Advanced Separations & Mass Spectrometry
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What is the key equation for resolution of a pair of analytes?
Rs = ΔtR / Wav, where Rs > 1.5 for baseline resolution.
What does the capacity factor (k') represent?
The ratio of time a solute spends in the stationary phase to the time spent in the mobile phase.
What is the equation for k’ (capacity factor) given a spectrum?
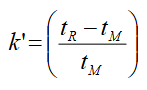
What is the relationship between the capacity factor (k’) and partition equilibrium constant (K)?
What does this mean?
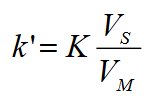
Means that the capacity factor (∴ retention time) is directly proportional to the partition equilibrium constant.
What is the equation for the capacity factor with respect to the velocity (u)?
k’ = (uM - uR) / uR
Where uM is the velocity of the mobile phase and uR is the velocity of the (retained) analyte species.
What is the relationship between occcupation of the mobile/stationary phases and velocity of the analyte (uR)?
uR = ( nmobile / ntotal ) x mobile phase velocity (uM)
What is K in chromatography?
The partitian equilibrium constant.
The ratio of the amount of analyte in the stationary phase to the mobile phase (assuming the compound is in equilibrium between them)
K = CS / CM
(where C is concentration)
What is the ideal range for the capacity factor (k')?
1 to 5, with a reality range of 0.5 to 20.
What is the significance of the selectivity factor (α)?
It indicates the ratio of capacity factors for analytes, essential for separation.
What is the equation for the selectivity factor (α)?
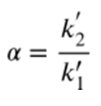
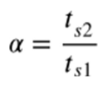
What does the van Deemter equation describe?
The dependence of plate height on flow rate using 3 factors (A, B and C).
What is the Van Deemter equation?
H = A + B/u + Cu, where A, B, and C are constants.
What are σ and τ in chromatography?
σ is the standard deviation from the mean retention time in length units
τ is the standard deviation from the mean retention time in time units
Describe the relationship between σ/τ and W.
σ/τ are the standard deviation of a peak.
95% of a peak is within ± 2τ (or ± 2σ)
So we use the approximation W (width) = 4σ = 4τ
What is the relationship between variance (σ²) and diffusion (equation)?
Variance is expressed as σ² = 2Dt, where D is the diffusion coefficient.
What is the importance of the peak width at base (W) in chromatography?
It is used to calculate resolution and efficiency of the separation.
What is the equilibrium constant (K) in the context of chromatography?
It is the ratio of concentrations of analyte in the stationary phase to that in the mobile phase.
How does the capacity factor (k') relate to the partition equilibrium constant (K)?
The capacity factor is directly proportional to the partition equilibrium constant.
What is the significance of achieving Rs > 1.5 in chromatography?
It indicates that the peaks are fully resolved, ensuring accurate analysis.
What is the effect of diffusion on band broadening in chromatography?
Diffusion leads to band broadening, which can affect the resolution of peaks.
How is the capacity factor (k') defined?
The ratio of the amount of analyte in the stationary phase to that in the mobile phase (nS/nM).
What does the migration velocity through a chromatography column depend on?
The distribution of the analyte between the mobile and stationary phases.
What is band broadening in chromatography?
The spreading of the analyte band as it moves through the column, affecting peak shape and resolution.
What is the significance of Gaussian shaped peaks in chromatography?
They indicate that band broadening is a statistically random process.
What does the diffusion coefficient (D) measure?
The rate at which a substance moves from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
What is the relationship between standard deviation (σ) and peak width (W) in chromatography?
W = 4σ, where σ is the standard deviation in length units.
What causes asymmetric band shapes in chromatography?
Skewing can arise from overloading (fronting) or stronger retention of small quantities of solute (tailing).
What causes fronting?
How is this corrected?
Overloading of the analyte sample.
Corrected by diluting the sample
What causes tailing?
How is this corrected?
The dilute analyte (after peak) is disproportionally impacted by strong groups on the silica so it retained for longer.
Corrected by masking these stronger groups.
What is plate height (H) in chromatography?
A measure of the variance of the band per unit length, indicating the efficiency of the column.
What is the relationship between plate height and standard deviation?
σ2 = Hx
where x is the distance the analyte travelled on the column.
What is one way of thinking of plate height?
The amount of distance on a column it takes for an analyte to equilibrate once.
It can also be thought of as the amount of varience you get per unit length of column (smaller value is better)
What is the eqaution for plate height with respect to variance?
