Edexcel geography A-level The Carbon cycle and energy security EQ1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
The cycle by which carbon moves from one earth sphere to another.
What is the carbon cycle?
It is a closed system but is made up of many interlinked subsystems which are open and have inputs and outputs.
Is the carbon cycle an open or closed system?
Sources (adding carbon to the atmosphere) and sinks (removing carbon from the atmosphere).
What do carbon stores function as?
Movements of carbon from one store to another.
What are carbon fluxes?
Stores and fluxes.
What are the 2 main components of the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle
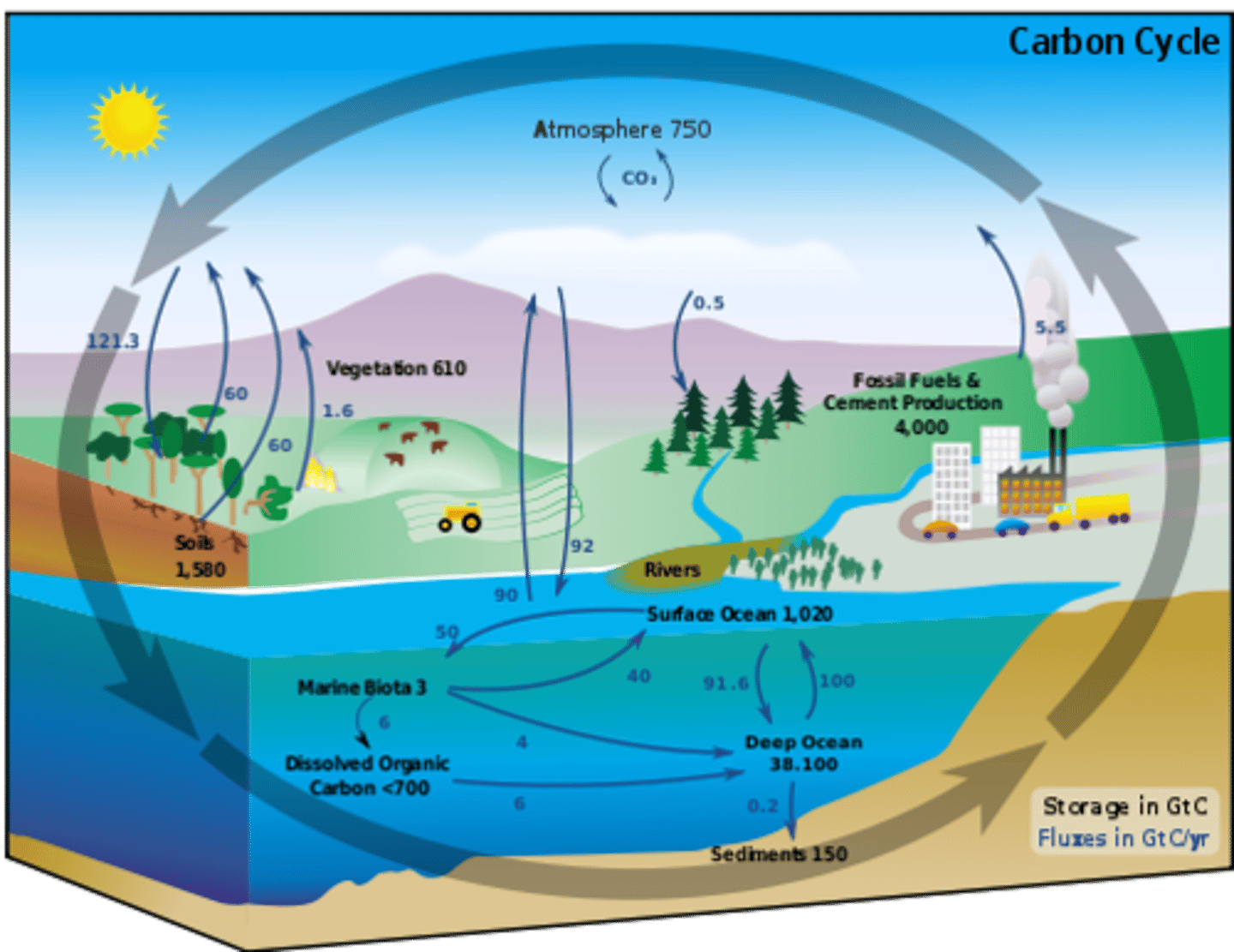
Atmosphere (the air) , hydrosphere (oceans, lakes rivers etc), lithosphere (rocks) and biosphere (plants and animals).
