An Overview of Body Systems
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Systems studied in Gross Anatomy
Skeletal, Muscular, Cardiovascular, Lymphatic, Nervous, Digestive, Respiratory, Urinary, and Reproductive
Skeletal System
body's framework, composed of bones (including cartilage, ligaments, and tendons)
What does the skeletal system provide?
support, protection, and enables movement while also storing minerals and producing blood cells
The two main parts of the skeletal system
axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton
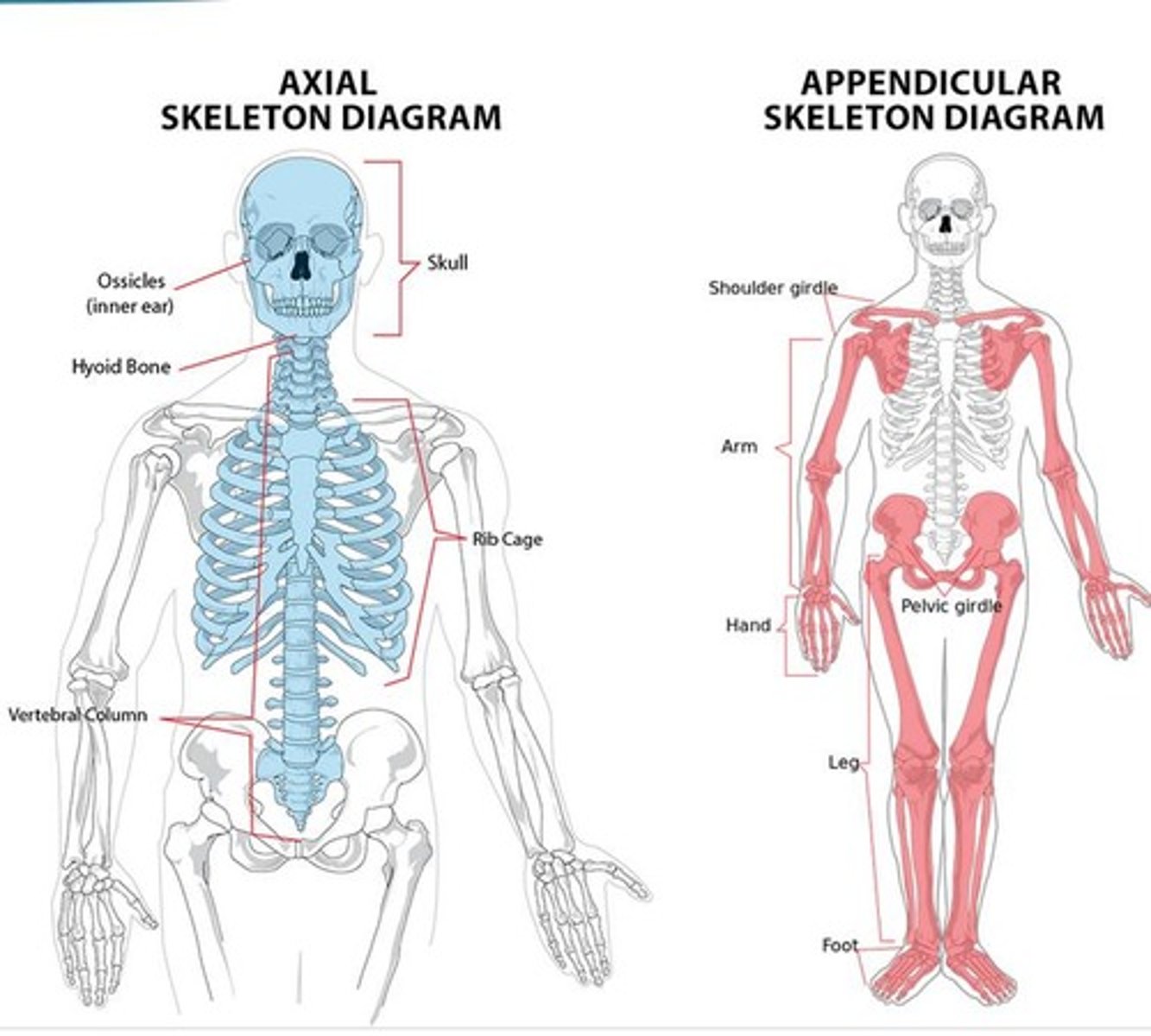
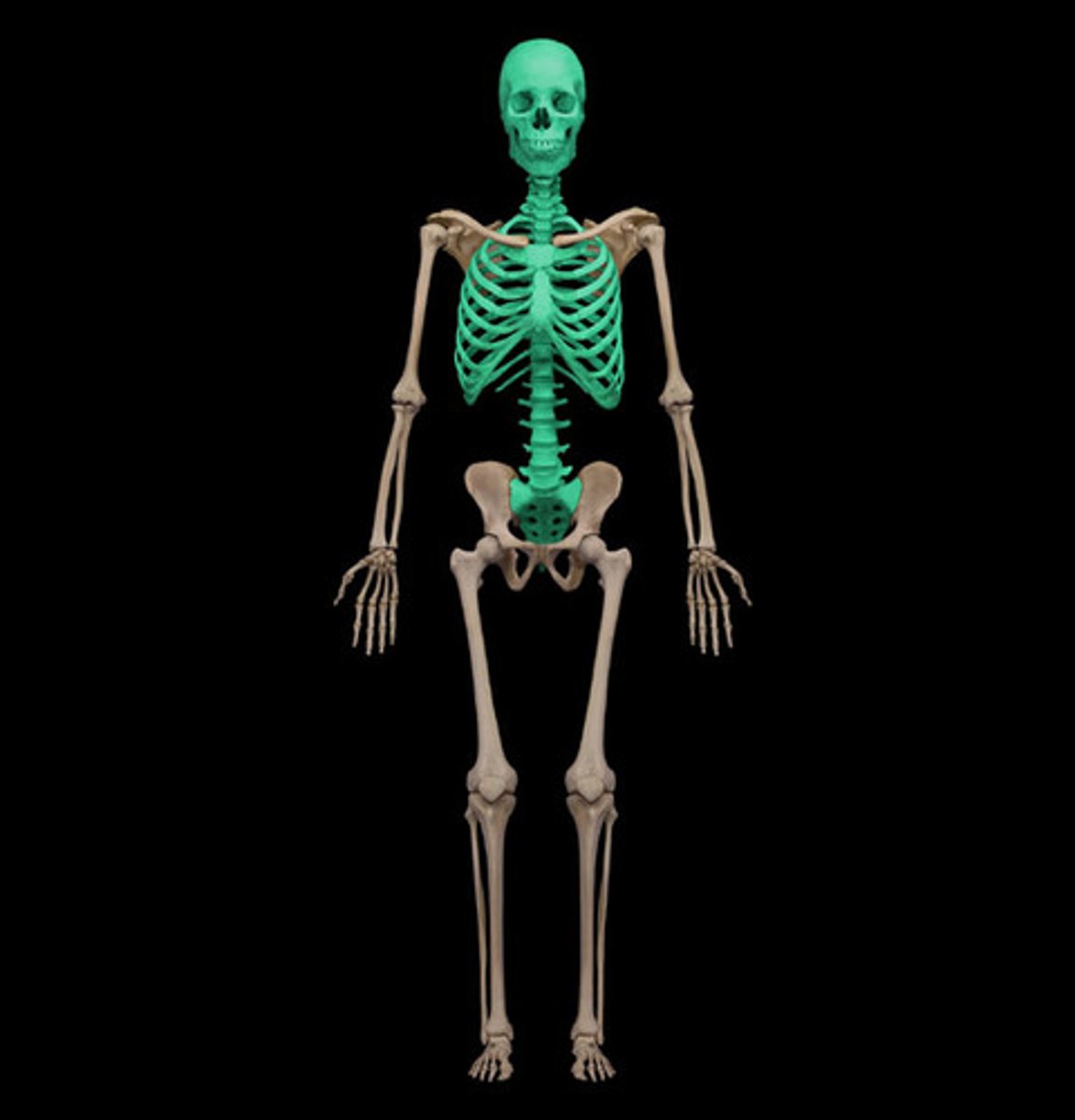
Axial skeleton
