Physics 11 Exam
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
exact values
when you count objects
when there is an exact conversion (ex: 1 foot = 12 inches)
- infinite sig figs
measured values
obtained from measuring tools
scalar quantity
magnitude only
-distance
vector quantity
direction and magnitude
- distance and [direction]
![<p>direction and magnitude</p><p>- distance and [direction]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9fce1749-b414-4b62-a0a1-5a1513534a6c.jpg)
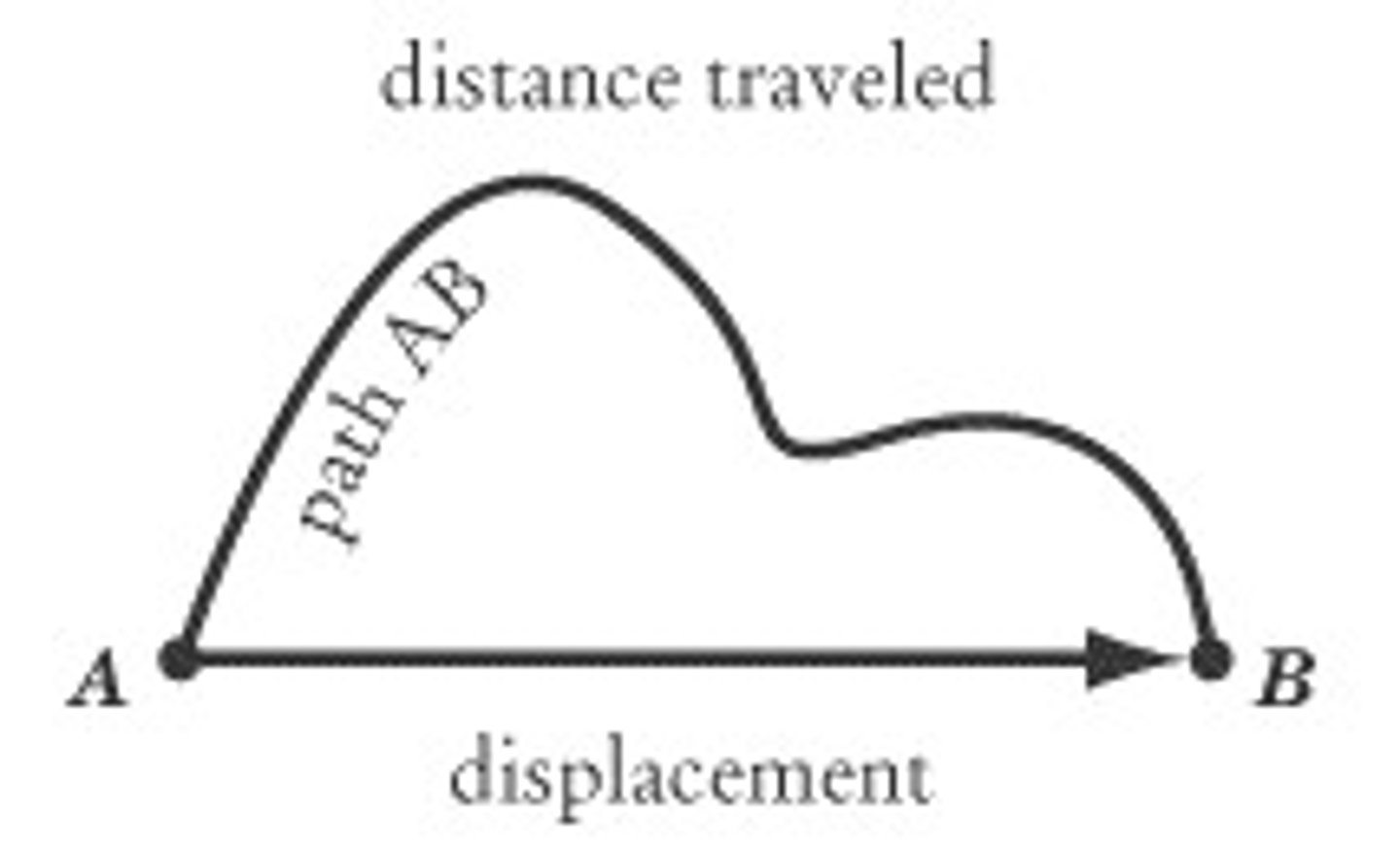
displacement
