814 Final: lines and tubes
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
PT procedures for ICU
- Connect to transport monitor before leaving beside.
- Ask nurse or family member to follow with a wheelchair.
- Take resting vital signs.
Common sites of peripheral IV's
- Antecubital
- Dorsum of hand or foot
- Radial aspect of wrist
Precautions of IV
- Joint ROM may be restricted.
- Contact nurse if dislodged and apply pressure.
- Watch for edema and leaking fluid.
What are central lines?
- Used for large central venous access (subclavian, femoral or internal jugular)
- May be connected to medication bags or CVP monitor.
- May be double, triple, or quadruple lumen.
Central line precautions (subclavian vs femoral)
- Subclavian: limit shoulder flexion and abduction to 90
- Femoral: limit hip flexion to 90. NO IR AND EX
What are PICC lines?
- Peripherally inserted central catheters used for long term access to medications.
PICC line precautions
- Limit shoulder flexion to 90
- Alert nurse if tender or swollen.
What are arterial lines used for?
- Continuous monitoring of system blood pressure
- Systolic or dysolic BP (MAP)
o Radial, femoral, dorsalis, pedis and brachial artery's
How to know if it is an arterial line?
- TRANSDUCER PRESENT at level of right atrium
What happens if the transducer is too high vs too low.
- Too high: low measurement
- Too low: high measurement
Arterial line precautions radial vs femoral
- Radial: limit extreme wrist ROM
- Femoral: limit hip flexion to 30
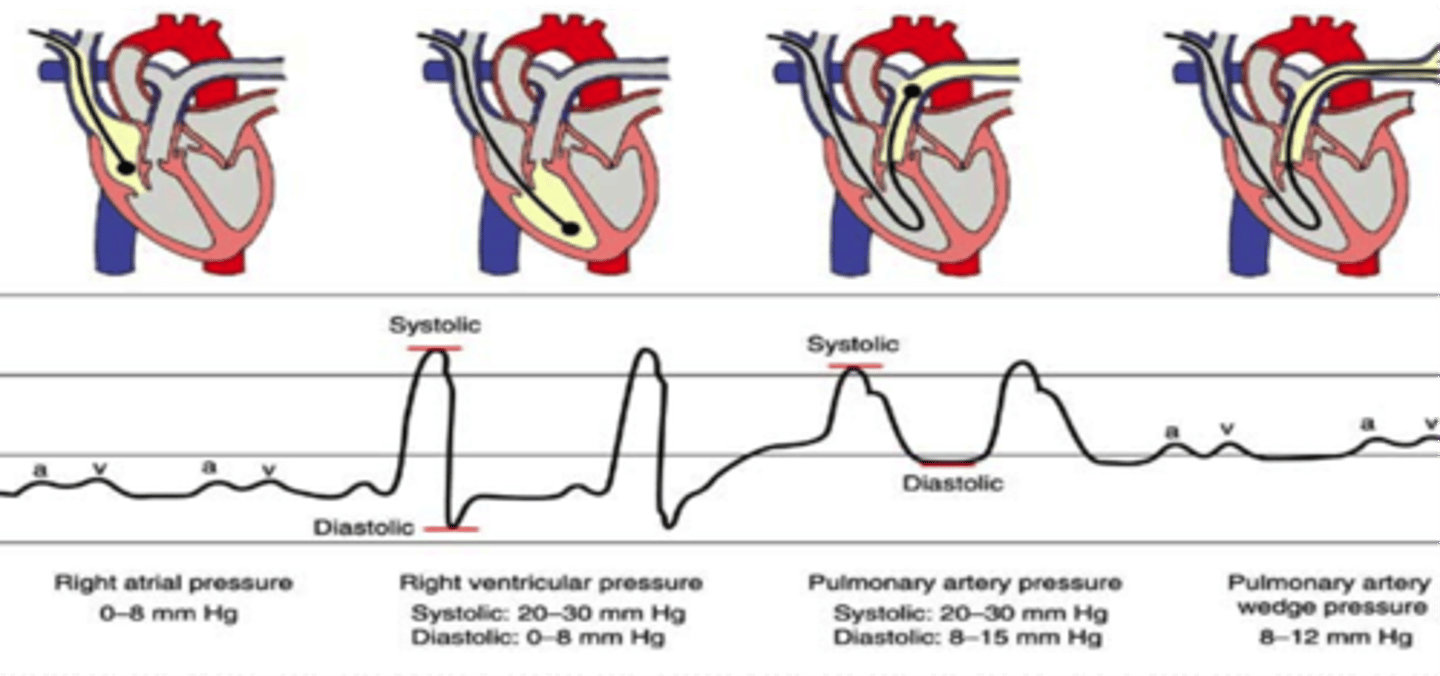
What is a Pulmonary artery catheter?
