Unit 9 Developmental Psychology
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Developmental Psychology
a branch of psychology that studies PHYSICAL, COGNITIVE, and SOCIAL change throughout the life span

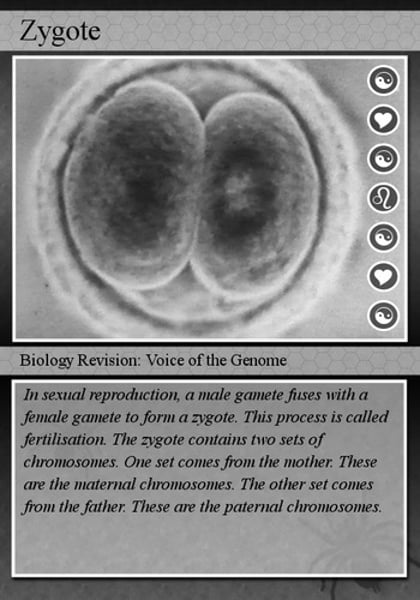
Zygote
1st stage in prenatal development: a fertilized egg, first 2 weeks of prenatal development
Fetus
3rd stage in prenatal development: human organism from 9 weeks after conception to birth
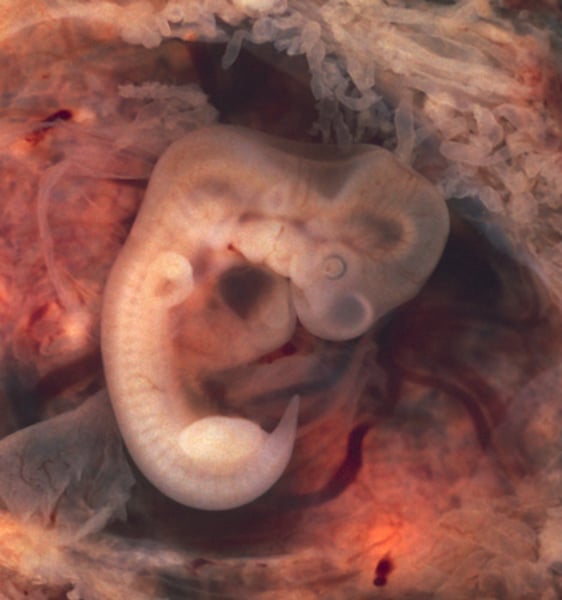
Embryo
2nd stage in prenatal development: from 2 to 8 weeks
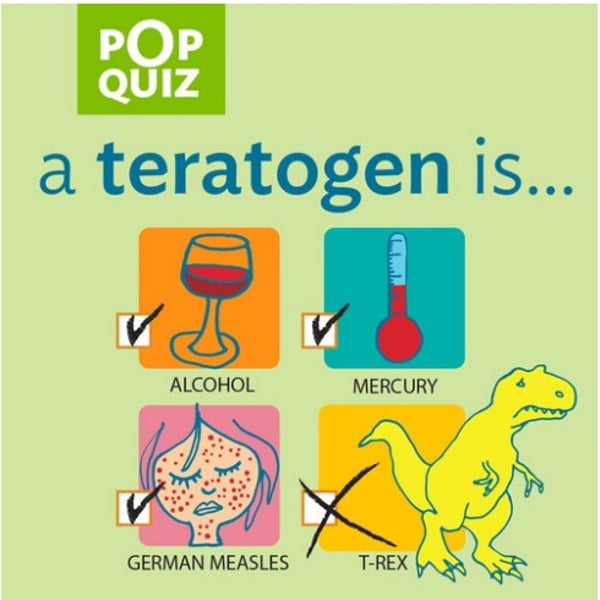
teratogens
agents (i.e. chemicals and viruses) that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
Attachment
The strong social-emotional bond a baby forms with his or her primary caregiver.

