HDFS Final Ch 13 Physical and Cognitive Development in Early Adulthood
1/223
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
224 Terms
What ages count as emerging adulthood? What about early adulthood?
Emerging adulthood: the end of secondary school, about age 18, to the assumption of adult roles at about age 25
Early adulthood: about age 25 to 40
What differentiates an emerging adult and a young adult?
emerging adult will refer to individuals age 25 and under (unless otherwise specified) and young adult will refer to all individuals under age 40, including emerging adults (unless otherwise specified).
When do all of the organs and body systems, including digestive, respiratory, circulatory, and reproductive systems, peak in functioning?
from emerging adulthood into early adulthood.
We may not think of young adults as aging, but the biological fact is that once individuals are physically mature with growth and physical development at adult levels, ____ —a pattern of gradual age-related declines in physical functioning—begins
senescence
What is senescence?
a pattern of gradual age-related declines in physical functioning
Measurable age-related changes in functioning occur by about age __, but most people do not notice these until middle adulthood. Aging entails gradual changes in appearance, strength, body proportions, and fertility.
30
In one individual the digestive system may show signs of aging earlier than the cardiovascular system, while it may be the other way around for another individual. What does this say about development?
Similar to development throughout infancy, childhood, and adolescence, development in early adulthood is multidimensional and multidirectional. Different parts of the body age at different rates, and development comprises both gains and losses in strength, endurance, and motor skill. In addition, organs vary in their rate of decline.
Age and physical development are closely related in childhood, but the link is much weaker in ____
adulthood
T/F: Young adults display a wide range of individual differences in physical functioning and aging.
T
____ is a critical component of a long and healthy life.
Activity
Parents’ lifespans predict those of their children, and identical twins share more similar lifespans than do fraternal twins, suggesting a role for ____ in aging
heredity
T/F: Parents’ lifespans predict those of their children.
T