What are the 4 carbon stores?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon compounds (eg methane, CH4).
What form is carbon in the atmosphere?
Dissolved CO2.
What form is carbon in the hydrosphere?
Carbonates in limestone, chalk and fossil fuels
Pure carbon in graphite and diamonds.
What form is carbon in the lithosphere?
As carbon atoms in living and dead organisms.
What form is carbon in the biosphere?
In size, capacity and location.
How do carbon stores vary?
Pentagrams or gigatonnes of carbon per year.
What are carbon fluxes measured in?
Between the oceans (hydrosphere) and the atmosphere and between the land (lithosphere) and atmosphere (via photosynthesis and respiration).
What are the 2 main carbon fluxes?
The Himalaya mountains started out as being ocean sediments rich in calcium carbonate (from corals, crustaceans and plankton). These were up-folded creating the mountains. They are one of the largest carbon stores on earth.
Talk about the geological origins of sedimentary carbonate rocks in the oceans.
Rocks were made 300m years ago from the remains of organisms. The remains sank to the bottom of water bodies where they were covered by silt and mud. They decayed anaerobically and were compressed by further accumulation of dead organisms and matter above. Eventually the heat and pressure turned them into carbon boring rocks that are burns today as fossil fuels to provide energy.
Talk about the geological origins of carbon derived from plants and animals in shale, coal and other rocks.
The decomposition of rock minerals in their original position by agents (eg water, O2, CO2).
What is chemical weathering?
The release of gas previously dissolved, trapped or absorbed in some material.
What is outgassing?
1) Chemical weathering
2) Outgassing
What are the 2 geological processes that release carbon?
CO2 in the atmosphere reacts with moisture to form weak carbonic acid. This falls as acid rain and reacts with surface minerals slowly dissolving them.
