BIOL 2111-02 Chapter 14: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
CNS, PNS, ANS
Order which the nervous system follows…
Norepinephrine
What does the abbreviation “NE” stand for?
Autonomic Nervous System
(definition) INVOLUNTARY nervous system, with the main goal being to MAINTAIN homeostasis.
Parasympathetic and Sympathetic
The 2 DIVISIONS of the ANS System…
Counter-balance each other
Parasympathetic and Sympathetic divisions…
Parasympathetic
(function) Controls REST, DIGESTION, and WASTE…
Parasympathetic
(definition) Keeps body energy LOW, while DIRECTIING digestion and elimination
Sympathetic
(function) Considered the FLIGHT OR FIGHT (stress) division…
Sympathetic
(definition) Prepares the body for THREATENING situations and EXERCISE…
Skeletal Muscle
Effectors of the Somatic Nervous System…
Glands, Smooth Muscle, Cardiac Muscle
Effectors of the Autonomic Nervous System…
Somatic
(efferent pathway) Motor neuron’s cell body found in the SPINAL CORD (VENTRAL HORN), and AXONS extend to the SKELETAL MUSCLE
ANS
This Nervous System has TWO efferent neuron chains…
Preganglion Neuron
The term used to describe the efferent pathway of the FIRST CELL
CNS to another Ganglion Neuron
The path PREganglion Neuron’s take…
Postganglion Neuron
The term used to describe the efferent pathway of the SECOND CELL
Parasympathetic
(efferent pathway) LONG preganglionic axon, SHORT postganglionic axon, ends near EFFECTOR ORGAN
Sympathetic
(efferent pathway) SHORT preganglionic axon, LONG postganglionic axon, ends near VETERBAE
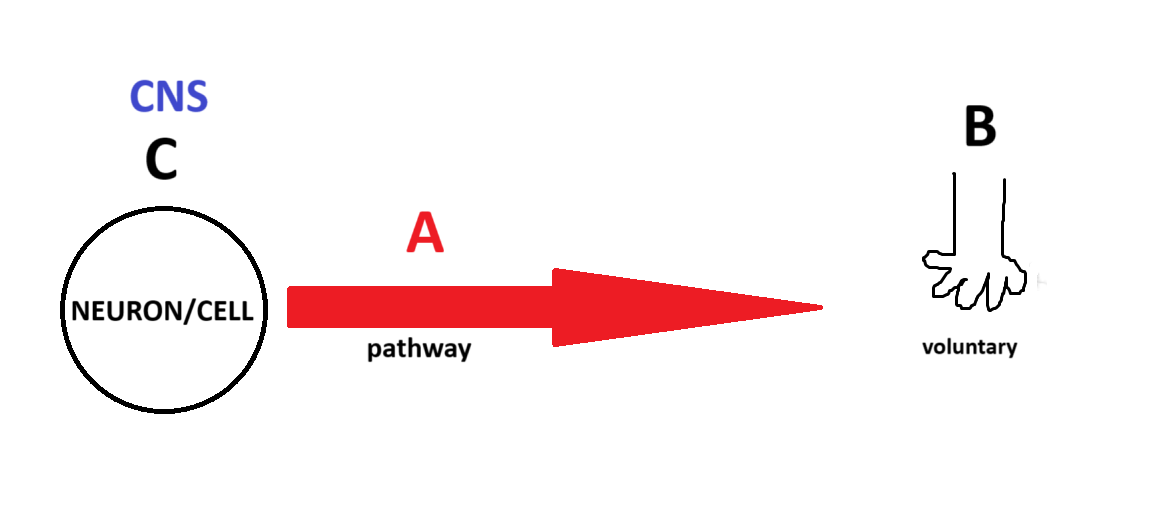
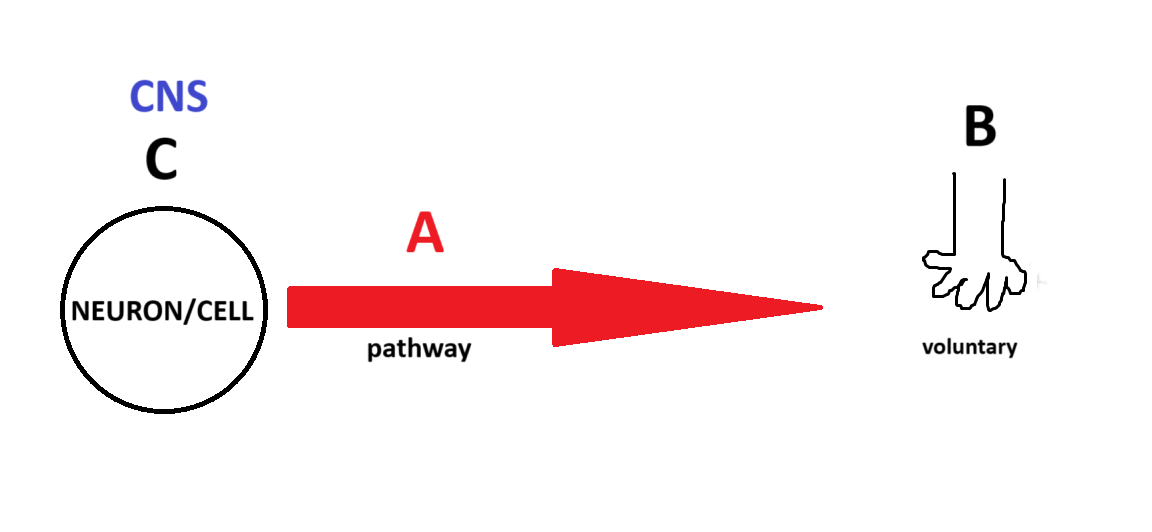
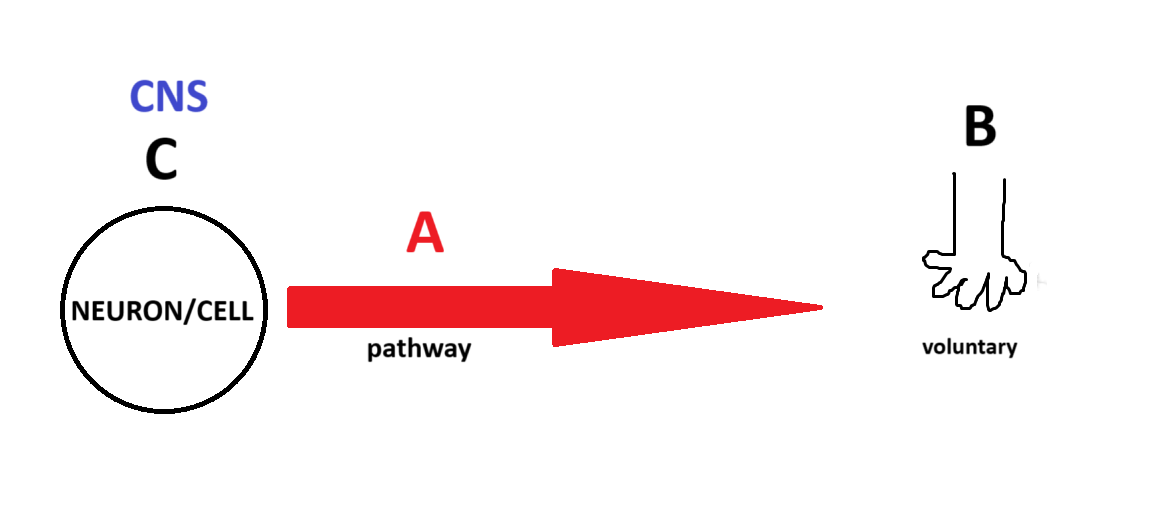
Somatic
(Somatic, Parasympathetic, Sympathetic) Which system is being depicted in the model?