distance from the starting point to final point
- doesn't depend on path
displacement = final distance - initial distance
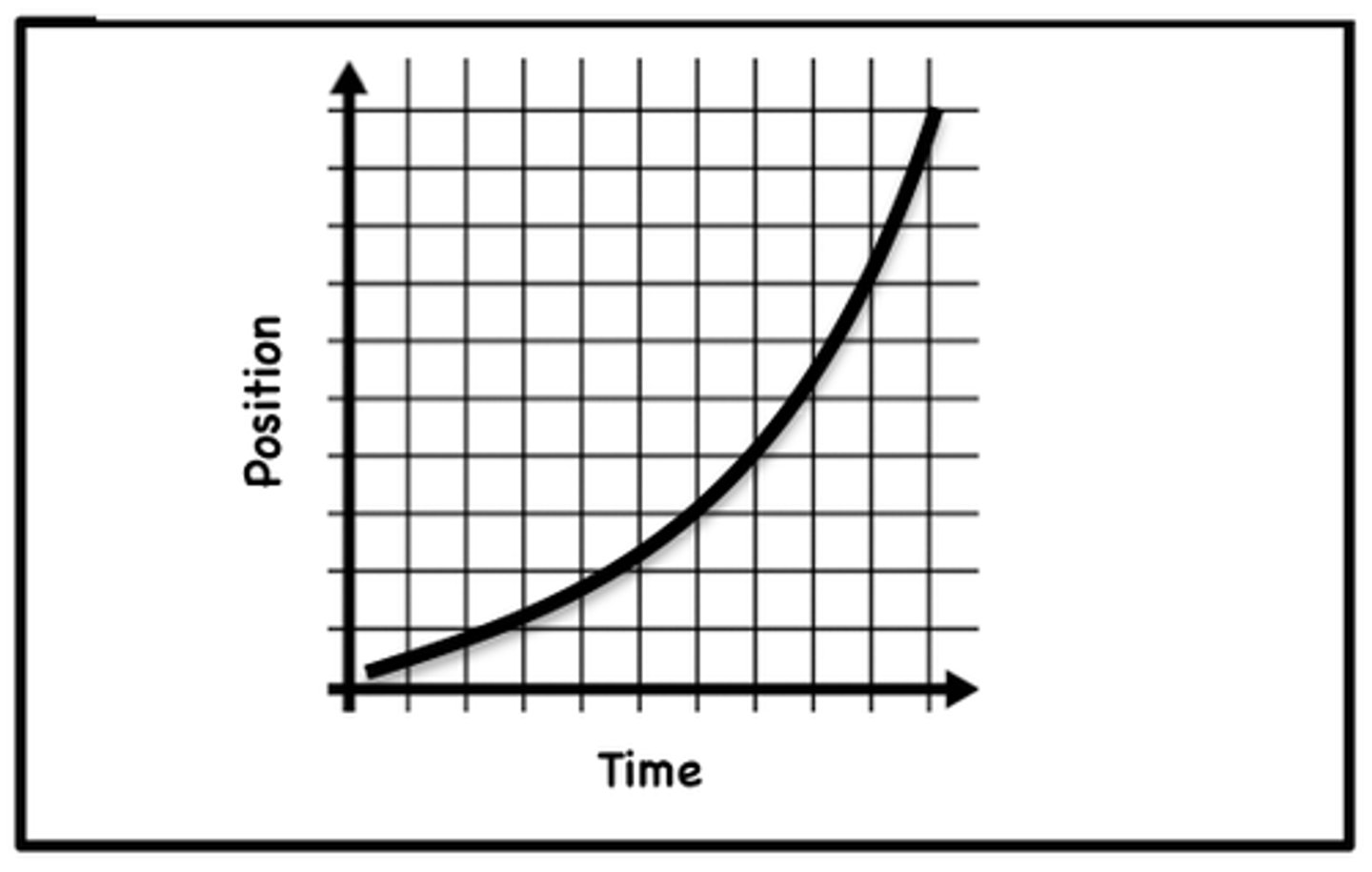
slope of P-T graphs
slope = rise/run
= velocity (m/s)
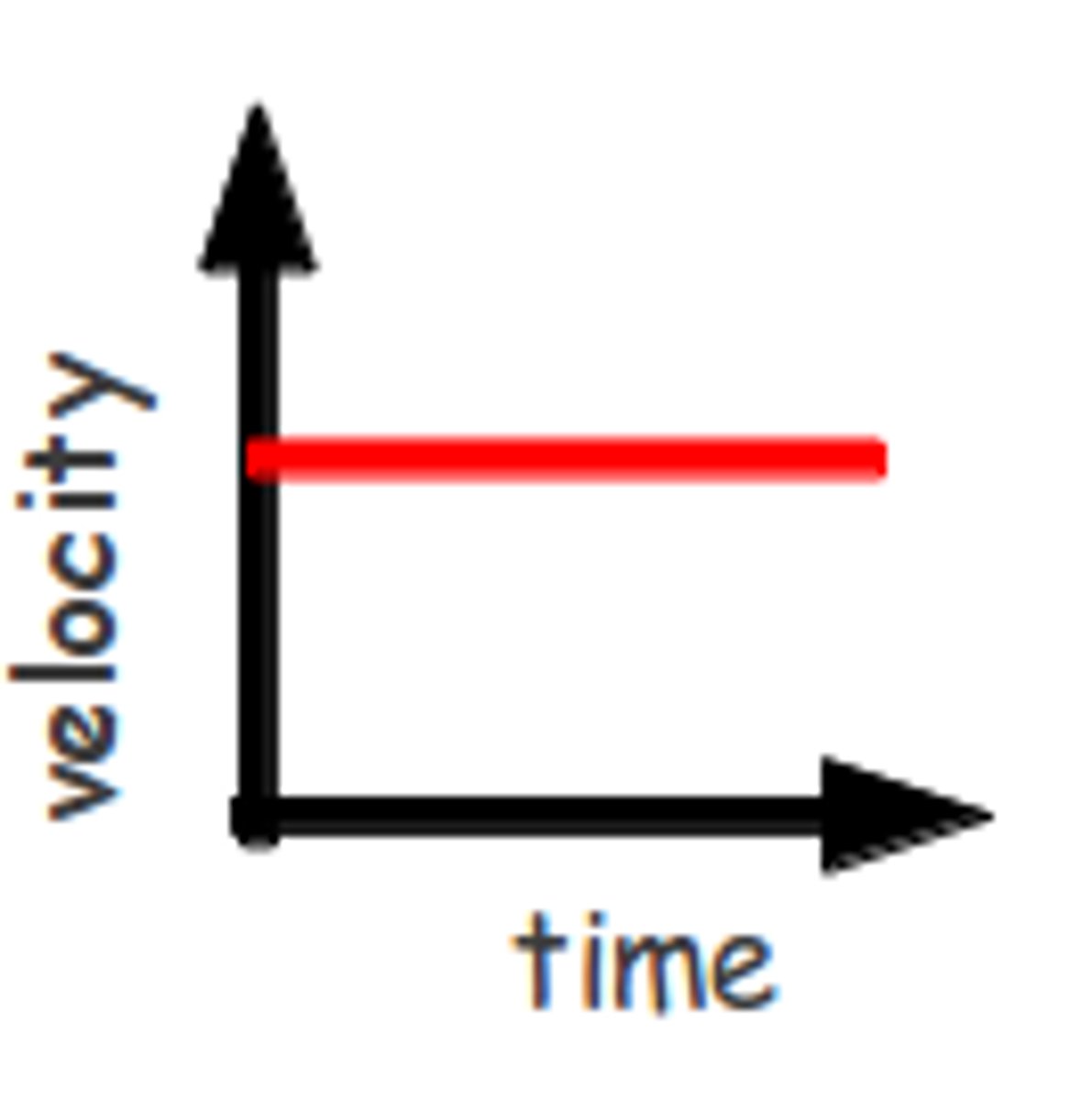
average velocity
displacement (with an arrow) / time
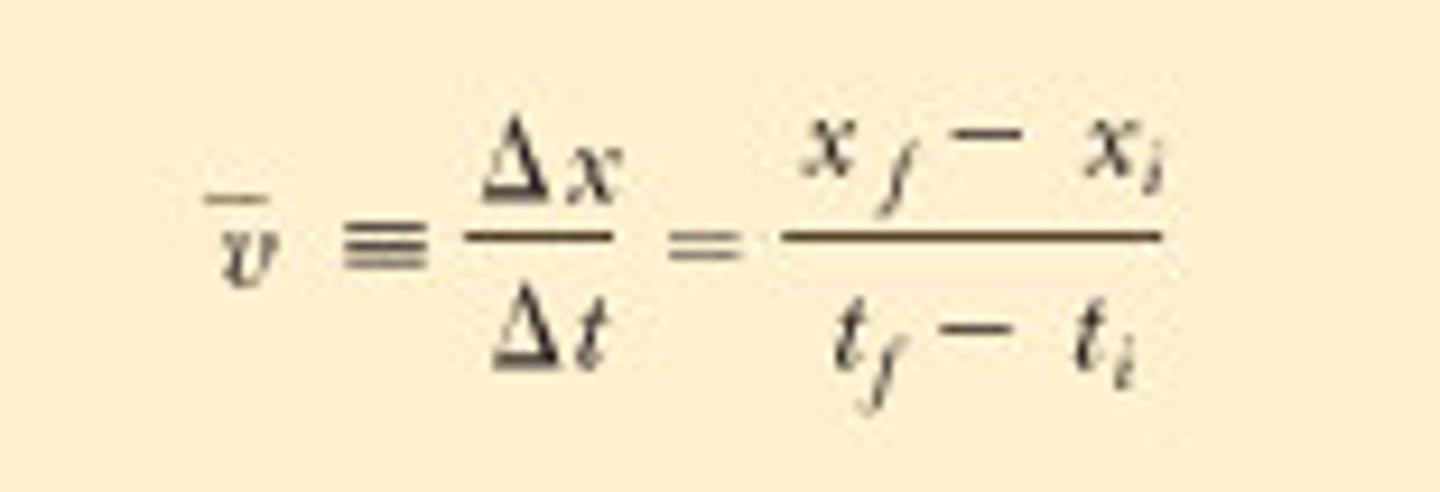
instantaneous velocity
find the slope at a specific point
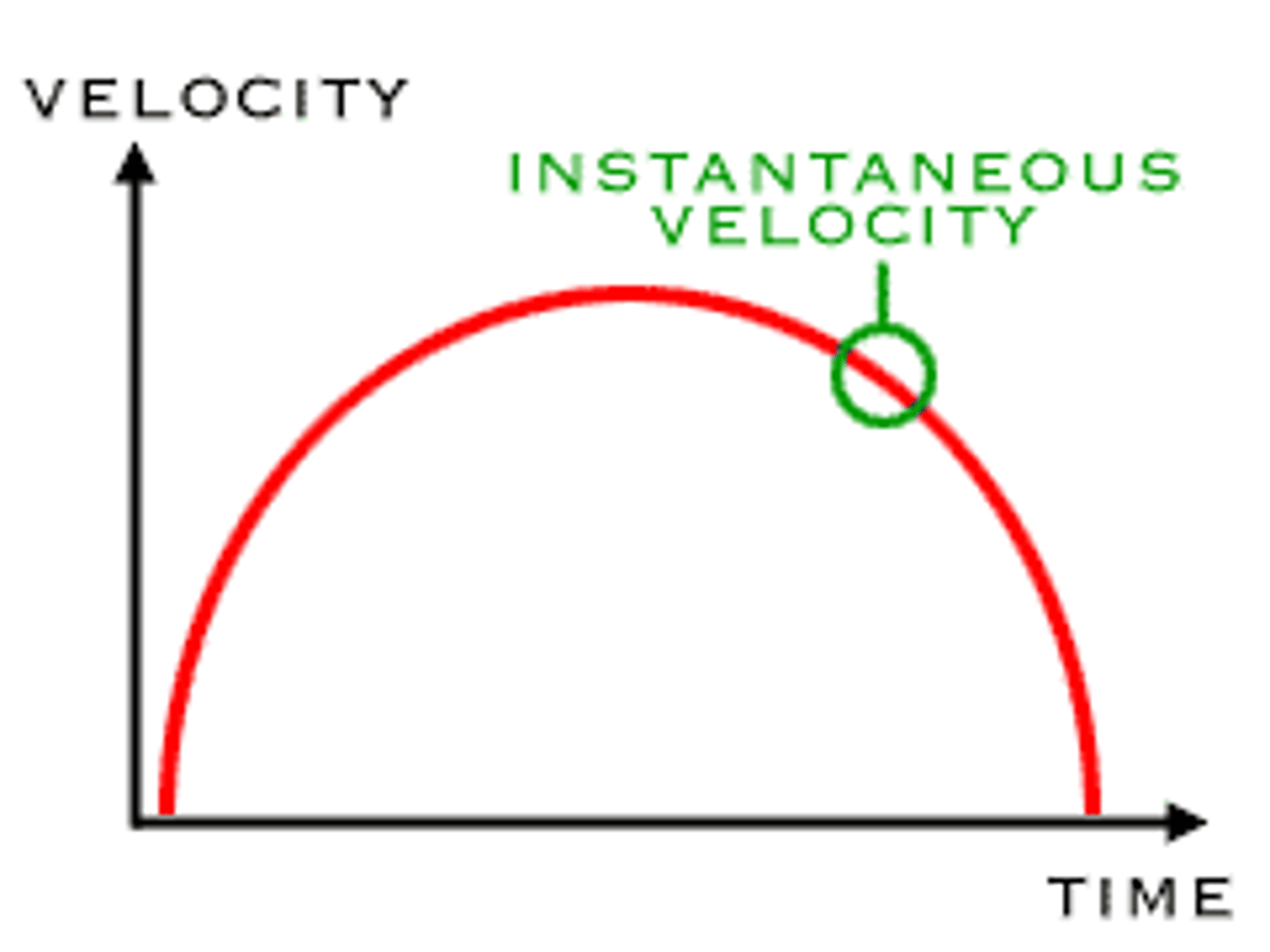
area under V-T graphs
= displacement
acceleration
rate of change of velocity
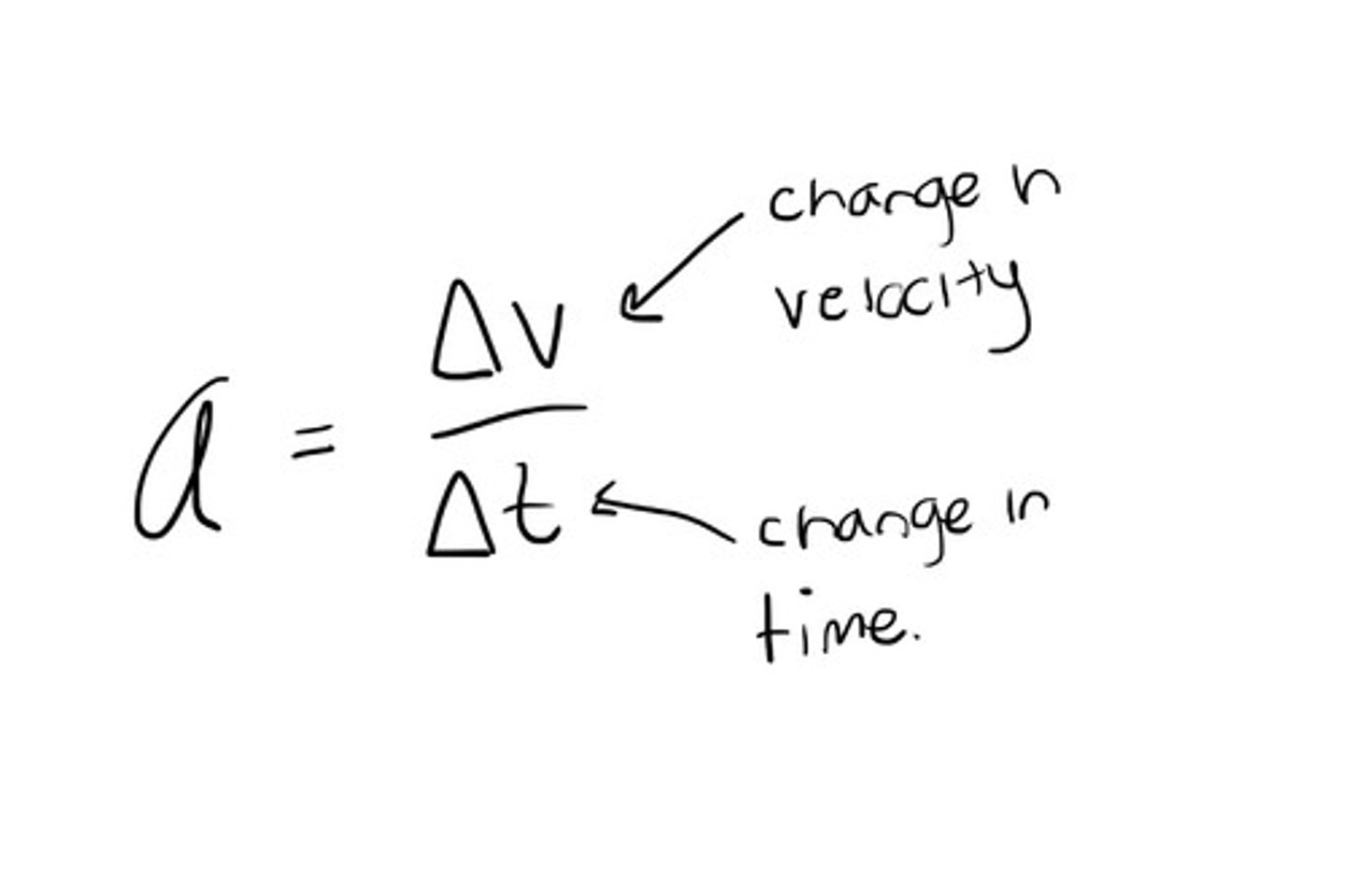
