Lec 11- Sugar, fat, salt
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
what are Canada’s food guide for carb, fat, and sodium intake
Carbohydrates:
● Total carbohydrate : 45-65%
of total kcal intake
● Limit intake of added sugars
to less than 10% of daily kcal
intake
Fat:
● Limit total fat to 20-35% of
total kcal intake
Sodium:
● Limit intake to 1500 mg/d
(14-50 yrs)
what are sugar functions besides sweetness
-Solubility
• Crystallization
• Color/flavor: Caramelization & Browning reactions; balance
• Moisture absorption (hygroscopicity)
• Texture
• Leavening: creaming butter/ sugar to trap air (aeration)
• Fermentation
• Preservation
T OR F: sugar is #1 additive in N.America?
TRUE:

what are sugar sources- sucrose
Sugar cane and sugar beets are the primary sources of sucrose (table sugar).
Canadian standard: Granulated sugar is 99.8% sucrose.
what are three granulated sucrose classifications?

what is invert sugar?
-Made by hydrolyzing sucrose to glucose and fructose
-Used to prepare glossy icings and frostings that help retain moisture in baked product
•Sweeter than sugar
•Ability to resist crystallization
•Strong hygroscopic nature :
o keeps baked goods moist longer
o enhances crust color and batter spread
what are two most common monosaccharides, where are they found?
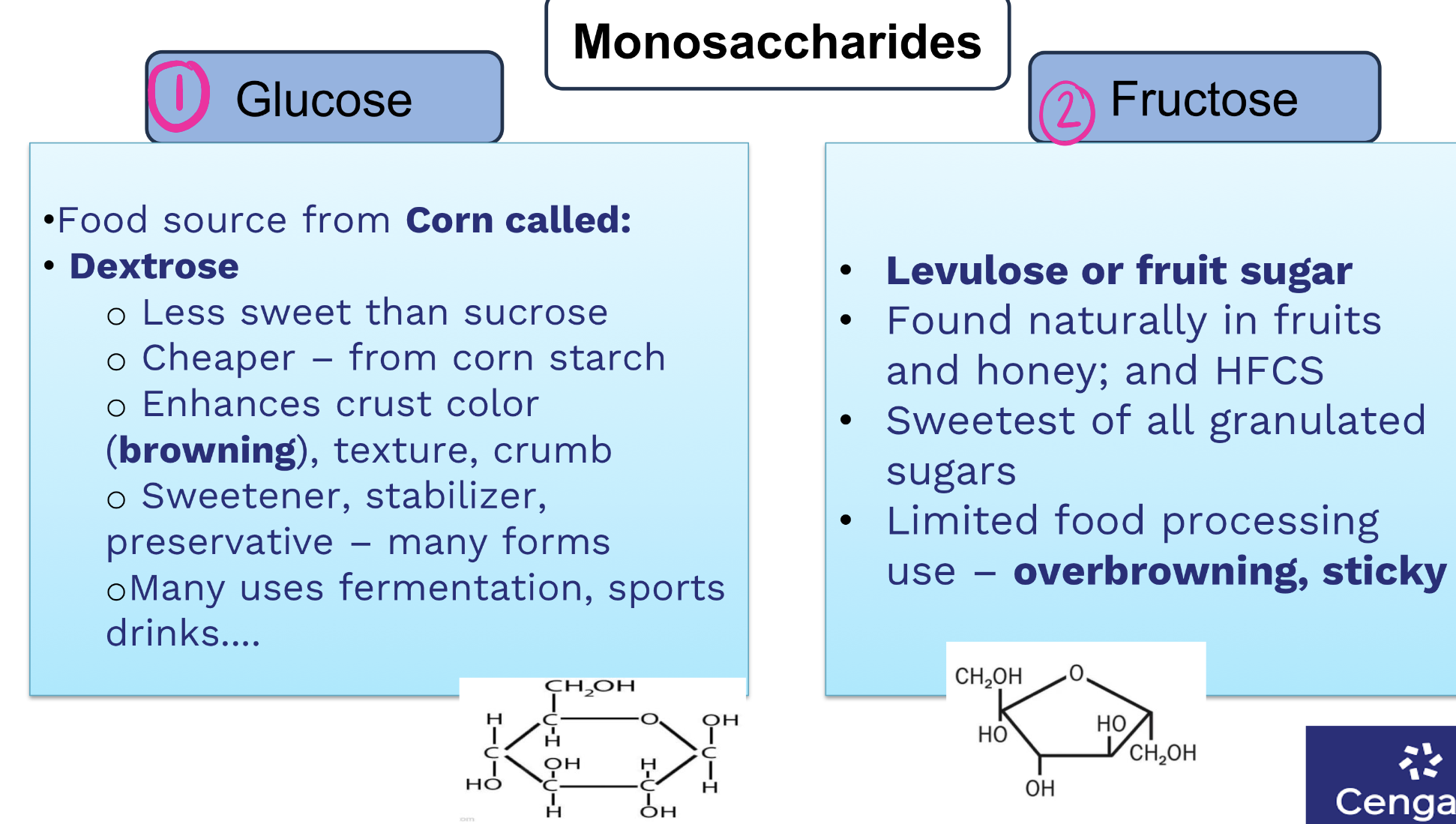
what are two most common disaccharides, where are they found?