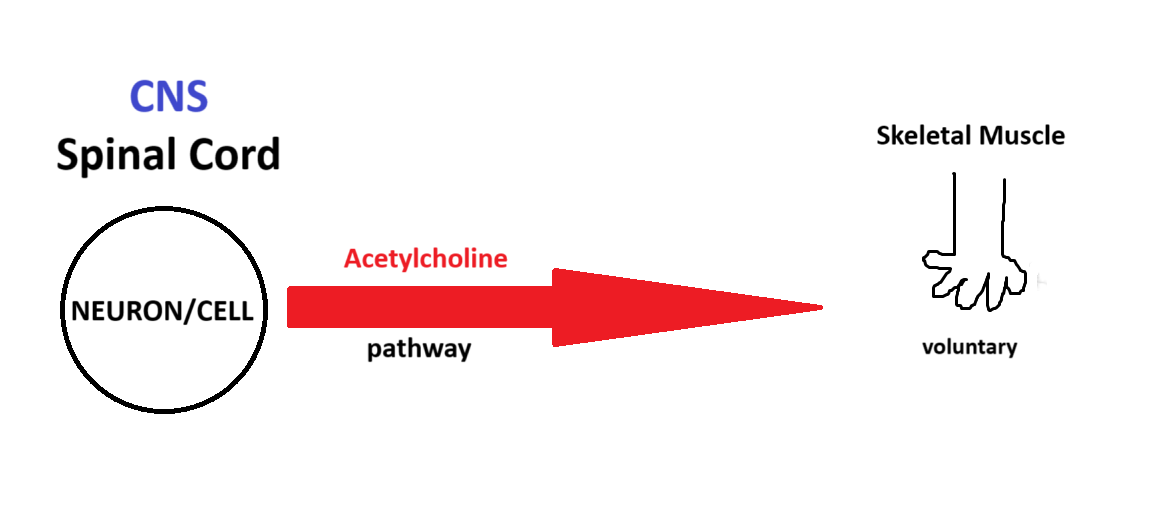
Acetycholine
A
Skeletal Muscle
B
Spinal Cord
C
Acetylcholine
A
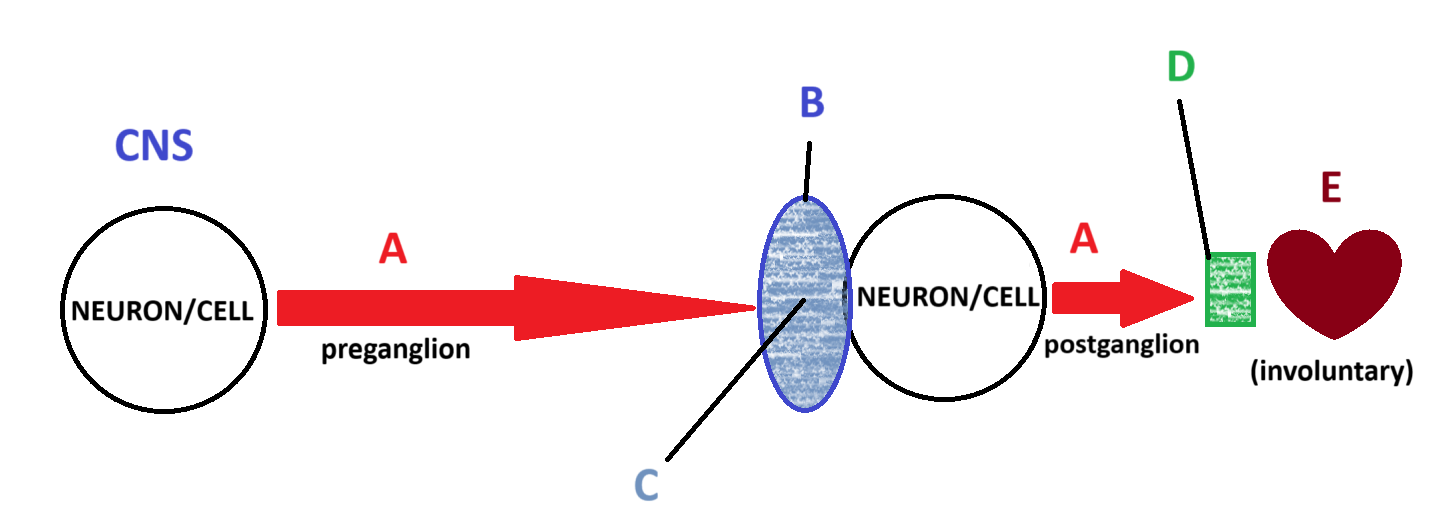
Ganglion
B
