Physiology of normal White Blood Cells
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
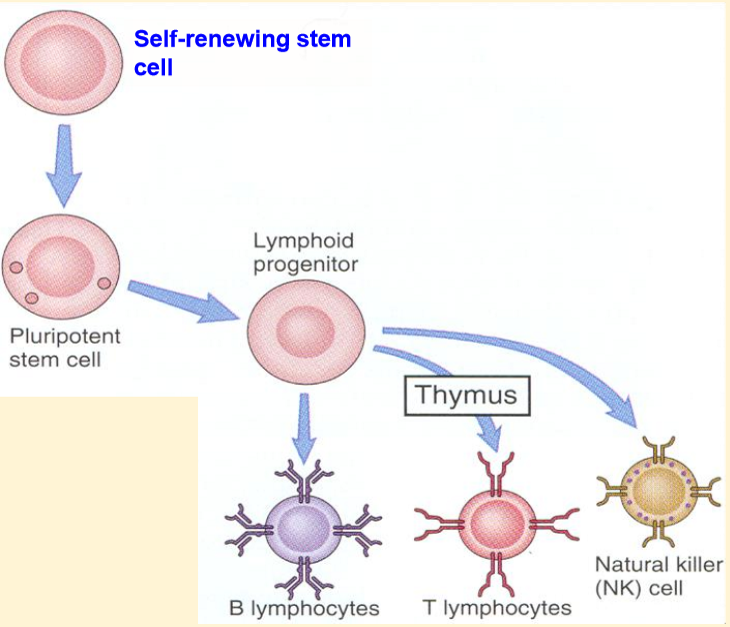
Haematopoiesis - lymphoid cells
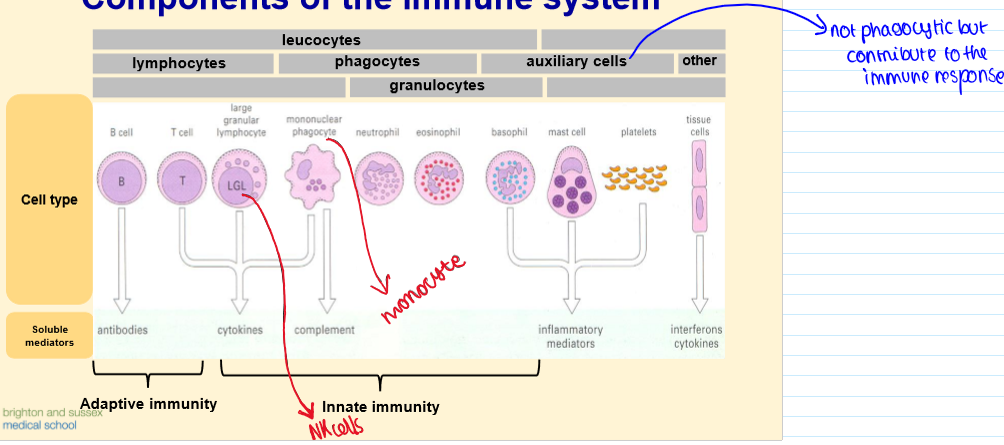
What are the components of the immune system?
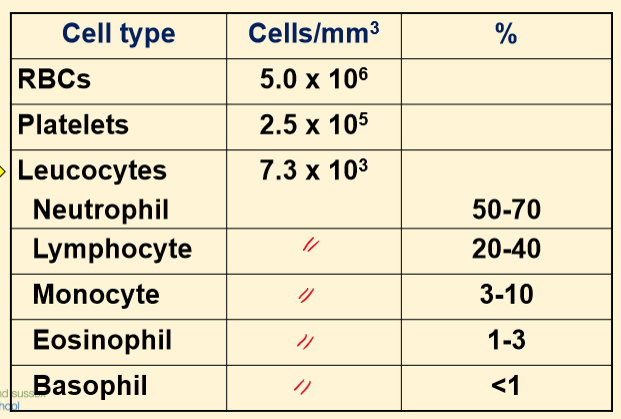
What is the blood cell count in adults?
What are NEUTROPHILS?
