Telescopes
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
In Astrophysics what lens is discussed?
Only converging (convex) lenses are discussed.
What is the focal length?
The distance from the centre of the lens to the focal point .
How does a thicker (more curved) lens affect the focal length?
the focal length gets shorter, the shorter the focal length the more powerful the lens.
What are the differences between real and virtual images?
Real images: light converges towards a focal point, always inverted, can be projected onto a screen.
Virtual images: light diverges away from a focal point, always upright, cannot be projected onto a screen.
What is the lens equation for a real image?
1/f= 1/u + 1/v
f= focal length v= distance of the image from the lens u= distance of object from lens
What is the lens equation for a virtual images?
1/f = 1/u - 1/v
f= focal length v=distance of image from the lens u= distance of object from lens
What is the focal point?
The point at which rays parallel to the principle axis of a lens are brought to focus.
How can images formed by lenses be described by?
Their nature (real or virtual), size (magnified, diminished, same) and orientation (inverted or upright)
What is the equation for magnification?
M= hi/h₀ or M=v/u
Where hi= image height and h₀= object height
Where v= distance from lens to image and u= distance from lens to object
What is a refracting telescope?
A telescope that uses two converging lens to project images of distant objects.
What does the ray diagram of a refractor look like?
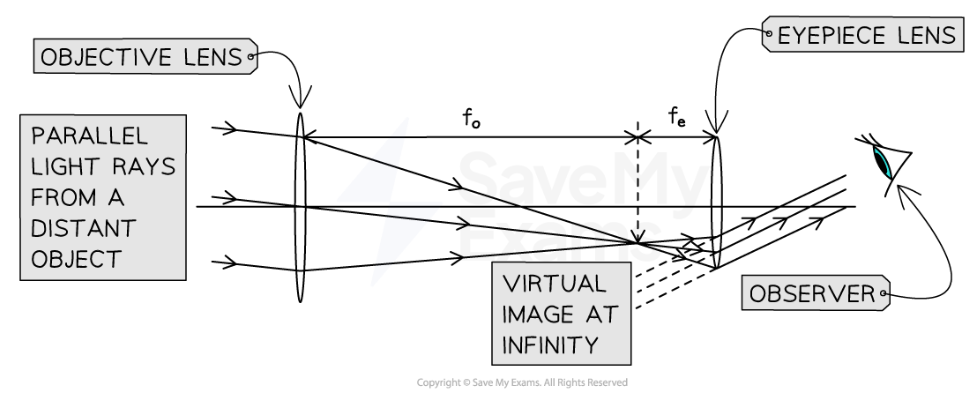
What is normal adjustment
When a refractor is adjusted so the final image is at infinity, both lenses must be arranged so their focal points meet at the same place, the focal length of the objective lens must be longer than the focal length of the eyepiece lens.
What is the angular size of an object?
The angle, in radians, subtended by an object of height h, at a distance d away given by: θ=h/d
How do you calculate the angle subtended by astronomical objects?
use angular magnification, defined as M= angle subtended by image at eye (β)/ angle subtended by object at unaided eye (α)
How do you determine angular magnification of a refracting telescope in normal adjustment?
M=β/α= focal length of objective lens/ focal length of eyepeice lens
What is the most common type of reflector?
The cassegrain telescope
How do reflectors work?
They use a primary and secondary mirror, the primary mirror is large and concave, the secondary mirror is smaller and convex, the rays are then directed through a gap towards an eye peice lens located behind the primary mirror. Rays enter the telescope parallel to the principal axis, curvature of mirrors doesn’t have to be the same, rays only cross in gap in primary mirror.
What is aberration?
A distortion in images produced by optical apparatus.
What are the two main types of aberration that affect images produced by reflectors and refractors?
Chromatic aberration and spherical aberration.
What is chromatic aberration?
Only in refracting telescopes, where different wavelengths of light are refracted by different amounts, causing edges of an image to appear coloured.
How can chromatic aberration be reduced?
by using a second diverging lens, which refracts light in the opposite direction.
What is spherical aberration?
Affects both refractors and reflectors, where rays of light come to focus at different points due to spherical curvatureof a lens or mirror, causing the image to become very blurred.