How does chemical weathering release carbon?
Volcanic eruptions and earthquakes release gas pockets of CO2 that exist in the earths crust. This mainly occurs along mid-ocean ridges, subduction zones and at magma hotspots.
How does outgassing release carbon?
The process by which CO2 is removed from the atmosphere and held in a solid or liquid form.
What is carbon sequestration?
It is the process that facilitates the capture and storage of carbon.
Why is carbon sequestration key?
The oceans. Most of the carbon here is stored in marine algae, plants and coral. The rest is in a dissolved form.
What is the Earth's largest carbon store? How is the carbon stored within it?
The processes operating in the oceans that circulate and store carbon.
What are carbon pumps?
1) The biological pump
2) The physical pump
3) The carbonate pump
What are the 3 oceanic carbon pumps?
Oceanic biological pumps
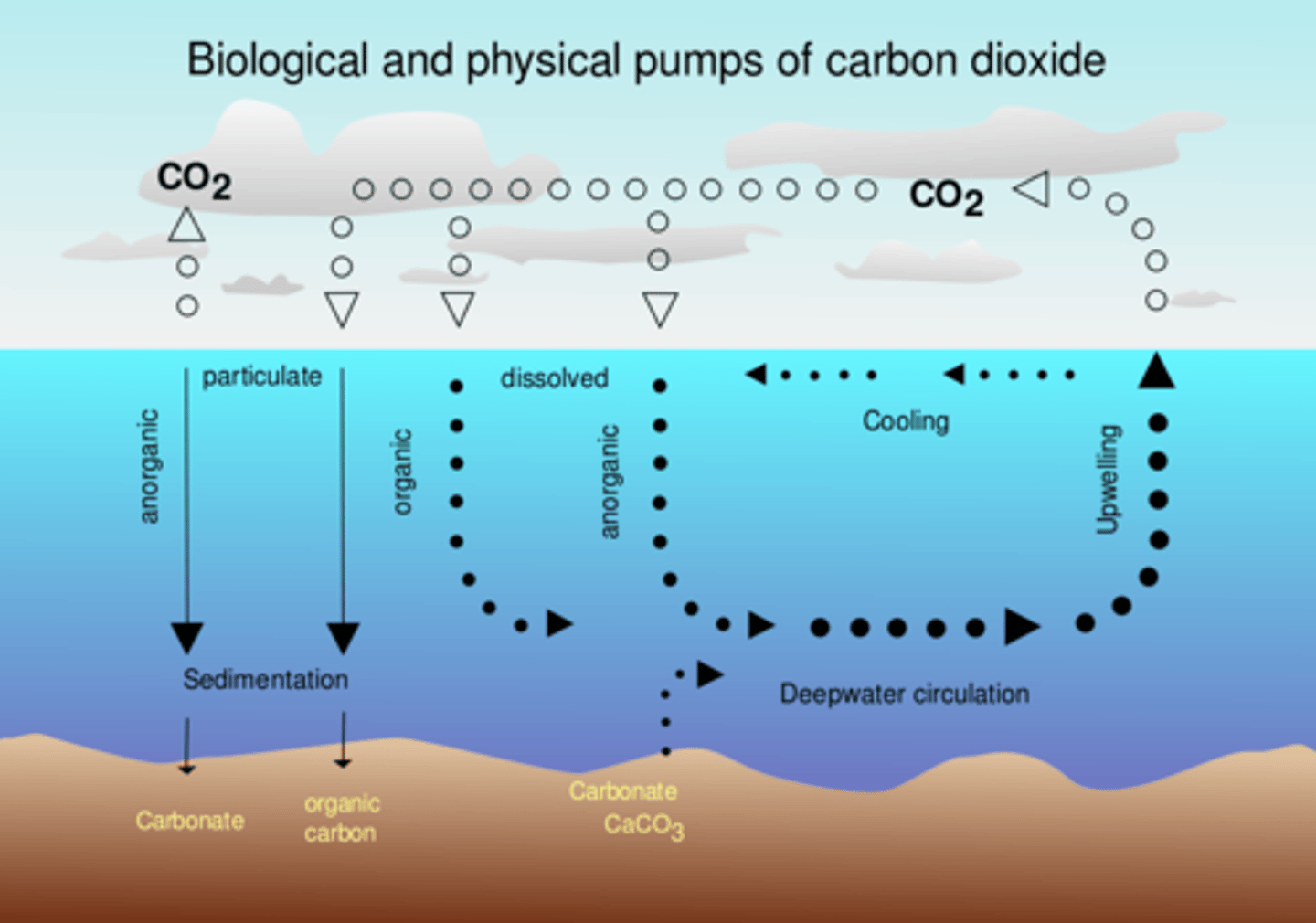
The pumps that move CO2 from the ocean surface to marine plants ( phytoplankton) by photosynthesis.
What is the Biological pump?
Microscopic plants and plant-like organisms drifting or floating in the sea along other organisms.
What are phytoplankton?
The process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesise (extract) nutrients from CO2 and water.
What is photosynthesis?
This pump moves carbon compounds to different parts of the ocean in downwelling and upwelling currents.
What is the physical pump?
Downwelling occurs in the oceans where cold, denser water sinks. These currents bring dissolved CO2 down to the deep ocean. Here, it moves in slow moving deep ocean currents staying there for hundreds of years. Eventually these currents ( that are part of thermohaline circulation) return to the surface by upwelling. The cold deep ocean water warms as it rises towards the ocean surface and some of the dissolved CO2 is returned back into the atmosphere.
Describe upwelling and down welling in the physical pump.