Maturation
biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience
Assimilation
the process of taking in new ideas into an existing cognitive structure

Accommodation
Changing our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information
Sensorimotor Stage
Piaget's 1st stage of COGNITIVE development (from birth - 2 years of age) during which infants know the world mostly in terms of their SENSORY impressions and MOTOR activities

Object Permanence
the understanding that objects continue to exist even when out of view (infants lack this understanding)

Preoperational Stage
Piaget's 2nd stage of COGNITIVE development (from about 2 to about 6 or 7 years of age) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic

Egocentrism
Piaget's theory that the preoperational child has difficulty taking another's point of view
Concrete Operational Stage
Piaget's 3rd stage of COGNITIVE development during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events

Conservation
the principle that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects (preoperational children lack this understanding)

Theory of Mind
The understanding that other people's behavior may be influenced by beliefs, desires, and emotions that differ from one's own

Puberty
the period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing
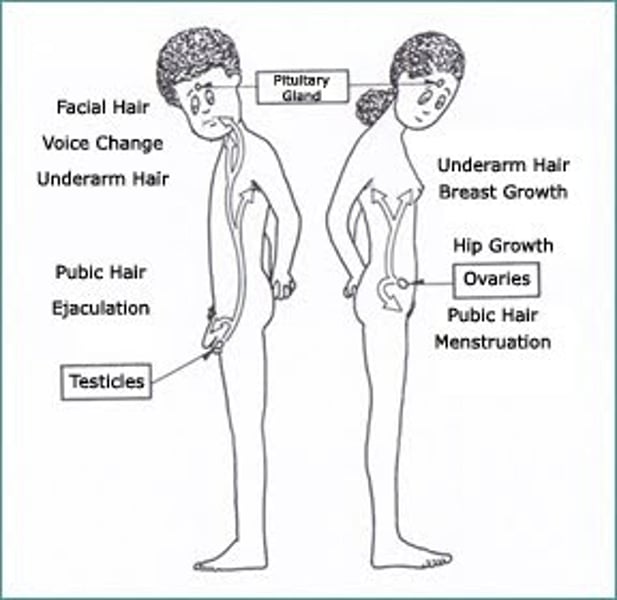
Primary Sex Characteristics
the body parts (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible
Secondary Sex Characteristics
Body parts associated with gender but are NOT directly involved in reproduction.
Formal Operational Stage
Piaget's 4th stage of COGNITIVE development during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts

Mary Ainsworth
studied how different ATTACHMENT styles affected kids with Strange Situation Study

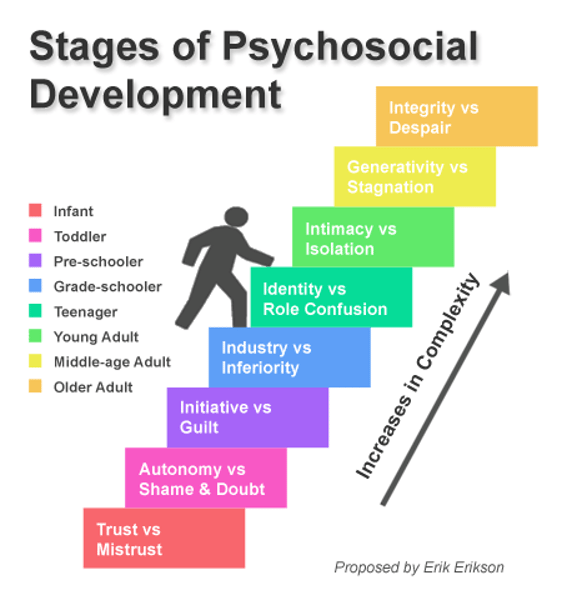
Erik Erikson
Developed 8 psychoSOCIAL stages of development: theory shows how people evolve through the life span through interaction with others. Each stage is marked by a crisis that requires resolution
Carol Gilligan
Studied girls and women, a follow-up to Kohlberg's moral development work, and found that they scored differently on Kohlberg's scale because they focused more on relationships rather than laws and principles.

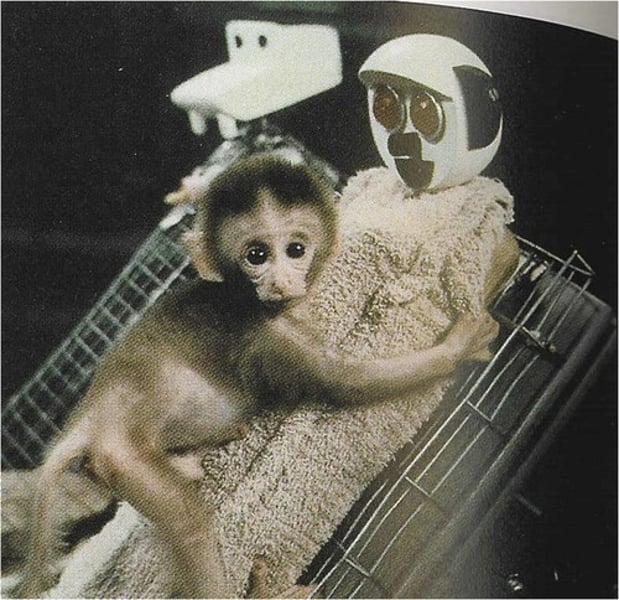
Harry Harlow
Experimented with baby monkeys and presented them with cloth OR wire "mothers;" showed that the monkeys became attached to the cloth mothers because of contact & comfort (1 factor of attachment)