H = σ2 / L
How is efficiency (N) defined in chromatography?
The theoretical number of plates in a column, calculated as N = L/H, where L is the column length and H is the plate height.
What does a larger efficiency (N) indicate about a chromatography column?
Larger N value means more plates so greater separation efficiency, hence higher resolution.
What does this equation tell you about the relationship between Rs and N?
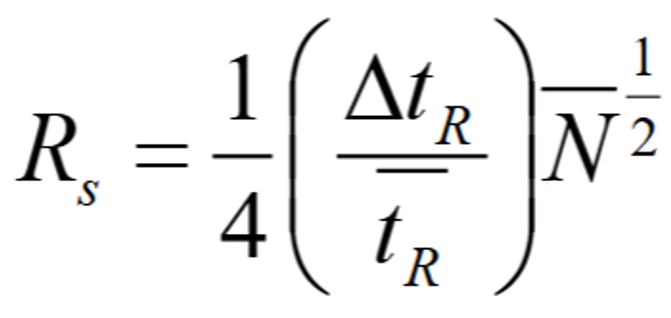
RS is proportional to √N
ie. doubling RS gives an increase in N of √2
What is the equation linking resolution and efficiency?
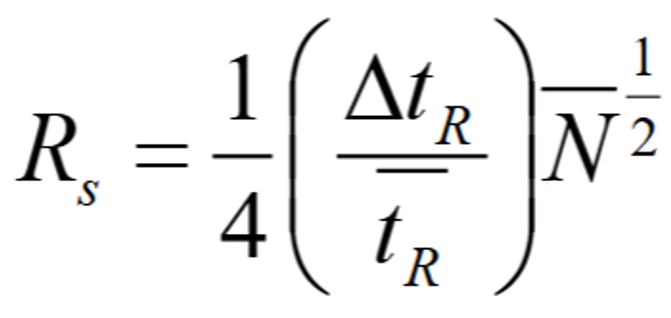
What do the lines on top of terms in the equation represent?
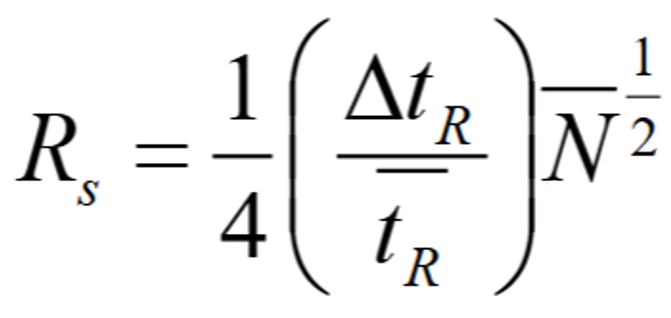
They denote averages
What does a larger plate height (H) indicate about a chromatography column?
It indicates poorer separation efficiency; smaller H values are preferred for better performance.
What is the resolution equation in chromatography?
Rs = (tR2 - tR1) / (Wav), where tR is the retention time and Wav is the average peak width.
What is the relationship between the standard deviation in time (τ) and the variance (σ2)?
τ = σ = W/4, where W is the peak width.
What does a small plate height (H) indicate about a chromatography column?
It indicates better separation efficiency and narrower bandwidths.
What is the formula for calculating the variance (σ2) in chromatography?
σ2 = 2Dt, where D is the diffusion coefficient and t is time.
What is the effect of column length (L) on efficiency (N)?
Efficiency (N) increases with column length (L), while plate height (H) is independent of L.
What does the van Deemter equation link in chromatography?
It links plate height (H) and flow rate (u) with the equation H = A + B/u + Cu.
What are the three terms contributing to plate height in the van Deemter equation?
A = multiple flow paths
B = longitudinal diffusion
C = Mass transfer/equilibration time
Which term in the van Deemter equation is 0 in Open Tubular Columns?
A (multiple flow paths) - solute doesn’t flow through the stationary phase, just over it so particle size doesn’t impact diffusion
Describe the constant A in the van Deemter equation.
A is the contribution of multiple flow paths to diffusion.
