NUR 242 Exam 2
1/225
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
226 Terms
List the parts of the chain of infection (in order):
- infectious agent
- reservoir
- portal of exit
- mode of transmission
- portal of entry
- susceptible host
infectious agent
something that contains bacteria, fungi, virus, parasite(s), or prion(s)
reservoir
the habitat of the infectious agent and is where it lives, grows, and reproduces itself or replicates
animate examples: people, insects, birds, animals
inanimate examples: contaminated soil, water, food, medical equipment, IV fluids, feces
portal of exit
the means by which the infectious agent can leave the reservoir
examples: any body orifice (ears, nose, or mouth), the skin, or blood or body fluids that leave the body through coughing, sneezing, etc.
mode of transmission
how a bacteria, virus, fungus, parasite, or prion moves from place to place
contact transmission
occurs when microorganisms move from an infected person to another person
droplet transmission
occurs when airborne droplets from the respiratory tract of a client travel through the air and into the mucosa of a host
can be from sneezing, coughing, singing, and talking
medical procedures like CPR and intubation can release droplets into the air
airborne transmission
occurs when small particulates move into the airspace of another person and carry infectious agents
these patients should be placed in a private room with negative air pressure (circulates the air outside of the building)
portal of entry
provides a place for an infectious agent to enter the individual so it can replicate or its toxin can act
examples: any body orifice or the skin
List factors that increase host susceptibility (8):
- age
- underlying disease (like HIV/AIDS)
- malignancy
- transplants
- medications (like immunosuppressants, antirejection meds, etc.)
- surgical procedures
- radiation therapy
- indwelling devices (like urinary catheters, central lines, etc.)
List the modes of transmission (5):
- contact
- droplet
- airborne
- vector
- vehicle
vehicle transmission
transmission of infectious agents to multiple individuals through a common source, such as contaminated food or water
example: food contaminated with e. coli
vector transmission
transmission of infectious agents through animals, such as an inset or rodent
examples: mosquitoes and rats
Who can be a susceptible host? (4)
- elderly
- infants
- immunocompromised
- anyone
What are the 2 types of contact transmission?
- direct
- indirect
direct contact
transmission occurs when microorganisms are directly moved from the infected person to another person without having a contaminated object or person between the 2
indirect contact
transmission occurs when microorganisms are moved from the infected person to another person with a contaminated object or person between the 2
List infections caused by airborne transmission (3):
- tuberculosis
- rubeola (measles)
- varicella (chickenpox)
List 2 infections spread through droplet transmission:
- influenza virus
- Bordetella pertussis
What type of transmission is the following an example of?
A patient has a draining, infected wound. The drainage touches a cut on the nurse's skin, leading to infection.
direct contact transmission
What type of transmission is the following an example of?
A patient who has a respiratory infection sneezes without covering the mouth and nose. A person a few feet away becomes infected because large mucus particles land in their mouth.
droplet transmission
What type of transmission is the following an example of?
A patient who coughed in their hand touches a door handle. Another person touches the same door handle and becomes infected with the same pathogen as the patient.
indirect contact transmission
What type of transmission is the following an example of?
A nurse enters a room where a patient who has a respirator infection was present for several hours. The nurse inhales small particles that remain in the air and develops an infection.
airborne transmission
What are the 3 types of body defenses?
- barriers (physical or chemical)
- nonspecific immunity
- specific immunity
What is the primary physical defense mechanism of the body?