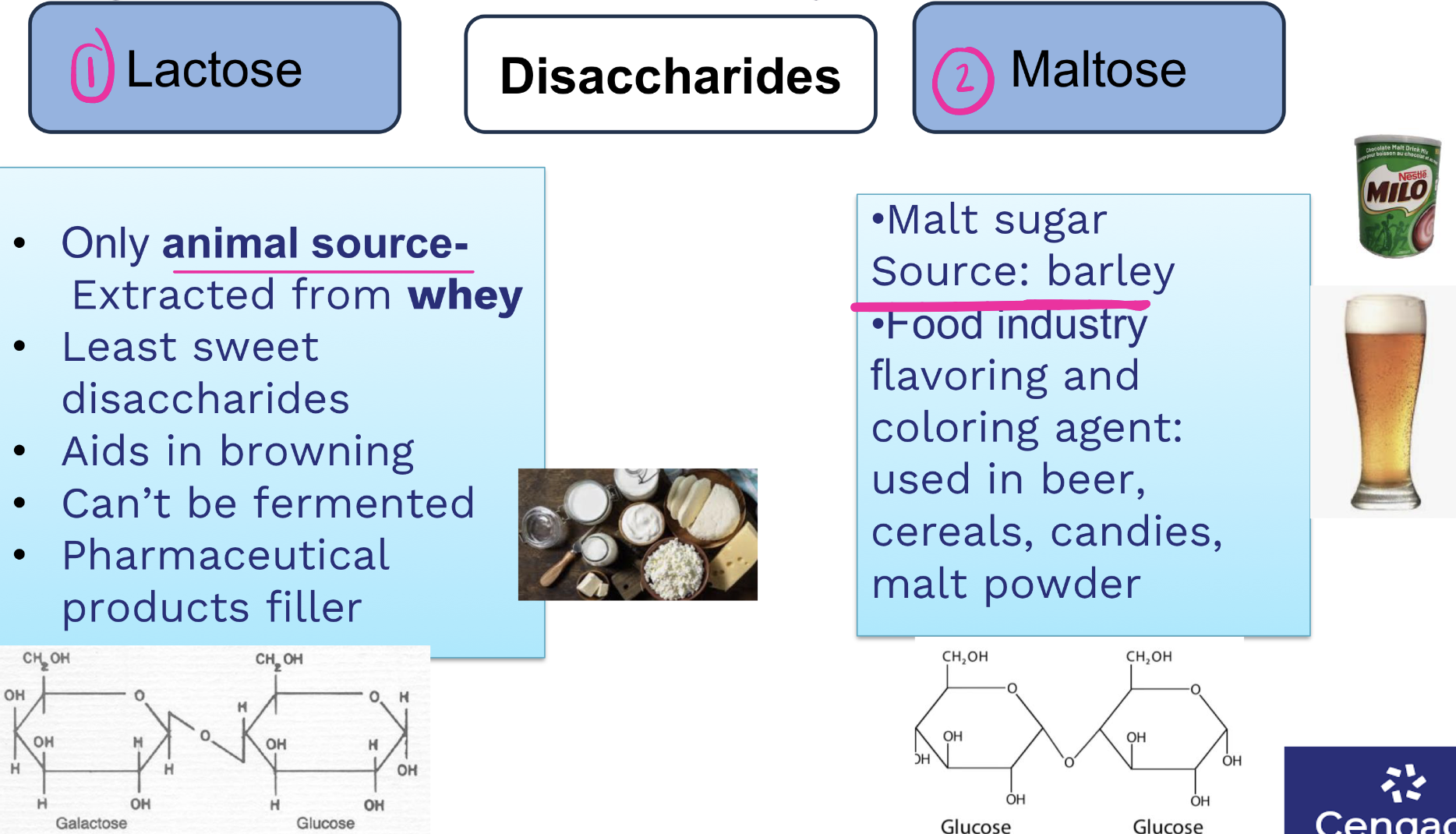
what are 6 types of sugar syrups, how do they vary ?