Larger SP particles means higher deviation in pathlength of the solute, hence more diffusion
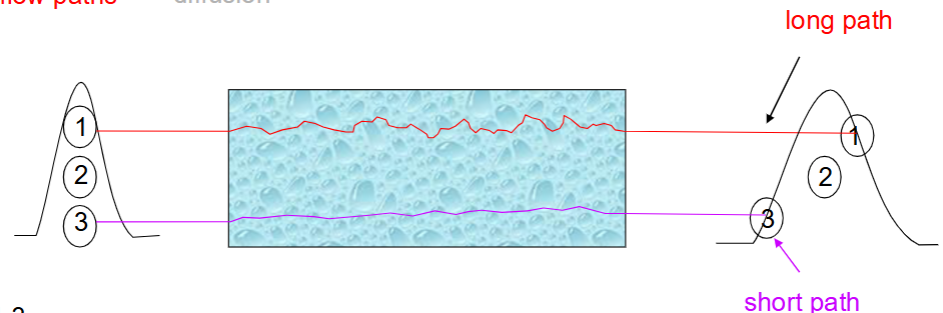
Describe the constant B in the van Deemter equation.
B is the longitudinal diffusion factor.
This is dependent on the time the analyte is on the column for, ie. flow rate and column length.
Describe the constant C in the van Deemter equation.
C is the equilibration time (/mass transfer) time.
This is the time taken for the analyte to move between the stationary and mobile phase.
This is related to the capacity factor, ie. the equilibrium between molecules in the mobile or stationary phase.
This can be improved by reducing the thickness of the stationary phase or increasing the temperature so that the molecules move between states more quickly.
Discuss the impact of flow rate on each constant in the van Deemter equation (and therefore H).
A - Multiple flow paths
B - Longitudinal diffusion
C - Equilibration time
A: This is independent of flow rate
B: Faster flow rate means less time on the column, so lower H
C: Increasing flow rate increases plate height because the flow rate is faster than the molecules can equilibrate between states, so diffusion increases.
Explain the trends shown in this graph, including the blue line.
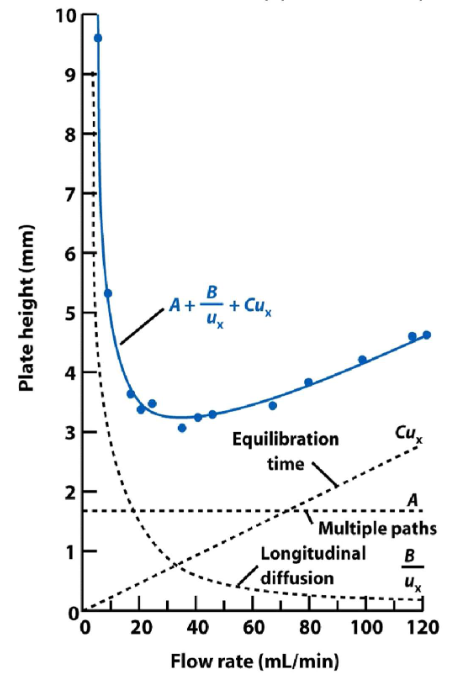
A is independent of flow rate.
B: Faster flow rate means less time on the column, so lower H
C: Increasing flow rate increases plate height because the flow rate is faster than the molecules can equilibrate between states, so diffusion increases.
The opposing contributions of B and C mean that there is an ideal flow rate which gives the lowest H value.
How does the flow rate affect band broadening in chromatography?
The extent of band broadening depends on the length of time the mobile phase is in contact with the stationary phase, which is influenced by the flow rate.
What is the order of elution in gas chromatography (GC) based on?
Within a compound class, elution occurs in order of increasing boiling point; for different classes, it depends on similarity to the stationary phase.
What are the two Gibbs equations?
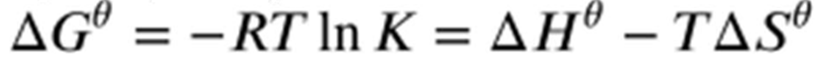
What is the equartion linking the apacity factor and boiling point?
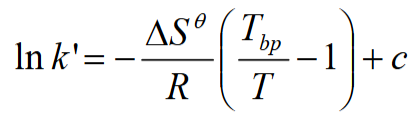
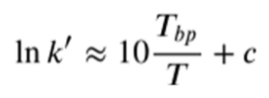
Due to Trouton’s rule (ΔS = -85 for many compounds) and R being constant so -ΔS/R = 10
Discuss how boiling point impacts the capacity factor using this equation
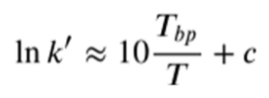
Increasing chain length of a homolous series increases the boiling point. Therefore, lnk’ increases as boiling point increases.