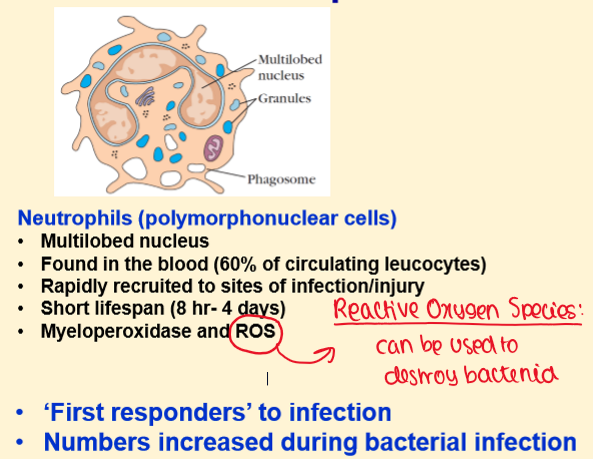
What are MONOCYTES?

What are MACROPHAGES?

What are EOSINOPHILS?
Have bilobed nuclei and granulated cytoplasm
Motile phagocytic cells that can migrate from the blood into the tissues; majority are located in tissues
What is the function of eosinophils?

What are BASOPHILS?
Lobed nuclei and heavily granulated cytoplasm
Non-phagocytic cells that circulate in the blood
What is the function of basophils?
1) recruited to sites of allergic reactions or ectoparasite infection
express FceRI
2) allergen can bind to allergen-specific IgE bound to the cell surface of basophils causing degranulation of effector mediators
3) Release pharmacologically active substances from cytoplasmic granules
4) Promote inflammation
Leucocytes and immunity

What are CYTOKINES?
Low molecular weight (< 30 kDa) regulatory proteins or glycoproteins
Act as the messenger molecules of the immune system
Secreted primarily by white blood cells
Also assist in regulating the development of immune effector cells
Generally act locally (paracrine signalling)
What are CHEMOKINES?
These are a type of cytokine that induce directed chemotaxis in local responsive cells
Chemokines function mainly as attractants for leucocytes, recruiting monocytes and neutrophils to the site of infection
What is an important monocyte chemokine?
MCP-1 – Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (Also known as CCL-2)
Important for recruitment of monocytes
What is the function of MCP-1?
1) Recruit leucocytes (monocytes and neutrophils in particular)
2) Chemotaxis of blood leukocytes
3) Increase in expression of adhesion molecules
What is likely to happen in a tissue where MCP-1 is increased?
1) Increase in adhesion molecules on leucocytes
2) Chemotaxis of leucocytes from blood towards endothelium
3) Migration of leucocytes from blood into tissue
Inflammation
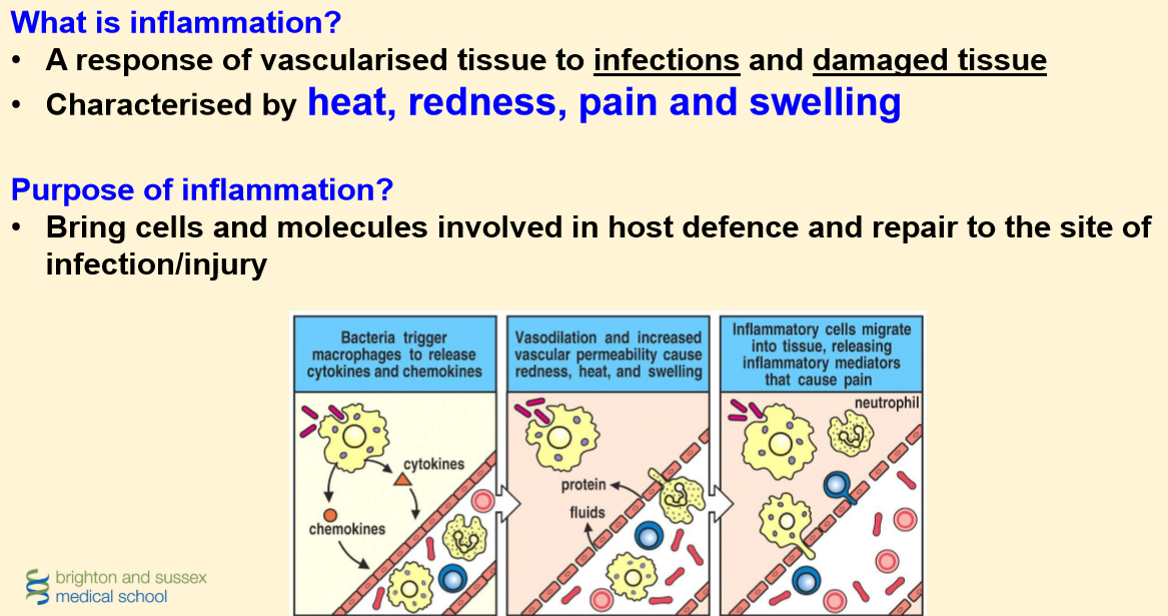
What are the components of the inflammatory response?