- Cather that travels through venous catheter to right atrium and ventricle to pulmonary artery
- Monitors cardiopulmonary pressure.
Pulmonary artery catheter precautions
- PAP waveform should be present if PAwP is displayed contact nursing.
- Watch shoulder ROM
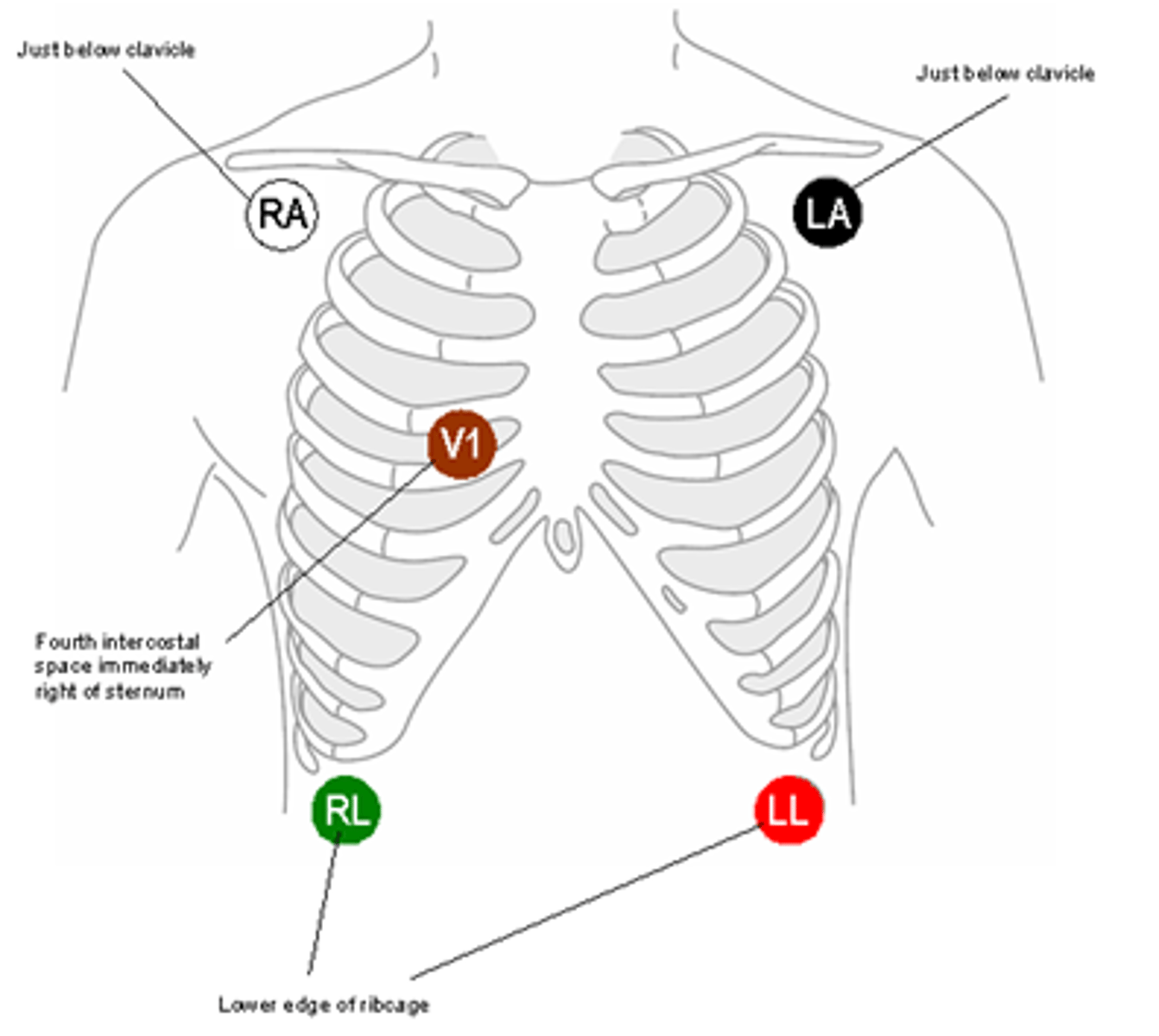
ECG monitoring
- Measuring heart rate and rhythm to detect heart blocks and arrythmias.
