Lecture 19 - Reptiles
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are the differences between Amphibians and Reptiles?
Reptiles have:
1) Amniotic egg
2) Tough, scaly skin to protect against desiccation
3) More efficient lungs & circulation
4) Excrete nitrogenous waste as uric acid
5) More complex nervous system → better vision
What are the characteristics of frog or fish eggs?
1) Still need a yolk sac for food
2) Don’t have a problem with:
-Collapse, Desiccation, waste disposal, or gas exchange
What are the problems terrestrial eggs face?
1) Needing shell to prevent desiccation or collapse
2) Makes waste disposal difficult
3) Trouble with gas exchange
4) Trouble obtaining food
What must a true terrestrial egg have?
1) Protection against desiccation
2) A place to store wastes
3) A gas exchange mechanism
4) Food storage
What are the characteristics of the shell & shell membrane of the Amniotic egg?
1) Provides physical support and protection from desiccation
2) Slightly porous to permit gas exchange
3) Many lack hard shell
What are the characteristics of the Amniotic egg?
1) Extra-embryonic membranes: Amnion, Allantois, Chorion, & Yolk sac
2) Not part of the embryo & drops off when no longer useful
What are the characteristics of the Yolk sac in the Amniotic egg?
1) Evolved millions of years before Amniotic egg
2) Food storage

What are the characteristics of the Amnion in the Amniotic egg?
1) Fluid-filled sac surrounding embryo
2) Protection from desiccation and shocks
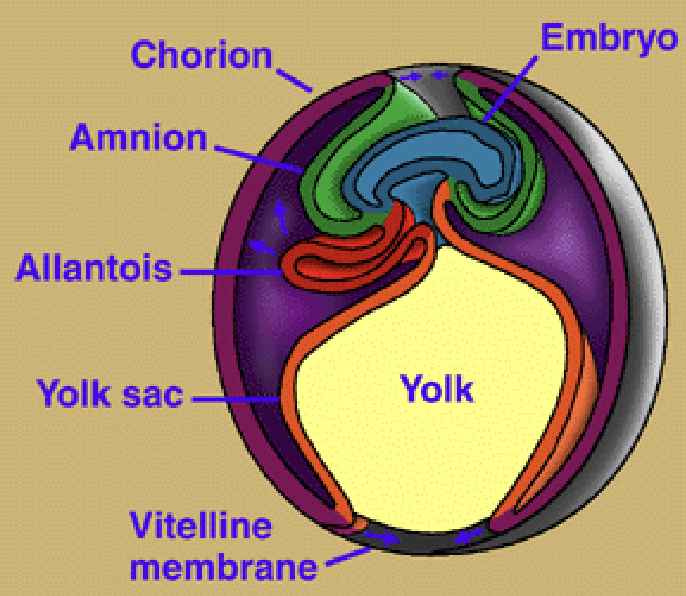
What are the characteristics of the Allantois in the Amniotic egg?
1) Enlarged bladder that collects nitrogenous waste from yolk
2) Allows CO2 to diffuse out and O2 to diffuse in
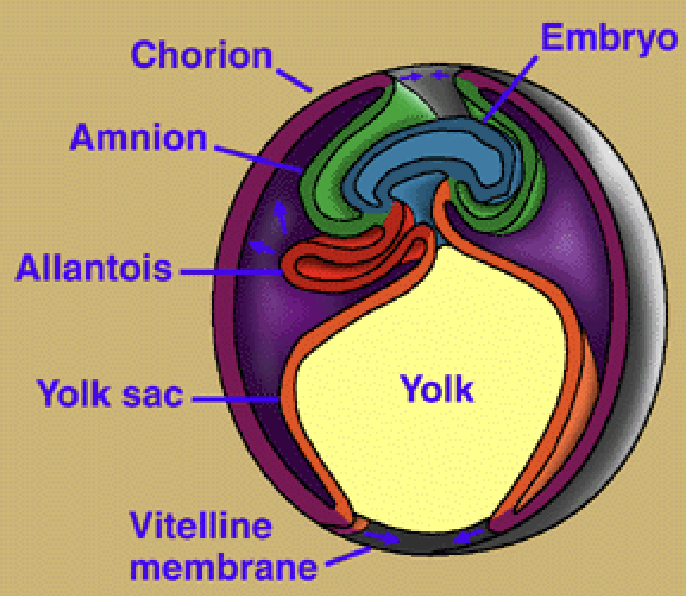
What are the characteristics of the Chorion in the Amniotic egg?
1) Outer membrane - encloses whole embryo
2) Fuses with Allantois to diffuse gases better
What are the consequences of having shelled eggs?