the skin
List the 3 major functions of the skin:
- reduce loss of water
- protect against abrasion and microorganisms
- provide a permeable barrier against the environment
What things diminish skin integrity? (6)
- dry/cracked skin
- adhesive tape
- some chemicals
- unintentional injury
- intentional breaks in the skin
- insect bites
skin tear
a break or rip in the outer layers of the skin
the epidermis separates from the underlying tissues
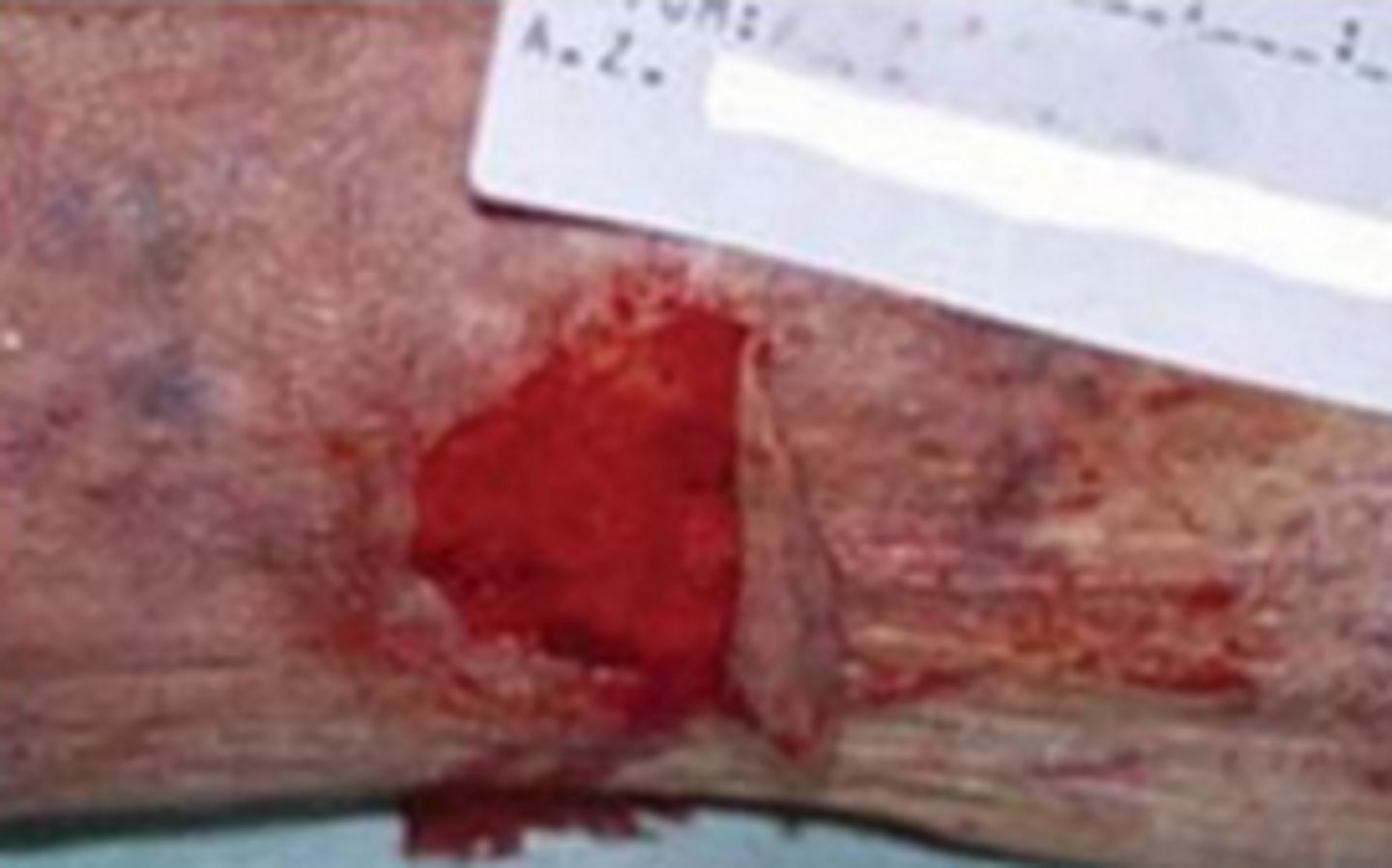
mucous membranes
the membranes that line body cavities that open to the outside of the body
examples: the linings of the mouth, nose, eyes, rectum, or genitals
How can the mucous membranes be damaged?
if it dries out, it can lead to cracking
can also be damaged by intentional or unintentional injury
cilia
short hair-like structures that help prevent particulates from entering the body
How does the GI act as a defense against infection?
it secretes acids and enzymes that can destroy or neutralize some foreign invaders
nonspecific immunity
neutrophils and macrophages and their work as phagocytes
both neutrophils and macrophages are released during the inflammatory response
phagocytes
eat and destroy microorganisms, thereby helping to protect the body from harm
specific immunity
refers to the work of antibodies (also called immunoglobulins) and lymphocytes
antibodies bind to infectious agents and call tot he white blood cells and complement to destroy them
inflammatory response
body's natural defense that is activated when the body is injured, when foreign substances are present, or when an infectious agent attacks
List the basic steps of inflammation:
- pattern receptors on cell surface recognize harmful stimuli
- inflammatory pathways activated
- inflammatory markers released
- inflammatory cells recruited
List infectious inflammatory response triggers:
- viruses
- bacteria
- other microorganisms (like fungi)
List noninfectious inflammatory response triggers:
- physical (like burns, frostbite, trauma, etc.)
