Major Brain Structures & functions
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
3 primary sulci
sagittal sulcus: logitudinal fissure
central sulcus: sulcus of Rolando
lateral sulcus: Sylvian fissure
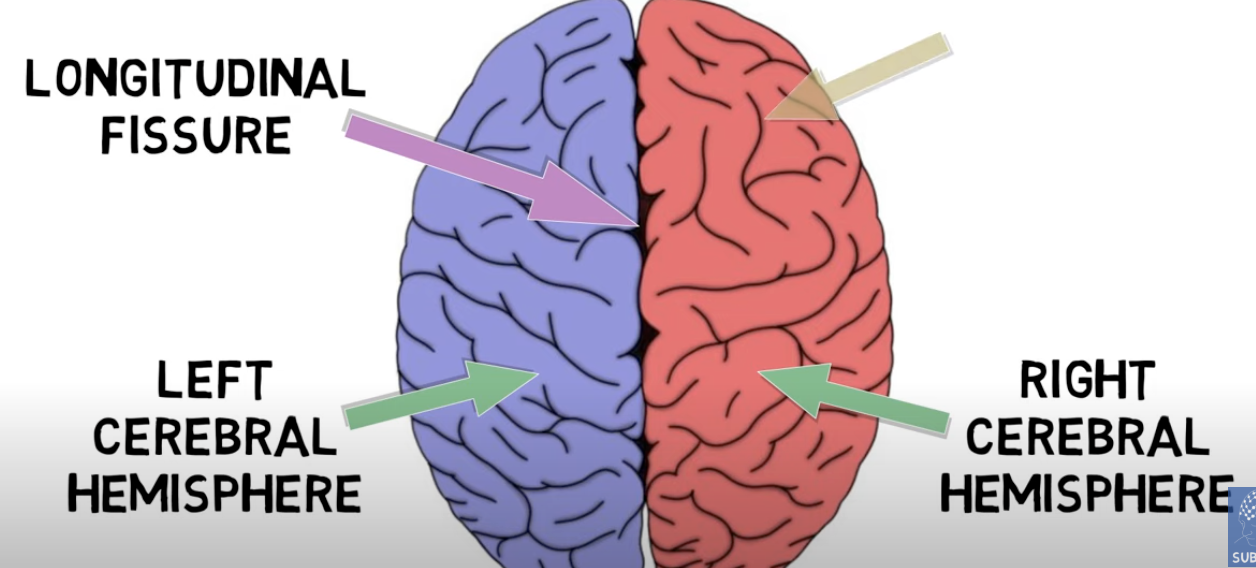
longitudinal fissure / sagittal sulcus
crevice that divides the brain into 2 cerebral hemispheres
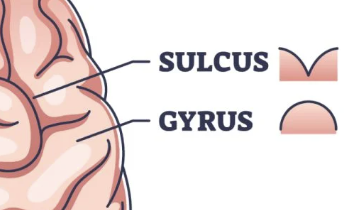
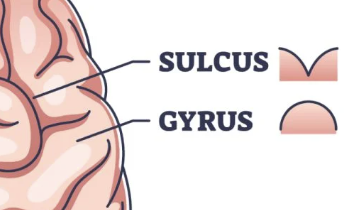
sulci
the sunken, concave furrows of the cerebral cortex (i.e., outside layer of the brain)
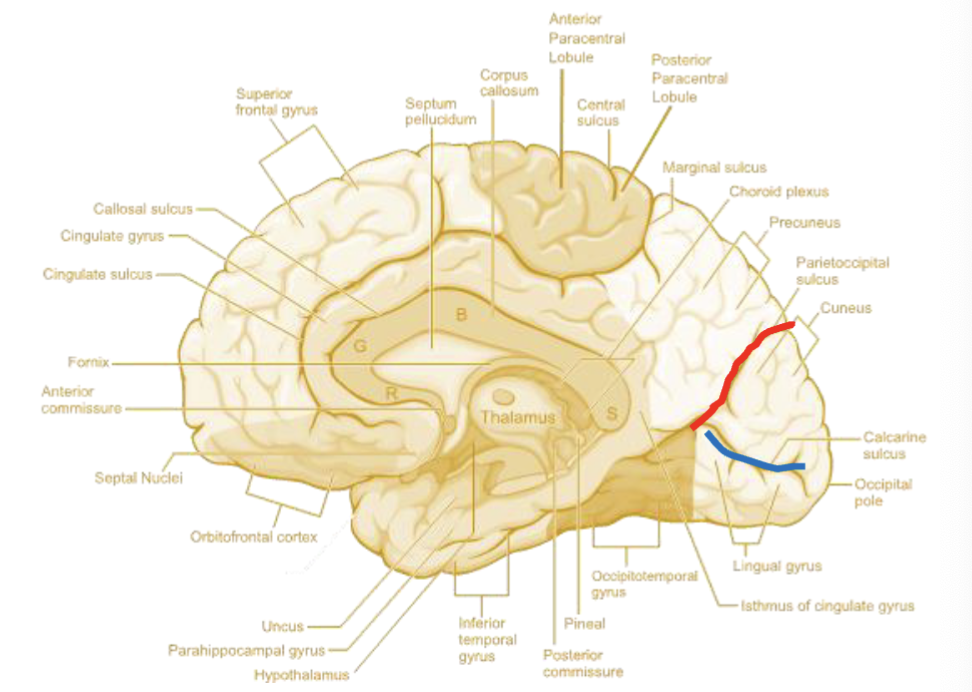
calcarine sulcus
divides primary visual cortex into:
cuneus
lingual gyrus
gyri
the convex ridges of the folds of the outside layer of the brain (i.e., cerebral cortex)
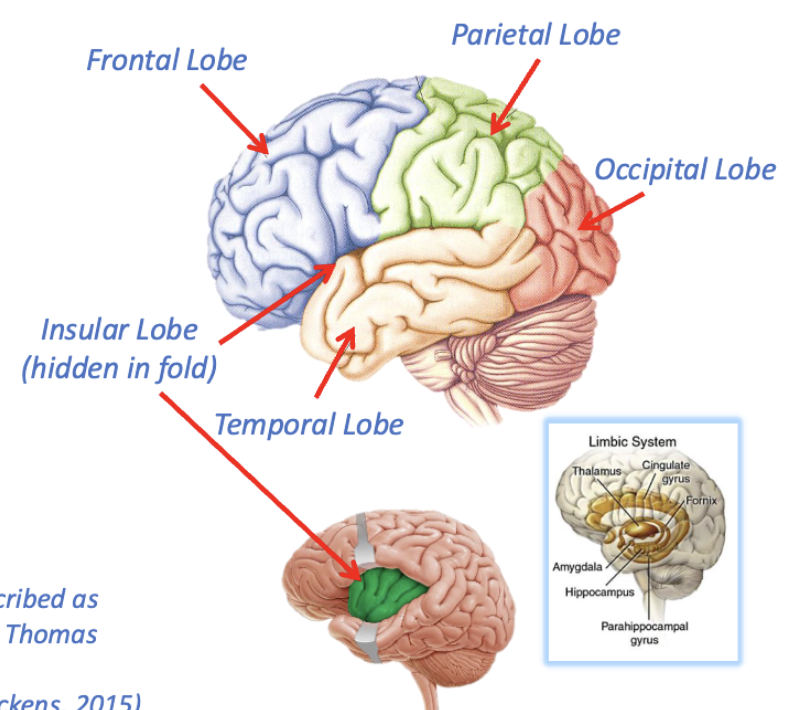
landmarks of the cerebrum
5 lobes
limbic system/lobe
subcortical structures
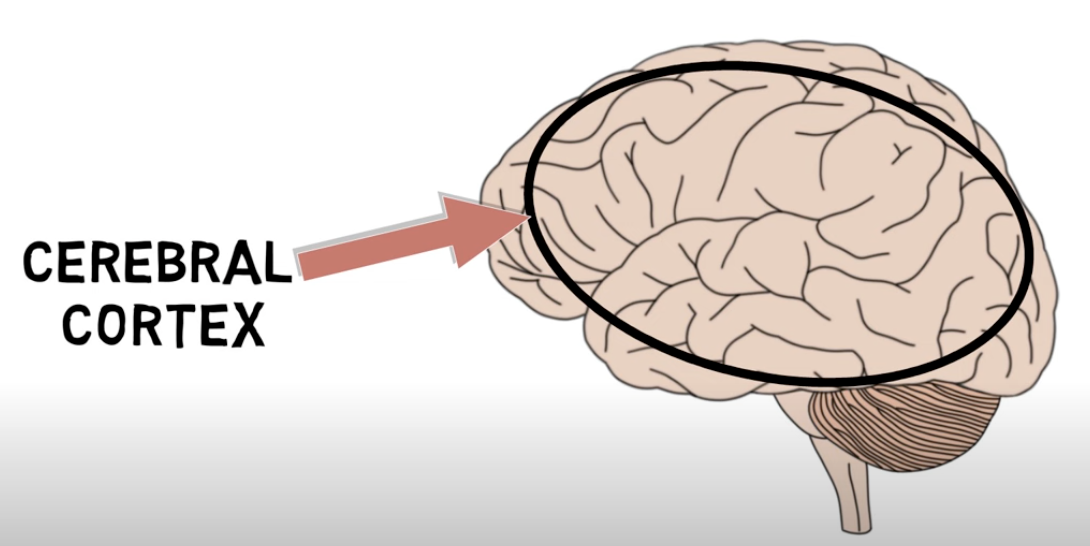
Cerebral cortex
where important lobes and association areas are located; the outside layer of brain
the 5 lobes
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, insular
the frontal lobe is located—