1) Blood vessels
2) Phagocytic leucocytes
3) Plasma proteins (e.g. complement, antibodies)
Process of inflammation
1.Blood vessels dilate
2.Blood vessels become more permeable
3.Circulating leucocytes migrate into tissue
4.Leucocytes are activated
5.Activated leucocytes destroy microbes and unwanted material
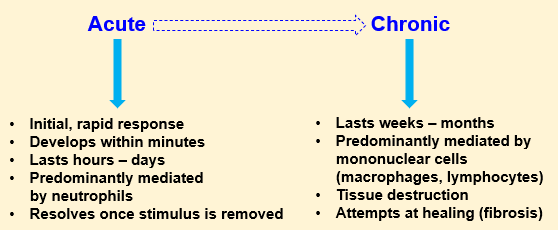
Acute VS Chronic inflammation
Recruitment of monocytes to sites of inflammation
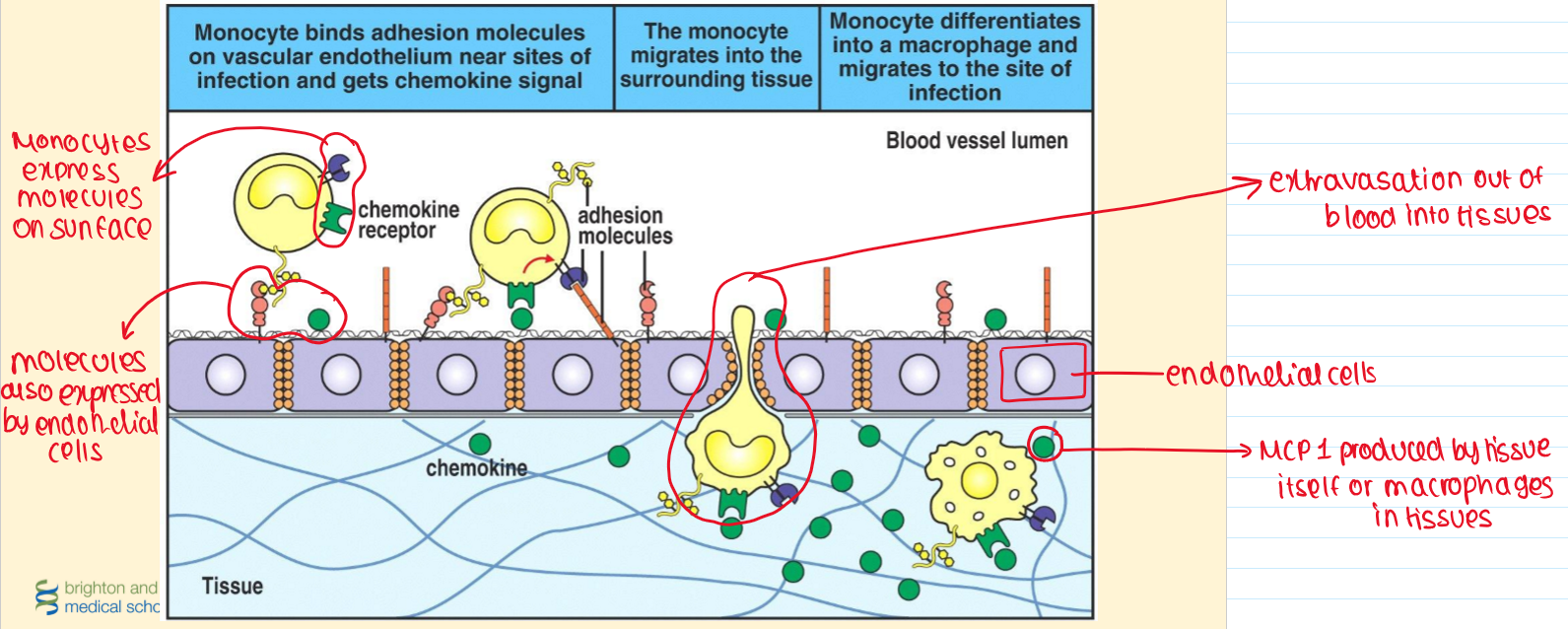
Cell adhesion to endothelium
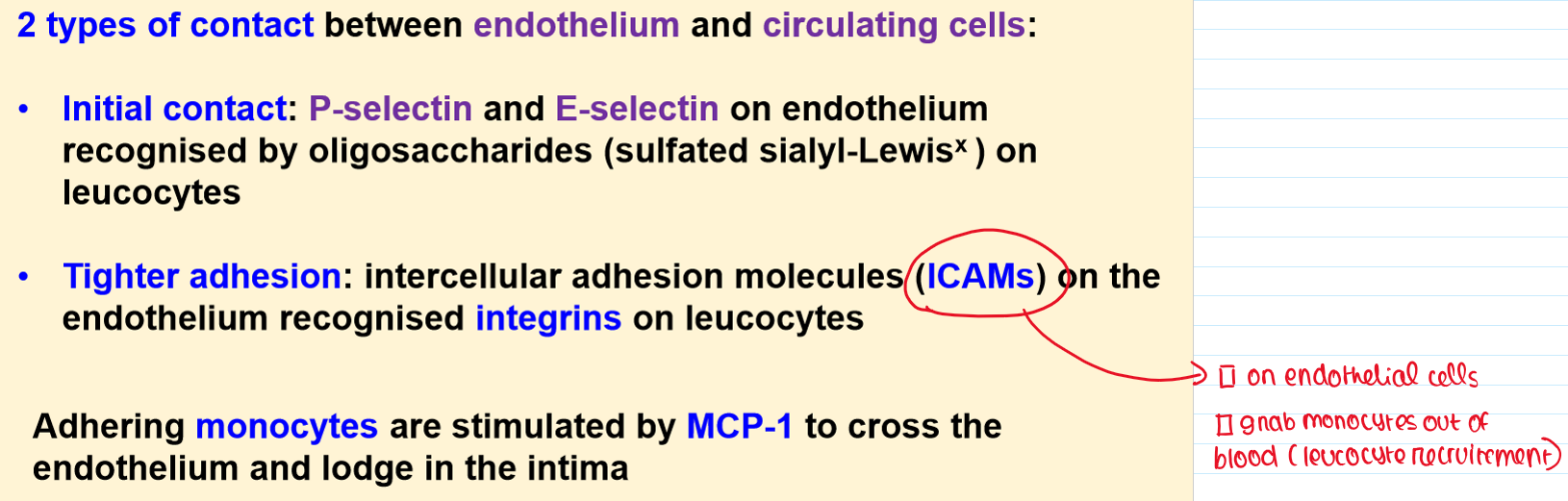
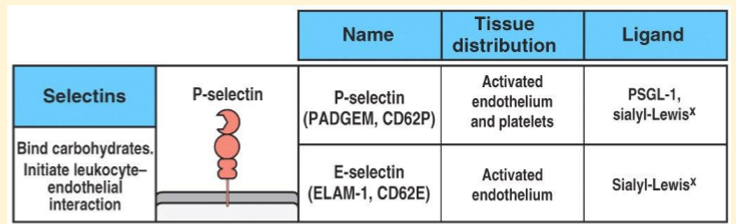
What is TRANSIENT INITIAL CONTACT?
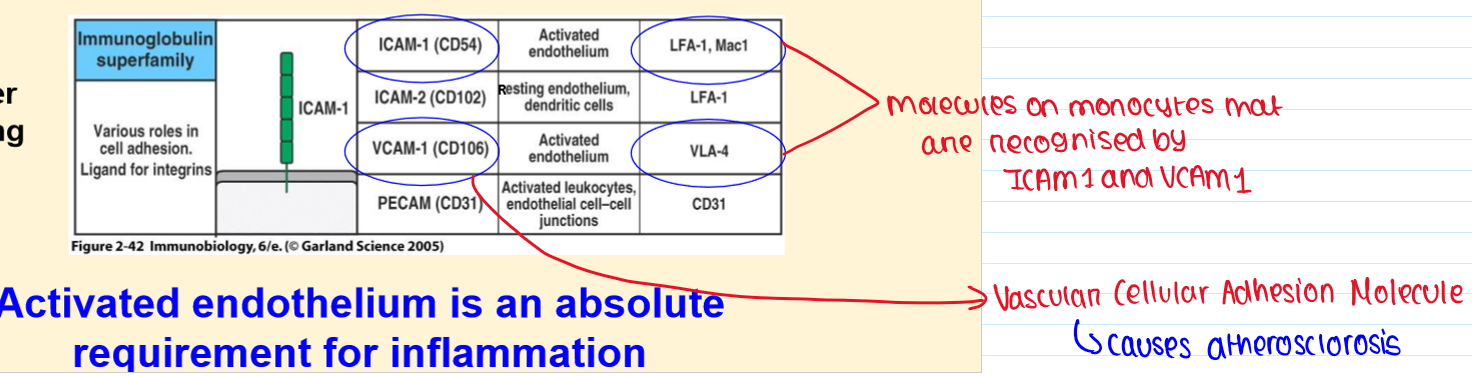
What is TIGHTER BINDING?