includes skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum - forming the central axis of the body
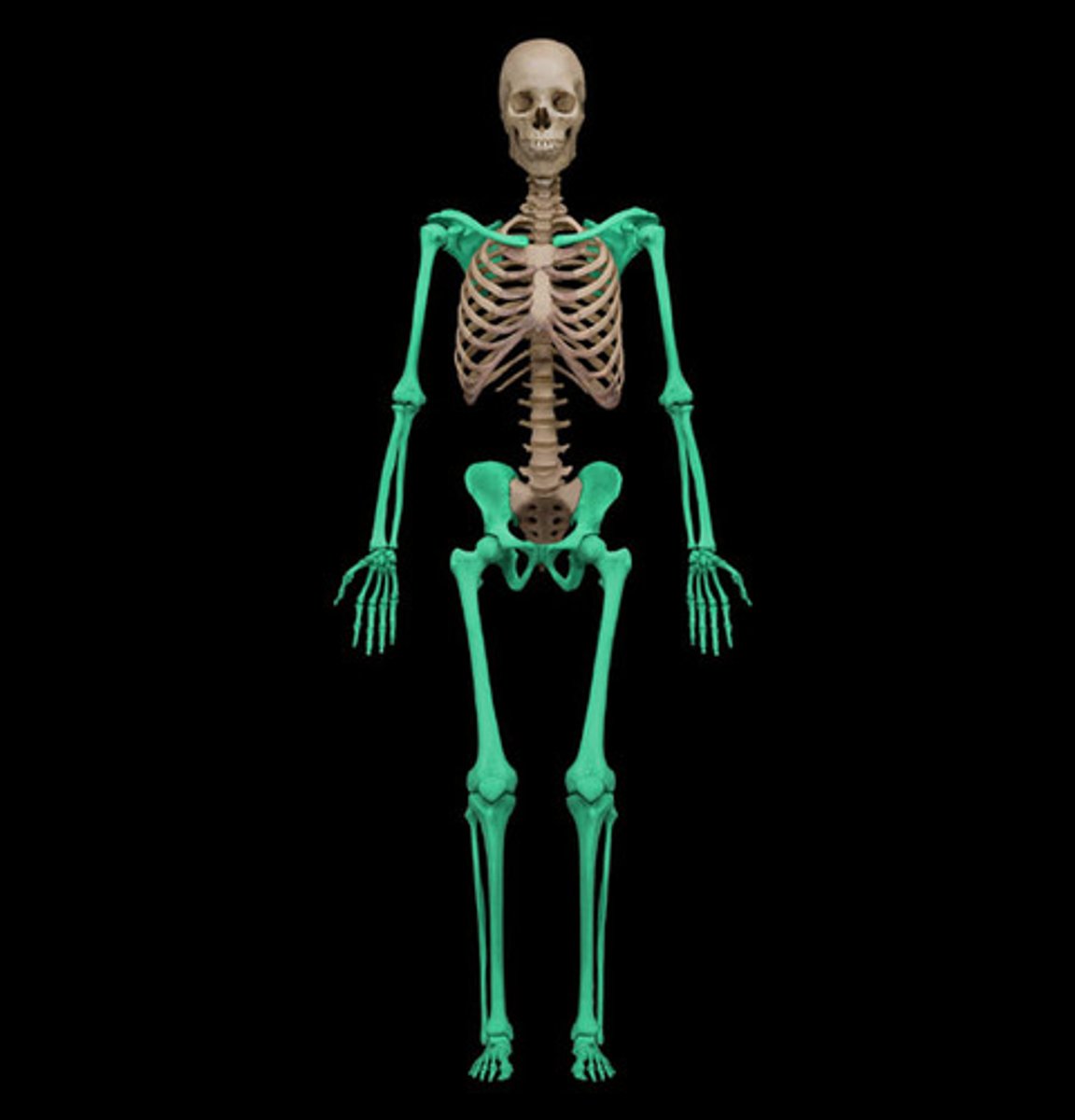
Appendicular skeleton
includes the bones of the limbs (arms and legs) and the girdles (pelvic and pectoral) that attach the limbs to the axial skeleton
Skeletal system main components
Bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, joints
Bones
206 bones in the adult human body - can be classified as different types (long, short, flat, sesamoid, and irregular) and tissues (compact or spongy bone tissue)
Cartilage
a flexible connective tissue that cushions joints and provides support in areas like the nost and ear
Ligaments