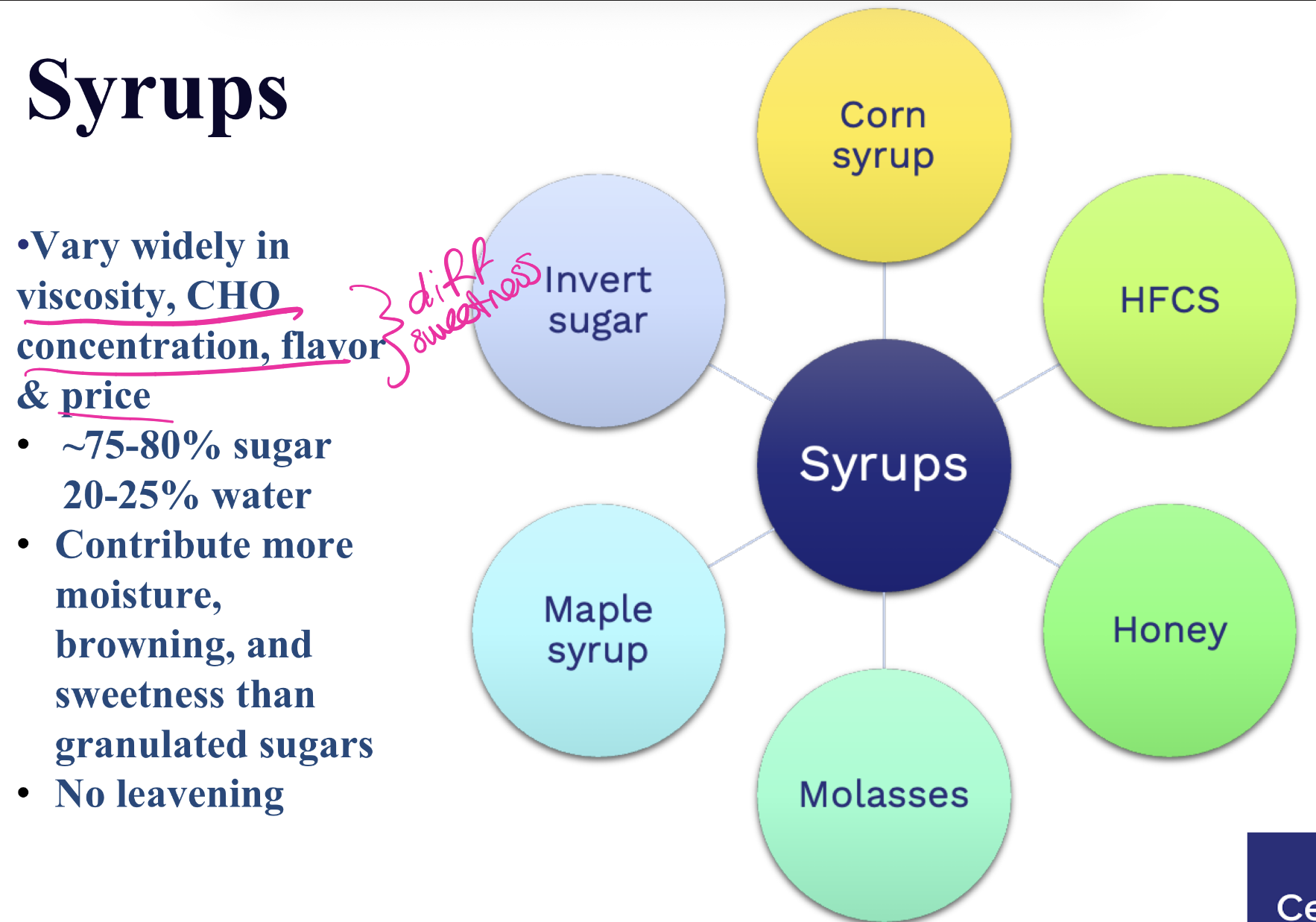
how is corn syrup,obtained, use, approx. sweetness?
CORN syrup:
•Viscous liquid: 75% sugars & 25%
water
•Used in soft drinks
•Cheaper than sugar
•Used as sweetener, thickener,
humectant
obtained from hydrolysis of cornstarch
HFCS:
High number of glucose—> converted to
fructose
• Sweeter than sucrose
• Ready for use in liquid food processing applications
• Widely used in processed foods
• Can’t be labeled as ‘natural’
• HFCS and obesity controversy
HONEY:
• Bees collect flower nectar (contains sucrose). During the flight back to the hive, convert it through enzymatic action into fructose
and glucose molecules.
