BIO 101 Chapter 2A Obj jc
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Matter
anything that has mass and takes up space
Energy
Ability to do work or create a change
Elements
pure substance consisting of atoms, cannot be broken down into other elements by chemical means
Three sub-atomic particles
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
Amount of elements essential to life
25
Atoms
smallest piece of an element that retains the characteristics of the element, individual building blocks of elements
Electron: charge, mass, location
Sub-atomic particle with a small mass (~0), negative charge, located surrounding the nucleus
Proton: charge, mass, location
Sub-atomic particle with a larger mass (1), positive charge, located in the nucleus
Neutron: charge, mass, location
Sub-atomic particle with a larger mass (1), no charge, located in the nucleus
Atomic Number
number of protons in an atom
Mass Number
protons and neutrons in an atom
Ions
Atom or element that gained or lost electrons
Isotopes
Alternate form of an element based on number of neutrons
Atomic Weight
Average mass of all the different types of that specific element
Radioactive Isotope
unstable isotopes that emit radiation as their nucleus decays
Molecules
Two or more combined atoms
Compound
two or more different elements that are chemically combined in a fixed ratio
Orbitals
a 3 dimensional region around an atom’s nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found
Amount of electrons that can be held in each orbital
2
Energy shells
Group of electron orbitals that share the same energy level
Amount of electrons that can be held in each energy shell
Maximum number of electrons in an energy shell = 2n^2
Position of an electron in relation to energy level
Amount of energy increases as you move away from the nucleus
Valence Shell
Outermost shell that has electrons
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom
Electronegativity
Ability to attract electrons, affinity for electrons
Chemical Bonds
Connection between atoms
Three types of chemical bonds in living systems
Covalent, ionic, hydrogen
Covalent Bond definition
Sharing of electrons
Ionic Bond definition
Transfer of electrons
Covalent bond: location and relative strength
intramolecular, stronger
Ionic bond: location and relative strength
intramolecular, stronger
Hydrogen bond: location and relative strength
intermolecular, weaker
Polar Covalent Bond
Unequal sharing of electrons
Non-Polar Covalent Bond
Equal sharing of electrons
What are the five life-supporting properties of water?
cohesive and adhesive
many substances dissolve in water
water regulates temperature
water expands as it freezes
water participates in life's chemical reactions
Cohesion
Attraction between water molecules
Adhesion
Attraction of water molecules with other substances
Solvent
Chemical in which other substances dissolve
Solute
Chemical that dissolves in a solvent
Solution
Mixture of solute and solvent
Hydrophobic
Water fearing, nonpolar substances
Hydrophilic
Water loving, polar or charged substances
Chemical Reactions
Breaking and forming of bonds
Reactants
Starting material in a chemical reaction
Products
Result of a chemical reaction
Balanced equation of photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O = C6H12O6 + 6O2
pH
Power of hydrogen, H+
pH Scale
Measurement of how acidic or basic a solution is, measurement of H+ concentration/hydrogen
Equation for disassociation of water
H20 = OH^- + H^+
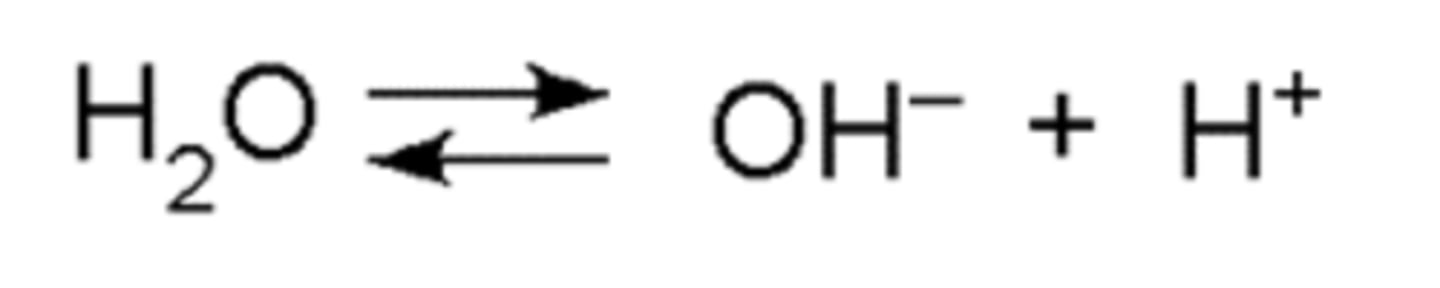
Acid
Molecule that adds H^+, hydrogen ions
Base
Molecule that adds OH^-, hydroxide ions