Yet kin relations for markers of biological age, such as strength, respiratory capacity, blood pressure, and bone density, are relatively small as health is influenced not just by genetics but by __ and ——.
context and lifestyle.
It may be that it is not lifespan that we inherit but a set of genetic factors that interact with ____ factors to may predict lifespan
environmental
One account of aging relies on cellular mutation, which is what?
damage to DNA and chromosomes.
Research with animals shows that cell mutations increase/decrease exponentially with age
increase
Cellular mutations are associated with age-related diseases and ____. Some of this damage may be due to __ ___, highly reactive and corrosive molecules that form when oxygen corrodes cells and strip off electrons.
cancers; free radicals
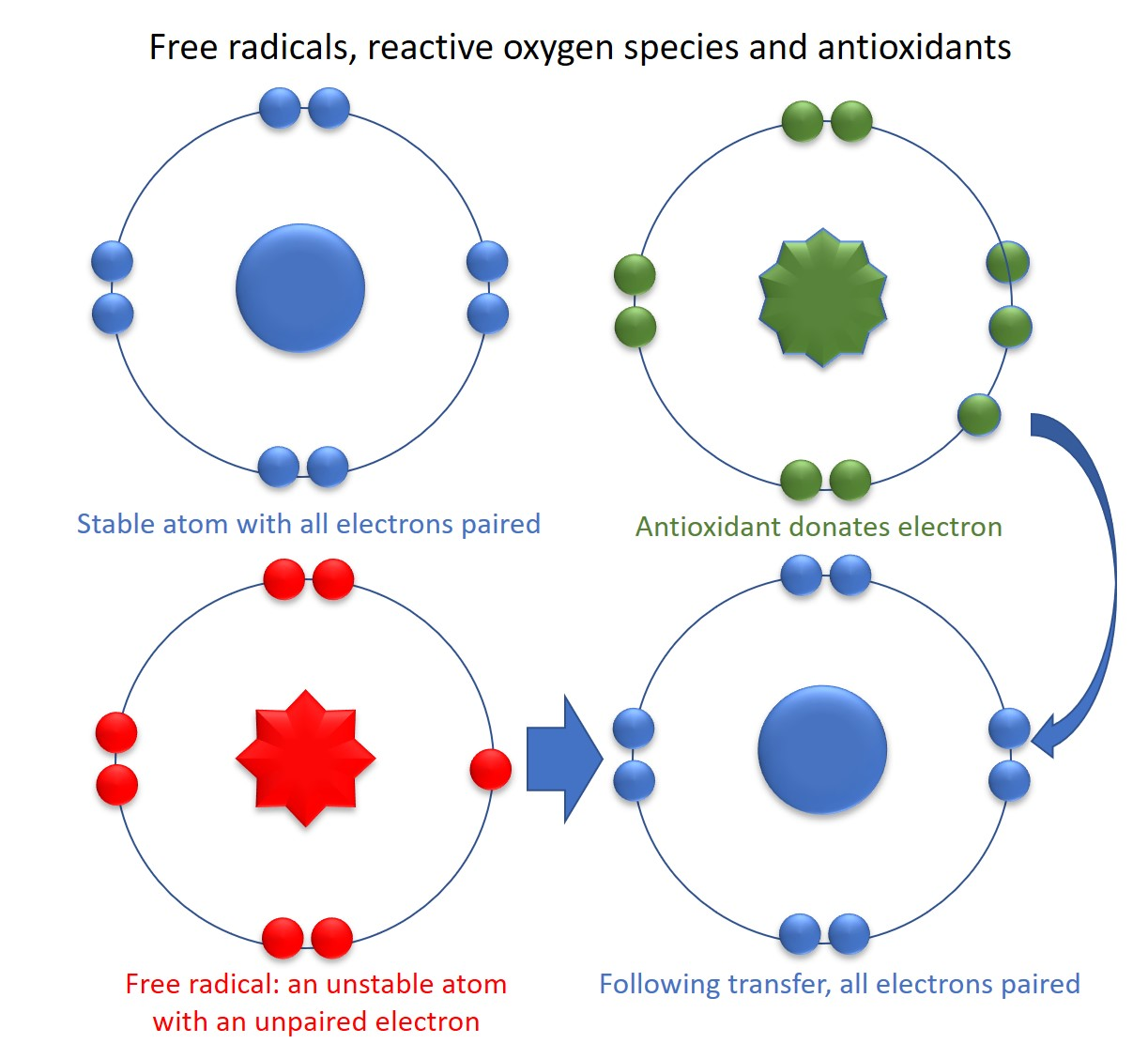
What are free radicals?
highly reactive and corrosive molecules that form when oxygen corrodes cells and strip off electrons.
Free radicals destroy cellular materials in an attempt to
replace the missing electrons.
Free radicals may increase the likelihood of many age-related diseases, such as cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and arthritis, and predict ___
mortality
Aging occurs at the ___ level.
cellular
A diet rich in _____, including vitamins C and E and beta carotene, may protect against damage from free radicals
antioxidants
T/F: Aging is complex and free radicals likely account for a majority of change
F. Fee radicals likely account for only a proportion of change
Human cells have the capacity to divide about __ times in their lifespan
50
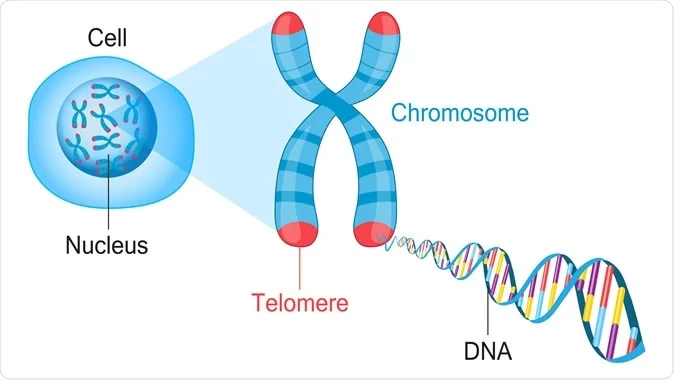
Each time the cell divides, ____—tiny caps of DNA located at both ends of the chromosomes —become shorter. Shorter telomeres may protect the cell from common mutations that occur with repeated divisions, but they also reduce the cell’s capacity to
telomeres; reproduce itself.
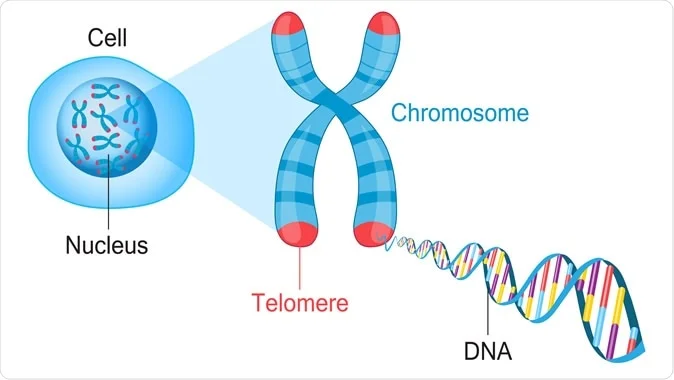
What are telomeres?
Each time the cell divides, telomeres—tiny caps of DNA located at both ends of the chromosomes —become shorter.
T/F: Telomeres that shorten past a critical length cause the cell to stop dividing altogether.
T
Telomeres that shorten past a critical length cause the cell to stop dividing altogether, leading to increases in
disease, cell death, and body aging
Telomere length is associated with
dozens of cancers
T/F: Telomere length may serve as a biomarker for aging.
T