• Composition: 40% fructose, 35% glucose, 2% sucrose + traces of other CHOs
info on molasses, agave, maple syrup
MOLASSES:
Made by boiling juice of sugar
cane/beets during sucrose extraction
• Mainly sucrose, 65% less sweet than sugar
• Used to produce Rum
AGAVE:
• 1.5 X Sweeter than sugar
• Consists of 90% fructose
-Used as sugar substitute
• Tequila is made from
blue agave plant
MAPLE SYRUP:
•Sap from maple trees boiled into smooth syrup
•Maple sugar is a product of maple syrup
what are 3 main unique characteristic sugar alcohols
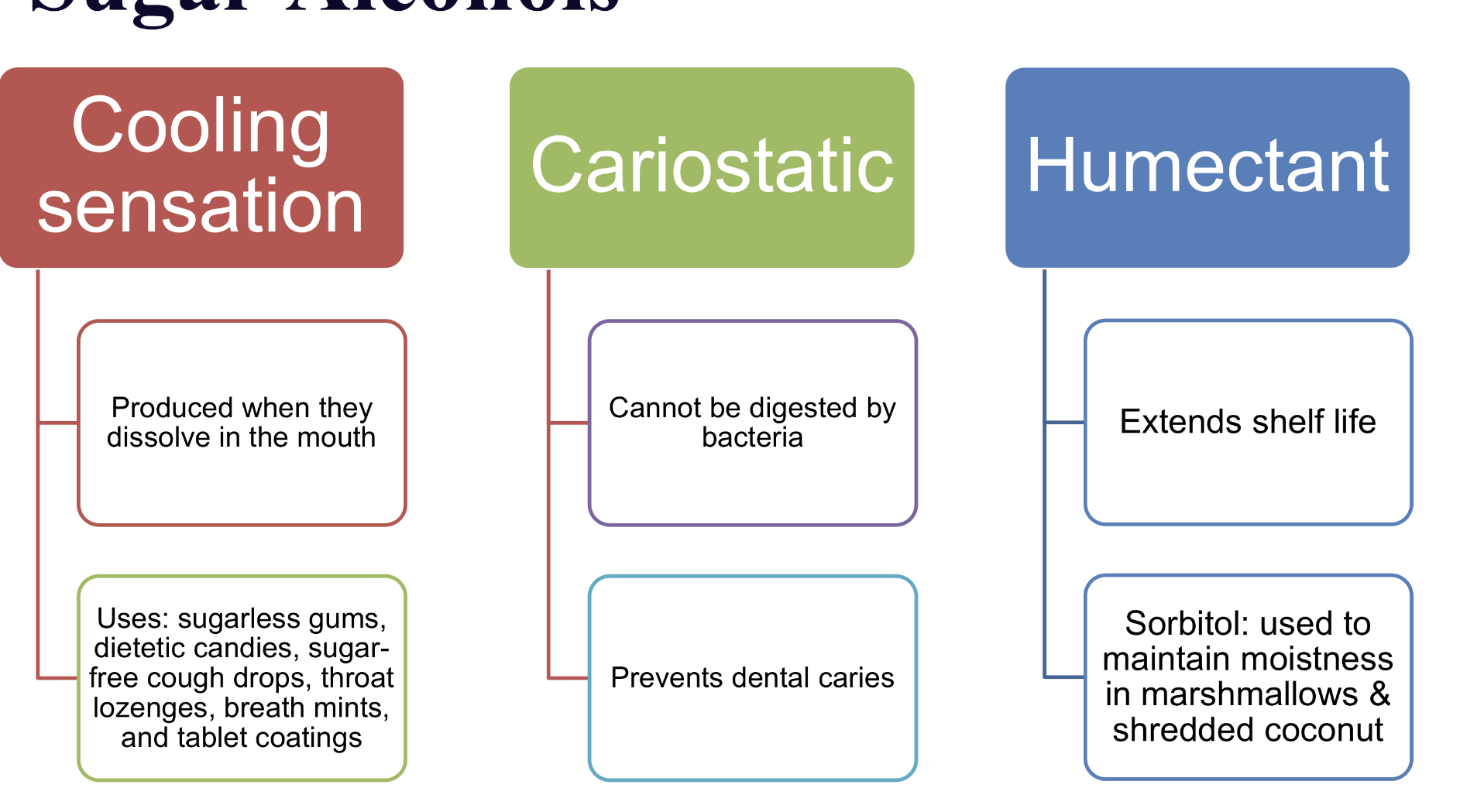
sugar alcohols: names, obtained from, what re some pot. issues
they are More slowly absorbed from the small intestine than other sugars SO
• Side effects such as gas, bloating, pain &/or diarrhea with consumption of more than 10g per day
• The Nutrition Facts Table lists sugar alcohols on a separate lineunder 'Carbohydrates

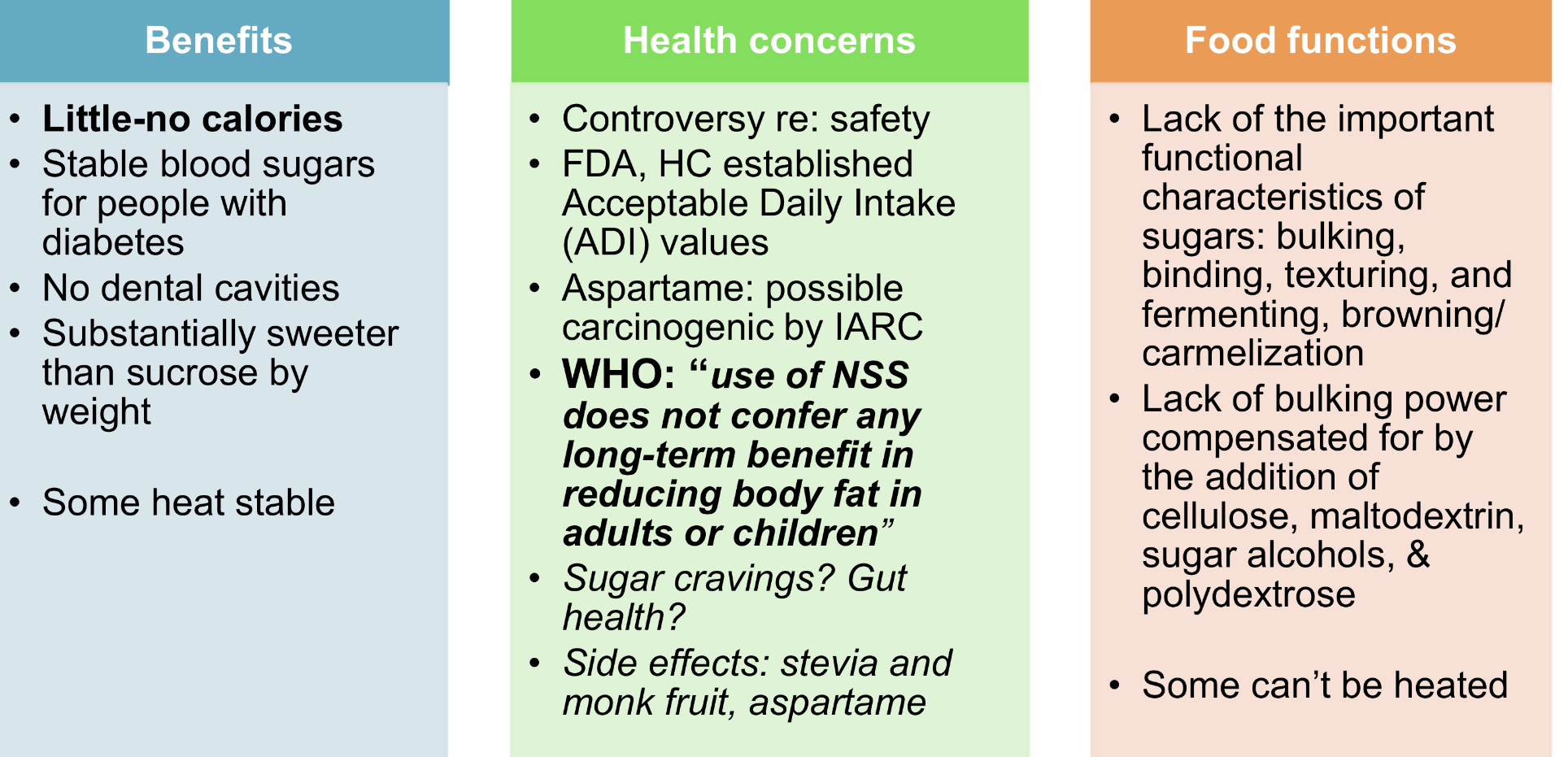
nonnutritive sweeteners: benefits, health concerns, food functions?
aka: intense/artificial/substitute sugar
regulated by HC
does sucrose in or dec boiling temps?
INCREASES boiling temp:
sugar molecules attract water molecules, forming hydrogen bonds and interfering with the ability of water molecules to escape into the air as vapor.
It takes more energy, and therefore a higher temperature, for the water's vapor pressure to equal the atmospheric pressure and for the solution to begin to boil.
why is crystallization important for?
Vital for manufacturing confectionaries
• Affects finished product's quality, Starting point for crystal formation:
o Small foreign particles, changes in temperature, nicks or cracks on the container's surface
• Formation of one crystal can trigger the entire mixture to crystallize
• Baked goods: the high oven temperature causes the surface of the dough to dehydrate, inducing sugar crystallization
explain hygroscopicity affects in food
= moisture absorption
Influences the moistness and texture of foods
• Degree to which sugars draw moisture from the air differs
• Fructose and honey: most moisture absorption capability
• Sucrose/Sugars attract water, causing baked goods to retain a
soft, moist texture & preventing drying and extend shelf life
• Store baking mixes in airtight containers because sucrose gets
lumpy if absorbs too much moisture
o Additives in commercial baking mixes to prevent ingredients from lumping or caking
how do sugars contribute to texture and mouthfeel?