at the front of the brain, anterior to central sulcus (sulcus of Rolando)
superior to lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure)
the frontal lobe contains—
motor cortex (including primary motor cortex)
prefrontal cortex
frontal lobe functions:
head & body movement (motor)
decision-making, planning, pursuit of long-term goals, impulse control (prefrontal)
executive functions
working memory
social skills & personality
speech production (Broca’s)
Broca’s area is located in—
Frontal lobe, usually leftside brain
Cental sulcus
fold that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe
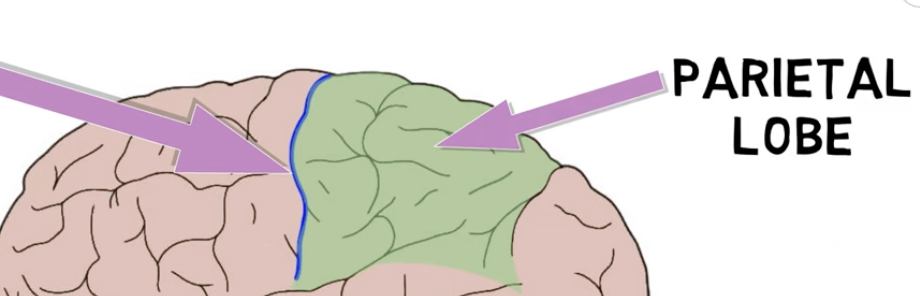
the parietal lobe is located—
at the top of the brain
posterior to central sulcus (sulcus of Rolando)
superior to lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure)
parietal lobe functions:
Multimodal sensory center
primary somatosensory cortex:
processing somatosensory information (sensations from body)
touch
thermal
visual-spatial processing/ proprioception
superior parietal lobe: attention mechanisms
inferior parietal lobe: language
verbal working memory