- 5 leads on adults and two on children
ECG lead colors
- RIGHT: white on top of green
o Snow on mountains
- Left: black on top of red
o Smoke over fire
- Brown in the middle
ECG precautions
- ECG electrodes may become disconnected (replace)
- Transport with you to monitor out of bed activities.
Pulse oximetry function
- Measured oxygen saturation
Common pulse oximetry sites
- Finger
- Earlobe
- Toes
Pulse oximetry precautions
- If reading low try to move it, if it still reads low contact nursing.
What is a foley catheter used for?
- Urine output of the bladder
Foley catheter precautions
- Must be below level of the bladder.
- Contact nursing in pt. reports extreme discomfort
What is a rectal drain used for?
- Used to contain frequent loose stool.
- Collection bag or vacuum
What are post operative drains used for?
- Use following abdominal and thoracic surgery to collect fluid and blood.
o Jackson Pratt (bulb) or hemovac
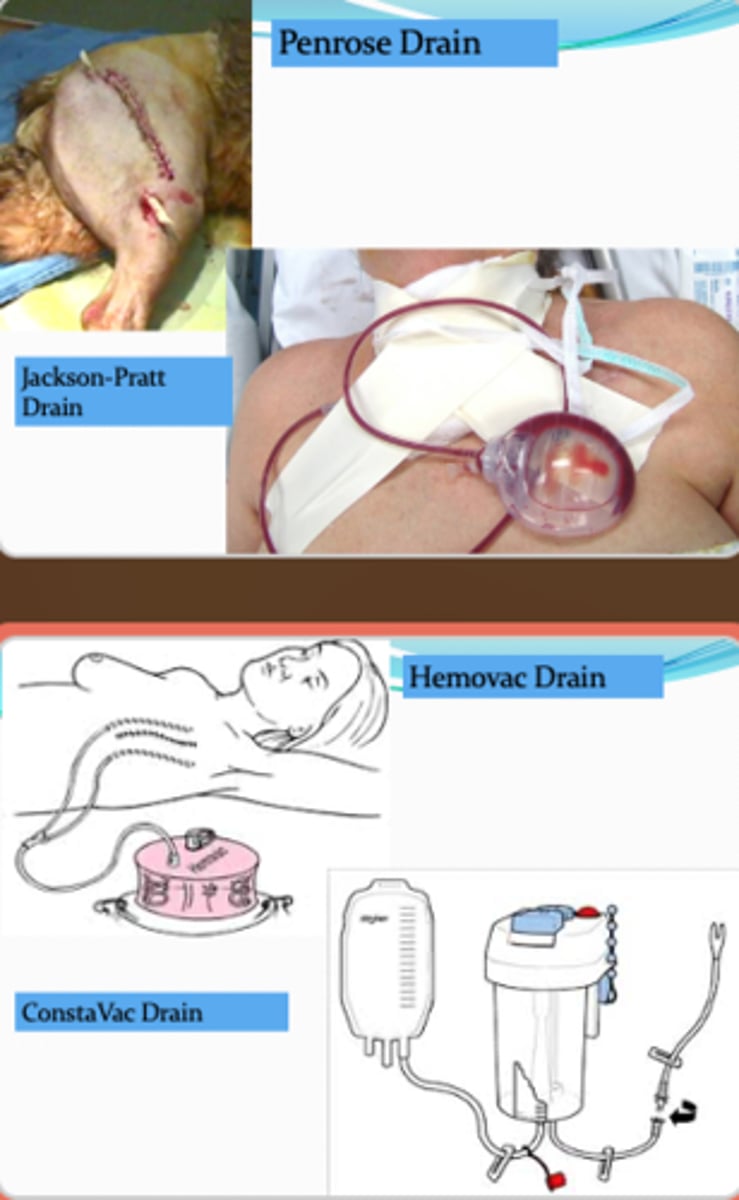
Post operative drain precautions.