• Baked goods: Add structure by producing finer texture grain by preventing overdevelopment of gluten & starch structures (prevents tough dough);enhancing flavor & browning
• Jams, jellies: Pectin
• Soft drinks feel flat in the mouth (bulking agents added) without sugars
• Meringues: sugar forms a supportive coating around the air bubbles within batter
(keeps them light and fluffy)
what are 7 main fat/oil functions in food
• Heat transfer
• Shortening
• Emulsion
• Flavor/mouthfeel
• Texture
• Satiety
• Nutrients:
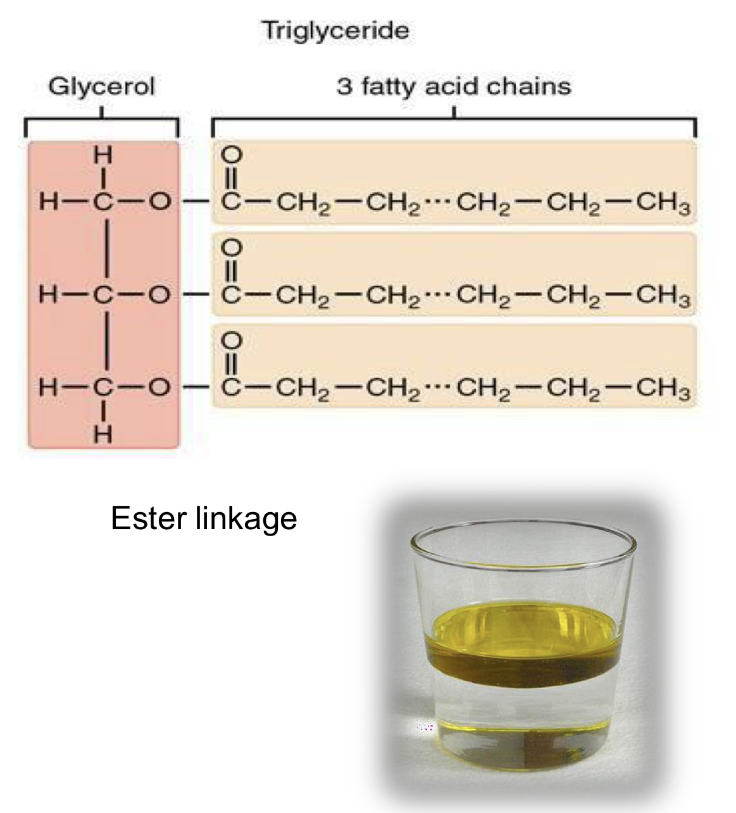
what are triglycerides made of?
95~% lipids
glycerol backbone and 3 FA chains
insoluble in H20
what is a FA form?
chain of carbons with an organic acid
(carboxyl group) on one end and a methyl
group on the other
can be saturated or unsaturated
what are examples of sat, mono, poly fats?
Chain length determines classification (long, medium, short)
Saturated fats
● Meat, whole-milk, butter, cheese, coconut oil, palm oil
Monounsaturated fats
● Olive oil, canola oil, avocados, nuts (peanuts,
almonds), seeds (sesame)
Polyunsaturated fats
● Omega-3: Canola oil, walnuts, flaxseeds, fatty fish (salmon, tuna, herring)
● Omega 6: Soybean oil, corn oil, non-hydrogenated margarine
what is plasticity vs solubility properties of fat?
