What is Science + Atoms and Periodic Properties
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
The property of mass is a measure of how heavy an object is.
False
A referent is a familiar object one can use to describe the property of an object
True
Measurement information used to describe something is called data.
True
A 100-g piece of iron has twice the volume of a 50-g piece of iron.
True
The mass of 1000 cm3(cubed) of water is a kilogram.
True
The density of a 100-g piece of iron is twice as great as the density of a 50-g piece of iron.
False
A controlled experiment has all variables held constant.
False
The symbol ,u has the meaning of "is proportional to."
True
A theory is a hypothesis that has been shown to be correct by many experiments.
False
The symbol "A" is used to refer to an object's density.
False
Equations are used to
All of the above
Which of the following is not a SI unit of the property it measures?
volume-liter
In the text, the equation V=tk is used to describe the relationship between the volume of a gas tank and the time required to fill it. The symbol "k"
is the proportionality constant.
The English unit of volume closest in size to a liter is
quart.
If a cube of Jell-o is cut into two pieces, what total property of the new pieces change?
surface area
When something cannot be directly observed, it can be represented by a
model.
Claims that appear to be pseudoscience should be
tested experimentally.
The property of volume is a measure of
how much space the object occupies.
In the equation A = r² (pi) is a
numerical constant.
The re-creation of an event by comparing two situations in which all the factors are identical except one is called a
controlled experiment.
A tentative scientific explanation which may or may not be rejected upon further experimentation is called
hypothesis.
A statement describing a relationship that is observed in nature to occur consistently time after time is a (an)
scientific law.
Imagine a 10-g chunk of aluminum (r=2.7g/cm3) and 10-g chunk of iron (r+7.9g/cm3). Which of the following is true?
The chunk of iron is smaller than the chunk of aluminum.
A cube that measures 2 cm on each side has a surface area to volume ratio of
3
A scheme of thought that has survived a test of detailed examination for long periods of time is a (an)
scientific theory.
The most recently developed scientific theory is the
plate tectonic theory.
One of the basic differences between science and a pseudoscience is the lack of
valid and reliable experimental studies.
A tentative thought- or experiment-derived explanation is known as a (an)
hypothesis.
An event with two situations with all the influencing factors identical except one is a (an)
controlled experiment.
An experimental situation used as the basis of comparison is the
control group.
John Dalton reasoned that atoms exist from the evidence that
elements always combined in certain fixed ratios.
The atomic number of an element is the total number of
Protons
Neutral atoms of a given element have the same
All the choices are correct.
Atoms electrically excited in an incandescent gas
emit characteristic frequencies of light.
Noting that the spectra of glowing hydrogen always shows the same pattern was evidence supporting the idea that
electrons could only gain or lose specific amounts of energy in hydrogen atoms.
The modern quantum mechanical model of the atom differs from the classical Bohr model in that it
considers the electron to behave as a wave.
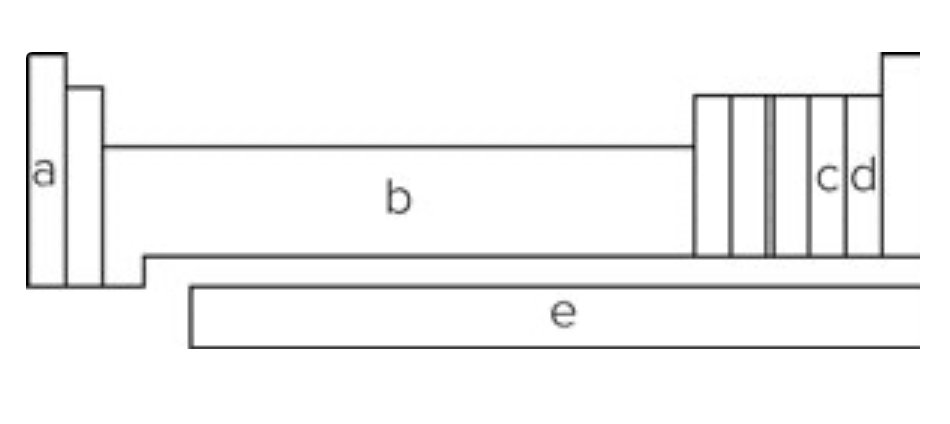
Using the diagram showing a periodic table, elements in the block labeled "b" are called
transition metals.
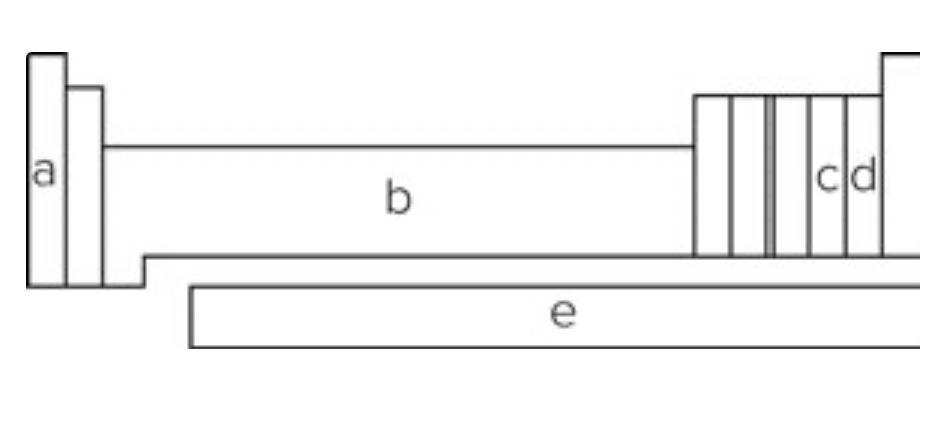
Using the diagram showing a periodic table, elements in which block are most likely to form ions with -1 charge?
d
The mass of any given isotope is based on the mass of
an isotope of carbon, which is assigned a mass of 12.
The isotopes of a given element always have
different masses and the same chemical behavior.
If you want to know the number of neutrons in an atom of a given element, you would
subtract the atomic number from the mass number.
Niels Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom
All the choices are correct
According to the quantum mechanical model, electrons exist in
orbitals
The quantum mechanical model of the atom differs from the Bohr model in that it
considers the electron as a wave
The proposal that matter, like light, exhibits wavelike behavior was
verified in diffraction experiments with a beam of electrons.
The electron was discovered through experiments with
electricity
Thomson was convinced that he had discovered a subatomic particle, the electron, from the evidence that
the charge-to-mass ratio was the same for all materials
Two isotopes of the same element have
the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons
If you want to know the number of neutrons in an atom of a given element, you
subtract the atomic number from the mass number
The existence of a tiny massive, and positively charged nucleus was deduced from the observation that
some alpha particles were deflected by metal foil
According to Rutherford’s calculations, the volume of an atom is mostly
empty space
Hydrogen, with its one electron, produces a line spectrum in the visible light range with
Four color lines
According to the Bohr model, an electron gains or loses energy only by
jumping from one allowed orbit to another
When an electron in a hydrogen atom jumps from an orbit farther from the nucleus to an orbit closer to the nucleus, it
emits a single photon with an energy equal to the energy difference of two orbits
The space in which it’s is probable that an electron will be found is described by an
orbital
The quantum mechanics model of the atom is based on
The quants, or measured amounts of energy of a moving particle
An ion is an atom that has additional
electrons
How many outer shell electrons do atoms represented on the far right-handed side of the periodic table have?
8
The Bohr model of the atom described the energy state of electrons with one quantum number. The quantum mechanics model uses how many quantum numbers to describe the energy state of an electron
four