- Secure drain before transfers and ambulation to avoid dislodging or occluding the drain.
o Safety pin
What is wound vac used for?
- Promotes tissue formation and removes infection from chronic and acute wounds.
Wound vac precautions
- Check seal.
- Avoid tensioning tube.
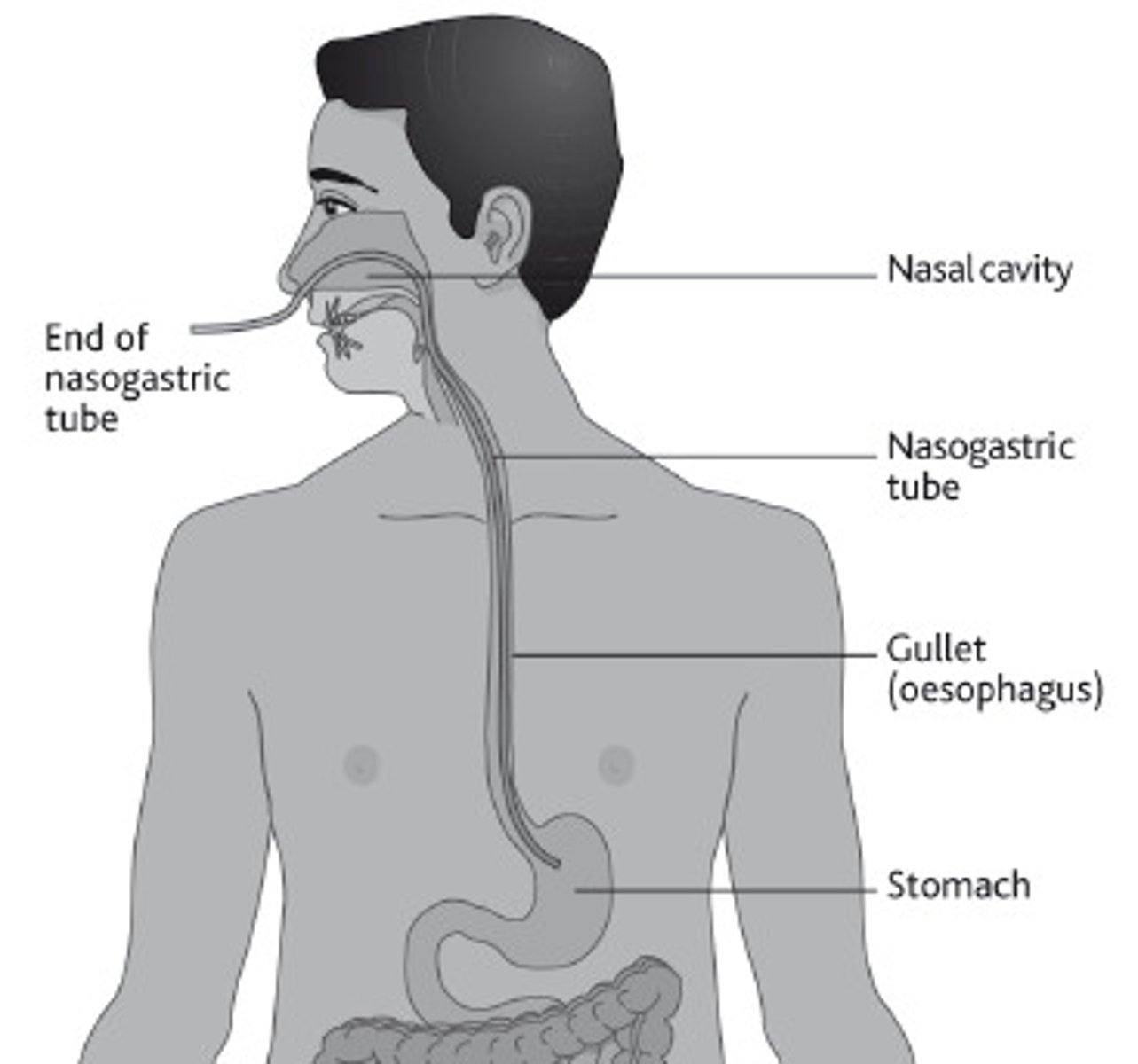
What are NG tubes used for?
