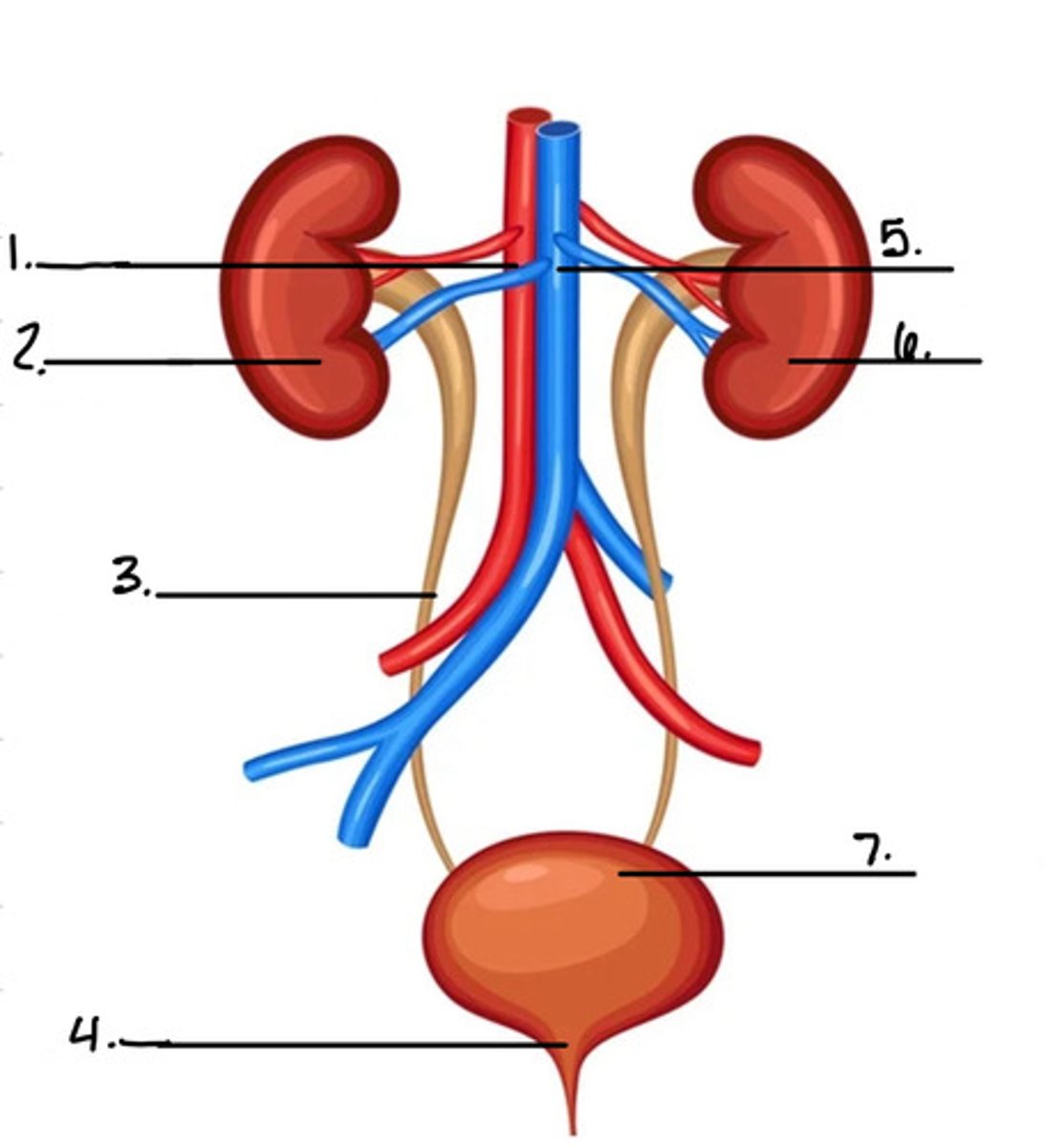
1. afferent arteriole
2. proximal convoluted tubule
3. glomerular capsule
4. distal convoluted tubule
5. collecting duct
6. loop of henle
7. peritubular capillary network
label the diagram
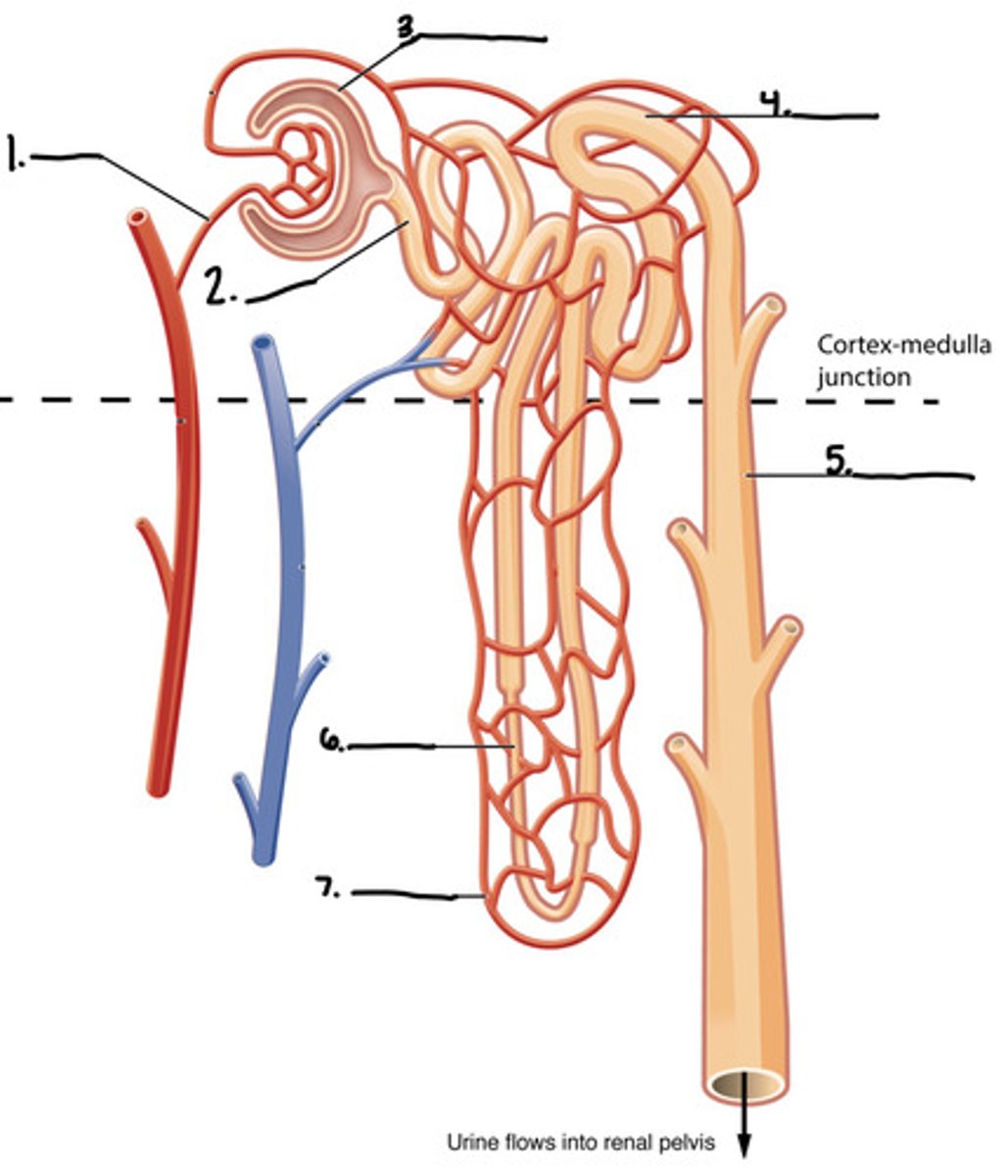
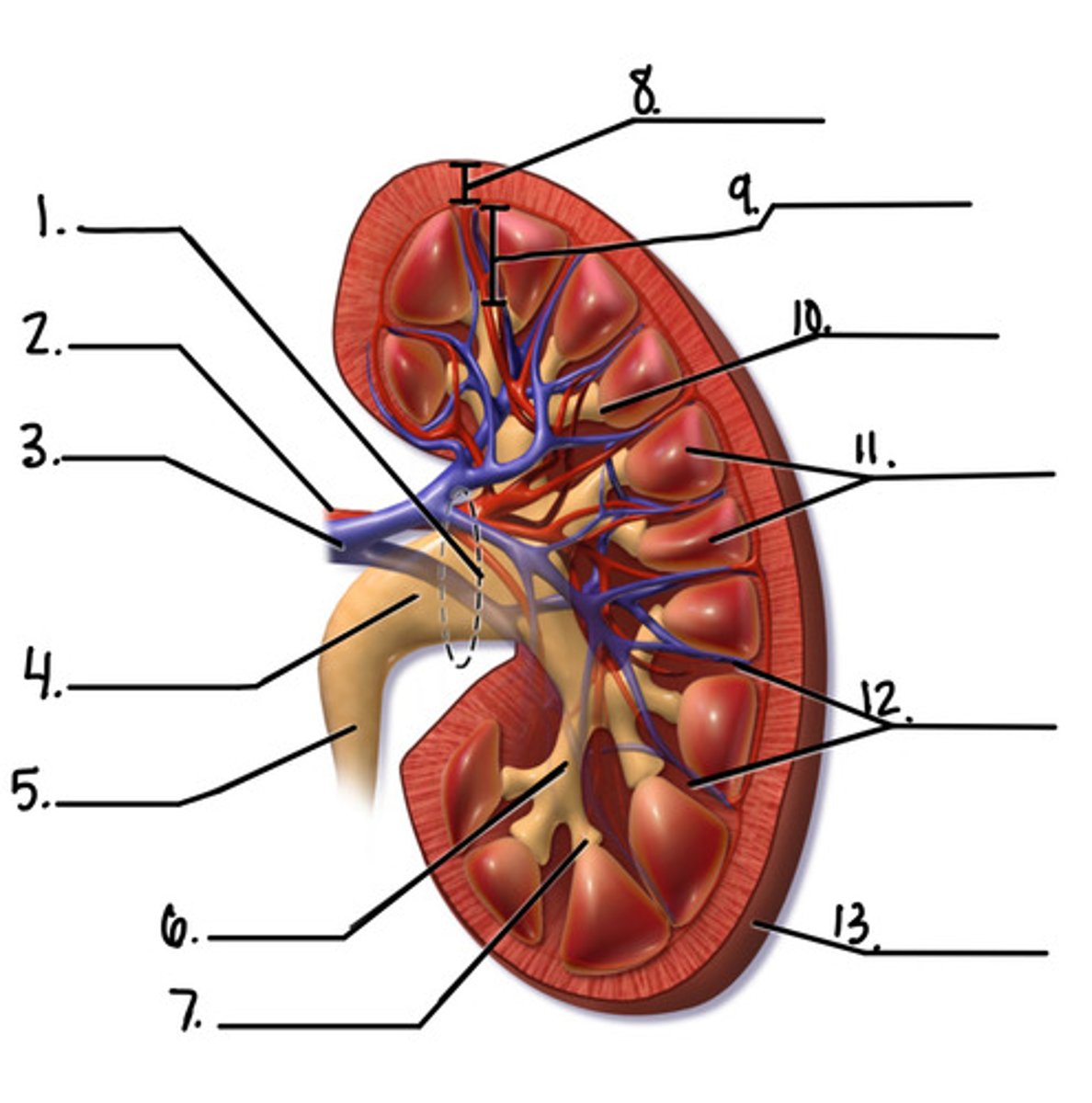
1. renal hilum
2. renal artery
3. renal vein
4. renal pelvis
5. ureter
6. major calyx
7. minor calyx
8. renal cortex
9. renal medulla
10. renal papilla
11. renal pyramids
12. renal columns
13. fibrous capsule
label the diagram
aorta-> renal artery-> afferent arteriole->glomerulus-> efferent arteriole-> peritubular capillaries-> renal vein-> inferior vena cava-> back to blood stream
follow the pathway of a red blood cell through the kidneys
aorta-> renal artery-> afferent arteriole->glomerulus->bowmans capsule-> PCT, loop of henle, DCT-> (if needed) additional regulation collecting tubule and duct-> urine-> minor calyx->major calyx-> renal pelvis-> ureter->urinary bladder-> urethra
follow the pathway of water through the kidneys
ureters
simply transport for urine and has peristalsis movement
urea
to much ____ can cause kidneys to shut down and/or kidney stones
internal urethral sphincter
what prevents/regulates men from urinating and ejaculating at the same time
podocyte
additional layer of filtering in bowmans capsule, helps filter small proteins
testes
primary organ of the male reproductive system
drop at puberty
maintain homeostasis-temperature
epididymis is attcahed
describe the testes
ejaculatory duct
has 2 seminal vesicles
testes and epididymis
located in the scrotum
250
how many lobes are in each testicle
1-4
how many seminiferous tubules are in each lobe
250-1000
how many seminiferous tubules are in each testicle
100 million
how many sperm are made daily
anterior pituitary
FSH and LH are secreted from where
goes to tubules to increase sperm development
function of FSH for male reproduction
increase testosterone
function of LH for male reproduction
Epididymis and 2 weeks
sperm is stored where and for how long?