Plasticity:
• Ability of solid fat to hold its shape but still
be molded or shaped under light pressure
• Determines fat’s spreadability
Solubility:
• Fats are generally insoluble in water
• Will dissolve in organic compounds:
•Benzene, Chloroform, Ether
trans vs cis unsaturated fatty acids
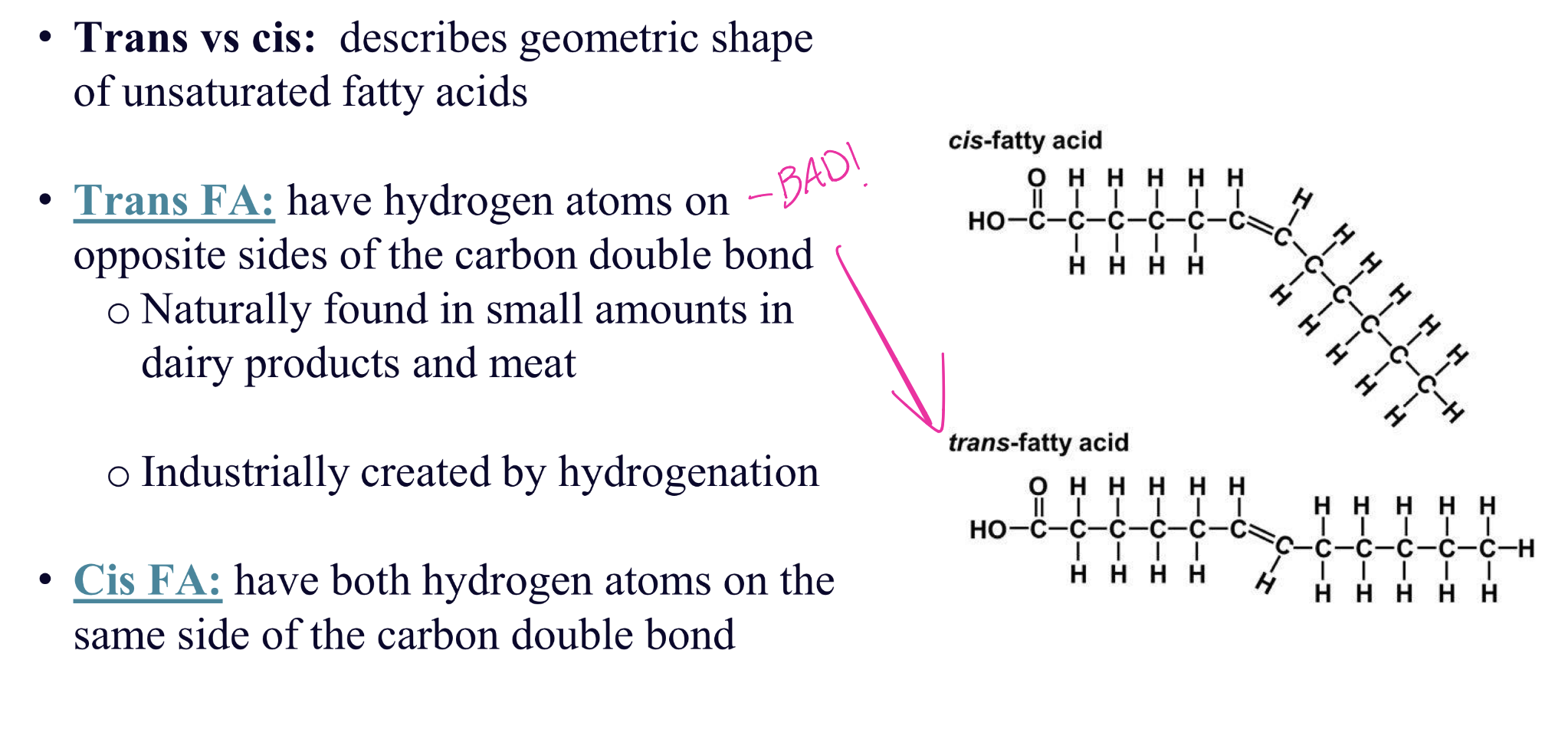
how does degree of sat, length of FA, cis/trans configuration, and crystalline structure affect MELTING POINT?
• Degree of saturation – More saturated, higher MP
• Length of the fatty acids: Longer chain, higher MP
• Cis–trans configuration: Cis configuration has kink, lower MP (less intramolecular forces)
• Crystalline structure: Larger crystals need more E to melt, so higher MP
what are 3 modifications of fats?
HYDROGENATION
used to harden vegetable oils by adding hydrogen atoms to double bonds in mono or polyunsaturated fatty acids to make them more saturated
- Increased solidity and lengthened shelf-life
- Increased risk of heart disease
WINTERIZATION
Removing high-melting point triglycerides in
vegetable oils that would otherwise crystalize during low-temperature storage (refrigerator)
- Oils are kept at low temperature for some time,
liquid and solids are separated by filtration
INTERESTERIFICATION
Rearranges fatty acids on the glycerol molecule with triglycerides, resulting in smaller fat crystals and smoother-consistency fat without producing trans-fatty acids
o Used to manufacture emulsifiers
o Lard: naturally grainy and soft at room temp but very hard when refrigerated
Interesterification creates smaller crystals in lard resulting in smoother texture with slightly higher melting point
what is shortening power of fats?