Discuss how temperature of the column impacts the capacity factor using this equation
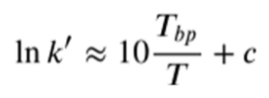
lnk’ decreases as T increases.
Ie. retention times get shorter as the temperature increases.
What is the temperature dependence of the capacity factor in GC?
The capacity factor (k') is linked to the boiling point (Tbp) and temperature (T), with ln k' scaling with 1/T.
What is Trouton's rule in relation to vaporization?
Trouton's rule states that the standard entropy of vaporization is approximately constant (~85 J mol-1 K-1) for many compounds.
What is the difference between isothermal and programmed temperature GC?
Isothermal GC maintains a constant temperature, while programmed temperature GC varies the temperature during the analysis.
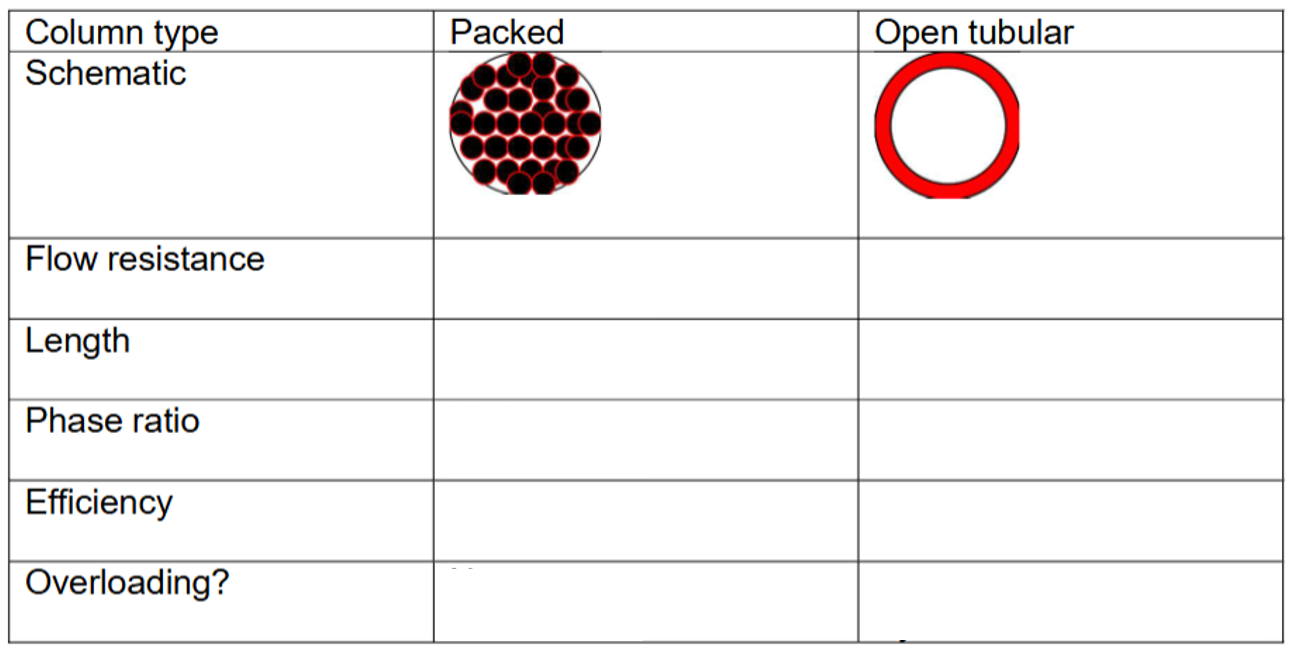
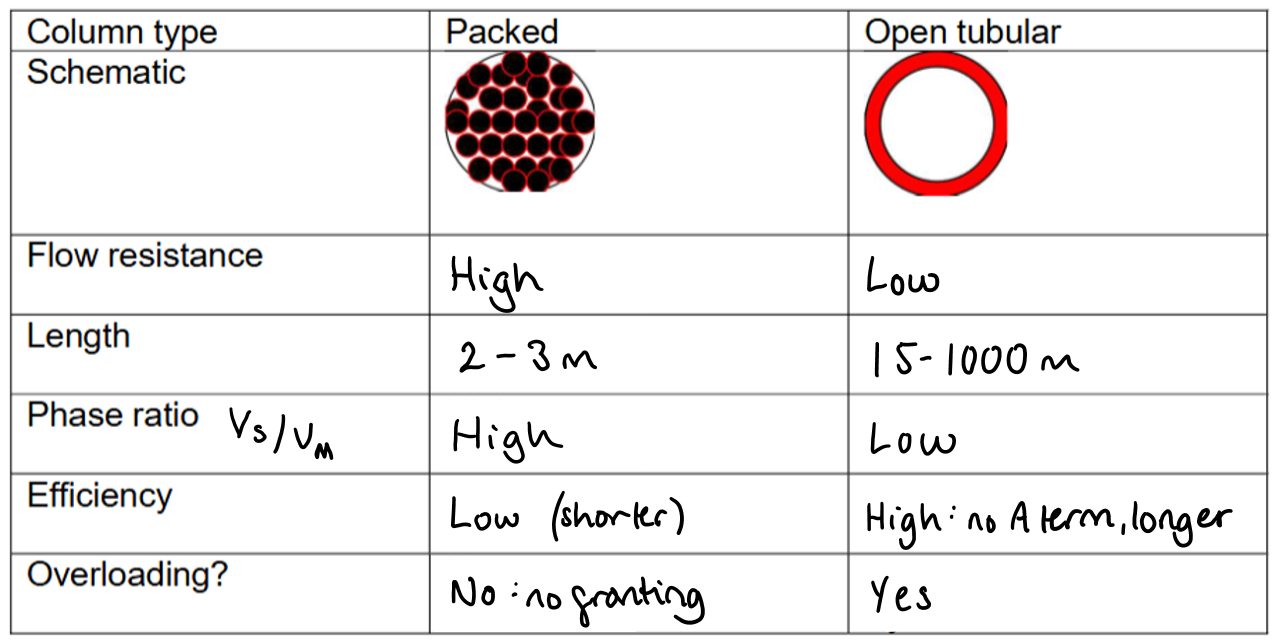
What are the qualitative differences between packed and open tubular columns in GC?
Packed columns have higher flow resistance and lower efficiency.
Open tubular columns have low flow resistance and higher efficiency.
Fill in this table
Describe the polarity of the phases in Reverse Phase LC
Stationary phase: non-polar
Mobile phase: polar
What does the length of an organic chain tell you about its hydrophobicity?
How does this impact retention time?
Longer chain - more hydrophobic
More hydrophobic molecules elute slower
