Circulatory System
1/47
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Protection
limits spread of infection
destruction of microorganisms and cancer cells
neutralization of toxins and pathogens
clotting to minimize blood loss
Heart Pumping
the heart creates enough pressure to overcome resistance in the arteries (left ventricle contracts and pressure increases or blood is forced into the aortic arch and pressure increases)
Heart Wall
consists of three layers
epicardium
myocardium
endocardium
Epicardium
outermost layer of the heart wall
visceral layer of the pericardium
sometimes overlying a layer of adipose tissue
largest branches of coronary blood vessels found here
mainly consists of simple squamous epithelium
Myocardium
thickest muscle tissue of heart
middle layer of the heart wall
main cardiac muscle
thickness is proportional to the workload of each individual chambers
Endocardium
lines the interior of the heart chambers (inner layer of the heart wall)
simple squamous epithelium
no adipose tissue
thickness varies inversely with the thickness of the myocardium
Right Atrium
receives blood from the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava and coronary sinus
covered externally by the right auricle
Right Venticle
blood from right atrium passes through the tricuspid valve and enters the right ventricle
covers most of the anterior portion of the heart
blood is pumped into pulmonary circulation through the pulmonary trunk
Left Atrium
makes up most of the posterior surface of the heart
receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs through the two right and two left pulmonary veins
Left Ventricle
blood enters from the left atrium through the mitral (bicuspid or mitral valve)
pumps blood into the systemic circuit through the aortic arch
First Step in Blood Movement through the Heart
deoxygenated blood from the body into the right atrium
Second Step in Blood Movement through the Heart
enters the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve
Third Step in Blood Movement through the Heart
blood gas exchange occurs in the pulmonary trunk
Fourth Step in Blood Movement through the Heart
oxygenated blood enters the left atrium
Fifth Step in Blood Movement through the Heart
blood enters the left ventricle through the mitral/bicuspid valve
Last Step in Blood Movement through the Heart
blood is moved into the aorta to be distributed around the body
Lub Sound
atrioventricular valve closes
ventricular pressure is greater than the atrial pressure
Dub Sound
semilunar (aortic and pulmonary) valves close
ventricular relaxation begins
Arteries
carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
red blood vessels
have a thick tunica media to provide strength to offset the pressure from heart contraction
the larger the artery, the more elastic fibers contained in middle layer
Veins
carry deoxygenated blood to the heart
blue blood vessels
tunica media consists of small bundles of smooth muscle cells, reticular fibers, and some elastic fibers
large veins (close to heart) have thin tunica media and very thick tunica external
tunica externa is well-developed
drainage system of the
Capillaries
gas and nutrient exchange between blood and tissues
Penetrate tissue to allow for material exchange
Are the switch between veins and arteries
Allow for diffusion across their membranes
Elastic Arteries
very thick walls located near the heart
makes up the aorta and its major branches
about 40 layers (laminae) in newborns, 70 in adults
important in stabilizing blood flow and acts as a pressure reservoir
Differences Between Veins and Arteries
arteries are always deeps
veins are deep and superficial
names of superficial veins are unique (basilic vein)
What vessel is used in diagnostics?
arteries
Vein System for the Brain
Dural Venous Sinuses
Vein System for the Digestive System
Hepatic Portal System
Naming Arteries and Veins
location
organ served
bone followed
What three major veins enter the heart?
superior vena cava
inferior vena cava
coronary sinus
Superior Vena Cava
drains all body regions superior to the diaphragm
Inferior Vena Cava
widest vessel in the body
drains all body regions inferior to the diaphragm
runs along the side of the abdominal aorta
Movement of Blood in Arteries and Capillaries
contraction of left ventricle supplies pressure
Left Ventricle Contracting Affecting Large Arteries
very high blood pressure to high blood pressure
muscle and elastic expand or contract to maintain the blood pressure
What are the 5 primary functions of blood?
transport
Protection against infection
Regulation on pH
Maintain body temperature
Clot formation
Pulmonary vs. Systemic circulation
Pulmonary
carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
Blood drops of CO2 and picks up oxygen in the lungs
Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the hearts
Significantly shorter route
Systemic
carries oxugenated blood from the hearts throughout the body
Carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart
Significantly longer route
Name the 3 layers of the wall of the heart
epicardium
Myocardium
Endocardium
What are the 4 chambers of the heart
right atrium
Left atrium
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
What is interventricular septum
The muscular wall that separates the heart into right halves
Name the 4 heart valves
tricuspid valve
Bicuspid (mitral) valve
Pulmonary valve
Aortic valve
What is the purpose of the chordate tendineae?
To prevent the artioventricular valves from being pushed into the atria during ventricular systole.
Systole
The heart is contracting and blood is pumped out to the entire body.
What produces the S1 sound?
The tricuspid and bicuspid valves closing at the start of systole
What produces the S2 sound
The semi lunar valves closing at the end of systole/ beginning of diastole
What triggers the heart to beat?