strong, fibrous tissues that connect bone to each other stabilizing joints
Tendons
strong, fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones, enabling movement
Joints
areas where two or more bones meet allowing for different types of movements
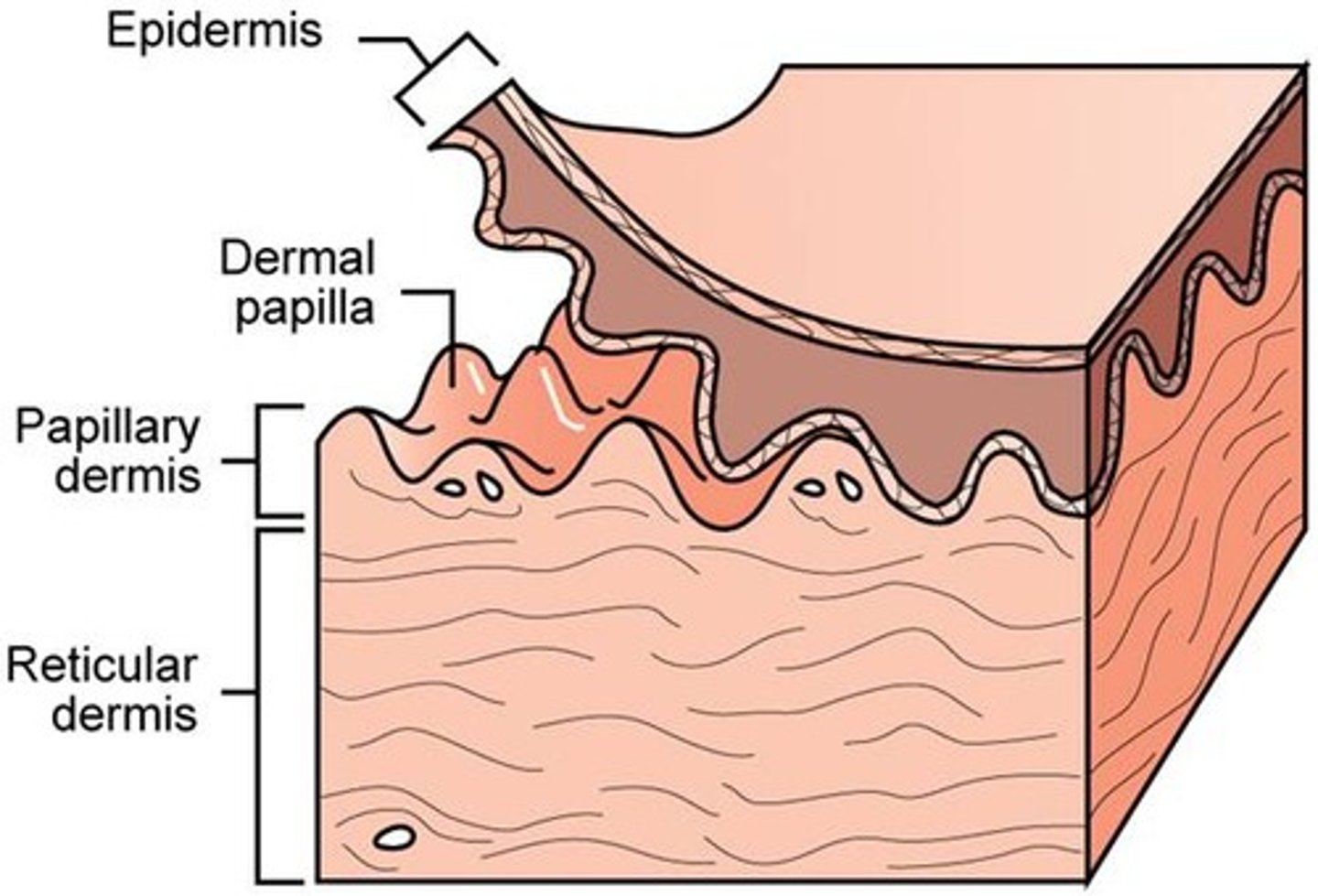
Skin
largest organ in the body, consisting of epidermis and dermis
Epidermis
outer layer that is avascular and varies in thickness
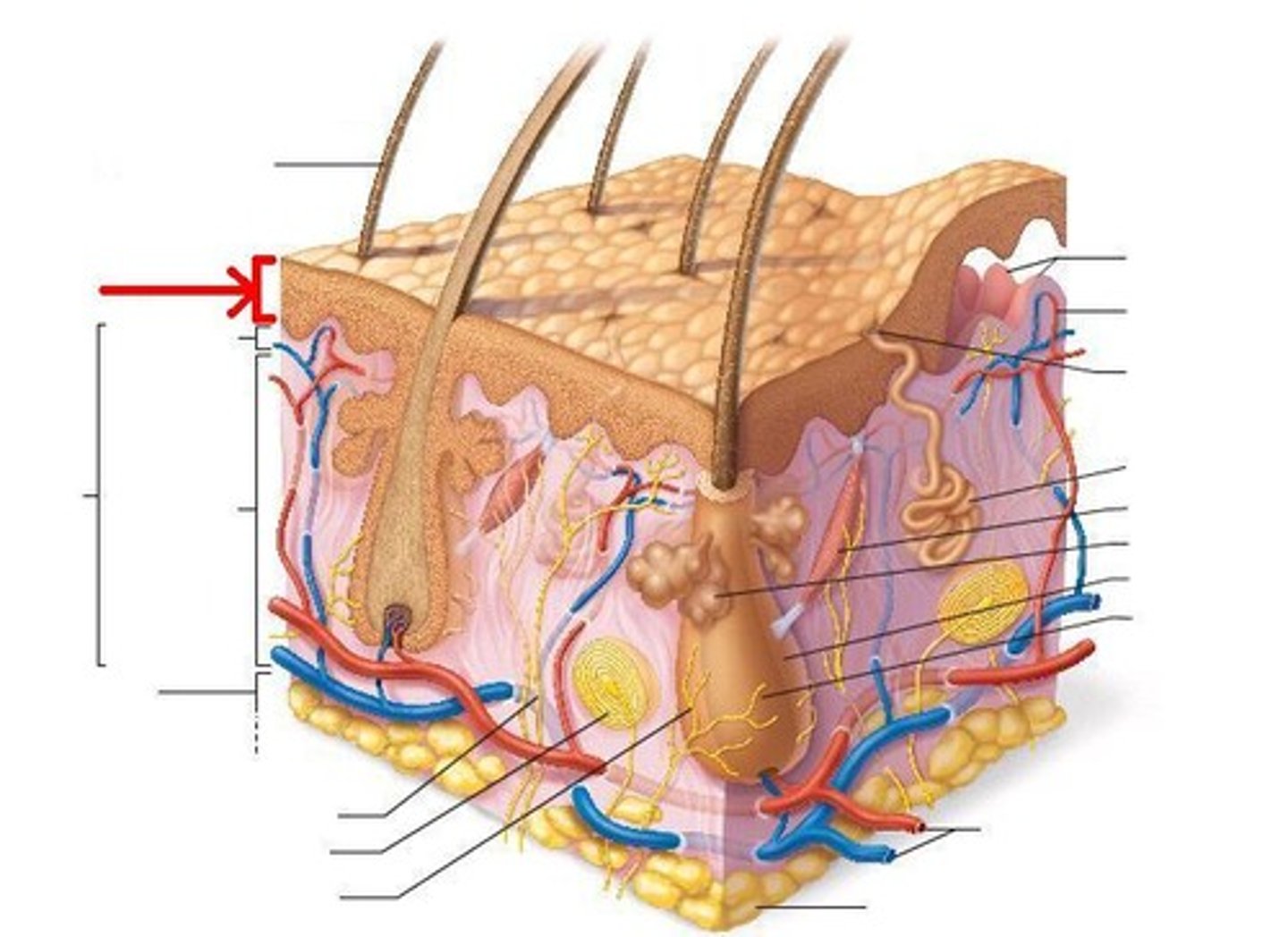
Dermis
dense bed of connective tissue
Skin function
mechanical and permeability barrier, and as a sensory and thermoregulatory organ - initiates primary immune responses
What are the 3 main layers of the skin?
epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer
Fascia
connective tissue containing varying amounts of fat that separate, support, and interconnect organs and structures, enable movement of one structure relative to another, and allow the transit of vessels and dnerves form one area to another.
What are the two categories of fascia?
deep and superficial
Superficial fasica
lies just deep to and is attached to the dermis of the skin
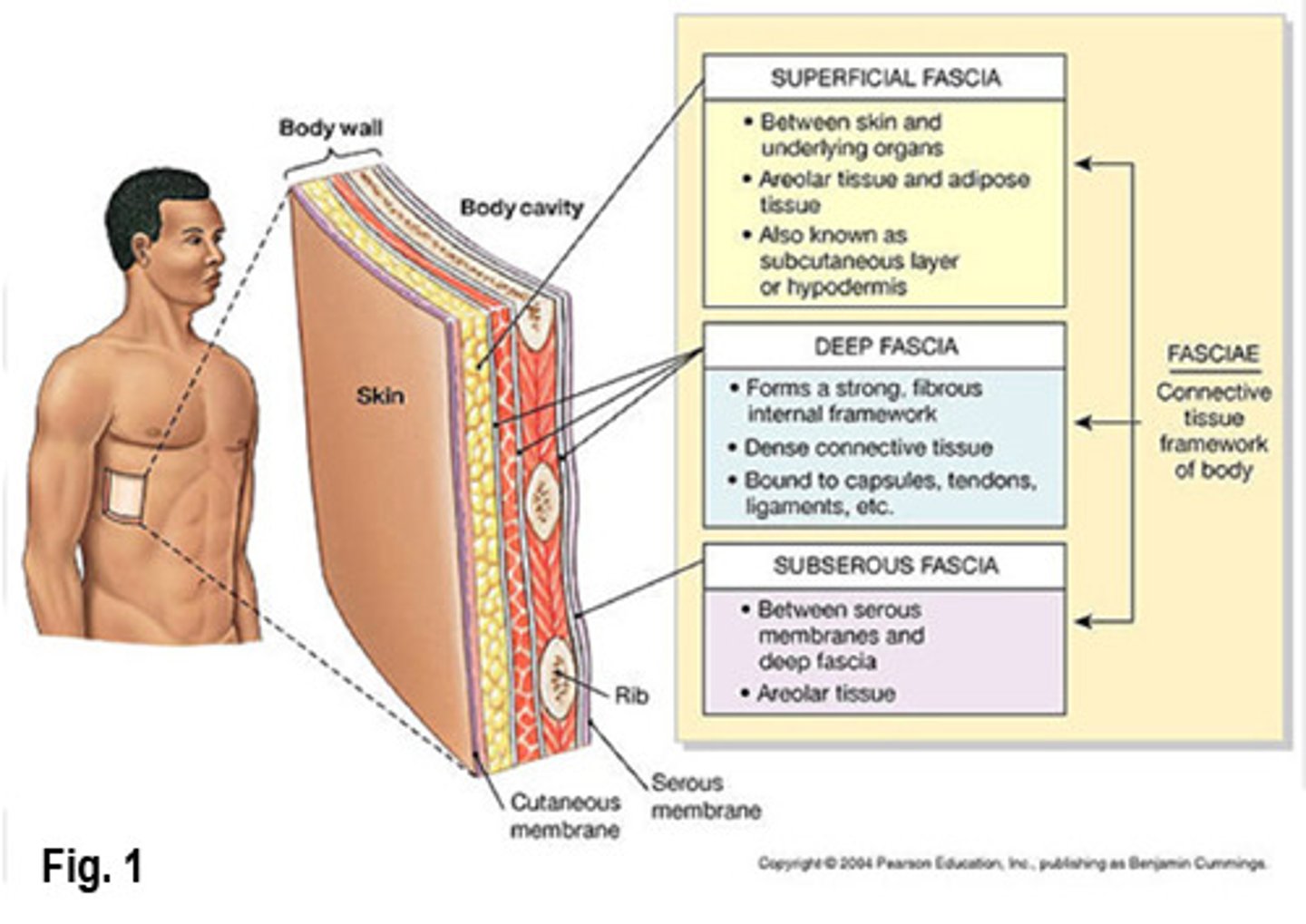
Deep fascia
forms a covering over deeper region of the body

What are the 3 types of muscle tissue that the Muscular System is composed of?
skeletal, smooth, and cardiac
Skeletal muscle
responsible for voluntary movements and posture
Cardiac muscles
found in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood
Smooth muscle
found in the walls of the internal organs and blood vessels, controlling involuntary movements like digestion
What do the skeletal muscles control?
voluntary movements (consciously control) like our arms and legs - attached to bones through tendons and are responsible for movement and maintaining posture
Where are the smooth muscles found?