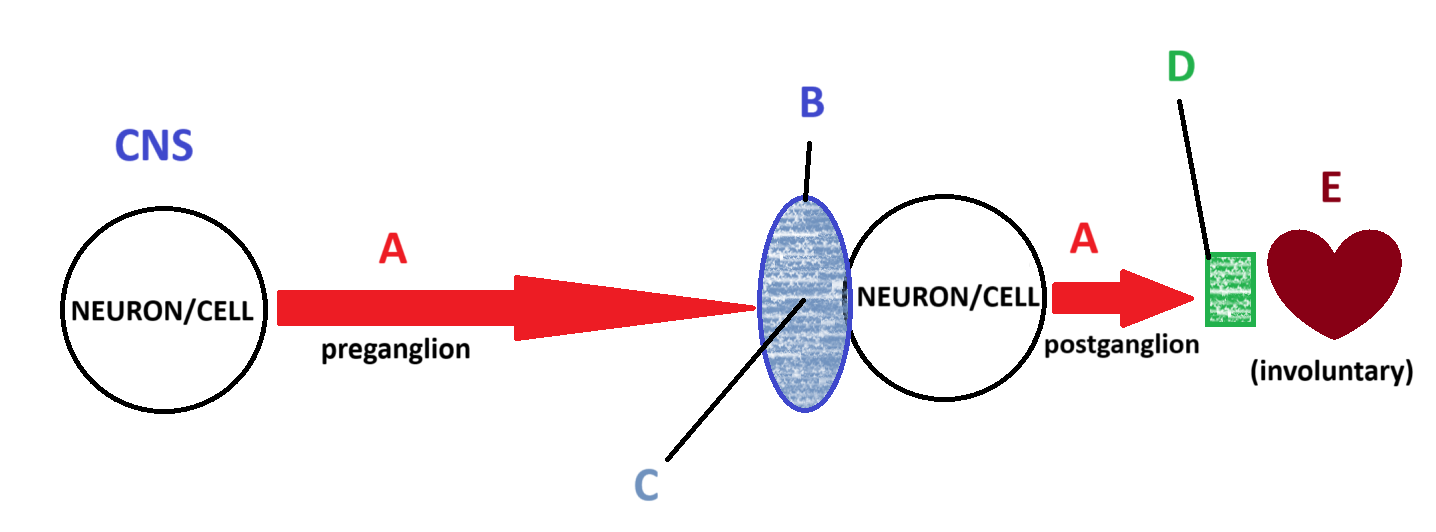
Nicotinic
C
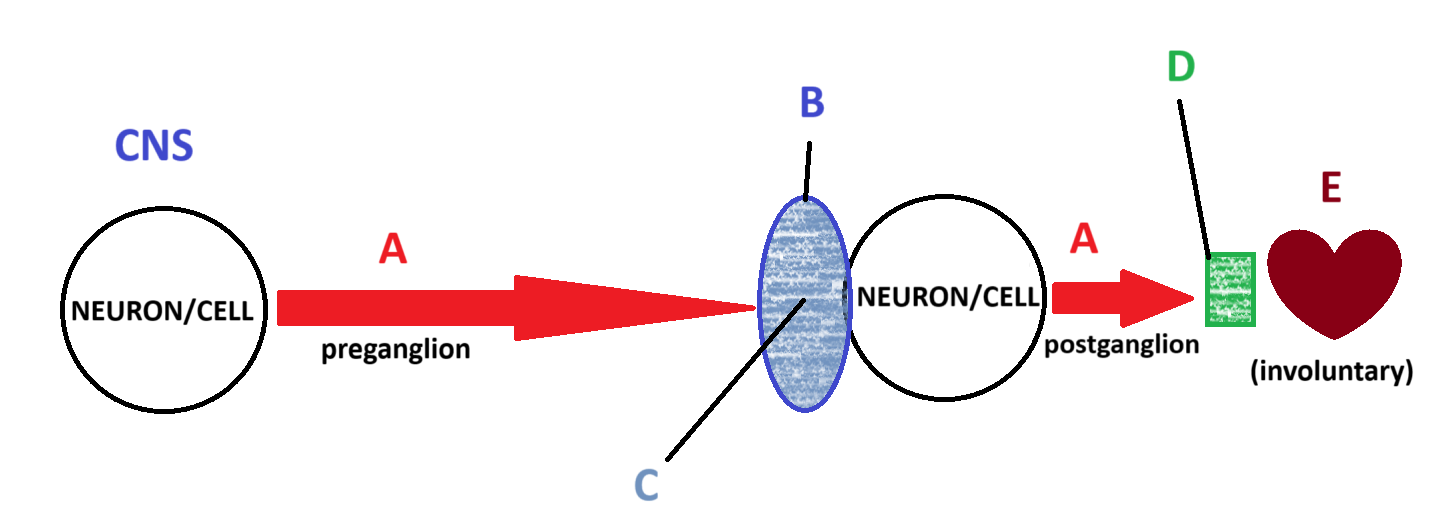
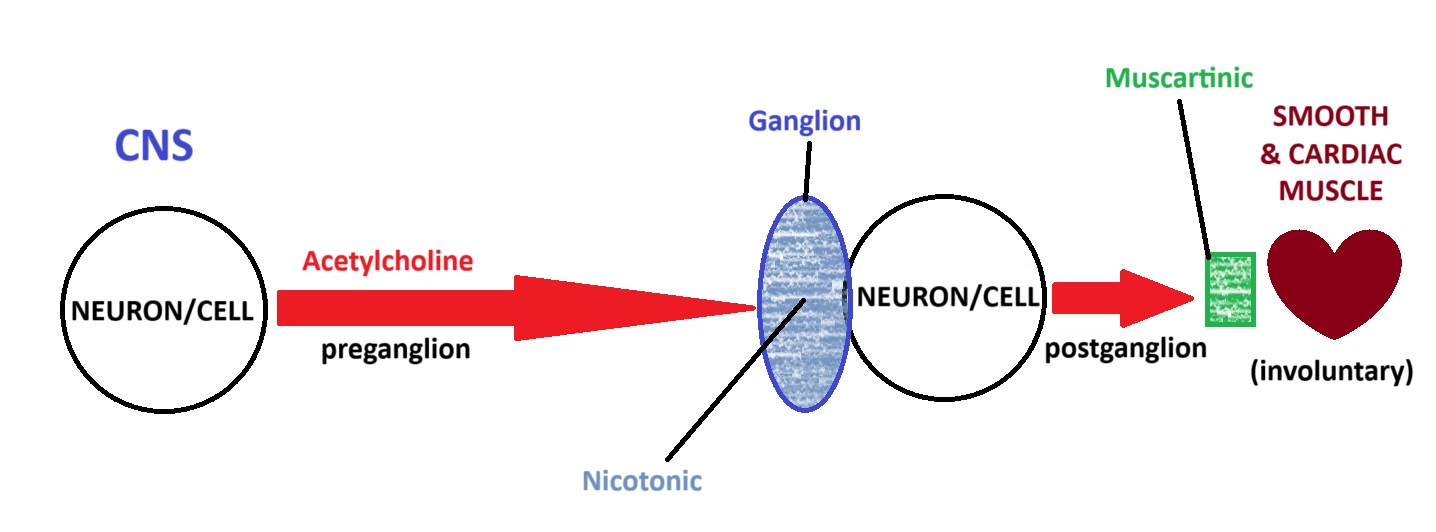
Muscartinic
D
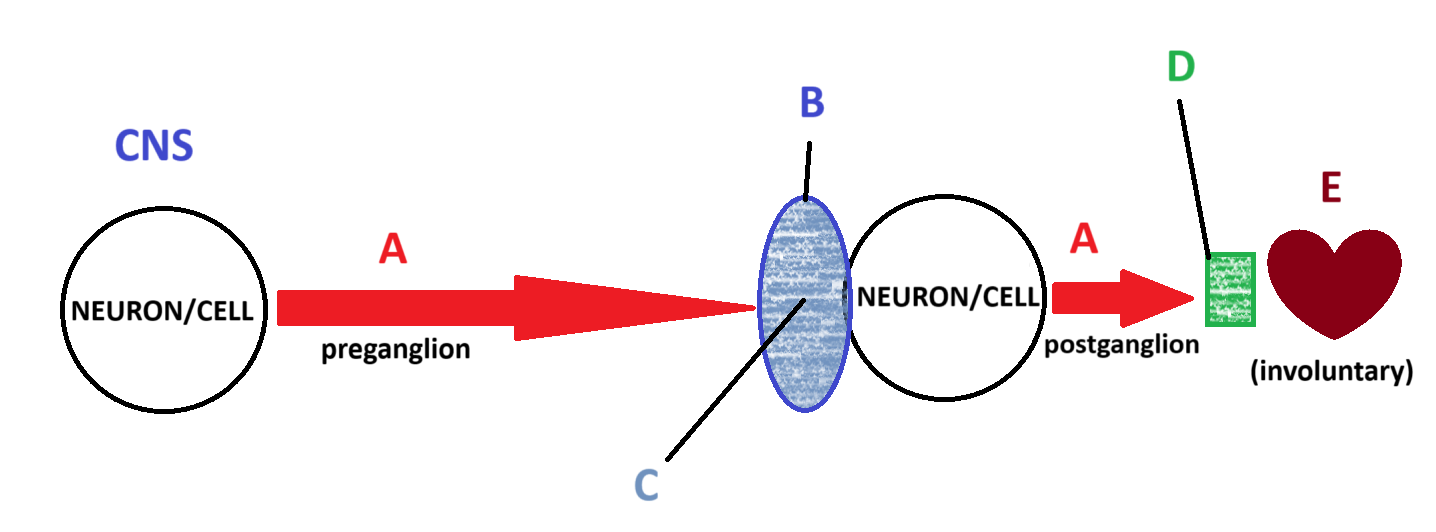