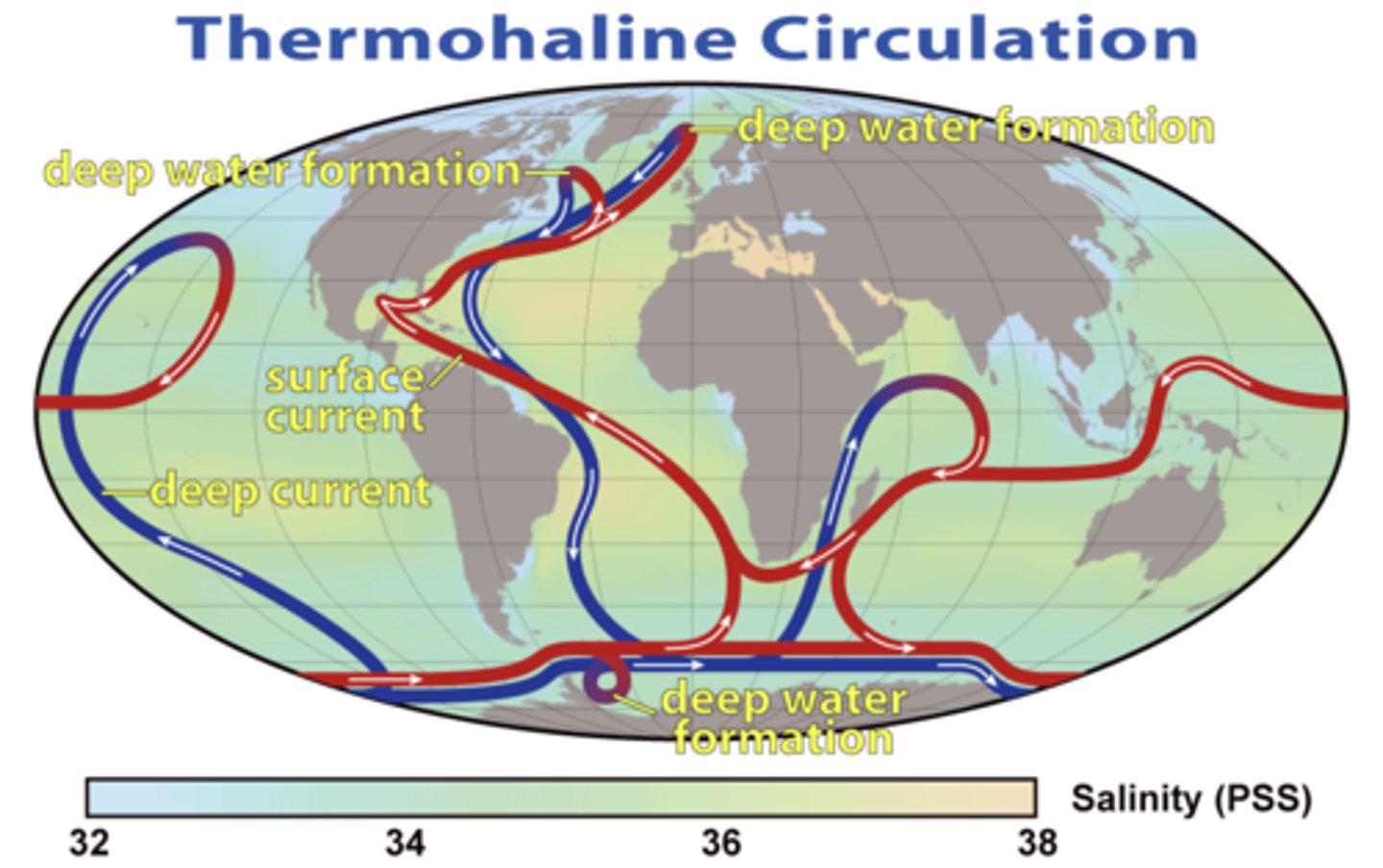
The global system of surface and deep ocean currents driven by temperature (thermo) and salinity (haline) differences between different parts of the ocean.
What is thermohaline circulation?
Thermohaline circulation
They form sediments from dead organisms that fall to the ocean floor. For example shells and skeletons of crustaceans, fish and corals that are rich in calcium carbonate.
What are carbonate pumps?
It is a giant conveyor belt that moves water of varying temps and salinities through the oceans.
How does thermohaline circulation play a vital part in the carbon cycle?
Plants sequester carbon out of the atmosphere during photosynthesis. Here it enters food chains and nutrient cycles of terrestrial ecosystems. When animals eat plants, the carbon they sequestered becomes part of the animals fat and protein.
Describe terrestrial sequestering
Respiration in animals returns some of the carbon back to the atmosphere.
Waste from animals is eaten by micro-organisms and broken down by detritus feeders.
When plants and animals die their remains fall to the ground and carbon is released into the soil as they decompose.
How is carbon in plants and animals returned to the atmosphere/soil?
1) Diurnally - during the day, fluxes are positive (from the atmosphere into the ecosystem) at night fluxes from the ecosystem to the atmosphere.
2) Seasonally - During winter CO2 levels increase due to the low levels of plant growth. When spring arrives and plants grow faster, these levels decrease.
In what 2 timescales do carbon fluxes within ecosystems vary?
Soils. Here biological carbon is stored in the form of dead organic matter. this can be stored for decades before being broken down by soil microbes then either being taken up by plants or released back into the atmosphere.
What are the biggest carbon stores on land?
Between 20% and 30%.