stomach, intestines, and blood vessels - help regulate body functions
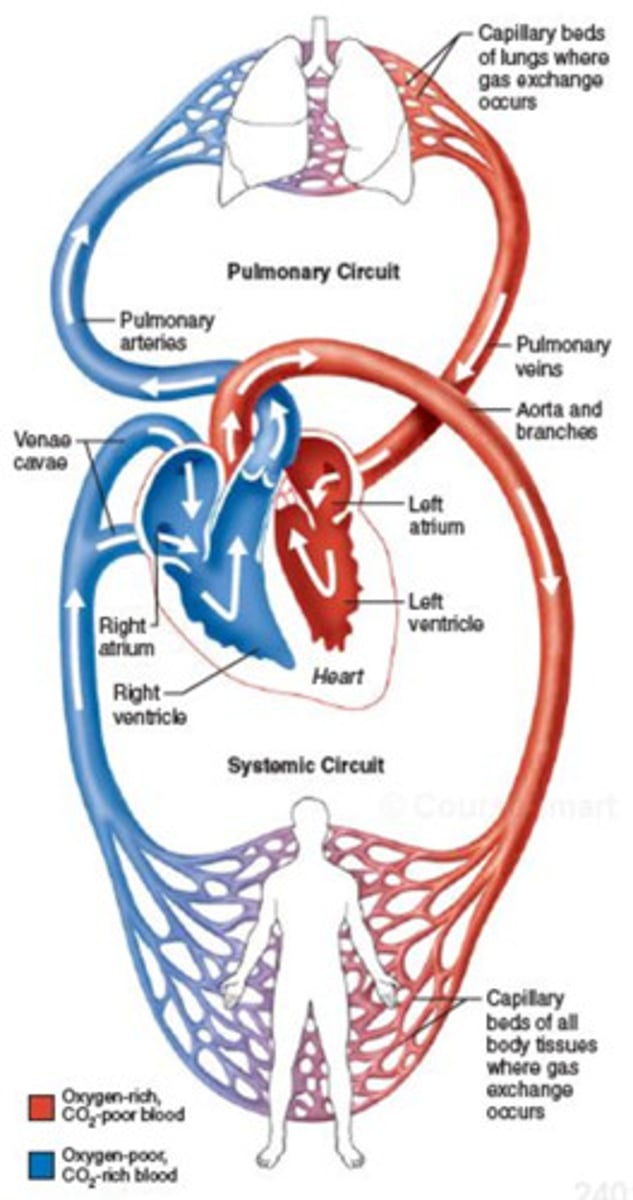
Cardiovascular system (circulatory system)
vital network responsible for transporting blood throughout the body
What does the cardiovascular system consist of?
heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries), and blood
The heart
acts as a pump, while the blood vessels serve as conduits for blood flow delivering oxygen and nutrients and removing waster products
4 chambers of the heart
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle
3 types of blood vessels
arteries, veins, capillaries
Arteries
transports oxygenated blood AWAY from the heart to the rest of the body (with the exception of the pulmonary arteries that carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs)
Veins
transports deoxygenated blood BACK to the heart (with the exception of the pulmonary veins that carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart)
Capillaries
connects the arteries and the veins and facilitates the exchange between blood and body tissues
Fluid that circulates throughout the cardiovascular system
consists of plasma and formed elements (RBCs, WBCs, and platelets)
Red blood cells (RBCs)
carry oxygen and carbon dioxide
White blood cells (WBCs)
are involved in the immune response
Platelets
help with blood clotting
How much blood does the average human contain?
5 liters (1.3 gallons of blood)
Cardio System
Lymphatic system