word reading & comprehension (phoneme-grapheme corr.), writing, number manipulation, semantic processing
association areas (“where”)
the occipital lobe is located—
at the very back of the brain
occipital lobe functions:
main area for visual processing (primary visual cortex)
association areas (“what”)
where is the primary somatosensory cortex located?
parietal lobe
where is the primary visual cortex located?
occipital lobe
the temporal lobe is located—
on the sides of the brain, inferior to lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure)
temporal lobe functions:
PRIMARY LANGUAGE AREA
hearing (primary auditory cortex)
object & face recognition
learning
hippocampus: short & longterm memory
language reception & comprehension
processing of colors, shapes, numbers
association areas (“What”)
the primary auditory cortex is located—
in the temporal lobe
Wernicke's area is located—
between the temporal & parietal lobes
Wernicke’s area functions:
language comprehension
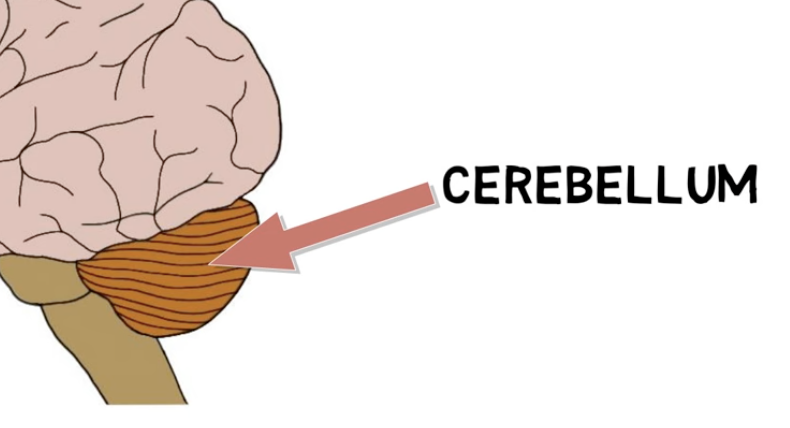
the cerebellum functions:
major roles in movement
motor coordination & control
balance & posture