How many % of the global carbon do soils contain?
- Climate
- Vegetation cover
- Soil type
- Land use
What does the actual amount of carbon stored in a soil depend on?
This dictates the rate of plant growth and decomposition, these both increase with temperature and rainfall
How does climate impact the amount of carbon stored in a soil?
This affects the supply of dead organic matter. This is heaviest in tropical rainforests and least in the tundra.
How does vegetation cover impact the amount of carbon stored in a soil?
Clay protects carbon from decomposition (clay rich soils have a higher carbon content).
How does soil type impact the amount of carbon stored in a soil?
Cultivation and soil disturbance increase the rate of carbon loss.
How does land use impact the amount of carbon stored in a soil?
- Cycle plays a key role in regulating the earth's temperature by controlling the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere.
- This affects the hydrological cycle.
- Ecosystems , terrestrial and oceanic depend on the carbon cycle.
Why is a fully functioning and balanced cycle vital to the health of the earth?
The increasing concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere that is warming it and causing concern.
What is the greenhouse effect?
Primarily water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and ozone. These gases both absorb and emit solar radiation creating the greenhouse effect that affects global temperatures.
What are greenhouse gases (GHGs)?
Methane (CH4) and Carbon dioxide (CO2)
What are some the most important greenhouse gases?
The greenhouse effect
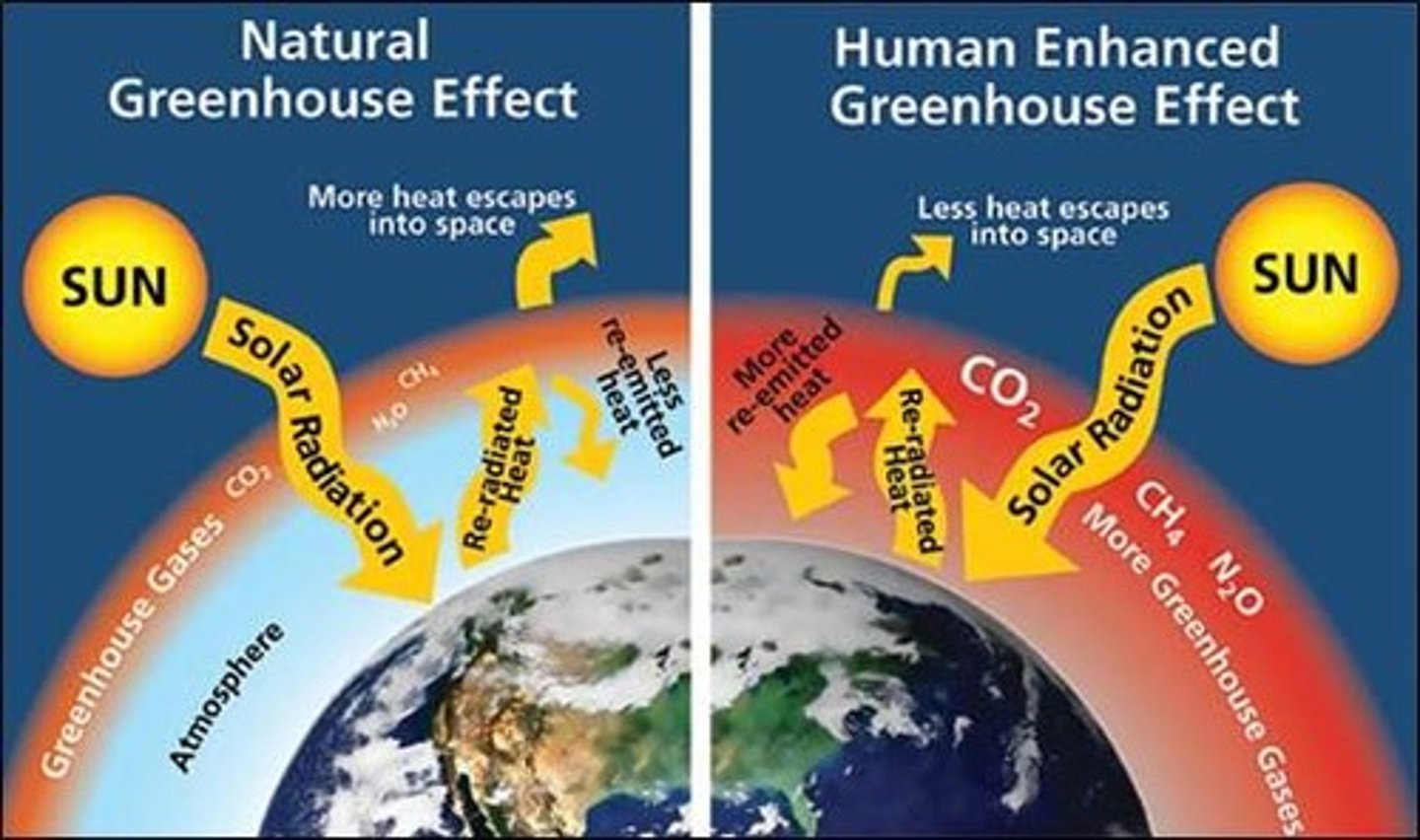
1) Solar radiation comes into earth from the sun by passing through the clear atmosphere.