Stress contributes to the shortening of telomeres, as well as oxidative stress, which results from ___ ____.
free radicals
For people of all ages, regular ____ activity contributes to longer/shorter telomeres, suggesting that behavioral factors can attenuate telomere shortening, and thereby aspects of aging
physical; longer
T/F: The immune system determines how the body adjusts to external stressors and pathogens encountered throughout life.
T
T/F: Chronic low-grade inflammation, immune activity that is not associated with infection or disease, is a hallmark of aging and associated with various age-related diseases including cardiovascular diseases, cancers, and diabetes
T
What happens to someone’s immune system as they age?
With age, the immune system becomes less able to differentiate healthy cells from pathology, may direct the body’s defenses against healthy cells, and may ignore harmful cells
T/F: From early adulthood through late adulthood, Black adults and those of low socioeconomic status tend to show more biological indicators of aging, especially low-grade inflammation and inflammatory biomarkers, than whites adults—and the disparities widen with age, suggesting the role of contextual factors and experience in immune system aging
T
Experiments with animals suggests that ___, specifically caloric restriction, may play a role in longevity. Animal studies suggest that a nutritious diet that is extremely low (about __% fewer calories than recommended) is associated with a longer lifespan and with less —— stress (resulting in fewer free radicals). However, the near-starvation diet is uncomfortable and may be difficult for a human adult to sustain
diet; 40%; oxidative stress
Age-related changes in the skin are gradual, predictable, unavoidable, and begin in emerging adulthood, at about age __.
20
Age-related changes in the skin are gradual, predictable, unavoidable, and begin in emerging adulthood, at about age 20. The connective tissue gradually thins, resulting in less elastic skin and some visible wrinkles around the eyes by age __
30
The skin becomes drier as __ glands become less active.
oil
Most adults in their 30s notice lines developing on their foreheads, and by their 40s these lines are accompanied by ___ feet around the eyes and lines around the mouth—markers of four decades of smiles, frowns, laughter, and other emotions.
crow’s feet
The rate of skin aging is influenced by exposure to the elements, such as (4)
sun, heat, cold, and pollution.