reabsorbed
if sperm is not used it is _____
sex
sperm determines____
XX
female sex chromosomes
XY
male sex chromosomes
bulbourethral gland
prostate gland
seminal vesicle
supportive glands of male reproduction
mid piece
mitochondria is located in what section of the sperm
acrosome cap
digestive enzymes are found in what section of the sperm
4
individual spermatogenesis make ___ sperm
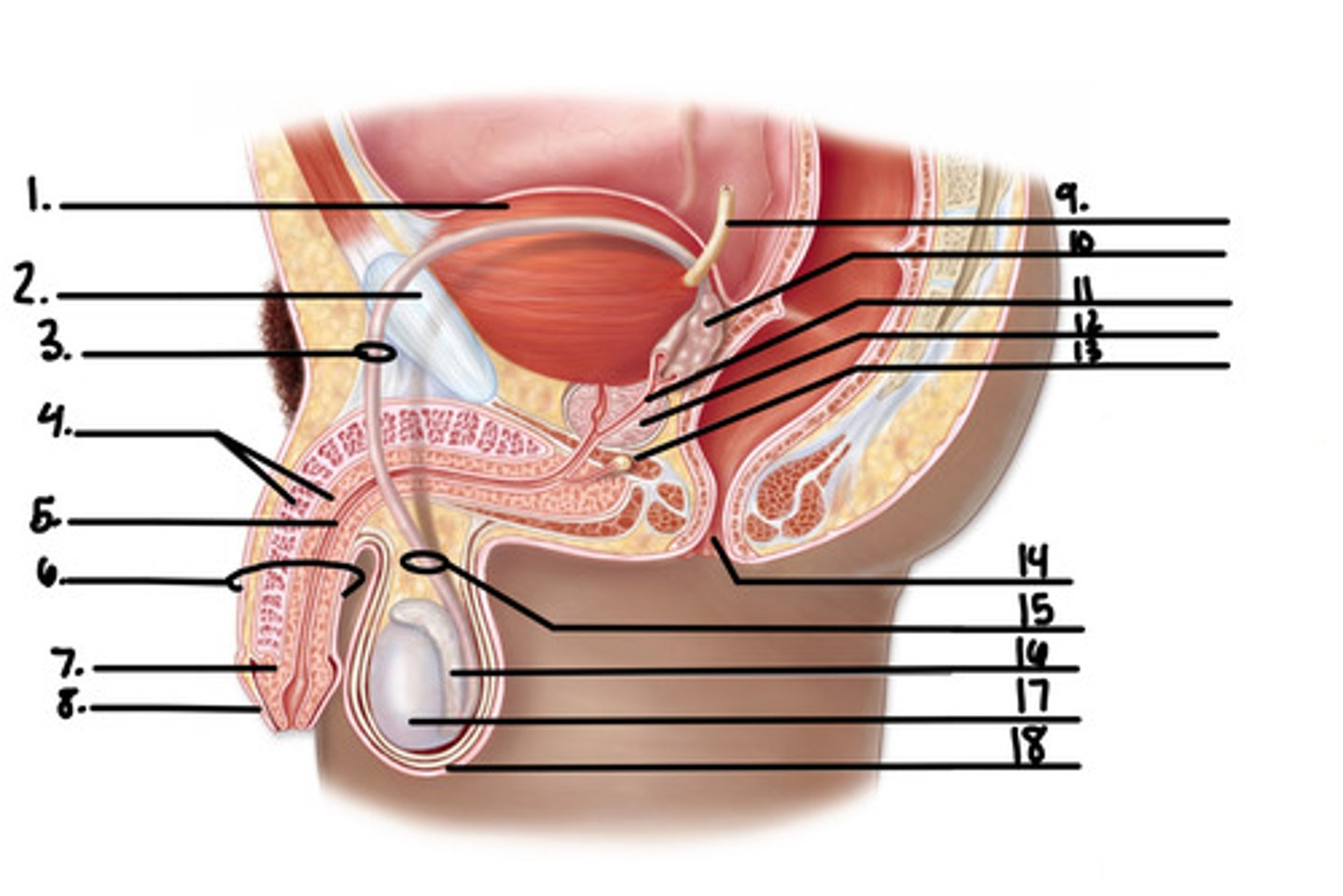
1. urinary bladder
2. pubic bone
3. vas deferens
4. erectile tissue of penis
5. urethra
6. penis
7. glans penis
8. foreskin
9. ureter
10. seminal vesicle
11. ejaculatory duct
12. prostate gland
13. bulbourethral gland
14. anus
15. vas deferens
16. epididymis
17. testis
18. scrotum
label the diagram
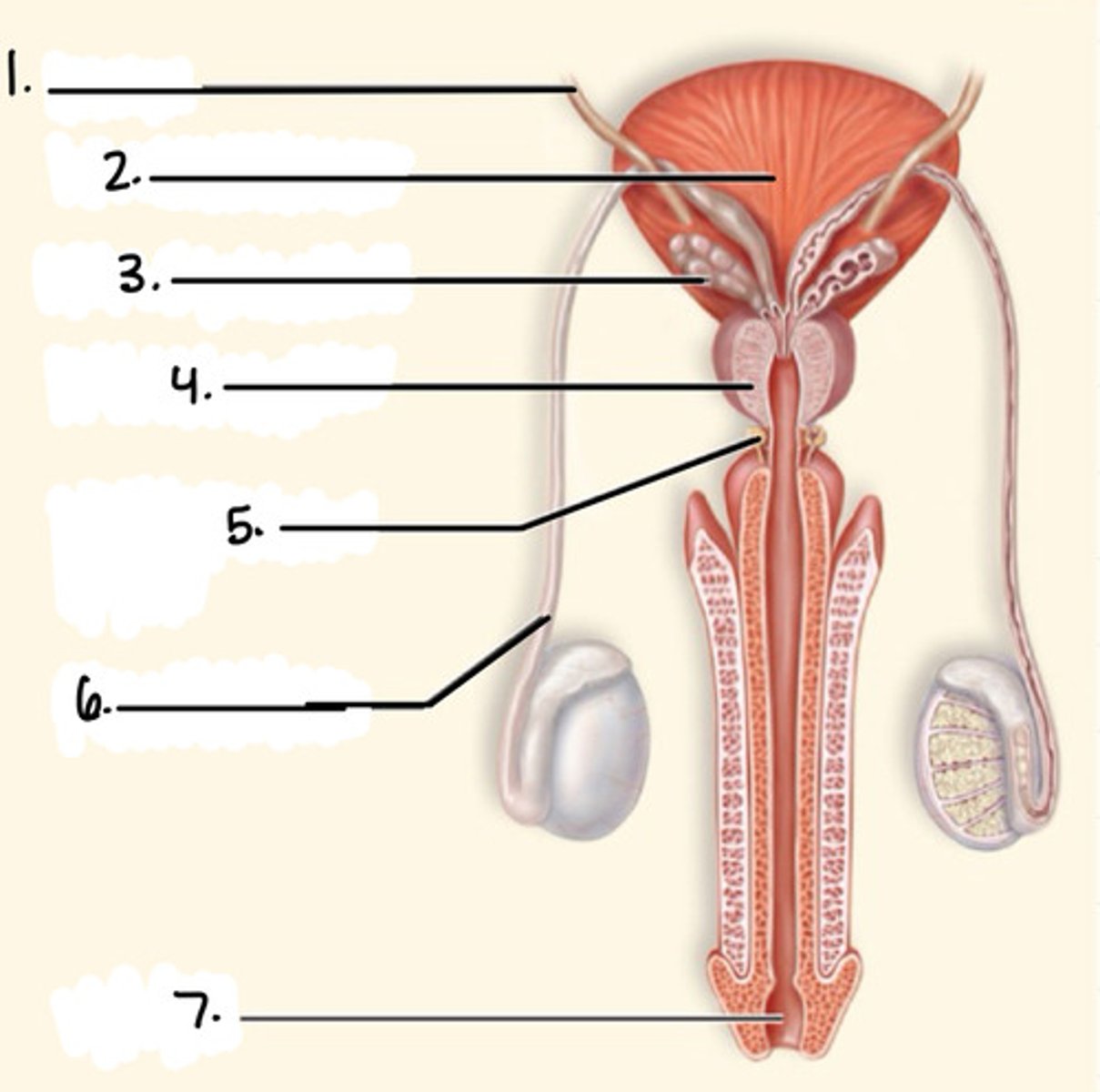
1. ureters
2. urinary bladder
3. seminal vesicle
4. prostate gland
5. bulbourethral gland
6. vas deferens
7. urethra