Smooth and Cardiac Muscle
E
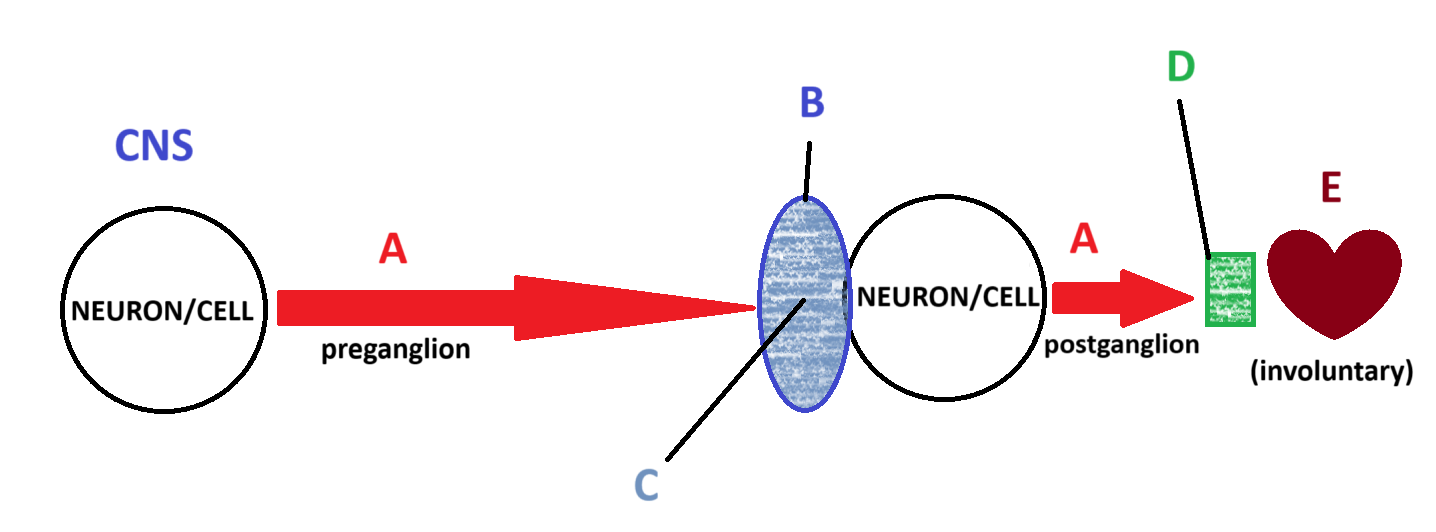
Parasympathetic
(Somatic, Parasympathetic, Sympathetic) Which system is being depicted in the model?