downward acceleration is due to
force of gravity
g constant value
9.80m/s [down]
gravitational force
force of attraction between earth + objects near/on its surface, as well as anything with mass
force
- push or pull on an object
- measured in Newtons (N)
gravitational force
an attractive force that acts between any two objects
mass
quantity of matter in an object
weight
force of gravity acting on an object
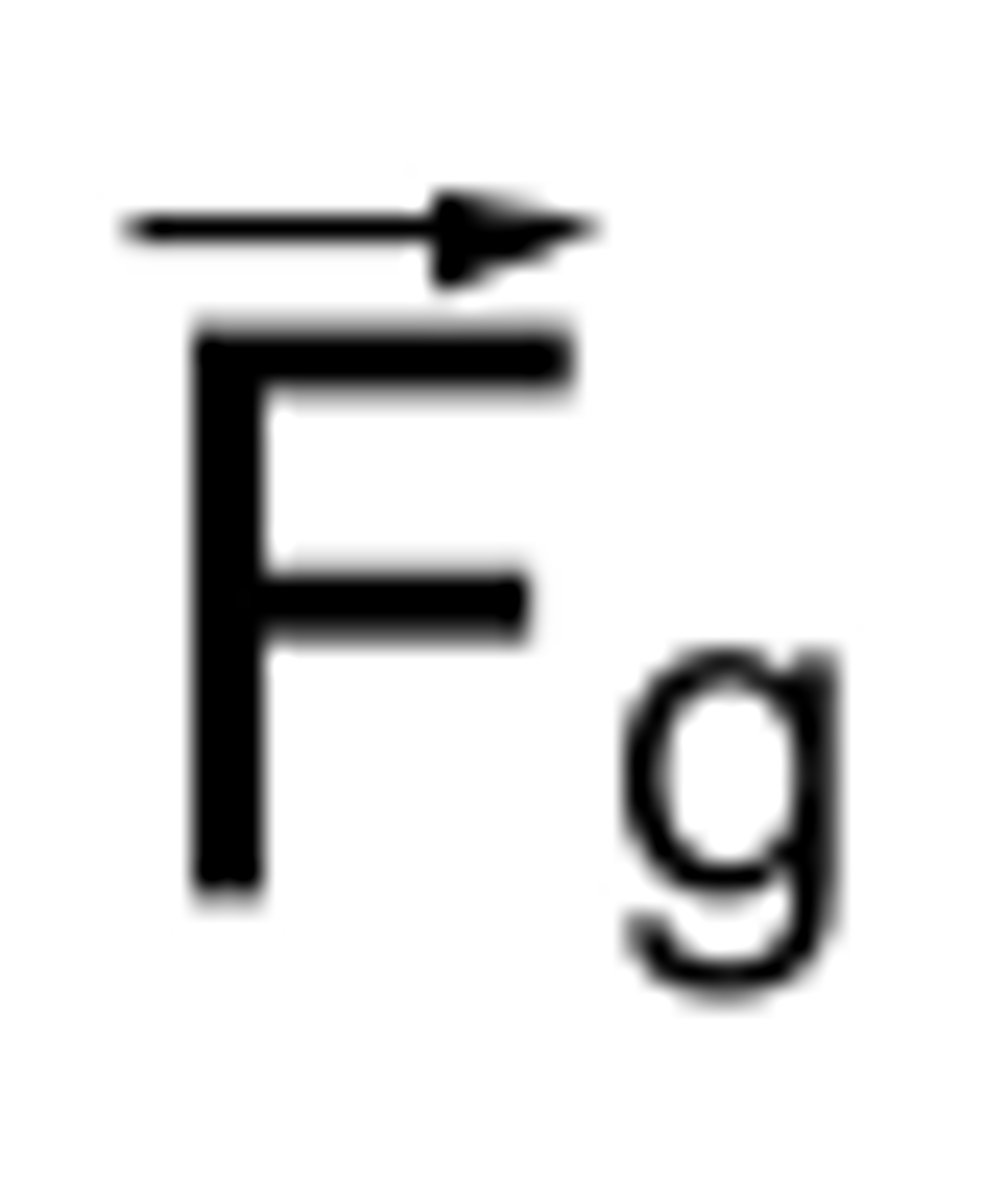
newtons law of universal gravitation
- the magnitude of Fg is directly proportional to the product of masses