__ __ __ __ is thought to be the most dramatic contributor to skin aging, responsible for about —% of skin changes, and the leading cause of — cancer
Exposure to the sun; 80%; skin cancer

Though more apparent in middle age, by age 30, some individuals begin to notice gray hairs, as the hair follicle cells that produce pigment, or color, become less abundant. Men who are prone to hereditary baldness typically begin balding in their __s.
30s
Physiological function, including muscle development and strength, tends to improve throughout the 20s, peaking at about age __
30
Adults’ performance on activities that require body coordination and bursts of strength, such as sprinting and playing basketball, tend to peak in the early __s whereas those that require endurance, such as distance running, peak in the early —s and show declines after age 40.
20s; early 30s
Muscle strength, as measured by the maximum force with which one can throw a ball, shows a gradual decline beginning at about age __ but is generally not noticeable to most people until middle age
30
most women are what age when they give birth to their first child?
their 20s
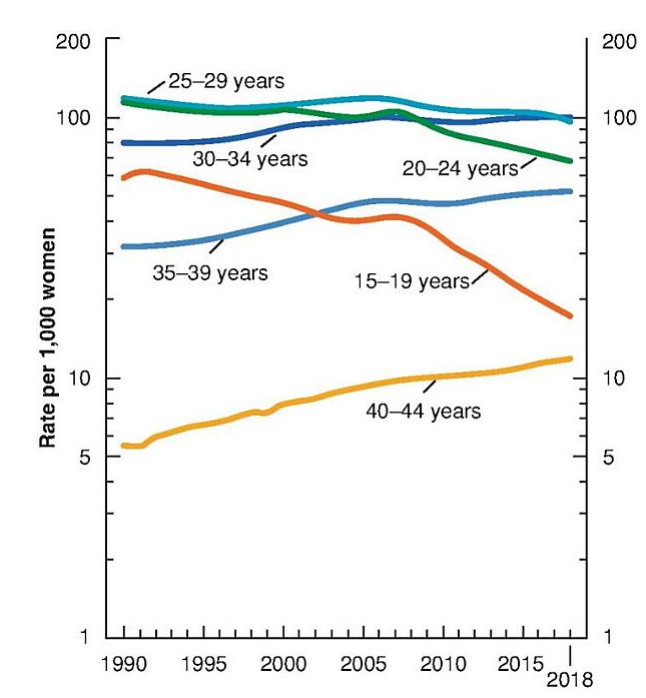
T/F: Births to women in their 30s and 40s have increased substantially since the early 1990s.
T (see graph)
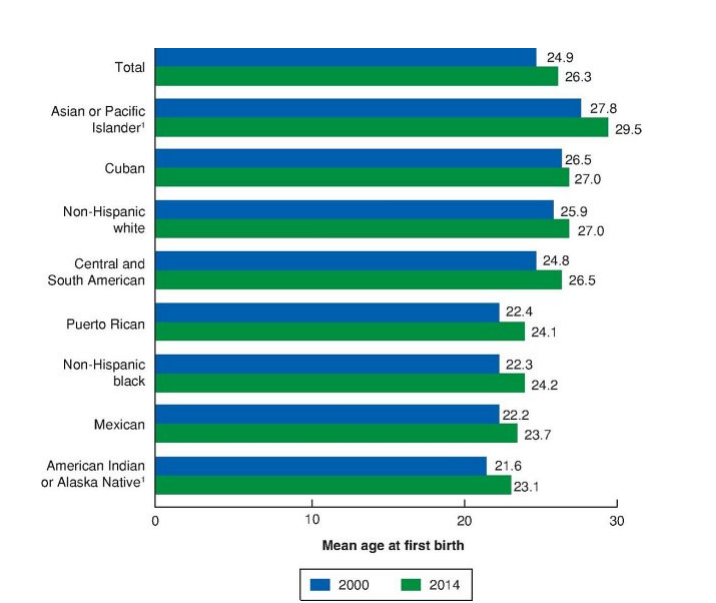
T/F: The average age at first birth has decreased for U.S. women across race and ethnicity
F; it has INCREASED
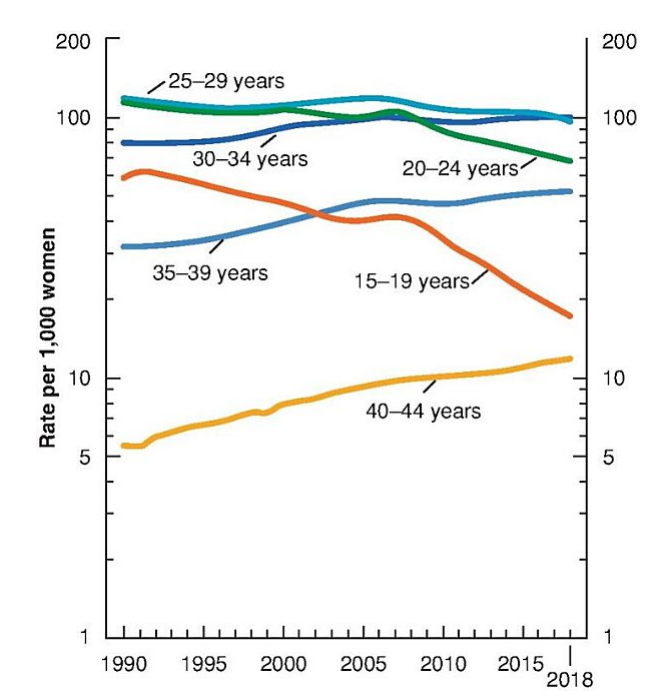
The increase in average maternal age at birth is thought to be a result of the dramatic decline in
adolescent pregnancy
Many young adults wait to have children until they have completed their education and established their careers. The maturity and financial stability that accompany the —s can make for better parents. However, reproductive capacity peaks in the __s and declines with age, increasing the risk for women in their mid-to-late 30s to experience difficulty conceiving
30s; 20s
Although women are born with about ___ ova, they decay with age and chromosomal anomalies accumulate, increasing the risk of pregnancy loss, or miscarriage
400,000 ova
A common cause of female infertility is the failure to ___, to release an ovum into the fallopian tube.
ovulate
With advancing age, ____ becomes less regular. There are also a variety of factors that can prevent __ (same word); some are treatable or preventable, such as drug and alcohol abuse, environmental toxins, obesity, and being underweight.
ovulation
T/F: Illnesses that affect the reproductive system, such as ovarian cancer and ovarian cysts, can also make it difficult or impossible to conceive.
T
Dwindling reserves of ova can prevent conception because it is thought that the body requires a ____ level of ova reserves in order to ovulate. The exact __ (same word) is unknown and, like other aspects of physical development, may vary with genetic and contextual factors
minimum
Men’s rate of change in reproductive capacity is significantly different from that of women; most men ___________.
remain able to conceive into older adulthood.