fine-tuning of voluntary movements
movement-related learning
the brainstem is divided into:
midbrain, pons, medulla
medulla (oblongata) is located—
just above the spinal cord, at the bottom of the brain stem
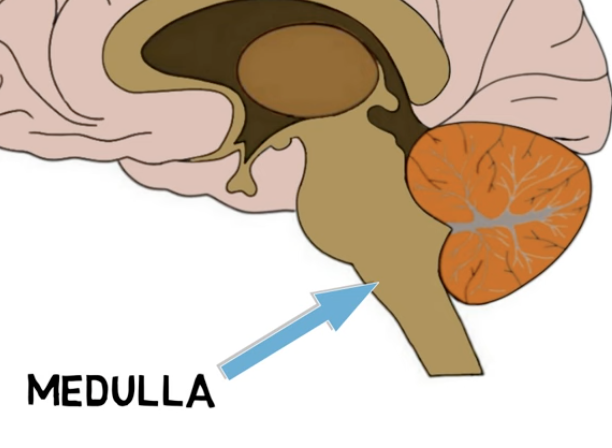
medulla functions:
regulation of vital functions (e.g., cardiovascular, repiratory)
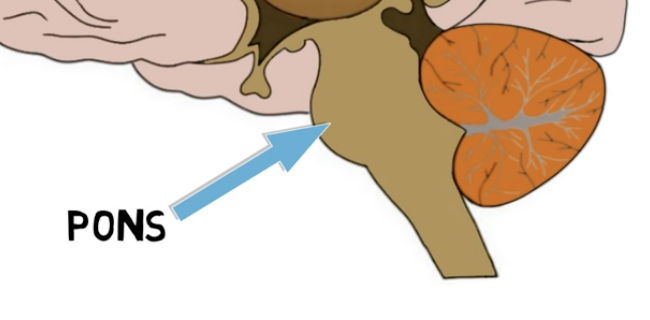
pons functions:
pathways that carry info to and from cerebellum
houses a group of nerves involved in sensory and motor functions of head & face (cranial nerves)
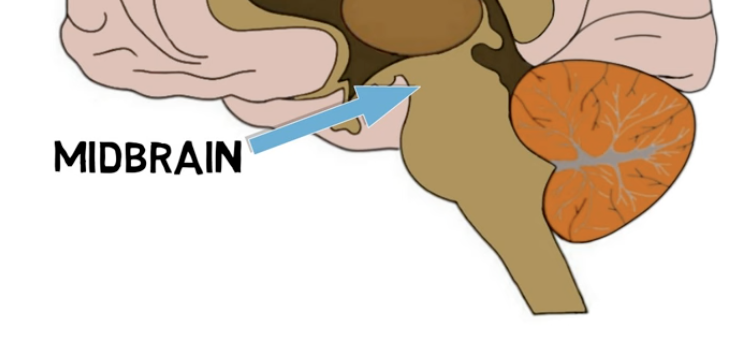
midbrain functions:
contain 2 largest dopamine-producing areas in brain
substantia nigra: dopamine neurons for movement (damage= Parkinson’s)
ventral tegmental area (VTA): dopamine neurons extending to various parts of brain
ㄴ⭐ nucleus accumbens: VTA-nucleus accumbens pathway is crucial for rewarding experiences (food, sex, addictive drugs)
substantia nigra & nucleus accumbens are part of
basal ganglia
the thalamus is located—
above the brainstem
basal ganglia functions:
movement
habit formation
reward processing
etc.