- the magnitude of Fg is inversely proportional to the square of the objects' distance
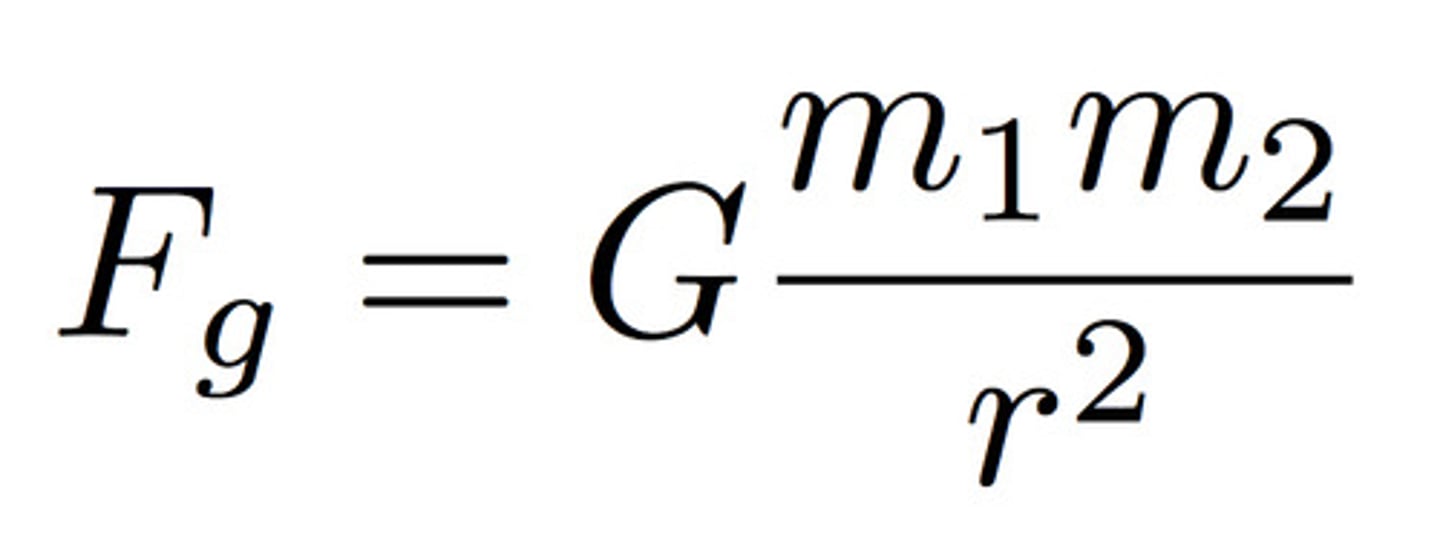
G constant
6.67x10^-11
inertia
resistance to change in motion
newtons first law of motion
an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by another force
- moving objects will eventually stop without external forces
newtons second law of motion
if there is a net external force, the object will accelerate
- acceleration is proportional to net force
- acceleration is inversely proportional to mass