- Used to decompress the stomach and empty stomach contents.
- Can be used for short-term feeding and drug administration.
NG tube precautions
- Do not allow tube to hang.
- Ask nursing to reposition tube if needed and disconnect from suction for ambulation.
What is a chest tube used for?
- To remove air or fluid from the lungs or mediastinal spaces after trauma or surgery
o Typically sutured and taped down to skin.
Chest tube precautions
- Chest trap must be maintained upright and below chest.
- Look for bubbles in the trap.
- Make sure tube is secure before ambulation and ask nursing to disconnect wall suction.
What is an endotracheal tube used for?
- Short term airway management for ventilation
- Tube can be inserted orally or nasal.
EET tube precautions
- Ensure tube is stabilized before transfer.
- Keep circuit tubing bellow so it does not empty into the airway.
What is a tracheostomy?
- Used for Long term airway ventilation.
- Allows access to upper airway and allows for easier suctioning.
Tracheostomy precautions
- Ensure tube is stable before transfers.
- Keep tubing below trachea, so it does not empty into airway.
What is the function of airway suctioning?
- Replaces the cough mechanism.
- Removes secretions.
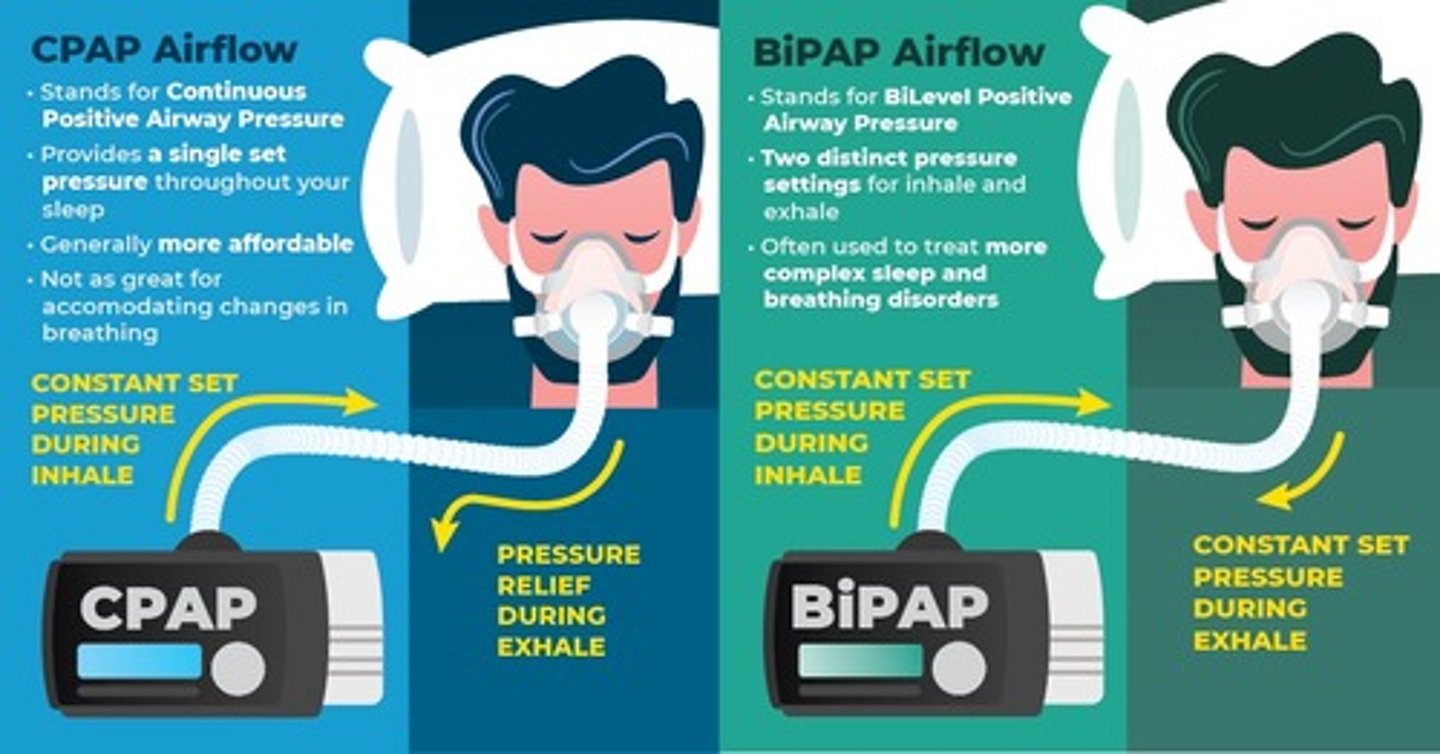
BiPAP vs CPAP
- BiPAP: blows air at high pressure for inhaling and low pressure for exhaling.
- CPAP: flow of air creates enough pressure when you inhale to keep airway open.
o Sleep apnea
Two types of airways equipmemt
- Nasal cannula (nares)
- Face mask
What does a non-rebreather indicate?
- Acute hypoxia
o Transplant
Dubhoff feeding tube.
- Introduced through nose to stomach.
- Used for short term feeding.
Dubhoff feeding tube precautions.
- Keep head out of bed more than 30 degrees with feeding.
Gastrostomy and jejunostomy tubes
- Placed through abdominal wall.