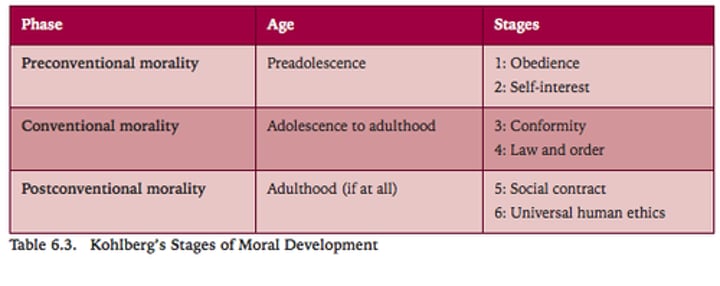
Lawrence Kohlberg
Moral Development Theory
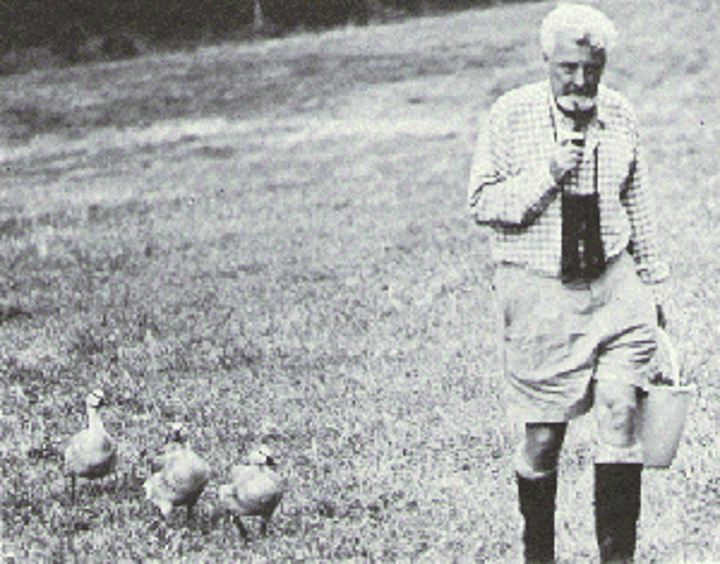
Konrad Lorenz
researcher who focused on critical attachment periods in baby birds, a concept he called imprinting;