newtons third law of motion
action reaction pair
friction
- static friction: prevents an object from starting to move
- kinetic friction: force that acts when 2 objects slide
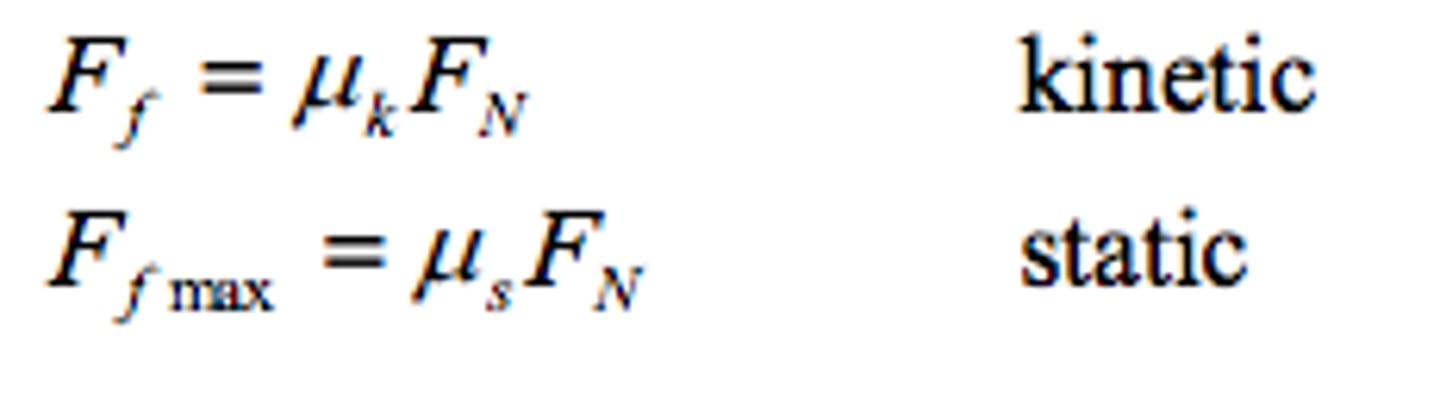
work
measure of energy transfer when an object is moved by an applied force
positive and negative work
POS: Force and displacement are in the same direction
zero work
When force & displacement are perpendicular
law of conservation of energy
- total amount of energy never changes
- energy cannot be created or destroyed