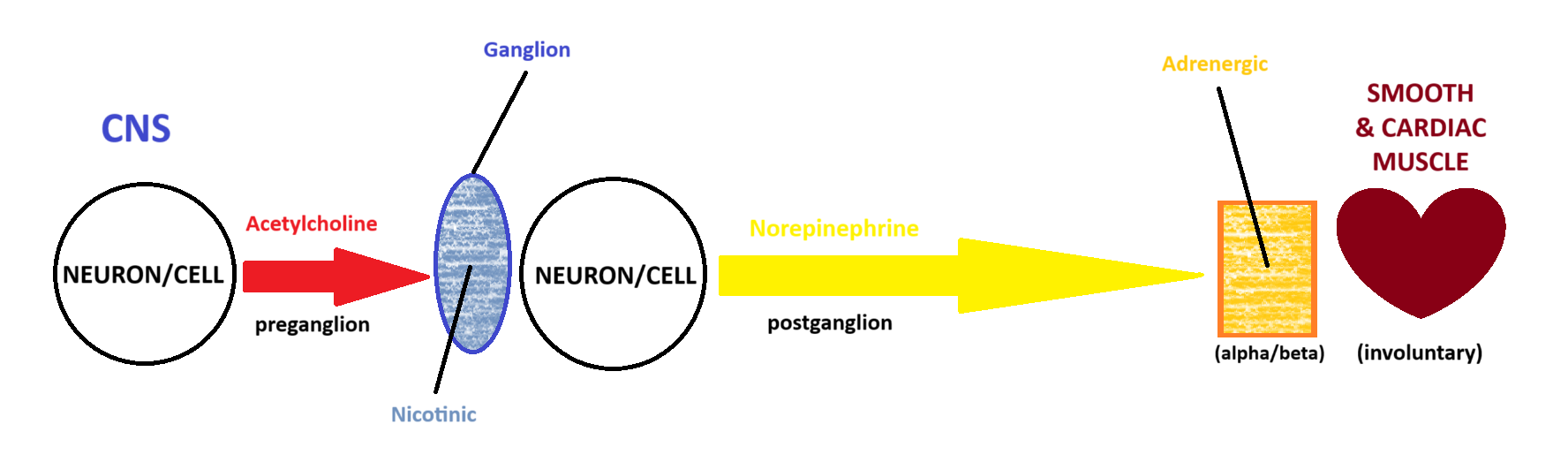
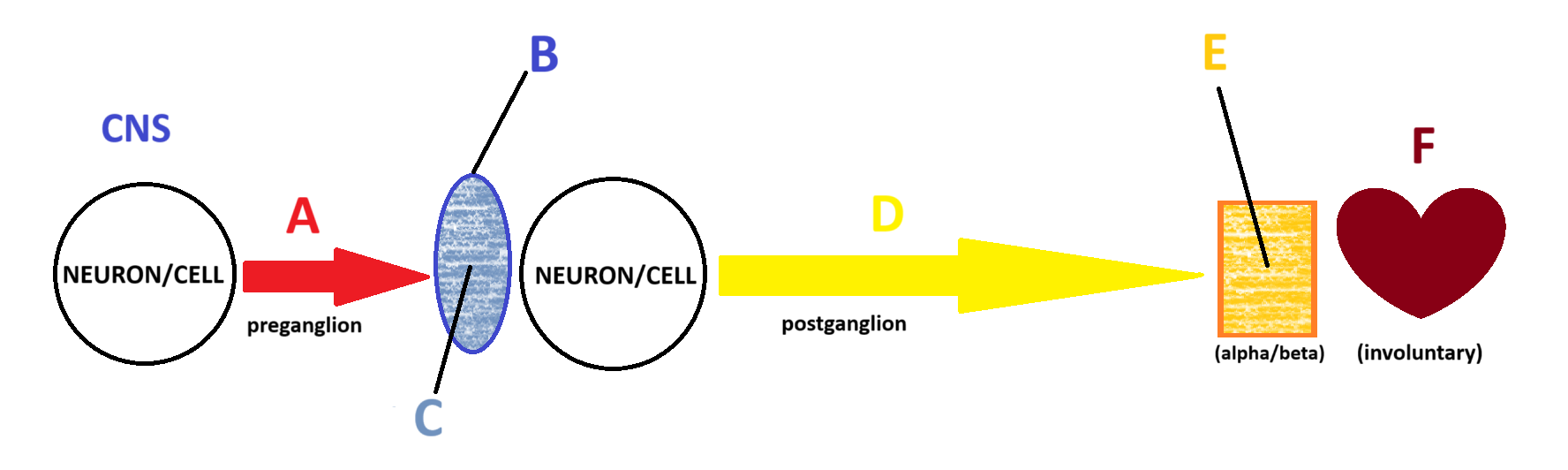
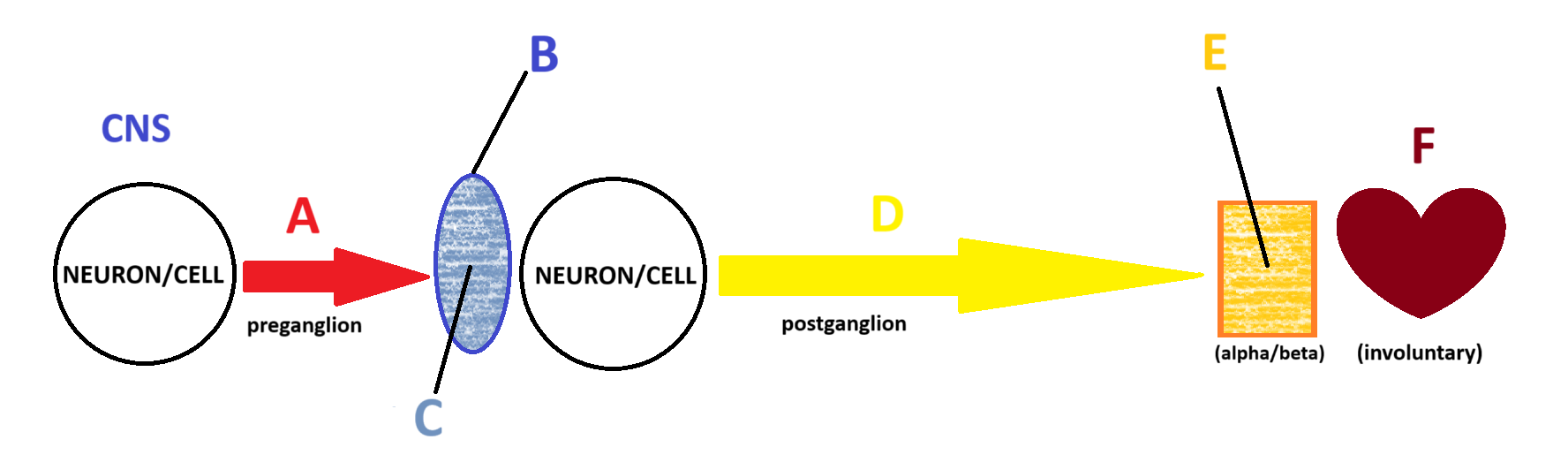
Sympathetic
(Somatic, Parasympathetic, Sympathetic) Which system is being depicted in the model?
Acetylcholine