Describe Eluent Strength (ε°).
How does the polarity of the eluent change ε° in RPLC.
Eluent strength: the adsorption energy of a solvent on the stationary phase, displacing the analytes.
A larger eluent strength means analytes spend less time on the stationary phase so elute quicker.
(Eluent strength is 0 for pentane on bare silica, everything else is relative)
In RP, a less polar solvent has a higher eluent strength (because the stationary phase is non-polar).
What is the equation for k’ with an organic modifier (in RP)?
log k’ = log k’w - SΦ
Where S is the organic modifier’s strength and Φ is the volume fraction of the OM in the water
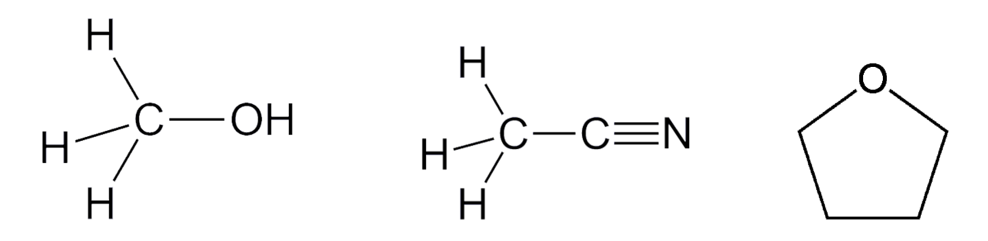
What are the 3 main OMs used?
Methanol (MeOH)
Acetonitrile (MeCN)
Tetrahydrofuran (THF)
What impact does phase volume have on k’?
Most silica is porous so has a high surface area.
Using noon-porous silica decreases the available surface area, so VS/VM decreases → k’ decreases as compounds elute faster
What is the equation linking variance and the diffusion coefficient?
σ2 = 2Dt
(t = time)
What is transverse diffusion?
Compare the rates of this is GC and LC.
Diffusion of the analyte perpendicular to the direction of flow, ie. the movement from one wall to the other in open tubular columns.
Faster in GC so smaller H
What is the relationship between particle size and plate height (H)?