- chemical (like fluoride, nickel, toxins, etc.)
- biological (like damaged cells)
- psychological (think excitement like when blushing)
List the stages of infection:
- incubation
- prodromal
- acute illness
- decline
- convalescence
incubation stage of infection
an infection enters the host and begins to multiply
asymptomatic
prodromal stage of infection
the patient begins having general "I don't feel good" symptoms
acute illness stage of infection
manifestations of the specific infectious disease process are obvious and may become severe
decline stage of infection
manifestations begin to wane as the degree of infectious disease decreases
convalescence stage of infection
the client returns to a normal or a "new normal" state of health
local infections
confined to one area of the body
can be treated with topical antibiotics and oral antibiotics
systemic infections
start as local infections and then spread to the bloodstream to infect the entire body
What should we look at with a WBC count in terms of diagnosing infection?
- overall count (normal is 5,000-10,000 per cubic mm)
- high WBC = infectious process likely
- low WBC = decreased ability to fight infections (also called neutropenia)
- differential (shows each individual type of WBC)
asepsis
the absence of infection/pathogens
hand hygiene
a broad term to cover any type of cleansing of the hands as in normal handwashing, alcohol-based hand sanitizers, using an antiseptic handwash or hand rub, and surgical hand antisepsis
medical asepsis
clean technique
practices that reduce the presence of disease-causing micro-organisms on surfaces
used in administration of: medications, enemas, tube feedings, and daily hygiene
surgical asepsis
includes techniques that ensures the sterility of items that will come in contact with the client, through use of equipment such as sterile gloves, in order to prevent pathogen transfer to the client
helps prevent surgical-site infections (SSIs)
sterile field, gown, gloves, mask, hats
used in: dressing changes, catheterizations, and surgical procedures
What are 6 important things to remember when preparing a sterile field?
- flat work surface that is 12-18 in from any walls or potentially contaminating objects (also close to the patient)
- check packaging to ensure no tears/holes/damage
- peel back the first flap away from the nurse's body
- peel the sides back one at a time
- peel the flap closest to the nurse's body
- the outer inch is contaminated so you want to add to the middle of the field
sterilization
involves cleaning instruments so that all micro-organisms, including bacterial spores, are eradicated
can be achieved with steam and then dry heat, ethylene oxide gas, or with chemicals
equipment must be cleaned before sterilization
standard precautions
infection prevention practices applied to all patients (whether or not they are known to have an infection)
used to protect self and others from blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions, nonintact skin, and mucous membranes
PPE can include: masks, gloves, face shield, gowns, glasses
contact precautions
at minimum: gown and gloves
What infections require contact precautions? (5)
- VRE
- C diff
- noroviruses
- any intestinal tract pathogen
- RSV
droplet precautions
minimum: mask
patient should wear a mask when leaving their room
What infectious agents require droplet precautions? (5)
- influenza virus
- adenovirus
- covid
- rhinovirus (common cold)
- mycoplasma pneumoniae
airborne precautions
patient should be in a negative pressure room
at minimum: N95 mask
protective isolation
used during approximately the first 100 days after a transplant
specific engineering and hospital designs that decrease the risk of environmental fungi to the client
no plants
health care-associated infections (HAIs)
infections that are acquired in a health care facility
What are the 4 major HAIs?
- central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs)
- catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs)
- surgical site infections (SSIs)
- ventilator-assisted pneumonias (VAPs)
infection control bundles
guidelines for practice that are bundled together to help prevent HAIs
multidrug-resistant infections
bacteria that are resistant to one or more classes of existing antimicrobials
What 3 ways to decrease the chance of transmitting MDROs?
- proper handwashing
- wearing gloves
- using contact precautions
What are 3 factors increasing the risk of infection?