A
Ganglion
B
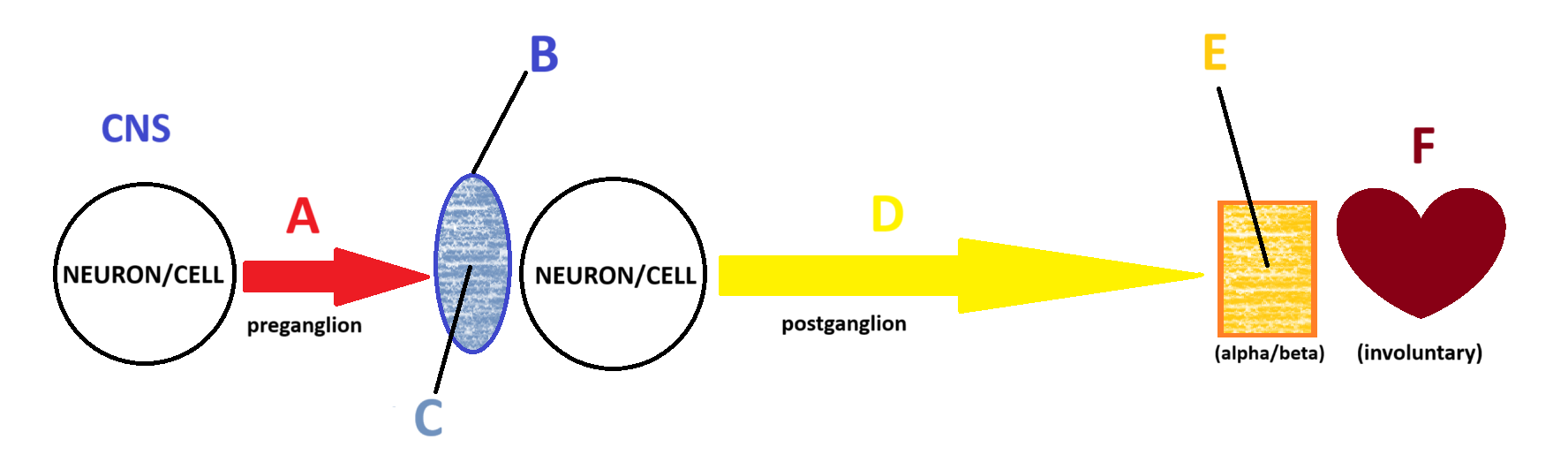
Nicotinic
C
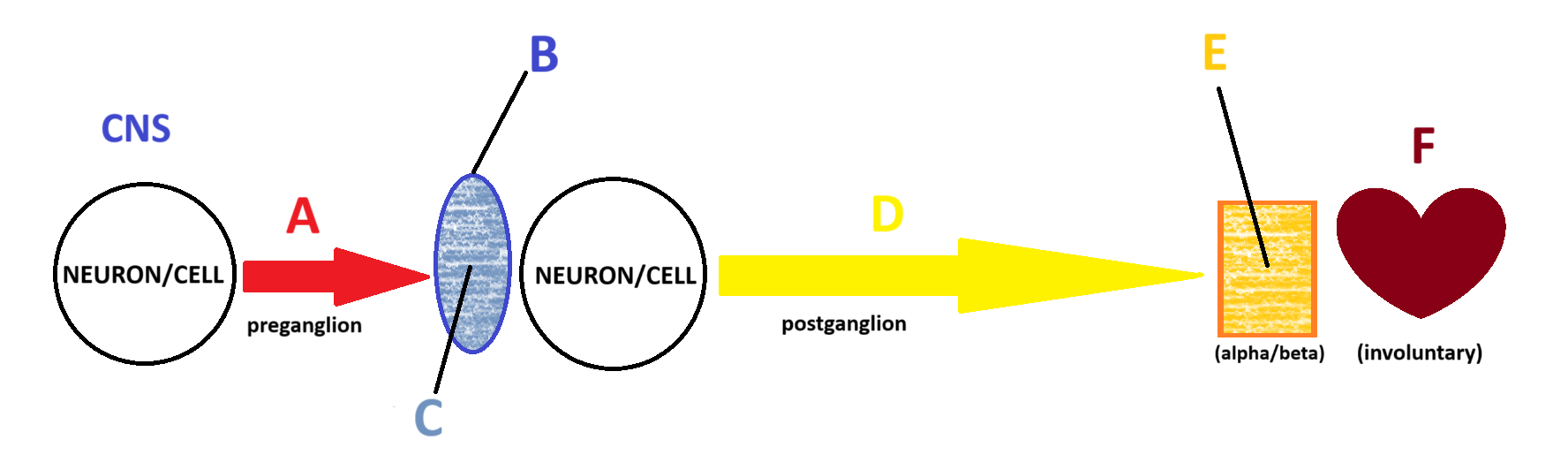
Norepinephrine
D
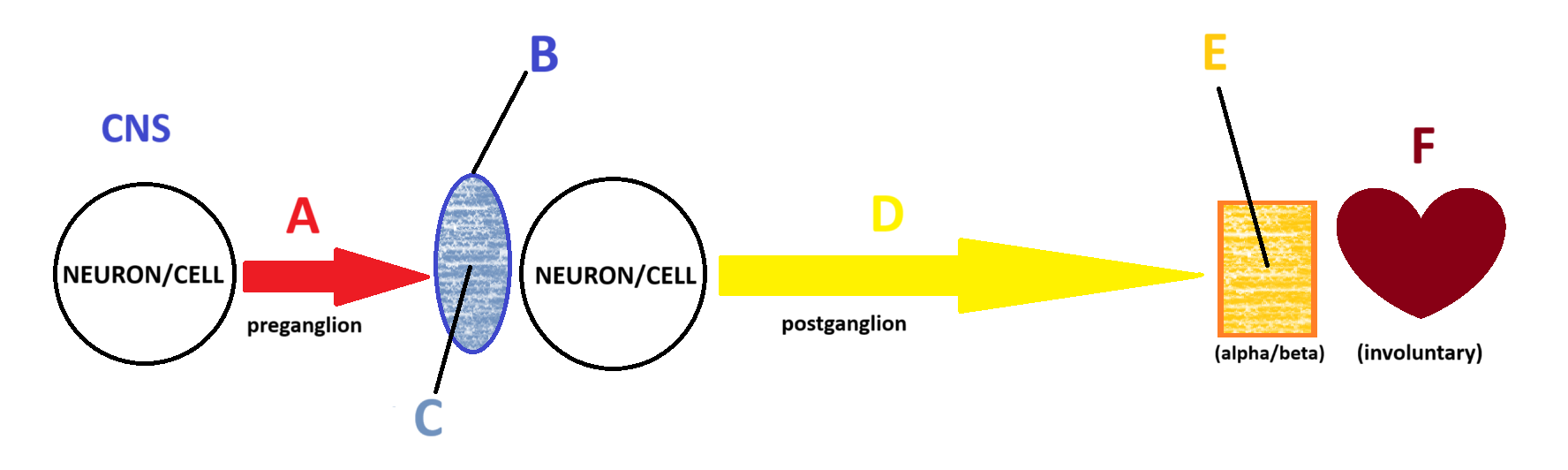
Adrenergic
E
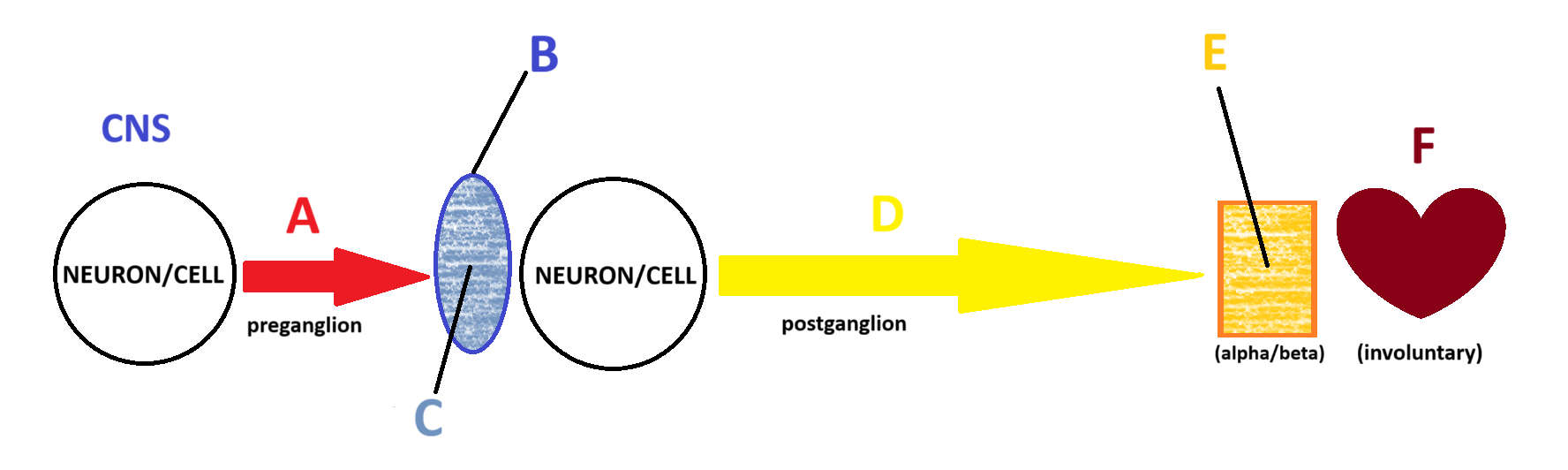
Smooth and Cardiac Muscle
F
Acetylcholine
(neurotransmitters) Which neurotransmitter is present in the Somatic Nervous System?
Acetylcholine
(neurotransmitters) Which neurotransmitter is present in the Parasympathetic Nervous System?