- energy that exists can only be changed from one form to another
- no energy is ever lost
Power
the rate at which work is done
- Si unit = W (watts)
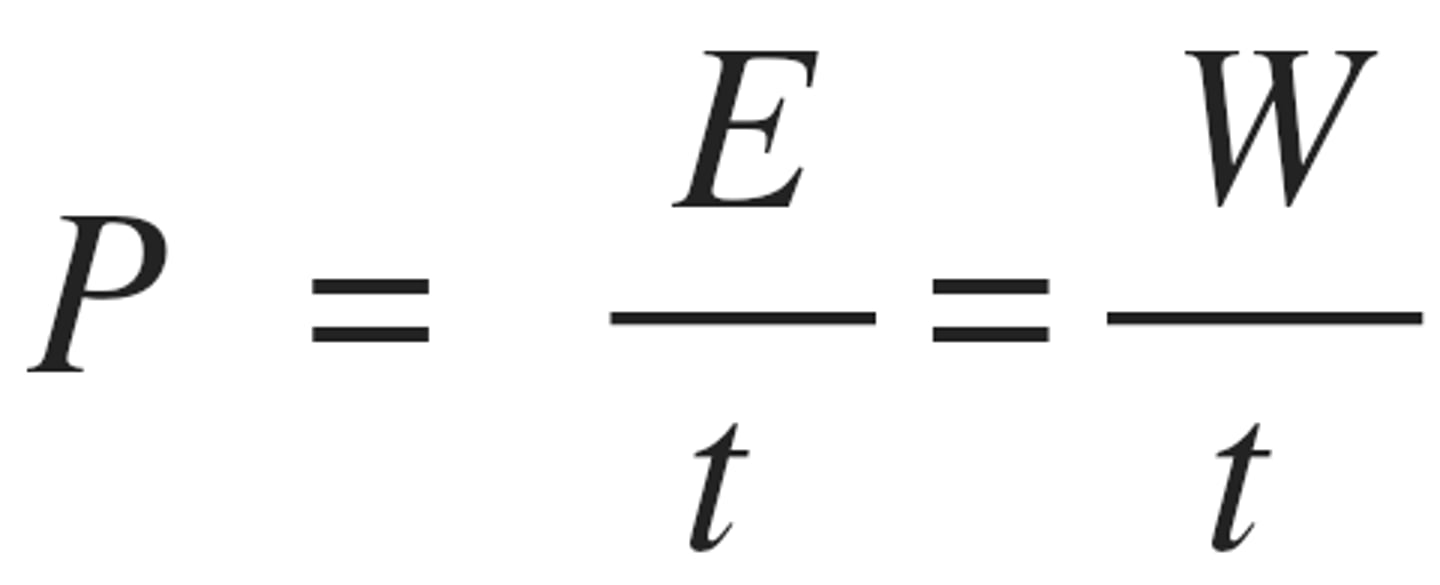
energy consumption
the conversion of produced/stored energy into heat
kinetic molecular theory of matter
- particles are always vibrating and rotating
- vibrations are motions within/between particales that increase and decrease distance between particles
thermal energy
- depends on mass, temp, and state of matter
- is internal energy associated with movement and interactions of particles
