Pedigree and Karyotype
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Pedigree
Visual representation of a families history
What a pedigree shows
Shows relationships between family members and can show which individuals have traits or diseases.
Circle
Females
Square
Male
Filled in
Trait is expressed
Not filled in
Trait is not expressed
Half filled in
Carrier for the trait
Roman Numerals
Generation
Arabic Numerals
Individuals within the generation
Horizontal lines
Relationships
Vertical lines
Offspring
Carrier
Doesn’t physically express trait but still has it
Characteristics of dominant pedigree
1 parent must have the trait and will NOT skip generations
Every affected individual has at least one affected parent
Affected individuals who mate with unaffected individual have a 50% chance of transmitting trait to child
2 affected individuals may have unaffected children (may be heterozygous)
Recessive Pedegree
neither parent is required to hv the trait since they can be heterozygous and will skip generations
individual who is affected may have parents who are not affected
All children of 2 affected individuals are affected
46
number of chromosomes a human has
23
How many pairs chromosomes are found in
Autosomes
Fist 22 pairs of chromosomes
Sex Chromosomes
23 rd pair of chromosomes are called
Males have ** chromosomes
XY
Females have ** chromosomes
XX
Dad
Parent that determines biological sex of offspring
Homologous pairs
These pairs are called ** pairs because One chromosome comes from mom and other from dad
Karyotype
Visual representation of an individual’s chromosomes
Nondisjunction
Cause of chromosomal abnormalities
When chromosomes fail to separate
Acrocentric
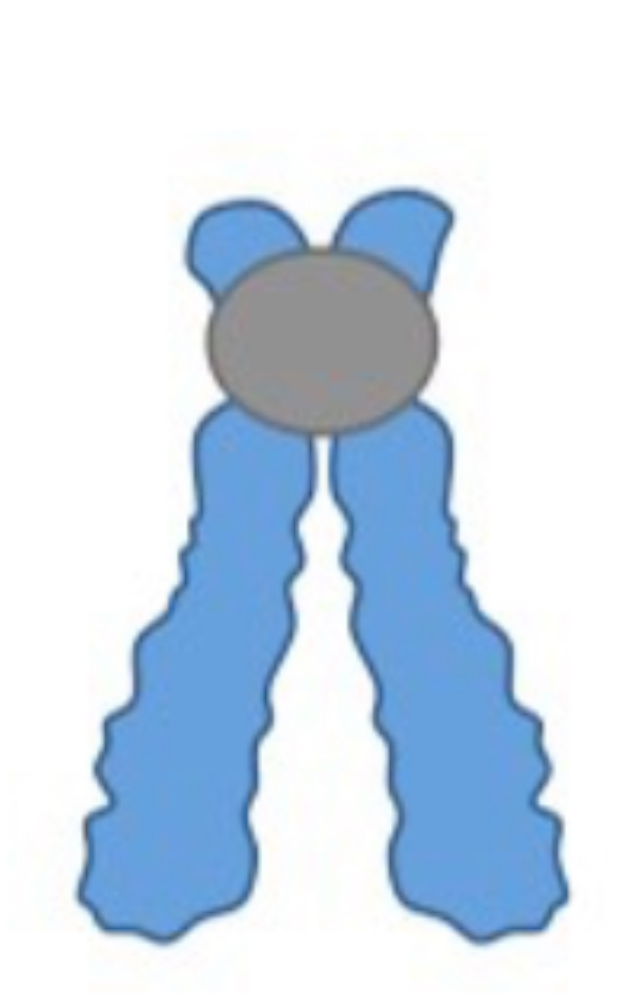
Submetacenyric
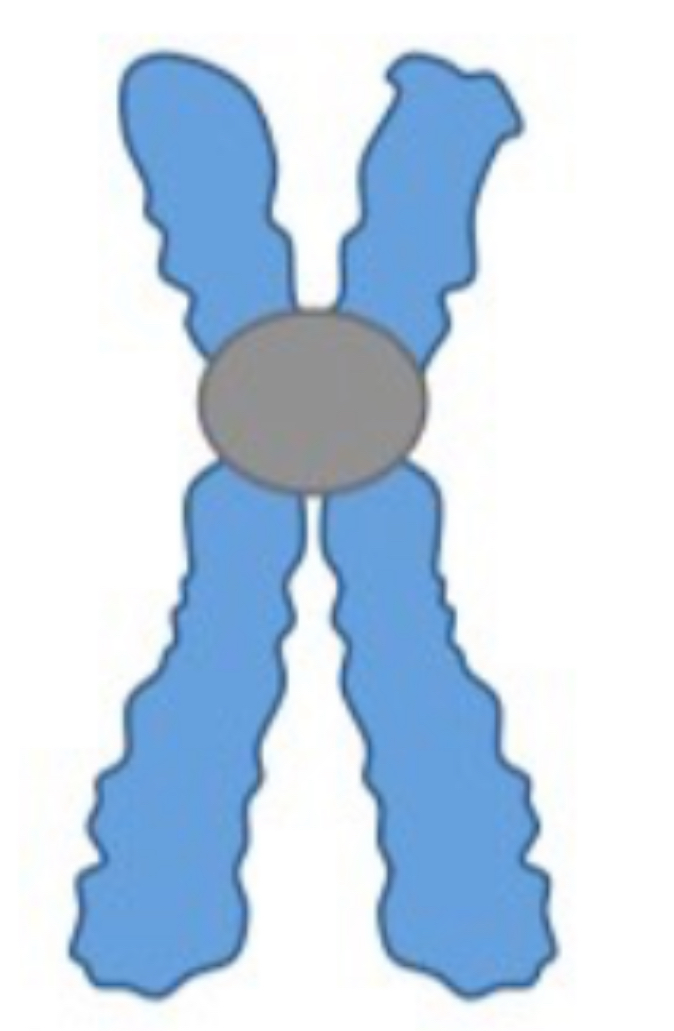
Metacentric
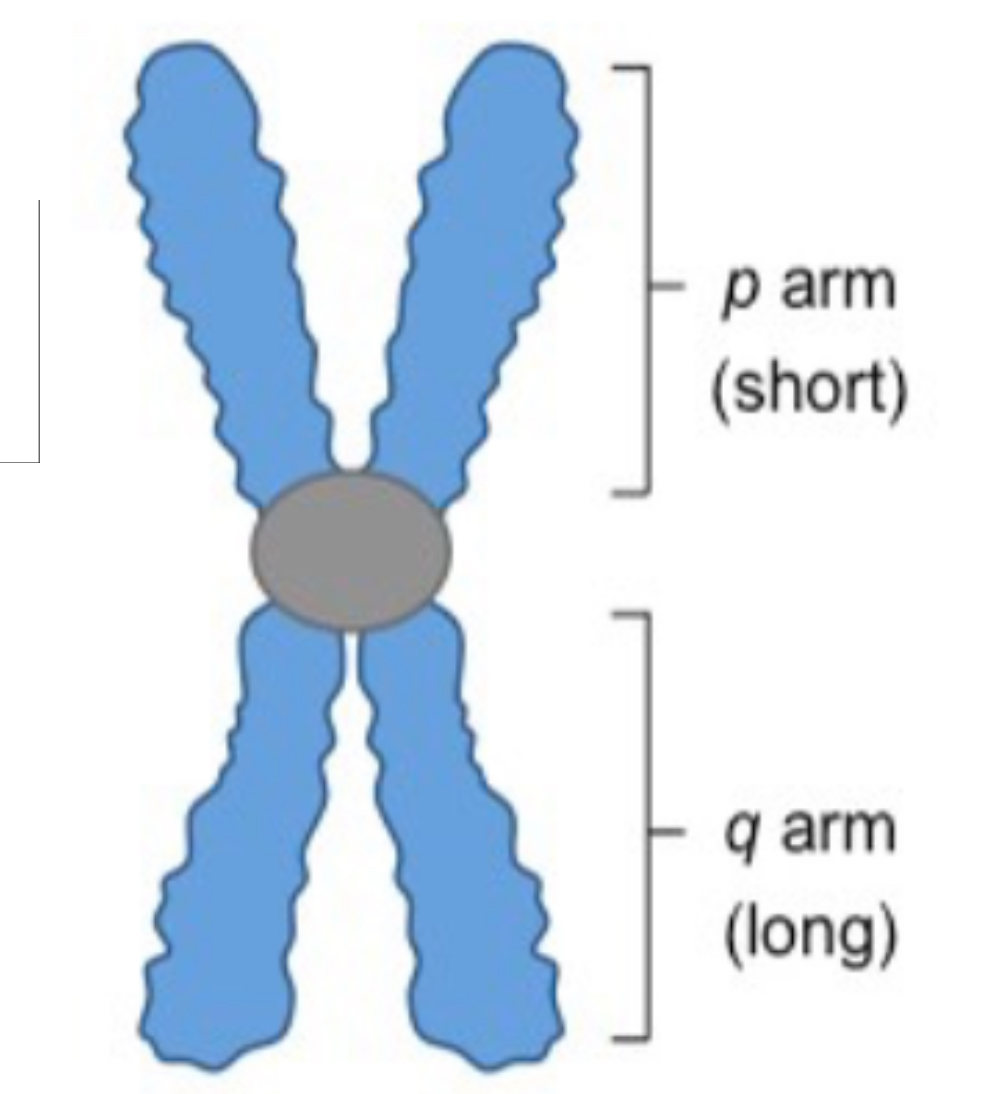
Aneuploidy
Organisms contain too many or too few chromosomes
Trisomy
These chromosomes are present in the chromosome pair
Monosomy
One chromosome is present in the chromosome pair.
3 steps in writing Karyotype Notation
start with total # of chromosomes
Add sex chromosomes
Add any missing autosomal chromosomes