A fat that tenderizes, or shortens, the texture of
baked products by impeding gluten development
• More saturated (solid) fats tends to be more
useful as shortening in baked goods
• Ex: pastries, biscuits, cakes, cookies
how do emulsifiers work? what are emulsions and the three stabilities
• Emulsifiers act as surfactant: surface-active agent that reduces surface tension between both phases (water and oil) so they can mix more readily
EMULSIONS: Liquid dispersed in another liquid with which it is usually immiscible (oil in water or water in oil)
o Temporary: separates on standing when left
alone
o Semipermanent: tendency to separate is
reduced by adding a stabilizers
o Permanent: does not separate
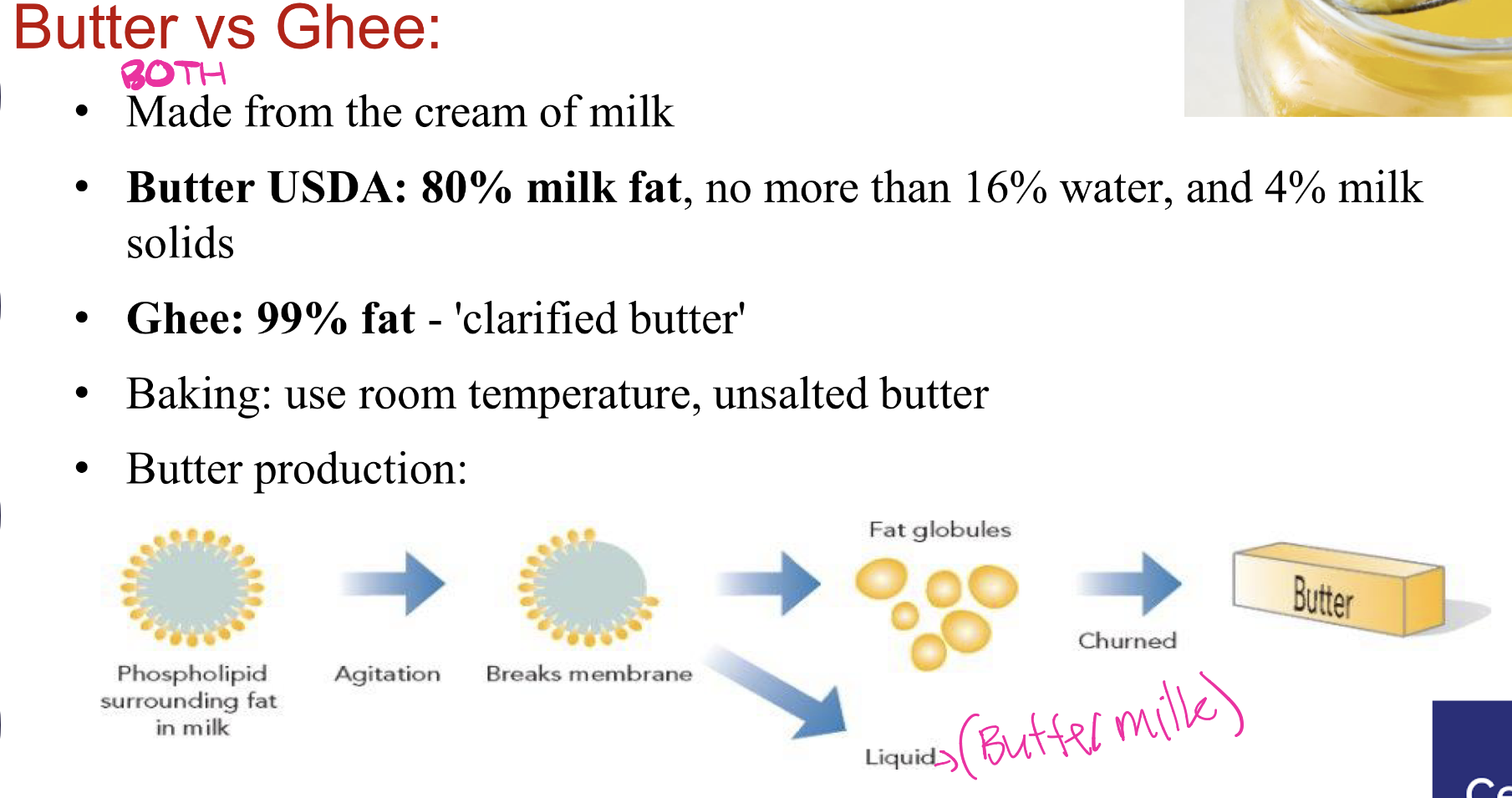
butter vs ghee
what are 3 processes involved oil production?
i) cold pressing: mechanically pressing the seeds, highest quality oil, small yield,
more expensive
ii) expeller pressing: squeezing the seeds at very high temperature generating some heat
iii) chemically removing the oil from seeds with solvents, majority of commercial vegetable oils (highest yield, more affordable, loss of nutrients, lower quality oil)
what is the process pf refining fats?
Refining: After an oil is extracted, it is left unrefined or refined (purified).
• Extracted oils contain impurities such as water, resins, gums, soil, colour compounds and free fatty acids that affect flavor/color/clarity/melting
point/smoke point and shelf life.
• Chemically and physically processed to remove undesirable components
WHEN REFINED:
-neutral, low-aroma, bland-flavored oil that does not influence taste of food
• Have a higher smoke point making them more suitable for frying
sodium vs salt
SODIUM: the Na element
SALT: a compound NaCl,
40% sodium, 60% Chloride
ex: 1000 mg salt = 400 mg sodium
1 tsp table salt = 2300 mg