1.3.2 - Externalities
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What are demerit goods?
A good that can have a negative impact on the consumer
What is a social cost?
A social cost is the cost of production or consumption of a product for soviet as a whole
What is the formula for social cost
Social cost = private cost + external cost
What is a private cost
A private cost is a cost that is experienced by the individual / firm directly involved in the economic transaction
What is an external cost?
An external cost is a cost experienced by third parties as a result of consumption of a good or service by another individual
What are externalities
Externalities are the third party effect from production and consumption of goods and services
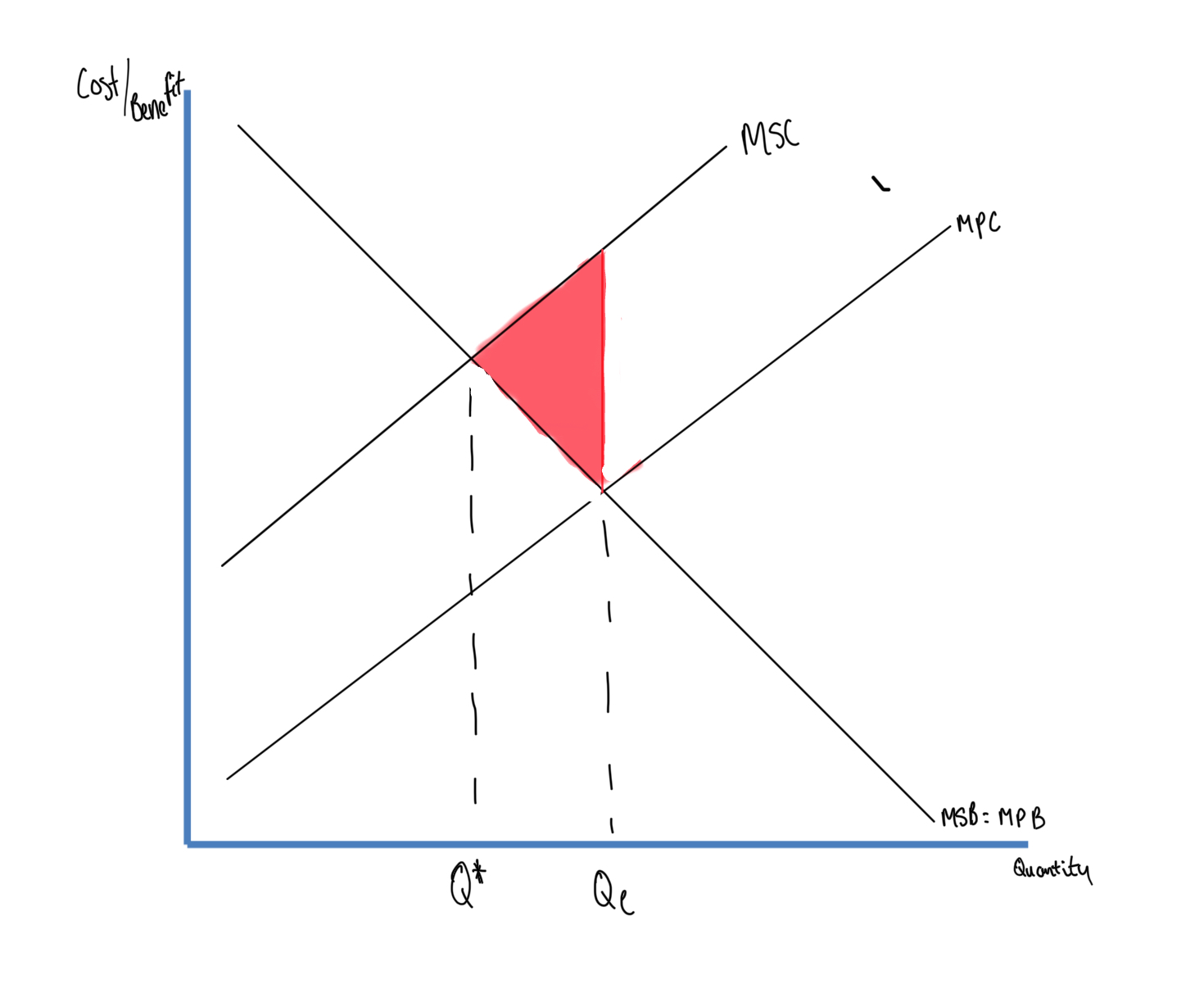
Explain this diagram
Deadweight welfare cost - the reduction of economic efficiency that occurs when the market is not in equilibrium
Extra units produced beyond Q* imposes an additional cost on society
MSC - marginal social cost
MPC - marginal private cost (supply curve in a free market)