In young men, sperm can be affected by anything that interferes with the functioning of the body, such as fever, stress, drug abuse, alcoholism, radiation, and environmental toxins. Exposure to these factors can reduce the number of sperm or affect their physical structure, activity, and motility. In this way, ___ and __ factors contribute to young men’s fertility.
lifestyle and contextual

The number and quality of sperm produced declines in middle adulthood, beginning at about age __
40
T/F: Few deaths among emerging and young adults are the result of illness.
T!

The leading cause of death in U.S. young adults age 19 through 39 is ____ ___ , followed by — and —, and then +++ and ++++
unintentional injury, suicide and homicide, cancer and heart disease
The most common fatal unintentional injury among emerging and young adults is ___ ____, followed by +++ +++ accidents, with accidents most common in adults under age __ and overdoses in adults age \\ and older.
drug overdose; motor vehicle accidents; 25; 25

What makes it difficult for emerging adults to eat healthily?
The absence of parental controls, access to an abundance of food, a busy schedule, and stresses associated with life transitions (such as to college and career) makes it difficult for emerging adults to eat healthily.
What BMI index defines obesity? What about overweight?
Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or above. Overweight is a BMI greater than 25.
T/F: Obesity has increased substantially over the last few years.
F. It’s decades.
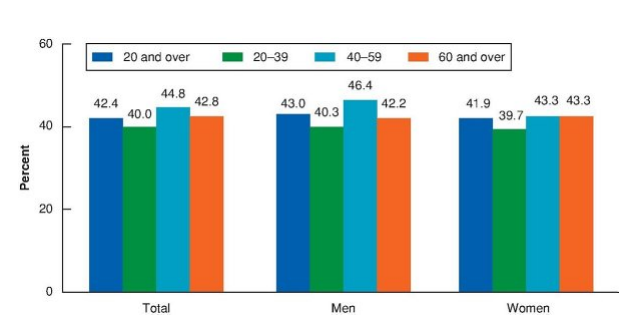
Over ____-___ of American adults over the age of — are overweight (31%), obese (43%), or severely obese (9%). Young adult men and women age 20–39 show similar rates of obesity (about 40% each)
three-quarters; 20
T/F: Obesity becomes more common from early to middle adulthood.
T
What are some reasons the prevalence of overweight and obesity has doubled over the past four decades?
With advances in technology, desk jobs have replaced many jobs requiring physical labor and many people have become less active.
Food has become more abundant in Western countries, especially sugary, fatty, and processed foods.
Increasingly, people in low- and middle-income countries consume Western diets.
With age, it becomes more difficult to avoid overeating because caloric needs drop between the ages of 25 and 50, and the metabolic rate—the amount of energy the body uses at rest—gradually falls as muscle cells decline in number and size.
A sedentary lifestyle, little physical activity, and screen time is closely associated with obesity.

Neighborhood disadvantage is associated with obesity through a variety of means, such as
poor access to green spaces, greater access to fast-food restaurants, and greater perceived stress
Individuals’ and families’ socioeconomic status influences the risk for obesity because fruits, vegetables, and lean protein are ___ relative to less-healthy sweet snacks, processed foods, and refined grains
costly

Obese adults often experience weight-related bias and discrimination from individuals and groups who have negative attitudes about obesity, such as the misconception that obesity is related to
self-control

Successful weight loss is most often a result of
lifestyle changes, such as regular moderate exercise coupled with a nutritionally balanced diet low in calories and fat
T/F: Regular moderate exercise enhances immunity and is associated with a reduced risk for chronic illnesses, such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer
T (this is pretty obvious)
Remaining active helps young adults maintain __ skill competencies, such as throwing speed and jumping distance, which predict overall fitness, percentage of body fat, and strength
motor
Physical fitness is linked to ____ performance throughout adulthood. Young adults who demonstrate high levels of cardiovascular fitness tend to perform better on measures of cognitive abilities, such as attention, reaction time, working memory, and processing speed than low-fitness young adults.
cognitive
T/F: Even if young adults demonstrate high levels of cardiovascular fitness, they tend to perform worse on measures of cognitive abilities, such as attention, reaction time, working memory, and processing speed than low-fitness young adults because of their age.
F. Young adults who demonstrate high levels of cardiovascular fitness tend to perform better on measures of cognitive abilities, such as attention, reaction time, working memory, and processing speed than low-fitness young adults.
U.S. national guidelines recommend how many minutes of moderate intensity activity each week (e.g., brisk walking, raking the lawn, or pushing a lawn mower)?
Or, how many minutes of vigorous intensity activity?
Plus muscle strengthening exercises on at least _ days each week
150 to 300; 75 to 150; 2 days each week
Physical activity tends to decline from adolescence into ___ adulthood, increasing the risk for poor health outcomes throughout adulthood
young
T/F: Adults who reported at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity each day were less likely to show anxiety and depressive symptoms than their less-active peers.
T
In North America, substance use, such as drug, alcohol, and tobacco, tends to begin during ___, peak in the early 20s, and decline through the 30s
adolescence
Substance use tends to decline as young adults become parents and transition into new family roles; however, substance use remains prevalent in adulthood, with about __% of adults age 35 to 40 reporting llicit drug use (other than marijuana) within the past year (about 30% including marijuana)
12

What is binge drinking?
defined as consuming five or more drinks in one sitting in men and four drinks in one sitting in women