The sa node (aka pacemaker)
What is a heart attack
The death of cardiac muscle due to lack of blood or O2
Diffrences between arteries and veins
Arteries
much thicker walls
Much more elastic, more rigid
Carry oxygenataed blood
The pressure is higher
You can feel the pulse
Come from the left ventricles
Veins
thinner muscle walls
Elastic
Carry deoxygenated blood
Much lower pressure
1 way valves
Blood id going to the right artia ( mostly)
what are the function of the heart valves, tricupid, bicuspid, aortic, pulmonary
The tricuspid valve prevents backflow from the right ventricle to the right atrium.
The bicuspid (mitral) valve prevents backflow from the left ventricle to the left atrium.
The aortic valve prevents backflow from the aorta to the left ventricle.
The pulmonary valve prevents backflow from the pulmonary artery to the right ventricle.
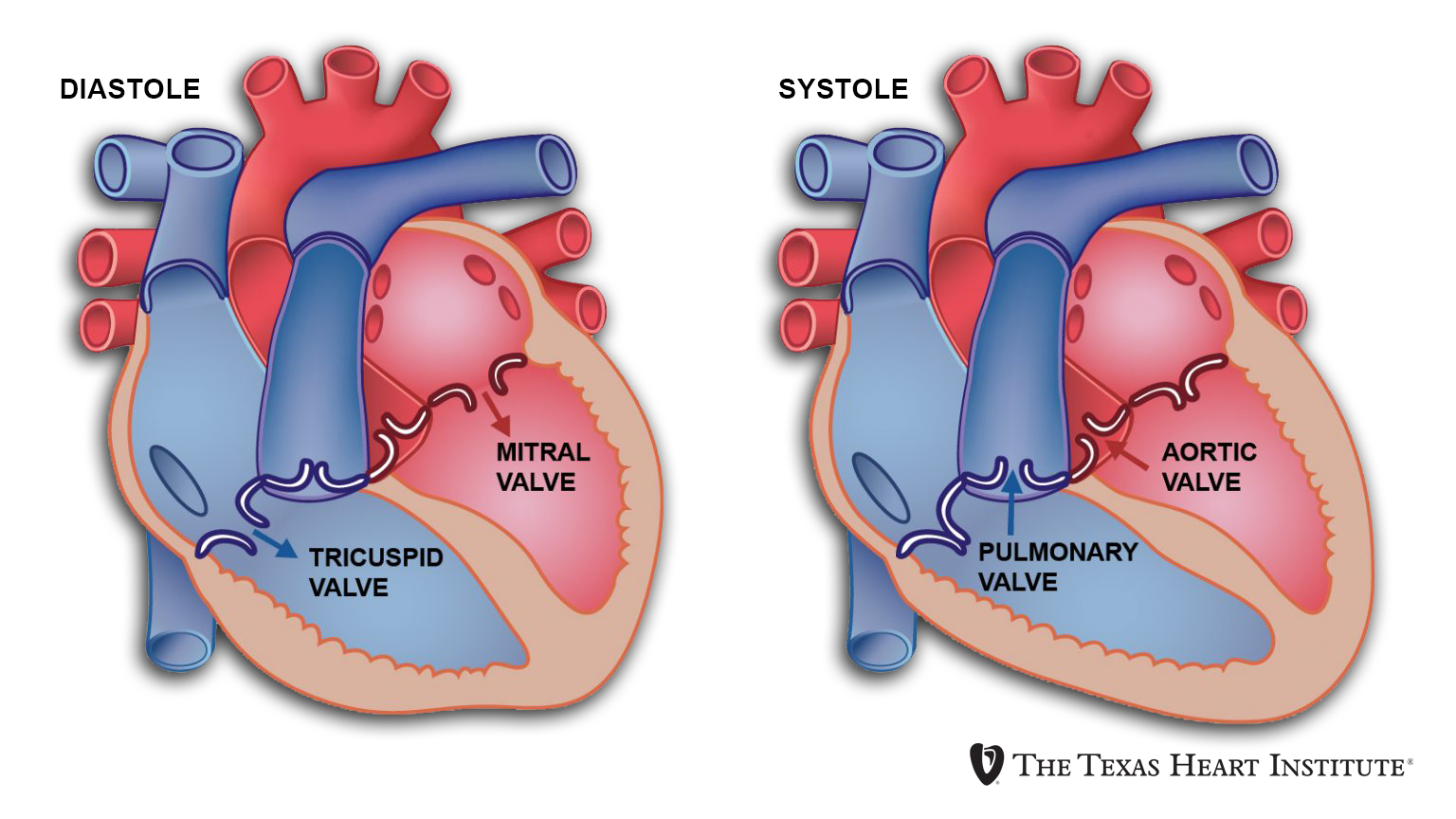
diastole
The heart is relaxed and blood is refilling