label the diagram
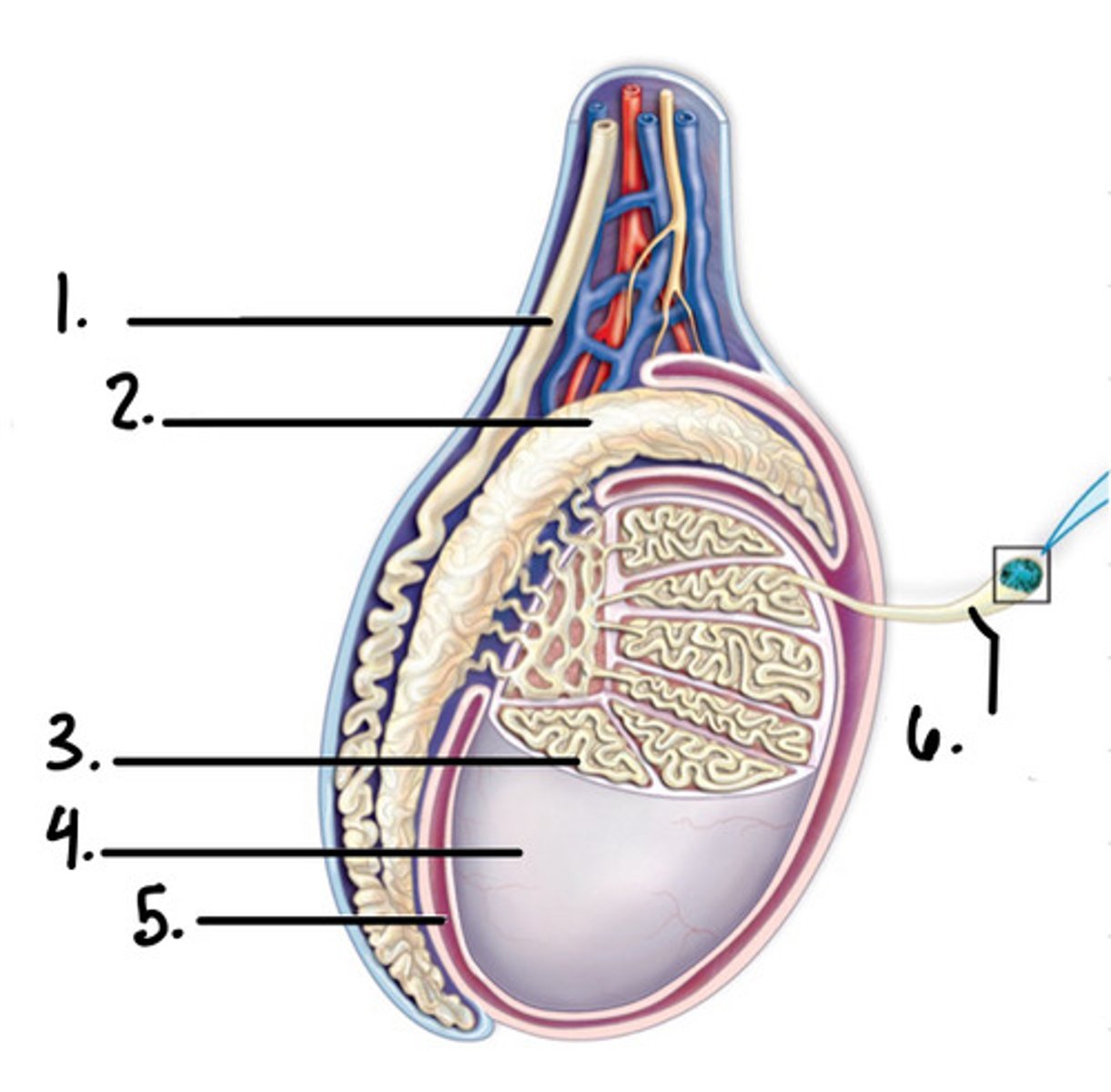
1. vas deferens
2. epididymis
3. lobule
4. testis
5. scrotal sac
6. uncoiled seminiferous tubule
label the diagram
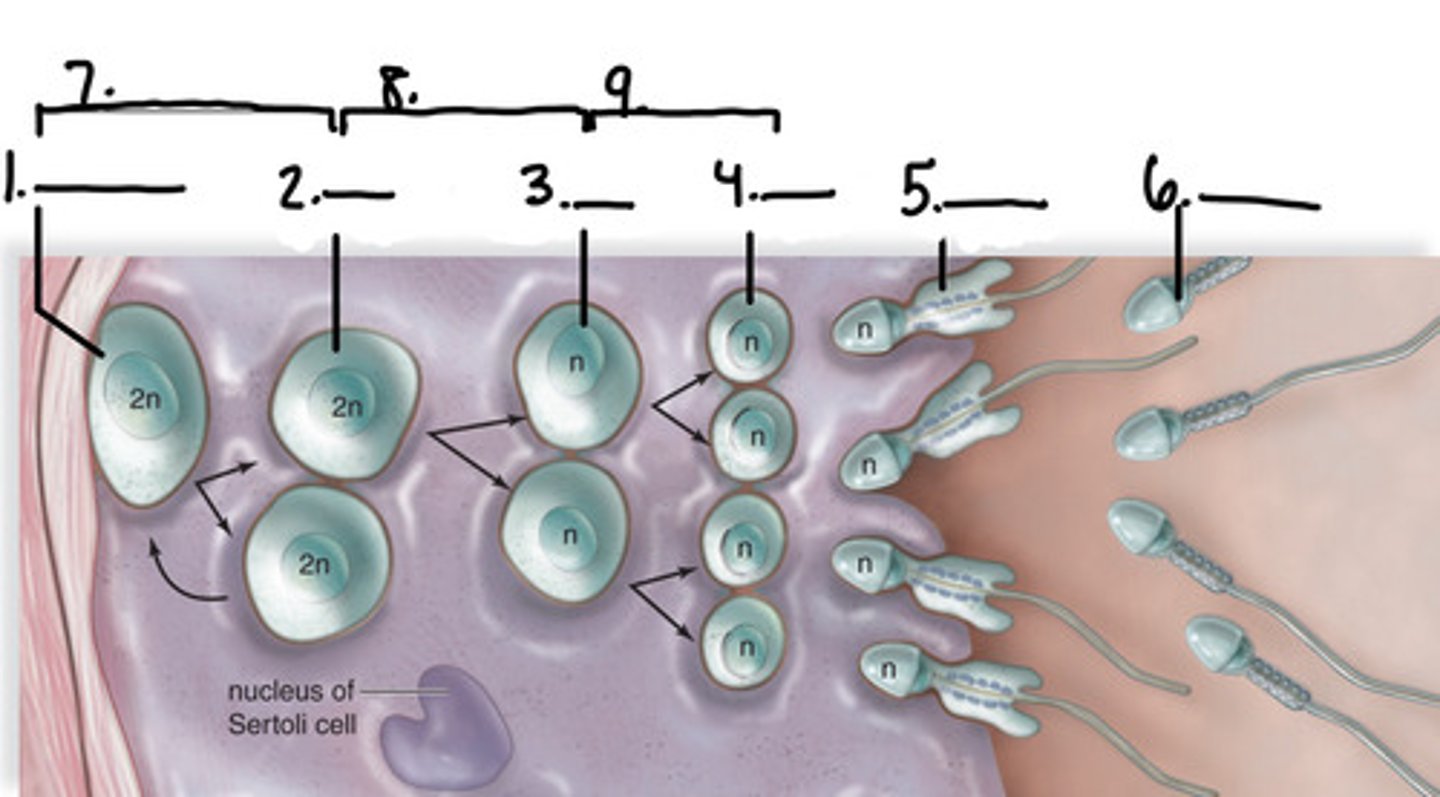
1. spermatogonium
2. primary spermatocyte
3. secondary spermatocyte
4. early spermatid
5. late spermatid
6. immature sperm
7. mitosis
8. meiosis I
9. meiosis II
label the diagram
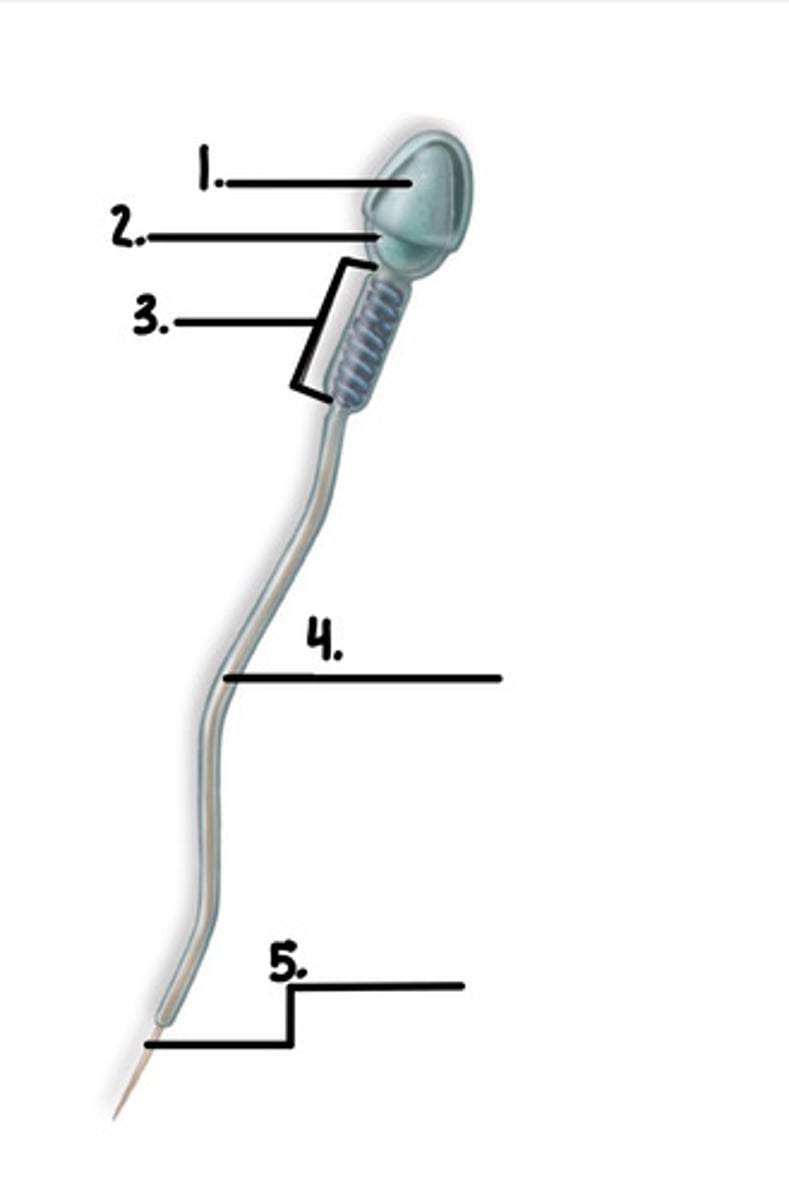
1. acrosome
2. head
3. midpiece
4. tail
5. endpice
label the diagram
puberty
when does sperm production start?
2 testes->2 epididymis->2 vas deferens->2 ejaculatory duct->2 seminal vesicle-> (merge to one tube) prostatic urethra(prostate gland)-> membranous urethra->(bulbourethral gland) spongy urethra-out the body
what is the flow of sperm
seminal vesicle
produce energy, monosaccharide-fructose
prostate gland
produce enzymes, water, and clot liquifying fluid
bulbourethral gland
produces a lubricant, acid neutralizing buffer, and H20
semen
sperm that has passed through the glands
3-5
sperm can live ___ to ___ days in female tract
condoms
immediate barrier- temporary- very effective
birth control pill
force cycle to become a 28 day cycle- helps regulate cycle
depo shot
eliminate release of eggs- throws off hormones
IUD
release chemicals, change cycle and interfere with sperm
birth control implant
in arm, pellet form, act like IUD, hormone regulation 3-5 yrs
fertility awareness
tracking womens cycle is______
withdrawal awareness
this method increases the risk of pregnancy by a lot
abstinence
not having sex
tubal ligation
tubes tied is also know as
vasectomy
seal of vas deferens
plan B
take within the first 72 hrs, interferes with hormones, within 24 hrs won't let fertilization happen
abortion
last resort, emergency- risk to mother/fetus is inviable
3
1 in ____ people have herpes
oral
type 1 herpes is _____
genital
type 2 herpes is _____
herpes
most common STD, causes sores and ulcers
AIDS
illegal to not share w/ partner you have this STD, life threatening, drugs to suppress, T-lymphocyte cant alert system that there is an issue
HPV- Human pappilomavirus
men can carry, but can't test for it-- number 1 cause of cervical and ovarian cancer, no external issues, blood test, clear out within 2-3yrs
gardsil
3 shot series to prevent HPV
FSH
hormone that makes follicles that grow
LH
hormone that matures follicles-oocyte
ovaries
primary organ for female reproductive system
ovary->fallopian tubes(fertilization)-> uterus-> vagina-> outside the body
basic flow of an egg/oocyte-embryo pathway
has 46 chromosomes- all XX- splits during ovulation into a secondary oocyte
describe a primary oocyte
has 23 chromosomes inside and a polar body on the outside containing the other 23 chromosomes
describe a secondary oocyte
28 days
avg length of a menstrual cycle
mature follicle- FSH around oocyte
days 1-13
describe the follicular phase
release of secondary oocyte from mature follicle
LH is released-24 hrs before ovulation starts
fallopian tubes connect to ovaries for 1 day
describe the ovulation phase
days 15-28 of cycle
ovary waits to restart if no fertilization
describe the luteal phase
11-12 yrs old
avg age puberty begins for girls
1.5 million
in utero how many eggs do fetuses start out with
400,000
by puberty girls only have ______ eggs left
20
____ eggs are shed each month
2
the vagina is a ___ way system
1
___ oocyte released a month
1. fallopian tube
2. uterus
3. fimbriae
4. ovary
5. vagina
6. fundus
7. fallopian tube
8. endometrium
9. myometrium
10. cervix
label the diagram