T/F: Generally, binge drinking and heavy drinking are highest in emerging and young adulthood.
T. With about one-third of adults aged 18 to 24 and 25 to 34 as well as one in five adults aged 35 to 44 reporting binge drinking within the past 30 days
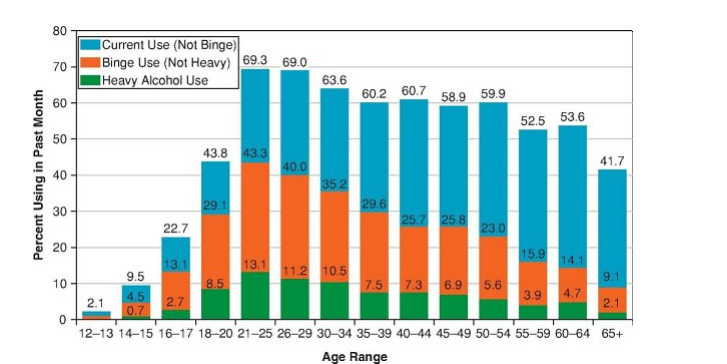
T/F: Binge drinking is associated with negative short- and long-term consequences for physical and psychological wellbeing, including fatal and nonfatal injuries, physical fights, driving after drinking, arrests and detentions, sexual assault, and threats to cardiovascular function, such as increased arterial stiffness
T

Each year, alcohol is implicated in how many traffic fatalities and in __% of all crimes
one-third traffic fatalities; 40% of all crimes.
Research with college students has suggested that binge and heavy drinking may be part of a “__ of __ phenomenon,” for which the transition out of high school increases the risk
stage of life phenomenon
T/F: Most emerging adults report experiencing more negative consequences of drinking than positive, contributing to the overall decline in alcohol substance abuse over the lifespan.
F. While it’s true alcohol use tends to decline as young people enter early adulthood, most emerging adults report experiencing more positive consequences of drinking (such as feeling social) than negative consequences (such as cognitive impairment), which contributes to high rates of binge and heavy drinking in this age group
T/F: Although emerging adults who attend college tend to drink more than their noncollege-attending peers, heavy drinking and alcohol-related problems are more common among emerging adults regardless of college enrollment
T
Often referred to as “____ ___,” alcohol use tends to decline as young people enter early adulthood.
maturing out
T/F: The transition to adult responsibilities such as career, marriage, and parenthood typically predicts declines in heavy drinking and alcohol-related problems.
T; “Maturing out”
T/F: Young adults who drink much heavier than their peers also show declines in the drinking characteristic of maturing out.
F. They do not show the declines in the drinking characteristic of maturing out.

Binge and heavy drinking are concerns because they both involve intermittent but high levels of alcohol consumption, which increases the risk of developing alcohol ___ and abuse into middle adulthood
dependence

What is alcohol dependence?
Alcohol dependence, also known as alcohol use disorder, is a maladaptive pattern of alcohol use that leads to clinically significant impairment or distress. Alcohol dependence is signaled by tolerance, cravings and withdrawal, inability to reduce drinking, drinking more or for longer than intended, neglect of activities and obligations, and continued use of alcohol despite alcohol-related psychological or physical problems.

What type of therapy might be effective to treat alcohol dependence?
aversion therapy (the use of medication that produces negative reactions to alcohol, such as vomiting) to spur a distaste for alcohol

By far the most commonly used substance, after alcohol, is ___, with 20% of 18- to 25-year-old emerging adults and 13% of 26- to 34-year-old young adults reporting use in the last month
marijuana

Young people consume marijuana for different reasons; those who cite ____ as their primary reason tend to report fewer marijuana-related problems than do those who list coping, relaxation, and enjoyment
experimentation

T/F: Marijuana use has decreased rapidly among emerging and young adults over the past 15 years.
F. Marijuana use has increased rapidly among emerging and young adults over the past 15 years correlating with changes in its legal status in U.S. states

T/F: Emerging adults are more likely to report medical use rather than recreational reasons for marijuana use
F. Emerging adults are more likely to report recreational use rather than medical reasons for marijuana use. Medical use becomes more common with age, especially in middle adulthood

T/F: Heavy marijuana use is associated with lower levels of academic attainment, lower income, greater levels of unemployment, conflict with partners, and poor life satisfaction.
T