Acetylcholine and Norepinephrine
(neurotransmitters) Which neurotransmitter is present in the Sympathetic Nervous System?
Somatic
(origin) Which nervous system is found in the VENTRAL HORN of the SPINAL CORD?
Parasympathetic
(origin) Which nervous system is found in the CRANIOSACRAL DIVSION?
Cell bodies in Cranial Nerves and the Sacral Spinal Cord
The Craniosacral Division is COMPOSED of…
Oculomotor, Facial, Glossopharyngeal, Vagus
(origin) The CRANIAL NERVES found in the Parasympathetic Nervous System…
Pupil constricts and changes lens shape
(function) Oculomotor
Glands of the head (lacrimal, nasal, salivary)
(function) Facial
Parotid salivary gland
(function/gland) Glossopharyngeal
90% of Parasympathetic fibers extend through every organ in the thoracic and abdominal cavity
(function) Vagus
Sympathetic
(origin) Which nervous system is found in the THORACOLUMBAR DIVISION?
Sympathetic Trunk
The THORACOLUMBAR DIVISON makes up the…
Somatic
(branching) Depends on the MOTOR UNIT (small/large)
Parasympathetic
(branching) MINIMAL
Sympathetic
(branching) EXTENSIVE
Parasympathetic
(effect and duration) LOCAL effect, SHORT-LIVED duration
Sympathetic
(effect and duration) DIFFUSED effect, LONG-LIVED duration
Norepinephrine
Which neurotransmitter has a LONGER affect than ACETYLCHOLINE?
Ion Channels and G-protein Coupling Receptors
What are two forms of receptors?
Neurotransmitter
Each (BLANK) will activate its own specific receptor
Nicotinic and Muscarinic
(receptors) What TWO types of RECEPTORS bind to Acetylcholine?
Nicotinic
(definition) Has an EXCITED EFFECT, found on PREGANGLIONIC CELL and requires an ION CHANNEL
Muscarinic
(definition) Can either have an EXCITED or INHIBITORY EFFECT, found on EFFECTORS, and requires a G-PROTEIN RECEPTOR
Alpha and Beta Adrenergic
(receptors) What TWO types of receptors bind to the Norepinephrine?
Alpha Adrenergic
(definition) Has either an EXCITED or INHIBITORY EFFECT, TWO subtypes (a1 and a2), found on EFFECTORS, and requires a G-PROTEIN RECEPTOR
Beta Adrenergic
(definition) Has either an EXCITED or INHIBITORY EFFECT, THREE subtypes (b1, b2, b3), found on EFFECTORS, and requires a G-PROTEIN RECEPTOR
A1 and A2
(receptors) What subtypes are found in Alpha Adrenergic Receptors? (2)
B1, B2, B3
(receptors) What subtypes are found in Beta Adrenergic Receptors? (3)
Agonist
(definition) a DRUG that BINDS to the RECEPTOR and ACTIVATES the receptor (mimicking a neurotransmitter)
Antagonist
(definition) a DRUG that BINDS to the RECEPTOR and INHIBITS the receptor (no activity)
Brain Stem, Hypothalamus, Cerebral Cortex
ANS is regulated by which nervous structures?
Brain Stem
(autonomic functions) Houses automatic centers
Hypothalamus
(autonomic functions) main ANS integrative center (control center) found within the brain
Cerebral Cortex
(autonomic functions) via limbic lobe connections INFLUENCES hypothalamic function
Somatic Reflex Arc
Visceral Reflexes contain the SAME 5 components as…
Two Motor Neurons
The key DIFFERENCE between Visceral Reflexes and the Somatic Reflex Arc is that Visceral Reflexes CONTAIN…
Referred Pain
(definition) PAIN arising in the VISCERA are perceived as SOMATIC IN ORIGIN, because VISCERAL PAIN TRAVELS along the SAME pathways as SOMATIC PAIN
Heart Attack causes pain in the Left Arm and Chest
Example of REFERRED PAIN…
Dual Innervation
(definition) visceral organs receive innervations from BOTH ANS divisions (parasympathetic and sympathetic)
Antagonism
Most innervation work by…
Antagonism
(definition) Two divisions (parasympathetic and sympathetic) have OPPOSITE EFFECTS (one increase, other decreases), which allows for precise control of visceral activity.
Cooperative Interaction
(definition) Two divisions (parasympathetic and sympathetic) WORK TOGETHER
Male Genitals leading to Ejaculation
Example of COOPERATIVE INTERACTION between Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Divisions…
Sympathetic
(function) Which division CONTROLS blood pressure by changing the size of the blood vessel?
Sympathetic Zone
(definition) At REST, there is CONTINUAL sympathetic activity to the blood vessel, keeping the vessels in a state of PARTIAL constriction.
Increase Contraction (vasoconstriction)
If the Sympathetic Nervous System INCREASES NOREPINEPHRINE…
Decrease Contraction (vasodilation)
If the Sympathetic Nervous System DECREASES NOREPINEPHRINE…
Parasympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) DECREASES Heart Rate
Sympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) INCREASES Heart Rate
Parasympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) CONSTRICTS (close) Eye Pupil
Sympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) DILATES (opens) Eye Pupil
Sympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) DECREASES SECRETION of Saliva Glands
Parasympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) INCREASES SECRETION of Saliva Glands
Parasympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) CONSTRICTS (close) Lung-Bronchioles
Sympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) DILATES (open) Lung-Bronchioles
Sympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) DECREASES Digestive Organs Activity
Parasympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) INCREASES Digestive Organs Activity
Sympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) RELAXES (stores urine) Bladder-Wall
Parasympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) CONTRACTS (eliminates urine) Bladder-Wall
Parasympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) RELAXES (eliminates urine) Bladder-Sphincters
Sympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) CONTRACTS (stores urine) Bladder-Sphincters
Sympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) CONSTRICTS Blood Vessels in the Stomach
Sympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) DILATES Blood Vessels in the Stomach
Sympathetic
(parasympathetic/sympathetic) CONTRACTS the Arrector Pili Muscle (goosebumps)