2) Solar radiation is absorbed by the earth's surface and warms it, and it's converted to heat causing the emission of long wave radiation back to the atmosphere.
3) Some solar radiation is reflected by the atmosphere and earth's surface.
4) Some infrared radiation passes through the atmosphere and is lost in space
5) Some of the infrared radiation is absorbed and re-emitted by the GHG mols. This directly warms the earth's surface.
6) The surface gains more heat and infrared radiation is emitted again.
What happens in the greenhouse effect?
Incoming short-wave radiation.
What is the earth's climate driven by?
- 31% is reflected back into space by clouds, GHGs and land surface.
- Remaining 69% is absorbed by the earth's surface (especially the oceans)
- Lots of radiation absorbed at the surface is re-radiated as long wave (LW) radiation.
- Lots of this LW radiation are prevented from returning back to space by clouds and GHGs
- The trapped LW radiation is the re-radiated back to the earth's surface.
What happens to short wave radiation in the atmosphere?
- Photosynthesis by terrestrial and oceanic orgs plays an essential role in keeping CO2 levels constant by taking CO2 in from the atmosphere.
- The amount varies spatially with net primary productivity.
How does photosynthesis help to keep a balanced carbon cycle?
The amount of organic matter that is available for humans and other animals to harvest and consume.
What is net primary productivity (NPP)?
- NPP is highest in warm, wet areas (tropical rainforests and shallow ocean waters)
- NPP is lowest in cold areas (tundra and boreal forests).
Where is NPP greatest and lowest?
It is an important aspect of ecosystems that helps in the normal functioning of the carbon cycle.
How does soil health help to keep a balanced carbon cycle?
The amount of organic carbon stored in the soil.
What does soil health depend on?
The balance between the soil's inputs ( remains, nutrients) and its outputs (decomposition, erosion).
What do soil storage amounts depend on?
Carbon
What is the main component of soil organic matter?
Moisture-retention capacity, structure and fertility.
What does carbon in soil give it?
A large reservoir of nutrients which condition the productivity of ecosystems.
What does a healthy soil have?
They have been burnt to provide energy and power since the beginning of the industrial revolution (mid 18th century).
When have fossil fuels been burnt since ?
Fossil fuels threaten the global carbon cycle as they change the balance of the carbon stores and fluxes.
Why is fossil fuel combustion a problem?
Half the CO2 emissions have remained in the atmosphere. The rest has been fluxed from the atmosphere into the stores (the oceans, ecosystems ans oils).
What has happened to the extra emissions created by fossil fuel combustion?
- A rise in the global mean temp
- More precipitation and evaporation
- Sudden shifts in weather patterns
- More extreme weather events ( floods, storm surges and droughts)
- Nature of climate change (some areas drier, some water etc)
What has the additional CO2 in the atmosphere lead to in terms of climate changes?
Sea level rise as ice sheets and glaciers melt with higher global temps.
Low lying countries (eg The Maldives) and major coastal cities (eg Dhaka, Bangladesh) are under threat from flooding by the sea.
What are the knock on effects that climate changes have made to sea level?
Decline in goods and services from ecosystems, a decline in biodiversity, changes in the distribution of species, marine orgs threatened by low oxygen levels and ocean acidification, bleaching of corals ect.
What are the knock on effects that climate changes have made to ecosystems?
Increased temps and evaporation rates cause more moisture to circulate around the cycle.
What are the knock on effects that climate changes have made to the hydrological cycle?