keep the body's fluid balance, defend the body against infection and in the absorption of fats and cell debris
What is the lymphatic system a network of?
smaller capillary - like channels that form larger vessels that ultimately connects with the large veins at the root of the neck
Nervous system function
complex communication network that can be separated into two parts based on structure or function
Structural Nervous System
CNS and PNS
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
nerves outside the CNS
Functional Nervous System
somatic and autonomic
Somatic
innervates the skin and most skeletal muscle
Autonomic
controls self-regulated action of internal organs and glands
Olfactory Cranial Nerve
sense of smell
Optic Cranial Nerve
eyes
Oculomotor Cranial Nerve
eye movement
Trochlear Cranial Nerve
eye movement
Trigeminal Cranial Nerve
sense touch, temperature, pain, CHEWING
Abducens Cranial Nerve
muscles around the eye
Facial Cranial Nerve
facial expressions
Auditory Cranial Nerve (vestibulocochlear)
hearing and balance
Glossopharyngeal cranial nerve
moves tongue, pharynx, swallowing, salivating
Vagus Cranial Nerve
Sensations of throat, larynx, thoracic, and abdominal organs
Accessory Cranial Nerve
supplies nerves to muscles of neck, trapezius, pharyngeal
Hypoglossal Cranial Nerve
movement of tongue
Ingestion
taking food into the body
Digestion
breaking down food into small molecules
Absorption
nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream
Excretion
removal of waste products
Digestive System
consists of G.I tract and accessory organs