Jean Piaget
Known for his theory of cognitive development in children

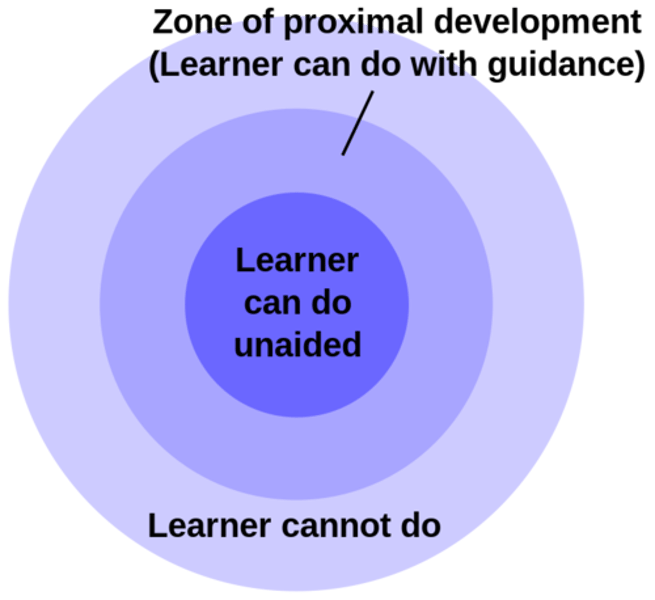
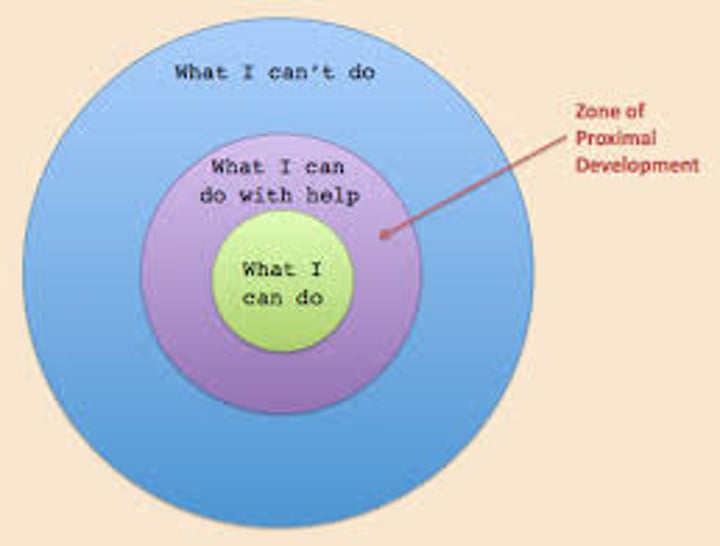
Lev Vygotsky
most famous for social-COGNITIVE development theory, zone of proximal development
Fetal alcohol syndrome
a medical condition in which body deformation or facial development or mental ability of a fetus is impaired because the mother drank alcohol while pregnant

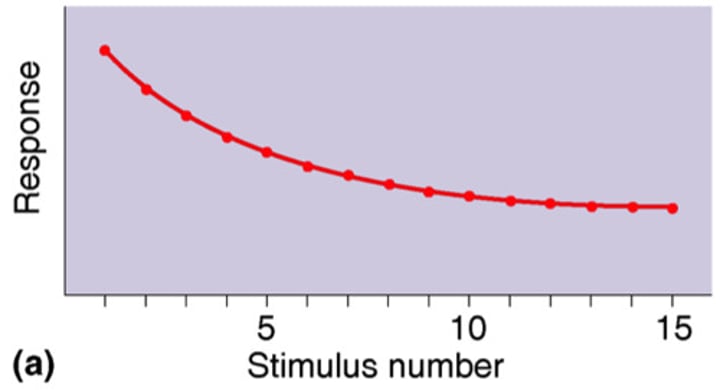
Habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner.
Cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating

Schema
a conceptual framework a person uses to make sense of the world
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
a disorder that appears in childhood and is marked by significant deficiencies in communication and social interaction, and by rigidly fixated interests and repetitive behaviors

Stranger Anxiety
the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age

Critical Period
a specific time in development when certain skills or abilities are most easily learned
Basic Trust
according to Erik Erikson, a sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy; said to be formed during infancy by appropriate experiences with RESPONSIVE caregivers

Self Concept
a sense of one's identity and personal worth

Gender Typing
The process of developing the behaviors, thoughts, and emotions associated with a particular gender.
Gender
the socially constructed roles and characteristics by which a culture defines male and female

X chromosome
The sex chromosome found in both men and women. Females have two X chromosomes; males have one. An X chromosome from each parent produces a female child.
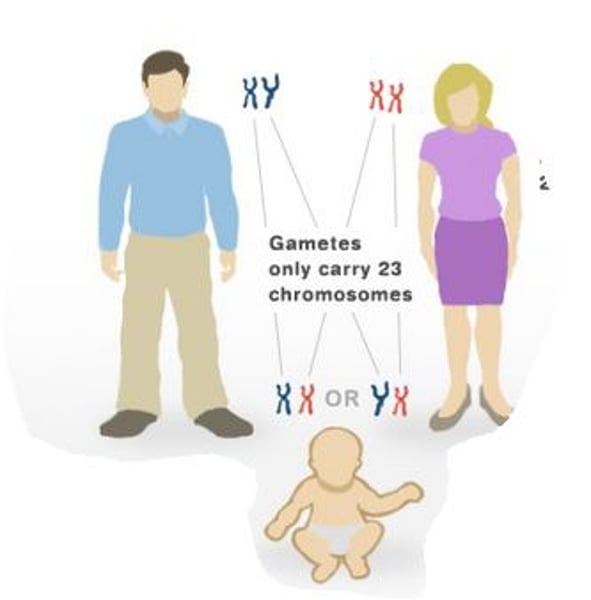
Y Chromosome
the sex chromosome found only in males
Testosterone
the most important of the male sex hormones. Both males and females have it, but the additional testosterone in males stimulates the growth of the male sex organs in the fetus and the development of the male sex characteristics during puberty
menarche
the first occurrence of menstruation in a woman

