3 Waves and Optics
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Waves
Oscillations that transfer energy not matter.
Transverse waves
Doesn’t require a medium to propagate, with oscillations perpendicular to the direction of travel.
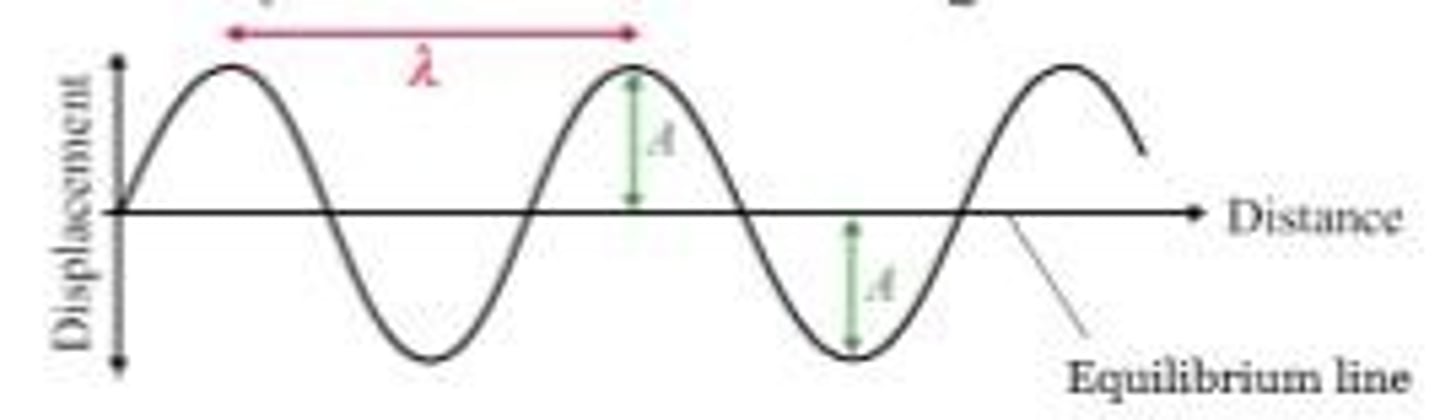
Amplitude (A)
Maximum Displacement from equilibrium.
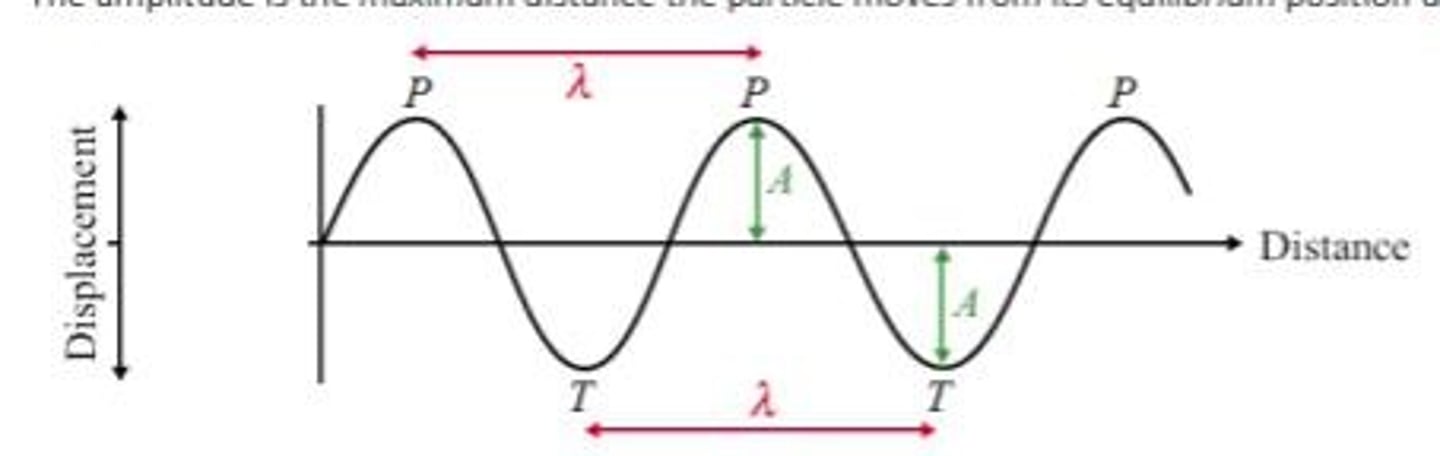
Wavelength (λ)
Length of one wave cycle.
Time Period (T)
Time for one wave.
Frequency (f)
How many waves a second.
Wave Speed (c)
Speed of wave.
In Phase
Refers to two or more waves that have the same frequency and phase, resulting in constructive interference.
Out of Phase
Refers to two or more waves that have a phase difference of 180 degrees, resulting in destructive interference.
Phase Difference
Depends on the fraction of wavelength

Path Difference
The difference between two sources of light measured in wavelengths.
Longitudinal Waves
Oscillates parallel to the direction of transfer of energy. Requires a medium to travel
Polarization
Restricts the oscillations of a wave to one plane.
Refraction
When light passes between mediums the light changes direction.
Total Internal Reflection
When the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle, causing light to be completely reflected back into the medium.
Critical Angle
The angle of incidence at which light refracts by 90 degrees.
Optical Fibres/Fibre Optics
Thin flexible piece of glass.
Material (Chromatic) Dispersion
Different wavelengths travel at different speeds in the same medium.
Modal (Multi-path) Dispersion
Caused by the pules taking different routes down the fibre, causes pulse broadening
Diffraction
When a wave passes through a gap they spread out.
Coherence
Waves are at the same frequency and have a constant phase difference.
Superposition
Process which two waves combine into a single wave when they overlap.
Constructive Interference
Creates a resultant wave with large amplitude.
Destructive Interference
Creates a resultant wave with small or 0 amplitude.
Double Slit Interference
Special case of superposition due to light traveling through 2 splits
Young's Double Slit Experiment
Showed the interference of light and proved light is a wave
Pattern of the double slit
A series of symmetric equally spaced bright and dark fringes about a central bright fringe which is directly behind the midpoint
Intensity of the light from a double slit
Decreases as distance from the centre increases
Central Bright Fringe
The brightest fringe in the interference pattern
Other Bright Fringes
Fringes that are bright but not the central one
Dark Fringes
Fringes that are not visible due to destructive interference
Single Slit Interference
Wide central maxima with a width twice that of the other maxima and the brightest
Diffraction Gratings
Series of narrow, parallel slits usually around 500 slits per mm
Zero-order Maximum
The first bright line directly behind the grating
First Order Maximum
The bright line at an angle θ from the zero-order maximum
Standing Waves
Two waves with the same frequency traveling in different directions will superpose to form a standing wave
Nodes
Positions on a standing wave where the amplitude is zero or very small
Anti-nodes
Positions on a standing wave where the amplitude is maximum
Harmonics
Increasing frequency causes different harmonics, with the first standing wave formed being the fundamental harmonic