G.I. tract
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine
Mouth
where the food is chewed and mixed with salvia
Esophagus
muscular tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach
Stomach
muscular organ that stores, mixes, and breaks down food with digestive juices
Large intestines
absorbs water and electrolytes, forming feces
Rectum
stores feces before elemination
Anus
the opening through which feces is expelled
Liver
produces bile which helps digest fats
Gallbladder
stores and released bile into the small intestines
Pancreas
produces enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
Respiratory system
intake of oxygen and expulsion of carbon dioxide
Keys parts of respiratory system
nose, mouth pharynx (throat), larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe), bronchi, lungs, and diaphragm
Nose and mouth
entry points for air into the respiratory system
Pharynx (throat)
passageway for both air and food connecting the nasal and oral cavities to the larynx and esophagus
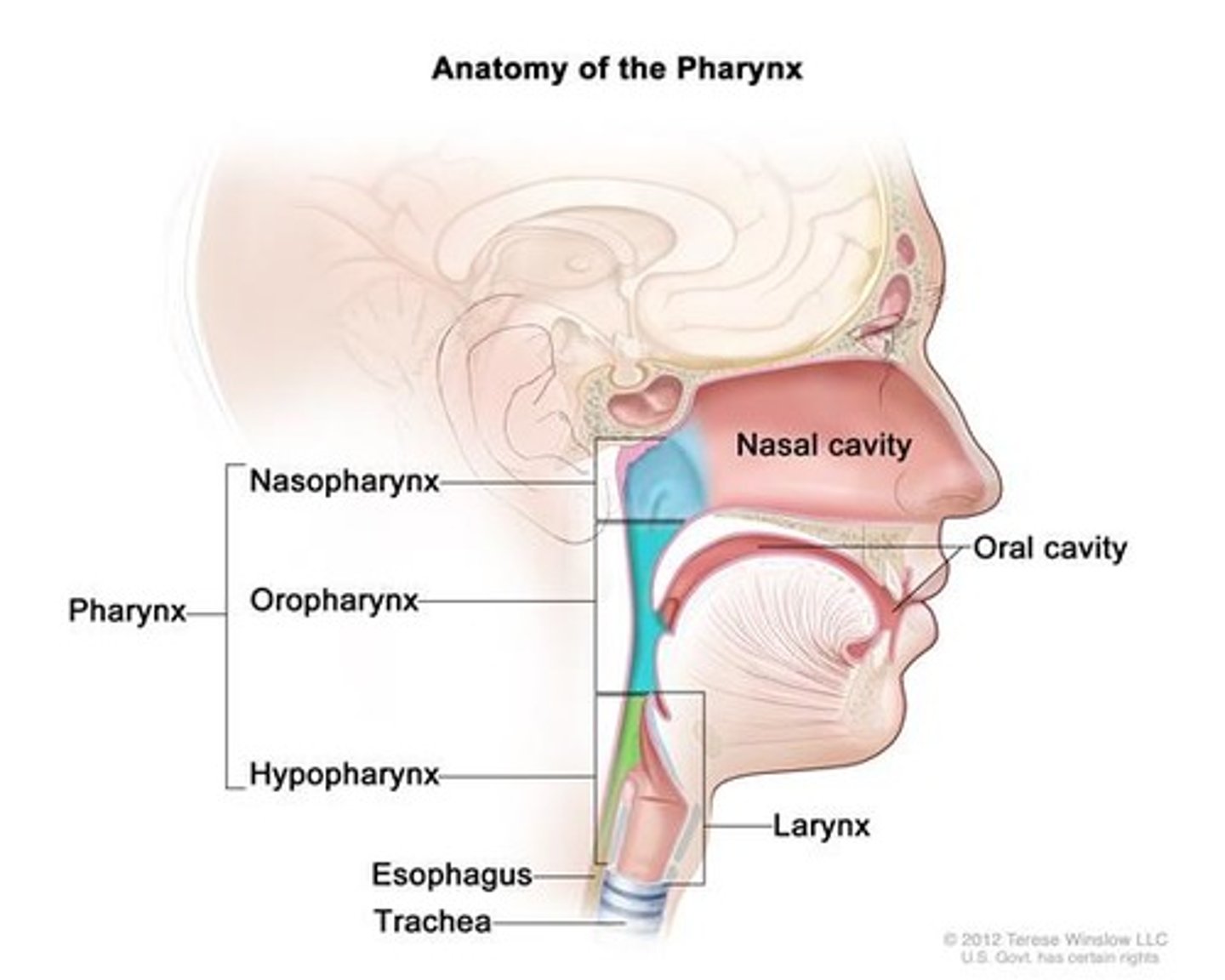
Larynx (voice box)
contains the vocal cords and is involved in producing sound as well as directing air into the trachea

Trachea (windpipe)
tube that carries air from the larynx to the bronchi
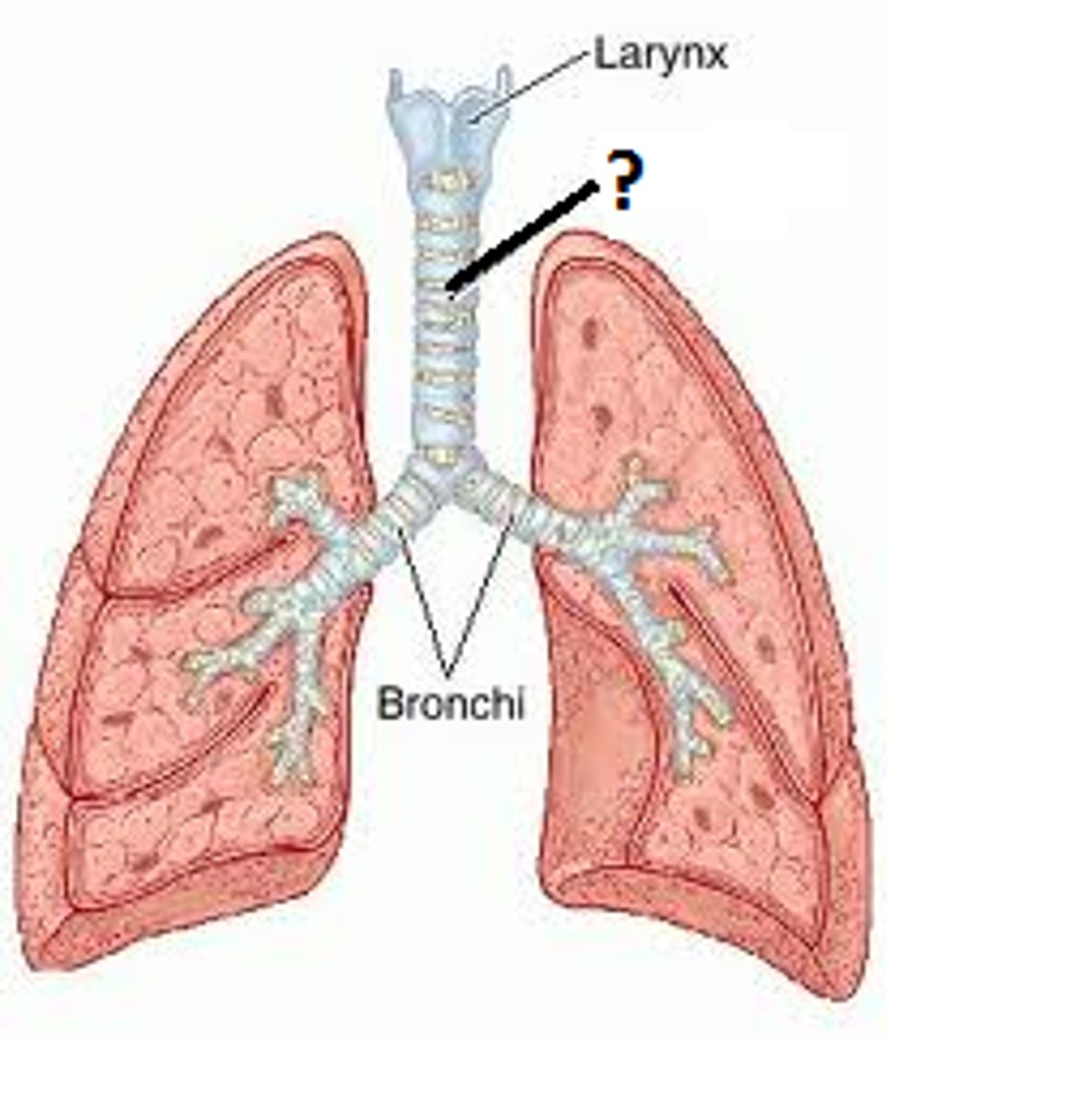
Bronchi
two large tubes that branch off from the trachea each leading to a lung

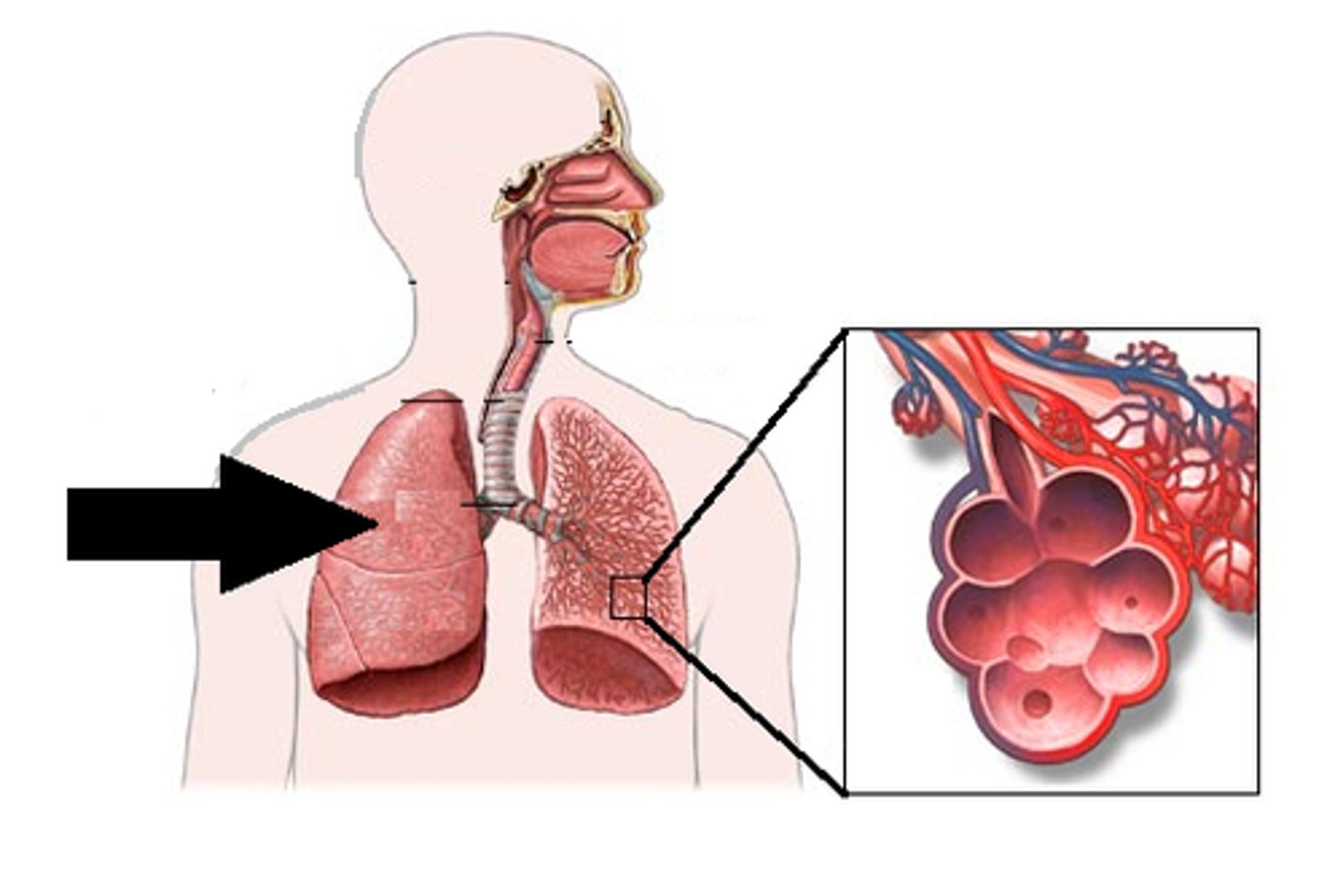
Lungs
main organs for respiration where the gas exchange (oxygen and carbon dioxide) takes place in tiny air sacs called alveoli