Increasing particle size increases plate height because the flow paths (A) are more variable (more band spreading) and it takes longer to diffuse through the pores (C).
However, at very low particle sizes, there is resistance to solvent flow.
Describe UHPLC
Using very small particle sizes and high pressures to increase efficiency.
What is Fused Core Technology?
When the core of a stationary phase particle is solid, and it only have pores within an outside surface layer.
This improves efficiency by reducing the C factor as the analytes aren’t diffusing through the pore.
What is the relationship between efficiency, column length and the variance?
N = L2 / σ2
What is the relationship between plate height, column length and the variance?
H = σ2 / L
What is the typical magnitude for efficiency in HPLC?
What about GC?
N = 104
Higher in GC (105) due to using a longer column.
How does particle diameter affect efficiency in HPLC?
Changes in particle diameter affect the C term in the van Deemter equation, impacting efficiency and plate height.
Explain this equation
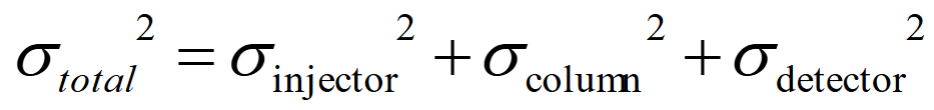
This is saying that any variance in your signal could be caused by factors involved in injection, by interactions on the column (discussed in detail) or by the method of detection used. These factors combine to give a total variance for the peak.
This is why NMR is not suitable as a detection technique (longer distance to transport = broader band), but UV-Vis or MS work well
Using this equation, calculate the % difference in retention time between compounds in LC to give the minimum baseline resolution. (N = 2.5 × 104)
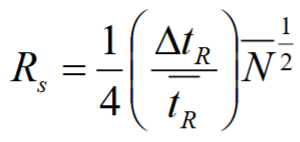
1) Rearrange:
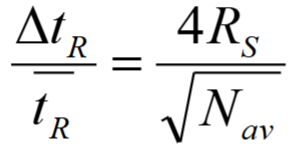
2) RS = 1.5
ΔtR / tR = 4(1.5) / √(2.5 × 104)
= 0.04
so 4% minimum difference in retention time for baseline resolution
What is the significance of the capacity factor (k') in chromatography?
The capacity factor indicates how well an analyte is retained by the stationary phase; it increases with boiling point.
What is the relationship between retention time and boiling point in chromatography?
Retention time increases as boiling point increases for a homologous series of analytes.
What is the difference between porous and non-porous silicas in chromatography?
Porous silicas have a larger surface area and different phase ratios compared to non-porous silicas, affecting separation efficiency.
What does the term 'efficiency' refer to in chromatography?
Efficiency refers to the ability of the column to separate analytes, often quantified by the number of theoretical plates (N).
What is the significance of the theoretical plates (N) in chromatography?
Theoretical plates indicate the efficiency of a column; more plates suggest better separation capability.
In RP-HPLC, in what order do analytes elute?
In the order of their hydrophobicity, with the most hydrophobic eluting last.
What is the significance of ε° in liquid chromatography?
It defines the solvent adsorption energy; higher ε° means solutes elute more rapidly.
What effect does changing the organic modifier have on k'?
Different organic modifiers have different 'S' values, affecting the retention factor k'.
What is the difference between isocratic and gradient elution?
Isocratic elution maintains a constant solvent composition, while gradient elution changes the solvent composition during the run (ie. adding more OM).
What is the relationship between plate height (H) and particle diameter (dp) in HPLC?
H is minimized at a particle diameter of around 10 µm, but smaller particles increase resistance to solvent flow.
What is Ultra-High Pressure Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC)?
A technique that uses particle sizes less than 2.5 µm for improved efficiency without significant loss at higher flow rates.
How is column efficiency in HPLC calculated?
N = L / H, where N is the number of theoretical plates, L is the column length, and H is the plate height.
What is the typical efficiency (N) in HPLC?
Typically around 10,000 theoretical plates.
What is the purpose of selected ion monitoring in mass spectrometry?
To increase the signal-to-noise ratio by detecting only ions of a desired mass.
What are the common organic modifiers used in RP-HPLC?
Methanol, acetonitrile, and tetrahydrofuran.
What is the significance of the phase ratio (VS/VM) in chromatography?
It influences the retention and elution characteristics of solutes.
What is the importance of monitoring performance metrics like k' and tR?
These metrics help assess and optimize the efficiency and effectiveness of chromatographic separations.