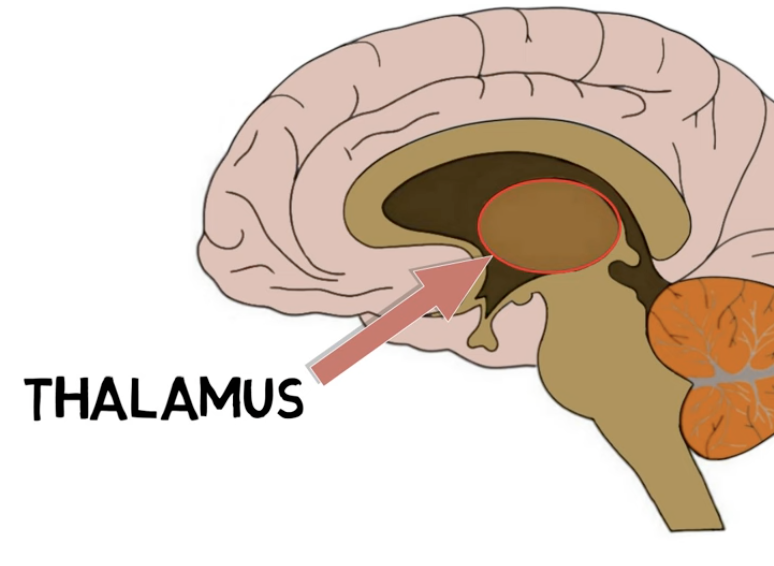
thalamus functions:
relay station transmitting neural impulses from different receptors to the cerebral cortex
ex)
all sensory info except olfaction ➡ specialized nuclei of thalamus ➡ cortex
pineal gland is located—
posterior to the thalamus
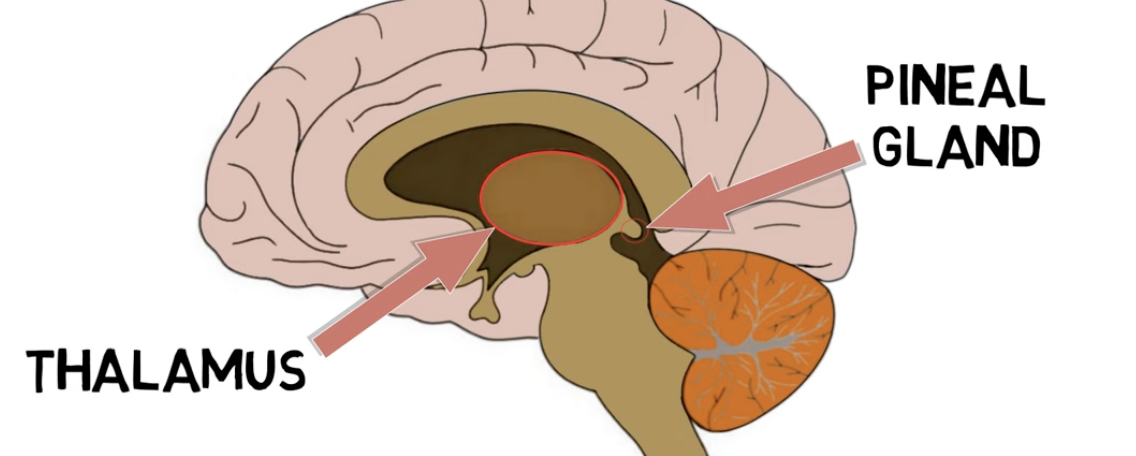
pineal gland functions:
secretes melatonin hormone
ㄴ melatonin: secreted mostly during darkness; regulates circadian rhythms
hypothalamus is located—
right below the thalamus
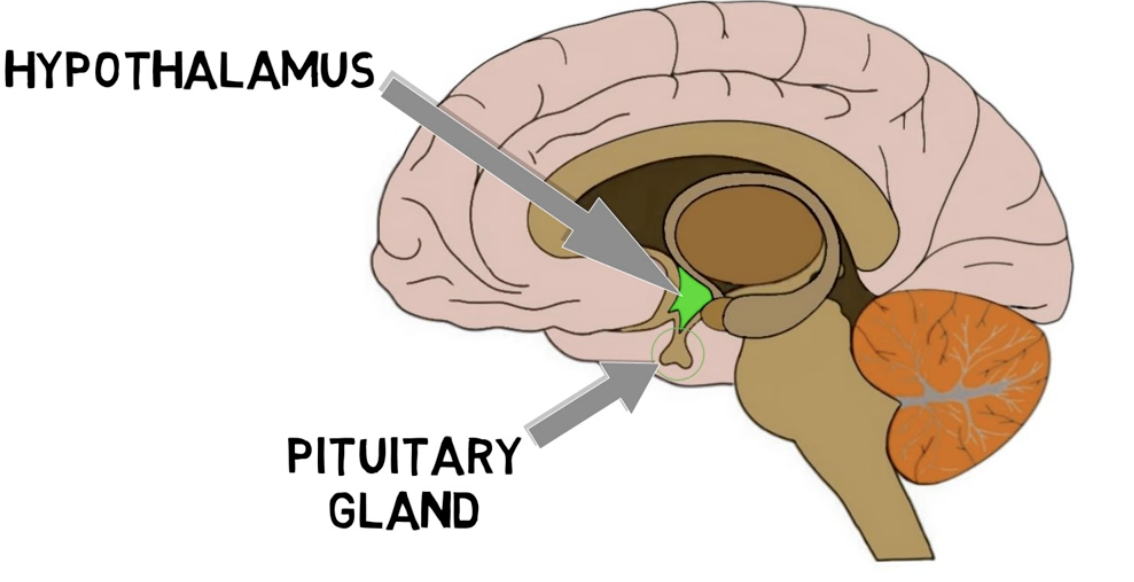
hypothalamus functions:
homeostasis 유지하느라 ㅈㄴ 일이 많은 애임
regulates:
thirst & drinking bx
hunger & feeding
body temp
stress responses
circadian rhythms
+++++
sends signals to 바로 밑 pituitary gland, to produce hormones
growth
thyroid-stimulating
follicle-stimulating
luteinizing hormone
++++++
makes oxytocin & vasopressin and sends them to pituitary gland to secrete in bloodstream