Diaphragm
muscle below the lungs that contracts and releases to facilitate breathing

Bronchioles
smaller branches of the bronchi within the lungs that lead to the alveoli

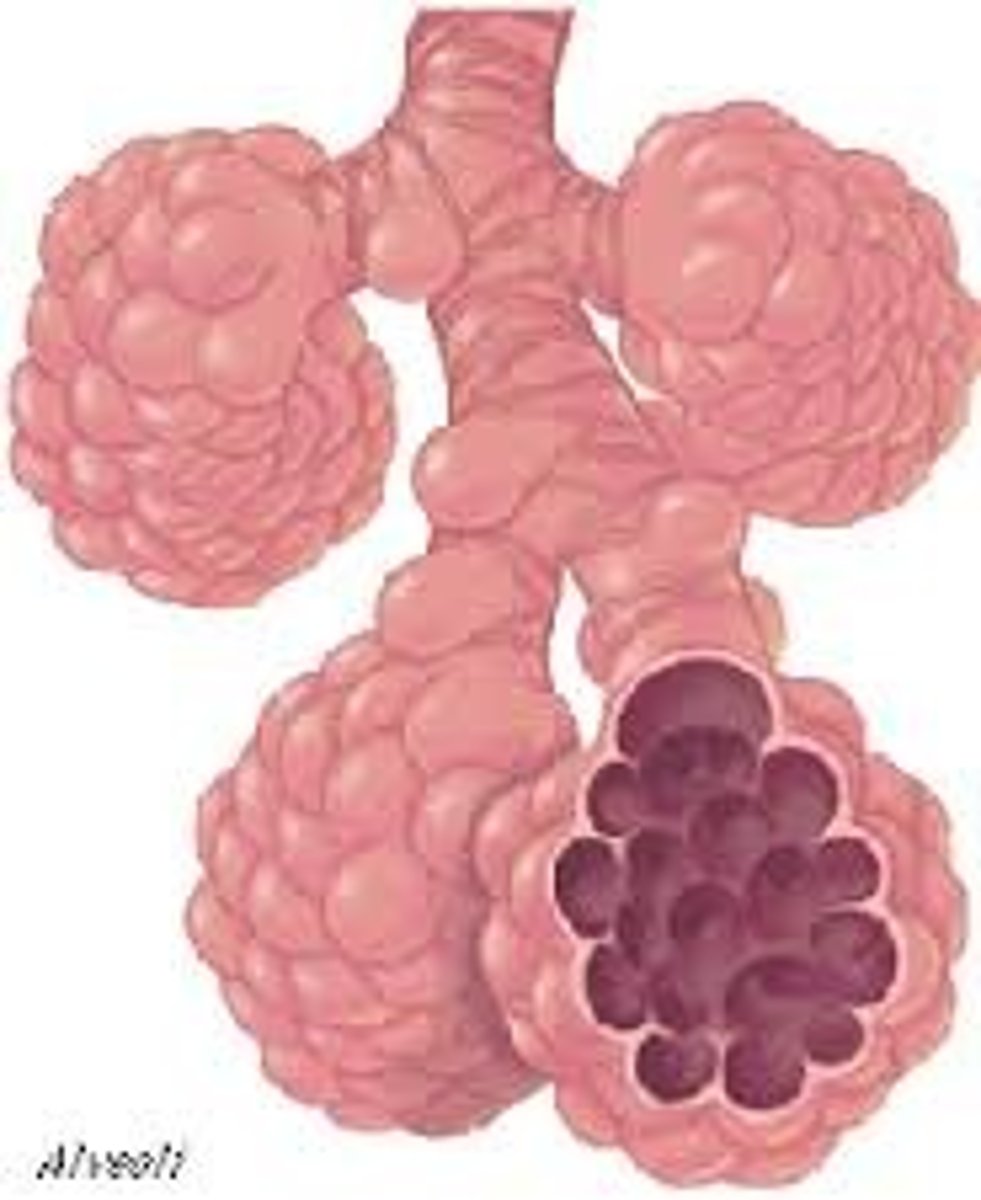
Alveoli
tiny air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between the air and the blood
Urinary system (renal/urinary tract)
filters waste from the blood and producing urine
What does the urinary tract consist of?
kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra - work together to remove waste, regulate blood volume and pressure and maintain electrolyte balance
Kidneys
two bean shaped organs located on either side of the spine, filter waste and excess water from the blood to produce urine
Ureters
tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder
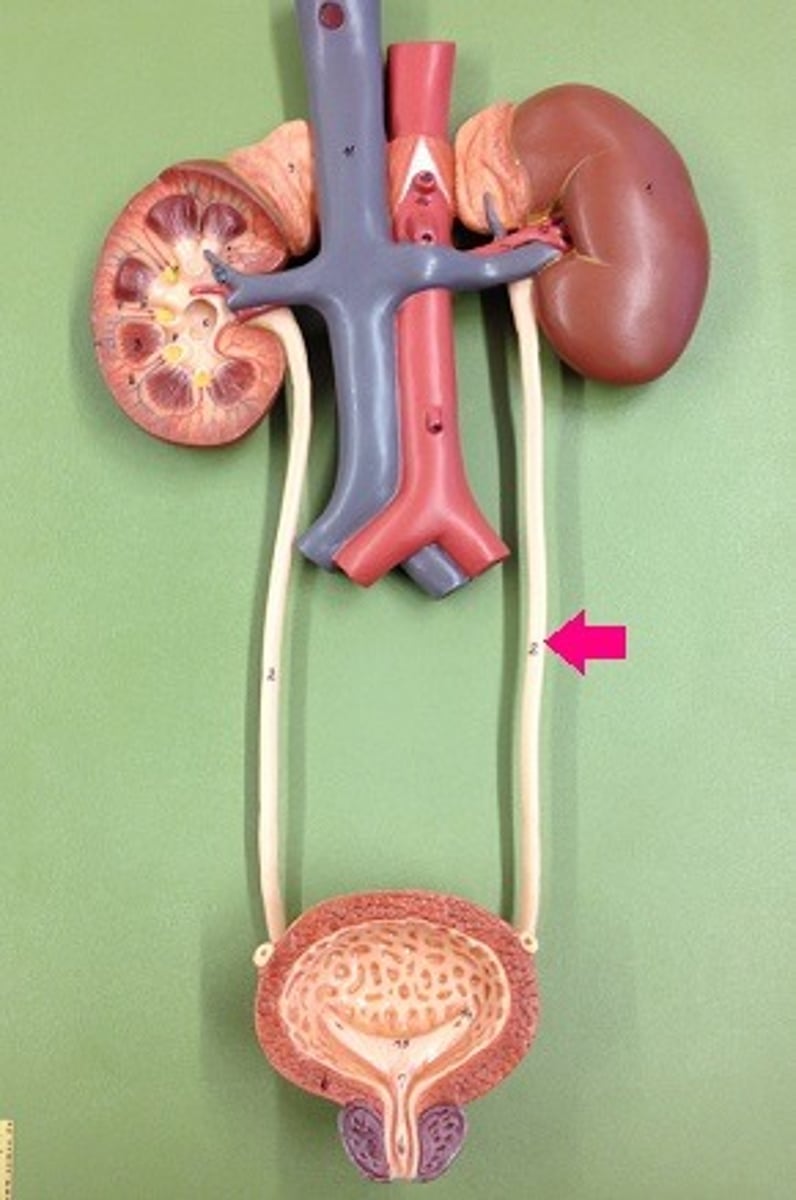
Bladder
muscular sac stores urine until it is ready to be released
Urethra
tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body during urination
Reproductive system
collection of organs and structures responsible for producing offspring
What is the reproductive system divided into?
primary reproductive organs and secondary reproductive organs
Primary reproductive organs
gonads
Gonads
testes (males) produce sperm and testosterone and ovaries (females) produce egg/ova
Secondary reproductive organs
ducts, glands, and external genitalia
Female reproductive system includes
ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva