Living Environment 2025 midterm
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
notes, review sheets, etc
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
unicellular organism
has one cell
multicellular organism
has many cells
autotrophs
make their own food
heterotrophs
get nutrients from their environment
a stimulus is a
signal
respiration
to make energy
aerobic organisms
need oxygen
anaerobic organisms
don’t need oxygen
metabolism
all chemical activities that take place in an organism
positive feedback
an increase in the change or output - *think positive = higher
negative feedback
a decrease in the change or output - *think negative = lower, minus
what are the 3 types of cell
plant, animal, bacteria
only plant cells have:
chloroplasts (photosynthesis), cell walls (shape/structure), large vacuoles (water storage).
cell membrane is made of
phospholipids (lipids)
passive transport
high → low *NO ATP*
active transport
low → high, *requires ATP*
isotonic solution
equilibrium, same amount of water on inside and outside
hypotonic solution
water diffuses INSIDE — “hypO - OH no its gonna explode
Hypertonic solution
water diffuses OUT
2 types of active transport
exocytosis, endocytosis
exocytosis
active transport, exit the cell (ex = exit)
endocytosis
active transport, enter the cell ( en = enter)
energy is formed in
chemical bonds
organic compounds contain
carbon and hydrogen together
carbohydrates are what kind of molecules
energy
building blocks of carbs
sugars (monosaccharides)
names for sugars end in
-ose
names for enzymes end in
-ase
dehydration synthesis
formation of a large molecule with the release of water molecules
hydrolysis
breaking of a chemical bond in the presence of water
a monosaccharide is
one sugar
a polysaccharide is
many sugars
energy storage in plants
starch
energy storage in animals
glycogen (carb)
carbohydrate in structure in plants (cell wall)
cellulose
lipids are
fats and oils
lipids are what kind of energy
stored / concentrated
fats, oils, waxes, and hormones are all
lipids
lipids are used for (4)
energy storage
cell membrane
cushions organs
insulates the body (like whale blubber)
structure of a lipid resembles what letter
E
lipids are made of
3 fatty acids 1 glycerol
carbs contain the elements:
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
proteins contain the elements:
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
what are the 4 macromolecules
Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids.
Lipids contain what elements
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Nucleic Acids contain the elements:
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous
building blocks of proteins
amino acids
amino acid structure (this is just an image)
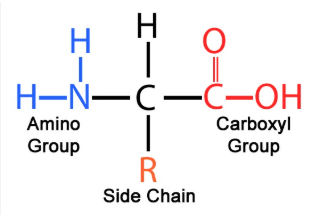
what determines protein shape
order of amino acids
what determines protein function
protein shape
many amino acids =
polypeptide (protein)
enzymes are classified as
proteins
what is an active site?
the surface of an enzyme where the substrate fits
a substrate is
the substance an enzyme acts upon
the following effect how an enzyme works (2)
temperature, PH
denaturation
enzyme changes shape
2 kinds of Nucleic Acids
DNA, RNA
nucleotides are made of
a phosphate group, a sugar, and one nitrogenous base (home sweet home)
4 DNA bases
Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine
4 RNA bases
Adenine Uracil Cytosine Guanine
DNA structure
double helix
Gene:
segment of DNA that contains instructions for an organisms traits - found on chromosomes
Allele
specific version or variant of a gene
genome
complete set of genetic material
genotype
combination of alleles for a given gene
phentotype
physically expressed trait (blue eyes)
genes are located
on chromosomes
chromosomes are located
in the nucleus
Homozygous dominant
2 dominant alleles (GG)
Homozygous recessive
2 recessive alleles (gg)
Heterozygous
one dominant and one recessive allele (Gg)
incomplete dominance
2 alleles blend (1 red 1 white phenotype is pink)
codominance
both alleles are shown (red and white petals)
Recessive blood type
o
Protein synthesis process
replication (DNA → DNA) , transcription (DNA →RNA), translation (RNA → amino acids)
rRNA
makes up ribosomes