- being in the healthcare environment
- having a medical device
- proximity to other patients
What should a nurse wear when administering medications to a client on contact precautions?
gloves and a gown
What should a nurse wear when performing a wound irrigation where splashing is expected in the facial area?
gown, gloves, and a face shield
What should a nurse wear when transporting a client who is on droplet precautions to the x-ray department?
mask (gloves based on facility rules)
What PPE item should be removed first?
gloves (technically gown comes off with gloves too)
What should a nurse wear when administering medications to a patient with a c diff infection?
gown and gloves (contact precautions)
hygiene
can be defined as actions and practices that decrease the spread or transmission of pathogens, thereby lessening the occurrence of illness
Langerhans cells
cells in the epidermis
role is to sense and kill pathogens that are found on the skin trying to enter the body
epidermis
outer layer of the skin
dermis
middle layer of the skin
provides skin with its strength and elasticity
hypodermis
aka subcutaneous layer
innermost layer of the skin
contains adipose tissue
acts as a cushion and stores fat
health promotion
viewed as facilitating the client's control over improving their general health
What are some factors that can affect hygiene? (5)
- culture
- religion
- developmental stage
- cognitive functioning
- personal preferences
What are some physiological considerations that can affect hygiene? (6)
- stroke
- spinal cord injury
- visual impairment
- bariatric challenges
- dementia
- amputation
What are hygiene considerations for a patient who had a stroke?
when dressing: the unaffected arm is used first to place clothing on the affected side
when undressing: the clothing is removed from the unaffected side first, then the affected side
What are hygiene considerations for a patient with a spinal cord injury?
these patients have an increased risk for the development of pressure injuries caused by hard surfaces when the skin is wet
bariatric clients
clients of increased weight or BMI
increased BMI causes distinctive physiological changes that affect skin integrity such as extremely deep skin folds, especially in the abdominal region
areas that are susceptible to deep skin folds include the groin, glutes, under the breasts, behind the knees, elbows, ankles, and the neck
foot care consideration:
clients who are at a higher risk for infection should have their feet more closely monitored as infections can cause serious foot problems
nail care consideration:
longer nail length has been shown to conceal a greater number of germs compared to shorter nail length
complete bed bath
bath administered to totally dependent patient in bed
the joint commission (TJC)
established in 1951
evolved as an impartial national organization that accredits hospitals and other health care facilities based on their safety performance, policy, procedures, practice, and outcomes
national patient safety goals (NPSG) and standards of compliance
initiated in 2002 by TJC
identify established relevant safety practices health care institutions should accomplish
since most health care organizations embrace and routinely practice these goals, they are cataloged into a register of adopted "standards of compliance" that must be met on a consistent basis
What are examples of patient identifiers?
- name
- DOB
- designated hospital number (NOT room number)
alarm fatigue
sensory overload from noise pollution created in part by the numerous distress alerts
Who should be screened for suicide?
- all patients who may be at risk for suicide
- patients with intentions of suicide
- all patients 12 and older whose primary admitting diagnosis is for a behavioral health condition
adverse event
any event that is not consistent with the desired or normal operation
What is a "time-out" in regard to surgery?
a pause in all personnel activities within the operating or procedure room to ensure correct client, site, and procedure
What are the components of transforming care at the bedside?
- have nurses spend 70% of their time at the bedside performing direct client care
- strengthen management through leadership development programs
- implement a rapid response team for the facility's medical and surgical units
- create frameworks for standardized communication
What does "ISBARR" stand for?
identity
situation
background
assessment
recommendation
read back
near miss
a potential error or event or circumstance that could have caused harm but was caught and avoided
patient safety event
an unexpected event or circumstance that occurred without injury to the patient
sentinel event
a critical, unexpected adverse event that caused severe physical or psychological harm to a patient, including death and dismemberment; permanent injury; or severe, temporary injury
root-cause-analysis (RCA)
the review process used to probe potential or actual errors
errors are reviewed and a determination is made as to whether human error or systems failure led to the error
also establishes a corrective action plan to address the problem or system error
List some barriers to event and near miss reporting (7):
- fear of repercussions
- lack of time to write the report
- unclear facility policies and standards
- bullying
- insufficient education and training
- lack of understanding of the roles and responsibilities of team members
- favoritism and influence of some employees