intimacy
the ability to form close, loving relationships

emerging adulthood
A period from the late teens to early twenties, bridging the gap between adolescent dependence and full independence and responsible adulthood

menopause
the time in a woman's life in which the menstrual cycle ends

cross-sectional study
a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another

longitudal study
research in which the same people are studied and retested over a long period

social clock
the culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement

Alzheimer's disease (AD)
an irreversible, progressive brain disorder, characterized by the deterioration of memory, language, and eventually, physical functioning
gender role
a set of expected behaviors for males or for females

imprinting
the process by which certain animals, mainly birds, form strong attachments during an early-life critical period. Studied by Konrad Lorenz.

temperament
a person's characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity that appears early in development and is largely genetic in origin
gender identity
our sense of being male or female

transgender
an umbrella term describing people whose gender identity or expression differs from that associated with their birth sex

adolescence
the transition period from childhood to adulthood, extending from puberty to independence

social identity
the part of the self-concept including one's view of self as a member of a particular social category

sexual orientation
a person's romantic and emotional attraction to another person

zone of proximal development
In Vygotsky's theory, the range between children's present level of knowledge and their potential knowledge state if they receive proper guidance and instruction
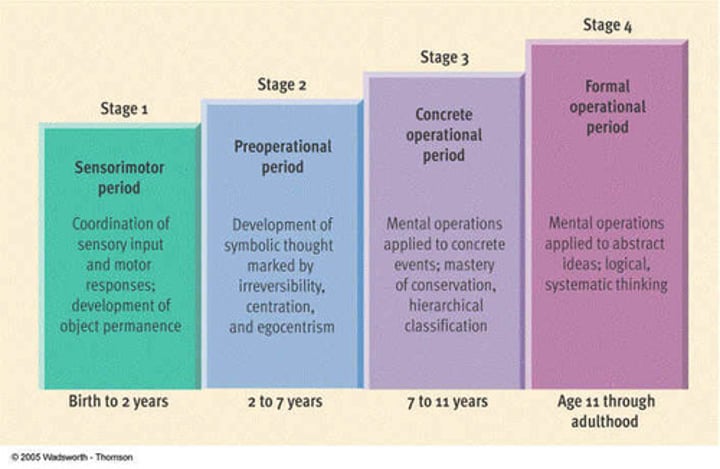
Piaget's stages of COGNITIVE development
1. sensorimotor
2. preoperational
3. concrete operational
4. formal operational
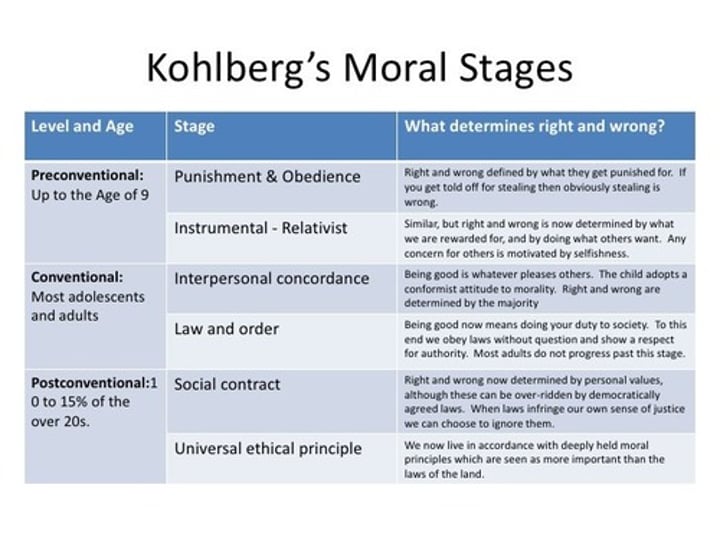
Kohlberg's stages of moral development
1. preconventional
2. conventional
3. postconventional
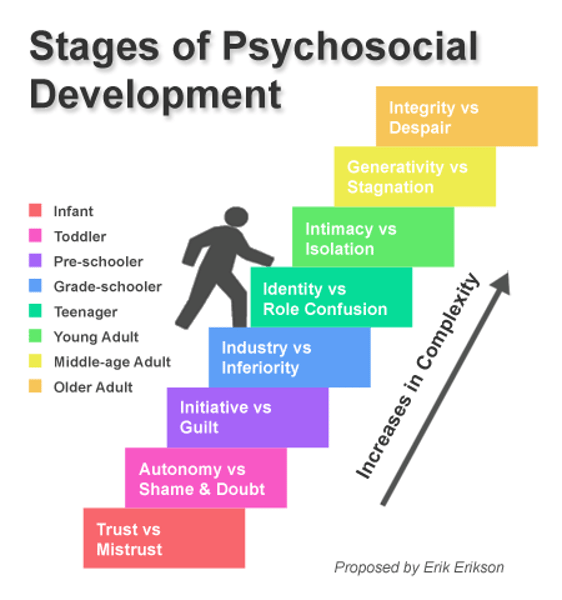
Erikson's stages of psychoSOCIAL development
1. trust vs. mistrust
2. autonomy vs. shame and doubt
3. initiative vs. guilt
4. industry vs. inferiority
5. identity vs. role confusion
6. intimacy vs. isolation
7. generativity vs. stagnation
8. integrity vs. despair
Trust vs. Mistrust (Erikson)
Infancy (to 1 year)
If needs are dependably met, infants develop a sense of basic trust.

Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt (Erikson)
Erikson's stage in which a toddler learns to exercise will and to do things independently; failure to do so causes shame and doubt

Initiative vs. Guilt (Erikson)
Erikson's third stage in which the child finds independence in planning, playing and other activities

Industry vs. Inferiority (Erikson)
6-11 years - Children busily learn to be competent and productive or feel inferior and unable to do anything well.

Identity vs. Role Confusion (Erikson)
13-19 yr, *most crucial* teens struggle with identity crisis, if healthy experimentation is fostered they attain identity achievement; if not, they face insecurity and low self-worth

Intimacy vs. Isolation (Erikson)
Adulthood: Young adults seek companionship/love or become isolated from others fearing rejection or disappointment

Generativity vs. Stagnation (middle adulthood)
middle-aged adults feel they are helping the next generation through their work and child rearing, or they stagnate because they feel that they are not helping

Integrity vs. Despair (Erikson)
Adulthood: Older Adults try to make sense out of their lives, they either see their lives as a meaningful whole or despair at unreached goals

preconventional morality
1st level of Kohlberg's stages of moral development:
self-interest; obey rules to avoid punishment or gain concrete rewards

conventional morality
2nd level of Kohlberg's stages of moral development: uphold laws and rules to gain social approval or maintain social order

postconventional morality
3rd level of Kohlberg's stages of moral development: actions reflect belief in basic rights and self-defined ethical principles

Diane Baumrind
theorist associated with parenting styles - authoritarian, authoritative, permissive, neglectful

authoritarian parenting
style of parenting in which parent is rigid and overly strict, showing little warmth to the child

authorative parenting
A parenting style that encourages the child to be independent but that still places limits and controls on behavior.

permissive parenting
A parenting style characterized by the placement of few limits on the child's behavior.

neglecting parenting
indifferent and uninvolved with child

Homosexuality
sexual attraction to someone of the same sex, related to genetics
dementia
a chronic or persistent disorder of the mental processes caused by brain disease or injury and marked by memory disorders, personality changes, and impaired reasoning. Alzheimer's is one form of this.

secure attachment
Infants use the mother as a home base from which to explore when all is well, but seek physical comfort and consolation from her if frightened or threatened

insecure attachment
Infants are wary of exploring the environment and resist or avoid the mother when she attempts to offer comfort or consolation

"use it or lose it" principle
The idea that practice strengthens neural connections, while infrequent use of certain skills may cause synaptic connections to weaken or degenerate. Pruning
infantile amnesia (childhood amnesia)
inability to recall events that occur prior to the age of three or so