the hippocampus is located—
in the temporal lobe
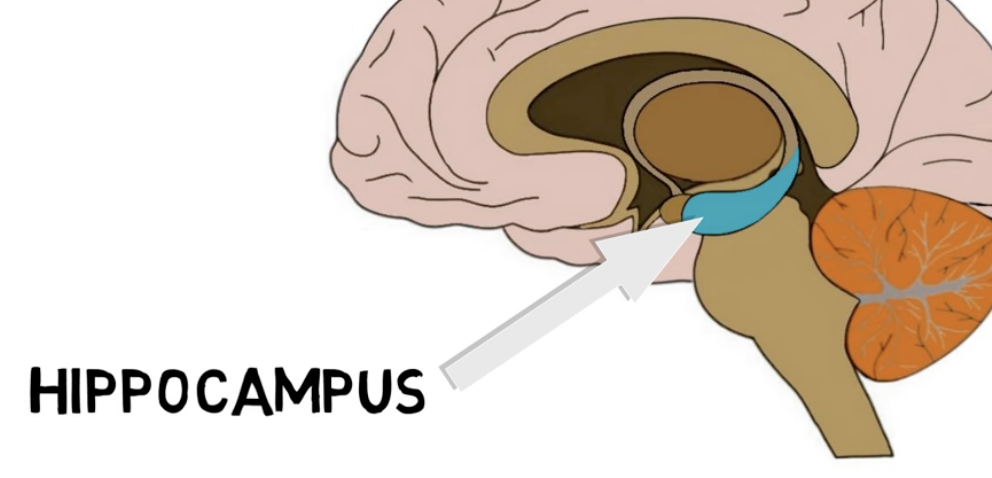
hippocampus functions:
memory, especially STM ➡ LTM tranfer
amygdala is located—
adjacent to the hippocampus
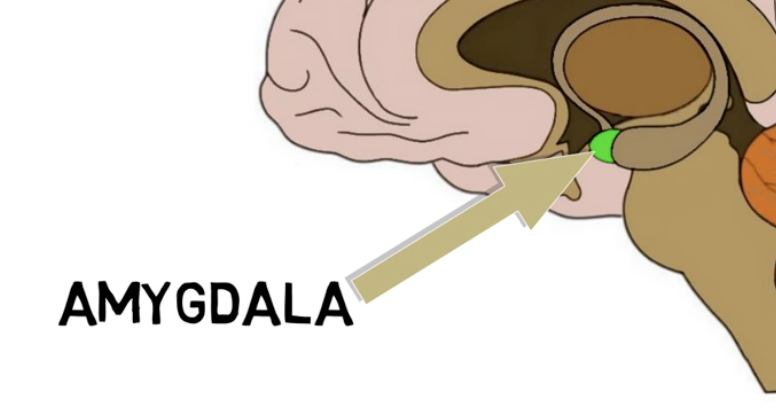
amygdala functions:
processing fear
fight/flight rsponse
***also involved in positive emotions like pleasure
corpus callosum functions:
connects left & right cerebral hemispheres (sides of the brain), enabling cross-communication
largest bundle of axons in the brain
cerebral ventricles
hollow cavities in the brain, that have special membranes producing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) functions:
surrounds brain in a protective layer
reduces strain forces (gravity, inertia) by suspending the brain
removes waste products from brain
helps regulate extracellular environment of neurons
Ventral stream
“what” pathway
Dorsal stream
“where” pathway