- Used for long term feeding
Gastrostomy and jejunostomy tube precautions
Ensure tube is stabilized prior to transfers.
Intra-aortic balloon pump function
- Decreased myocardial oxygen demand while increasing cardiac output.
- FEMORAL ARTERY
Intra-aortic balloon pump precautions
- Typically on bed rest
- Check lower limb circulation.
- NO HIP AND KNEE ROM
Ventricular assist device function
- Mechanical pump to assist the right and left ventricles in delivering blood to the body.
- Used for patients with heart failure or waiting for transplants.
Ventricular assist device precautions
- Closely monitor vital signs
- Keep hand pump near and know all emergency procedures.
Extracorpeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) details
- Used to treat respiratory failure.
- Bridge to recovery and transplants
Intracranial pressure monitor details
- Placed after head trauma to monitor to the pressure on the brains.
- Intraventricular catheter allows for drainage.
o Make sure catheter is at level of external auditory meatus.
ICP precautions
- Decrease activities that increase ICP
- Watch for signs of headaches, nausea, visual disturbances, or lethargic behavior.
Dialysis precautions
- Check with nursing to see in patient is stable.
- Ensure catheter and tubes are stable.
- NO HIP MOVEMENT WITH FEMORAL CATHERTER
Temporary pacemaker precautions (noninvasive vs transvenous)
- Noninvasive: NONE but do not drop
- Transvenous: bed rest and limit to 90 degrees shoulder flexion and abduction
ABCDEF bundle
- Awake
- Breathing coordination
- Choice of sedatives
- Delirium monitoring
- Early mobility and exercise
- FAMILY
Early mobility screen
- Response to verbale stimulus
- FIO2: less than 0.6
- PEEP: less than 10 cm h2o
- No sign of heart attack for 24 hours
- NO increased vasopressor infusion in two hours