temperature
measure of average kinetic energy of particles of a substance
- more kinetic energy > more movement > higher temp
temperature scales
0 C = 273K
latent heat
thermal energy needed for a phase change
latent heat of fusion and specific latent heat of fusion
- thermal energy transferred when phase change from SOLID > LIQUID
- SPECIFIC: thermal energy needed to melt 1kg of substance at its melting point
heat capacity and specific heat capacity
amount of thermal energy needed to change the temp of an object by 1K or 1C
principle of thermal energy exchange
when two substances at different temperatures are mixed, thermal energy lost by hotter substance = thermal energy gained by colder substance
electrical circuit
- source of electrical energy, conductor, and load (converts energy into light, heat, sound)
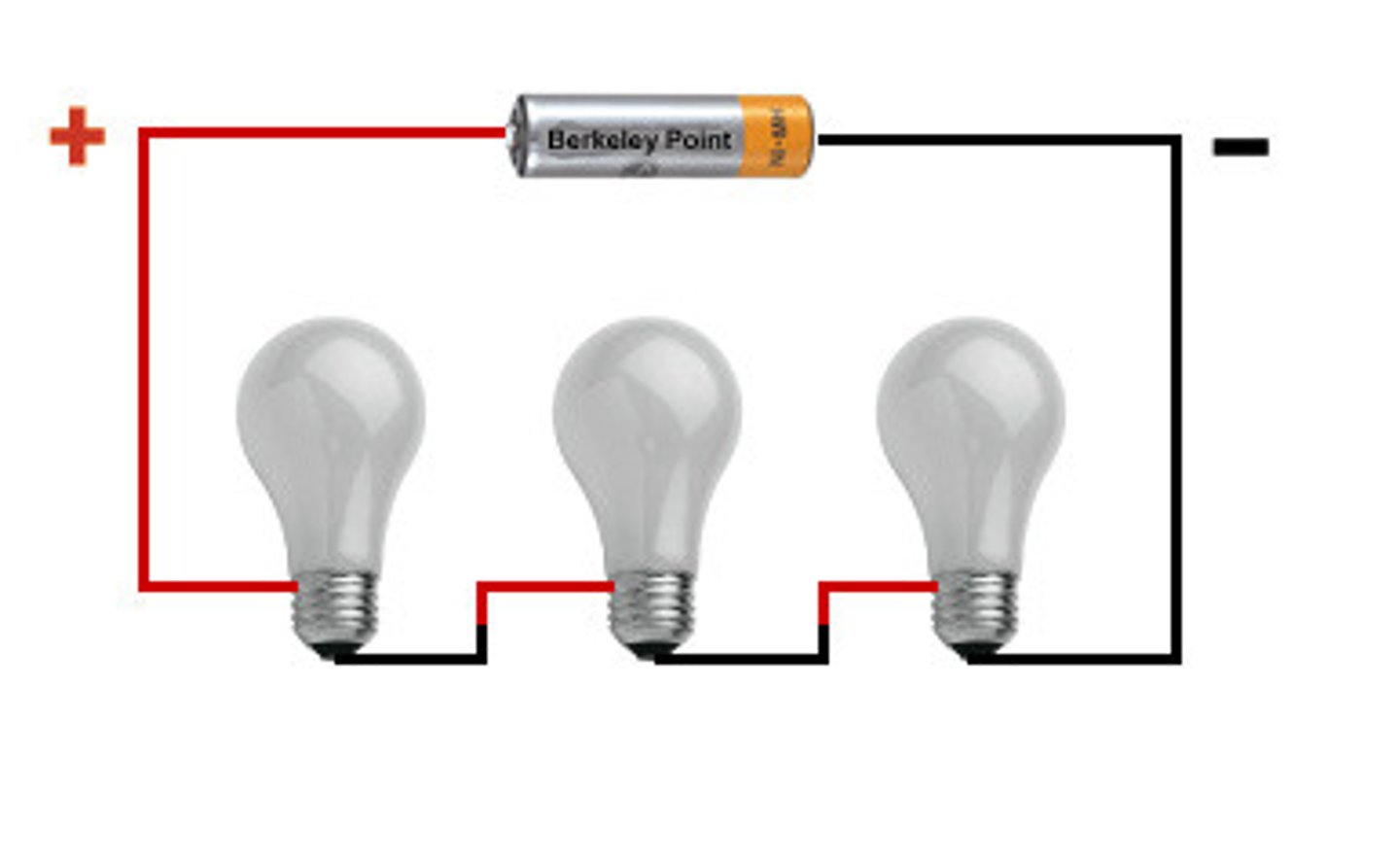
series circuits
A current that has only one path therefore is constant at all points
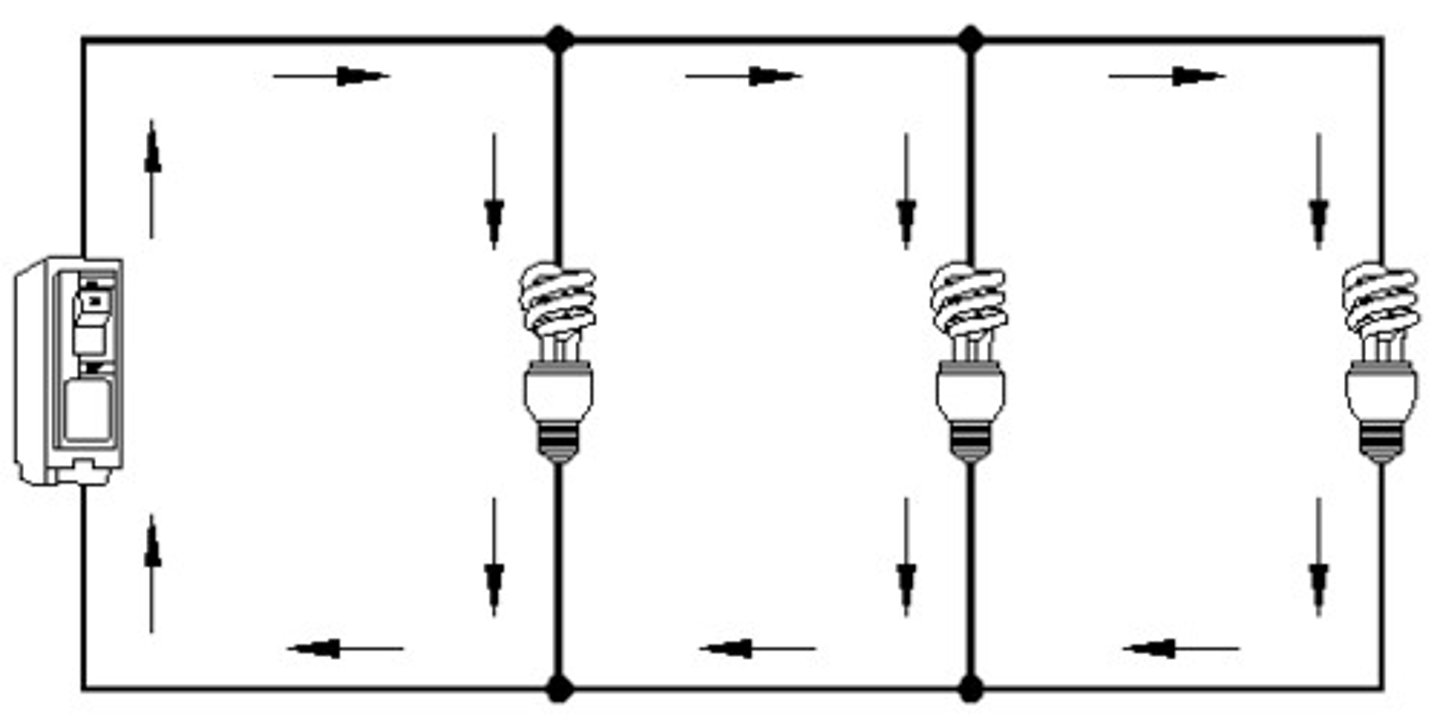
parallel circuit
A circuit that contains more than one path for current flow.
- potential difference is the same at all points