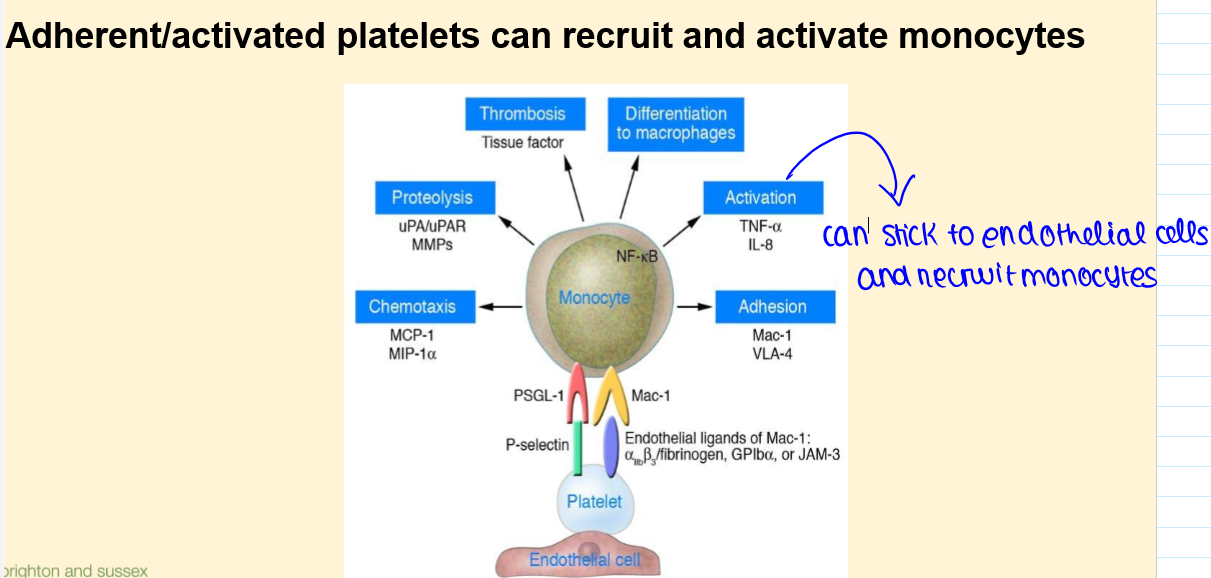
Platelet/Monocyte interactions
Recognition leading to phagocytosis
1) Macrophage mannose receptor
Ligand: Conserved carbohydrate structures
2) Scavenger receptors
Ligand: anionic polymers, acetylated and oxidised LDL
LDL is Low Density Lipoprotein which is a type of lipoprotein that contains high levels of cholesterol
3) Toll-like receptors (TLRs)
Ligand: range of ligands for various TLRs
4) Opsonization of pathogens (coating with circulating receptors) also important