How can spherical aberration be reduced?
For refractors, using a parabolic lens or it can be completely overcome in a reflector using a parabolic mirror.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a refracting telescope?
Advantages: require less maintenance, not as sensitive to temperature changes.
Disadvantages: difficult to make because of their size, very heavy, construction is hard, suffer from chromatic and spherical aberration, only able to observe wavelengths of visible light.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of reflecting telescopes?
Advantages: size, weight, easier construction, don’t suffer from chromatic aberration, spherical aberration can be eliminated,can be designed to observe wavelengths of light outside visible spectrum.
Disadvantages: secondary mirror blocks some light from entering primary mirror, secondary mirror and its support causes some diffraction, mirrors exposed to air so require constant maintenance.
What happens to light from any object passing through a circular aperture?
It will diffract and create inteference fringes upon the detector inside, the pattern is circular, the large central maximum is called an airy disc and is twice as wide as the further maxima.
What does the Rayleigh criterion state?
Two sources will be resolved if the central maximum of one diffraction pattern coincides with the first minimum of the other.
How can the resolution of a telescope be increased?
by reducing the amount the light diffracts by increasing the diameter of the aperture or operating at a shorter wavelength of light.
What is the equation for angular separation?
θ= s/d
where s= distance between the two sources and d= distance between the sources and the observer.
How can the Rayleigh criterion be written mathematically?
sources are resolvable when θ> λ/D
sources are just resolvable when θ≈ λ/D
sources are not resolvable when θ< λ/D
for a circular aperture: θ= 1.22λ/D
What is the collecting power of a telescope defined as?
A measure of the amount of light energy it collects per second, equivalent to the power per unit area or intensity of incident radiation collected.
What is the collecting power of a telescope directly proportional to?
The square of the diameter of its objective lens
Why are larger aperture diameter telescopes advantageous?
They have a greater collecting power so images are brighter, they have a greater resolving power so images are clearer.
How can the collecting power of two telescopes be calculated?
collecting power of telescope 1/ collecting power of telescope 2 = (diameter of 1/ diameter of 2)²
How can the resolving power of two telescopes operating on the same wavelength be calculated?
resolving power of telescope 1/ resolving power of telescope 2 = diameter 2/ diamteter1
What is an optical telescope?
One that detects wavelengths of light from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
What are some non-optical telescopes?
Radio, infrared, ultraviolet, x-ray
How is the operating wavelength range of a telescope greatly limited?
by the absorption of certain wavelengths by Earth's atmosphere. This means space- based telescopes are able to detect all wavelengths whilst ground based can only detect visible, narrow ranges of infrared and most microwave and radio.
What are the advantages of putting telescopes in space?
No absorption of electromagnetic waves by atmosphere, no light pollution, no atmospheric affects.
how do radio telescopes work?
They are ground based, made up of a detector and parabolic disc. much lower resolving power but greater collecting power than optical telescopes.
how do infrared telescopes work?
predominantly space-based, mirrors must be kept very cold to avoid inteference, must be built in dry, high- altitude locations since IR is strongly absorbed by water vapour. Have lower resolving power than optical telescopes but similiar collecting power.
How do ultraviolet telescopes work?
must be located in space, mirrors in UV telescoes must be smoother than in optical. higher resolving power but similiar collecting power to optical telescopes.
How do x-ray and gamma telescopes work?
x-ray: made from combo of parabolic and hyperbolic mirrors, must be located in space
gamma: don’t use mirrors byr specialised detectors, must be located in space.
both have much higher resolving power but much lower collecting power to optical telescopes.
What is a CCD?
A charge-coupled device, a detector that is highly sensitive to photons, incident photons cause electrons to be released, the number of electrons released is proportional to intensity of incident light, an image is formed on CCD which can be processed to give digital image.
What are the advantages of a CCD over the human eye?
the number of images captured in a time period and exposure time can be easily adjusted, information stored in CCD can be accessed remotely, generated image can be stored and analysed digitally, can detector larger range of wavelengths, has better resolution due to having smaller pixels, higher quantum efficiency.