1) Enclosed egg must be produced before laid
2) Fertilization must be internal
3) Males of copulatory organs or other methods of putting sperm into females body
What are the characteristics of scales?
1) Beta keratin - tough
2) Skin has few glands and protects against injury & moisture loss
3) Chromatophores for colour
4) Epidermal scales
What are the characteristics of jaws?
1) Amphibian and fish jaws are made for rapid closing, not crushing prey
2) Reptiles develop strong crushing jaws allowing for variety in diet
3) Needs appropriate jaw musculature
-holes in jaw allow muscles to bulge and attach to skull
What do holes in the jaw allow for?
Allows for sites of muscle attachment
What are the 3 types of different arrangements in jaw musculature, what do they mean, and what animals have them?
Anapsid: No holes, turtles
Synapsid: One hole, mammals
Diapsid: Two holes, lizards, snakes, crocs, & birds
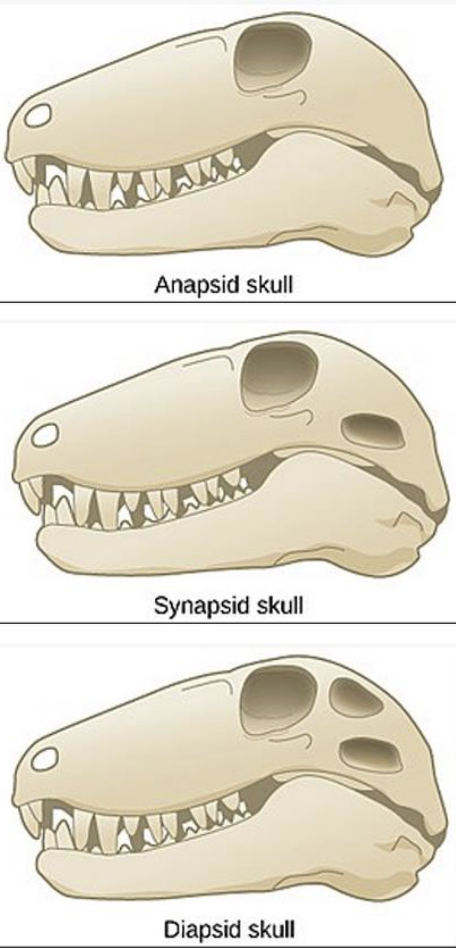
What are the characteristics of limbs?
1) If present, usually paired and pentadactyl (5 toes or fingers)
2) Some have evolved loss of limbs like snakes which is associated with elongation and how its easier to use curves of body to move
What are the characteristics of ribs?
1) Amphibians have reduced ribs
2) Reptiles have whole thorax enclosed in bony casket
What are the characteristics of gas exchange?
1) Use lungs, no cutaneous respiration like in Amphibians
2) Rib ventilation of lungs
3) Turtles respire through cloaca & neck skin, sea serpents respire through skin
What does a Metanephric kidney do & when is it developed?
1) Excrete solid waste (uric acid – white stuff)
2) Excellent water conservation
3) New origin from in fish & frogs
What are the extant Order of Class Reptiles and what animal do they contain?
Order Rhyncocephalia: Tuatara (NZ only)
Order Crocodylia: Crocs & Alligators
Order Chelonia: Turtles & Tortoises
Order Squamata: Lizards & Snakes
What are the characteristics of the Order Rhyncocephalia?
1) Parental eye (Squamata too)
2) Oviparous
3) Prefer lower temps
4) Sister group to Squamata
5) Diapsid
What are the characteristics of the Order Crocodylia?
1) Part of lineage that gave rise to birds
2) Complex social behaviour
3) Temperature sex determination (TSD)
4) Predators with secondary plate (allows breathing while mouth full of food)
What are the characteristics of the Order Chelonia?
1) Evolved around 200 MYA with little change
2) Characterized by a carapace (dorsal) and plastron (ventral)
3) Horny beak, no teeth
4) Migrate
5) All oviparous, some TSD
What are the characteristics of the Order Squamata?
1) Robust limbs or elongation and loss of limbs
2) Kinetic skull – disconnect entire skull to eat large prey
3) Some TSD & both oviparous and viviparous
4) Snakes rely on chemical cues → forked tongue
What is the eyesight like for Order Squamata?
In snakes: Very poor except in arboreal
In lizards: Day or night vision
What is the hearing like for Order Squamata?
Snakes: Deaf
Lizards: External ears
Other than hearing and eyesight, what do vipers have for sensory organs?
Pit organs → heat sensitivity
For freshwater crocs, what temperature determines the sex?
Under 30 C - all females
30-32 C - some males
Over 32 C - all females