Phagocytosis
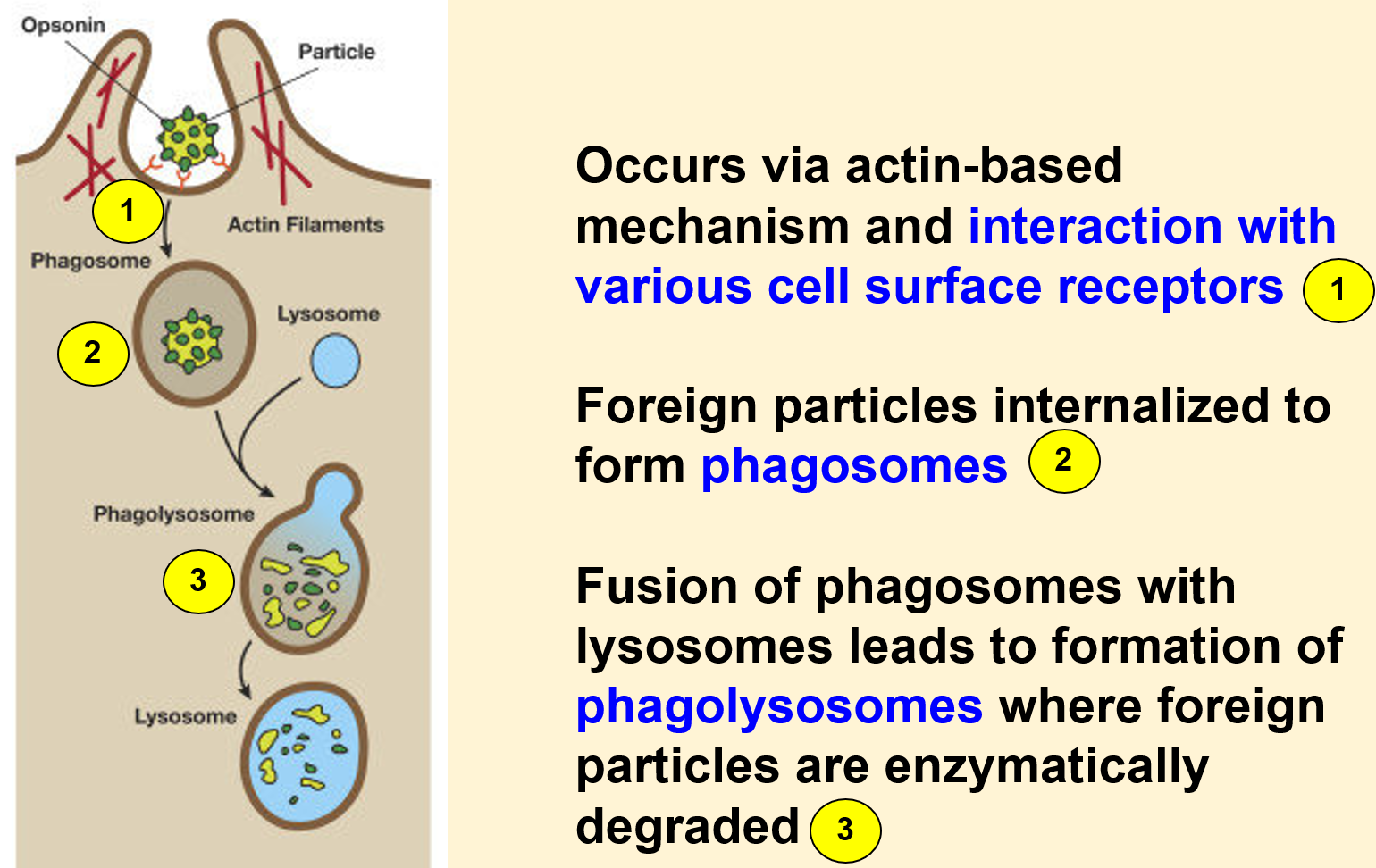
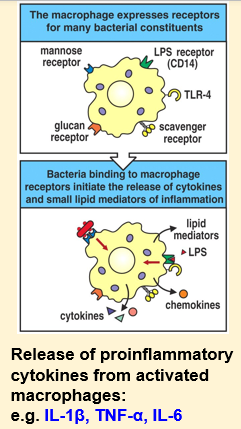
Example: activation of macrophages by pathogens
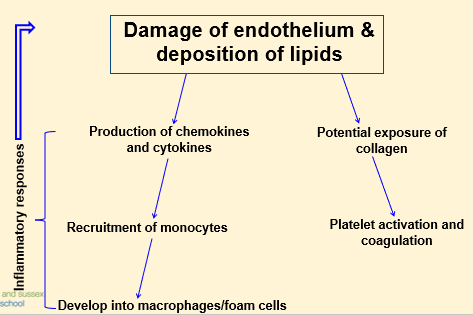
What is Atherosclerosis?
Build-up of plaque in lining of arteries
1) Involves 3 areas of pathogenesis:
Endothelial cell dysfunction
nflammation (mediated by monocytes/macrophages)
Dysregulation of lipid metabolism
Atherogenesis (development of atherosclerotic plaque)