MSB = MPB - marginal social benefit - marginal private benefit
Qe - free market equilibrium and it leads to over production
Q* - socially optimal output
With negative externalities social cost > private cost
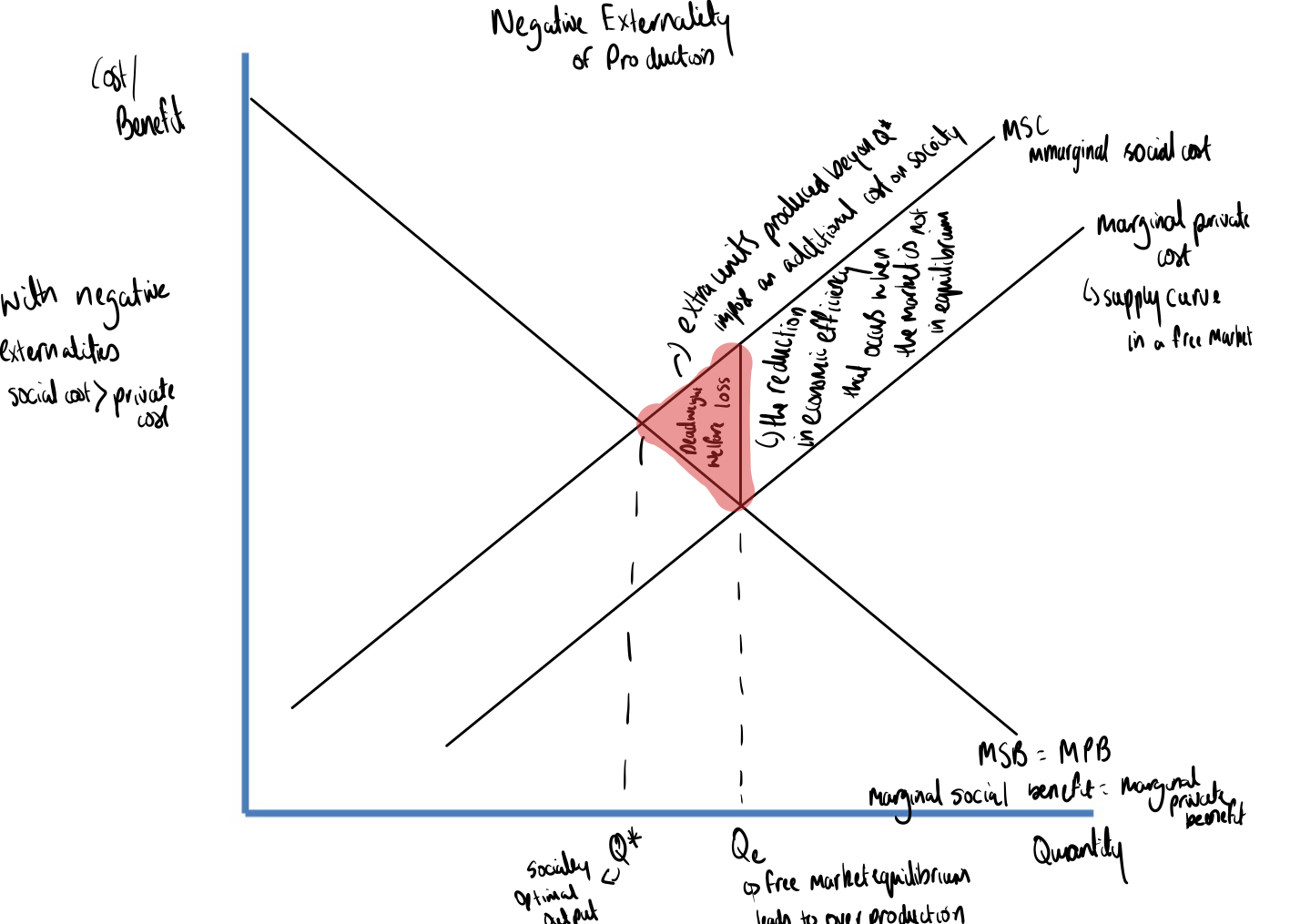
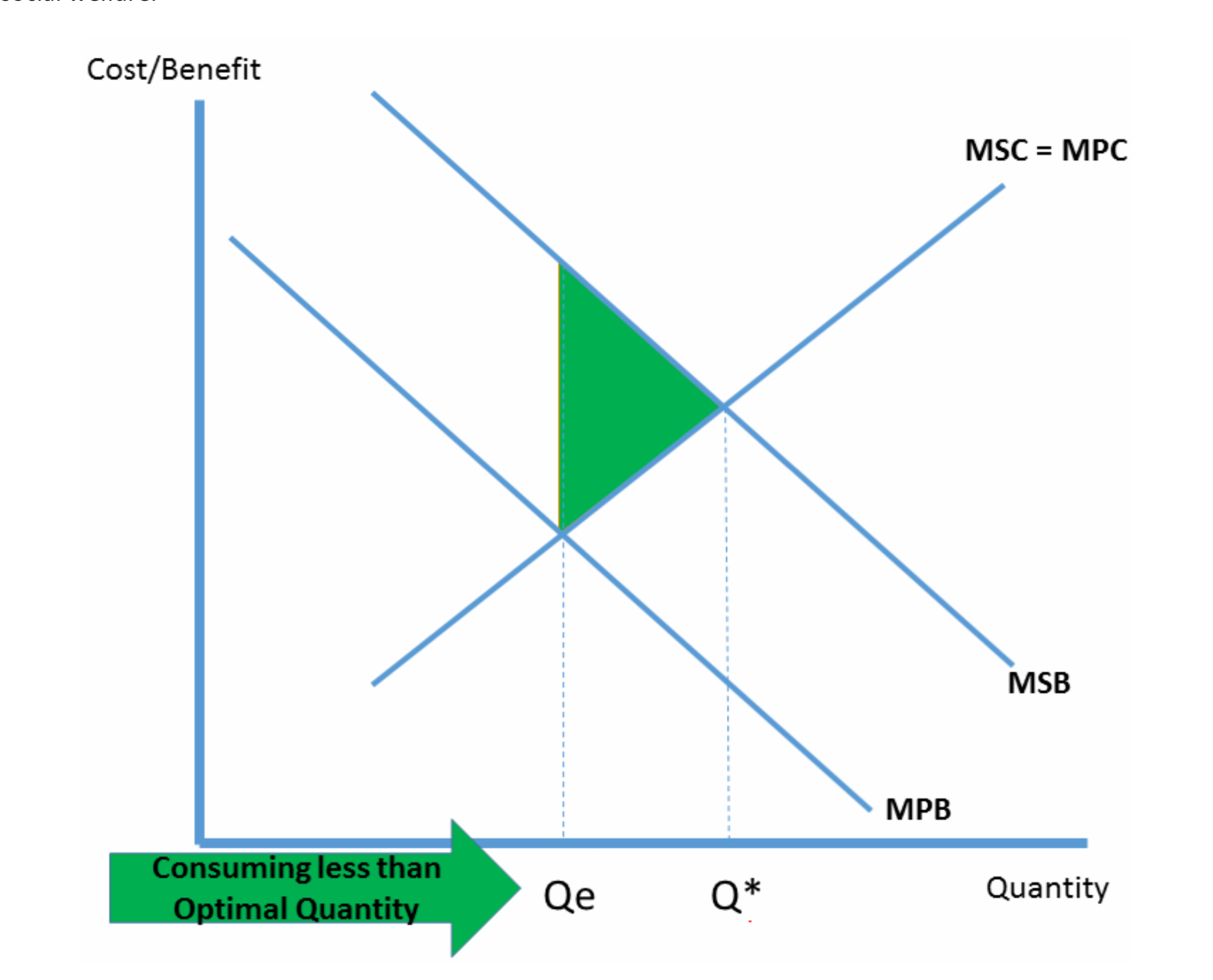
Explain this diagram
Qe - free market equilibrium and because they don’t know the value of the goods, they are under provided or under consumed which leads to market failure
With positive externalities of consumption social benefit > private benefit