Martin | enteral medication administration
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is enteral nutrition?
refers to the system of providing nutrition directly into the GI tract by bypassing the oral cavity
when would enteral nutrition be indicated?
in patient’s who lack the ability to maintain oral intake
what are examples of patients who are indicated for enteral nutrition?
Neoplastic disease (chemo, radiation, oral/head/neck tumors)
Organ dysfunction (liver/renal disease, organ transplant)
Hypermetabolic states (TBI, burns, postoperative surgery, sepsis)
GI disease (IBD, short bowel, pancreatitis, GERD)
Neurologic impairment (coma, stroke, TBI)
anorexia complications, failure-to-thrive
what is the enteral nutrition process?
1.assess the patient
2.prescribe an regimen
3.review the order
4.procure, select/prepare, label, dispense EN
5.administer
6.monitor and reassess the patient
7.repeat
what are examples of short-term enteral access devices?
Nasogastric (NG)
Orogastric (OG)
what are examples of long-term enteral access devices?
Gastrostomy (G-tube)
Jejunostomy (J-tube)
Gastrojejunostomy) (GJ-tube)
what are considerations of enteral access devices?
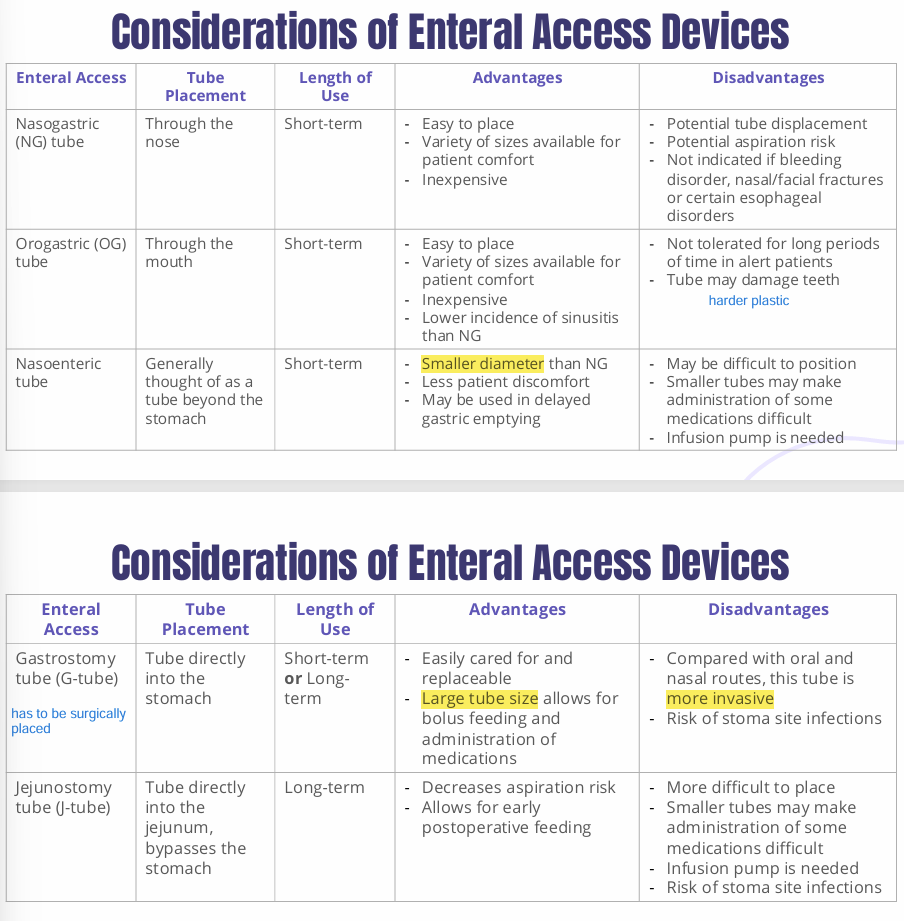
what can cause a tube to clog?
-narrow tube diameter
-tube location
-insufficient water flushes
-formula contact with acidic fluid
-incorrect medication (thick suspension, enteric-coated, ER formulations)
how can we prevent clogs?
-largest diameter
-flush before and after feedings (adult 30+ mL, peds lowest volume necessary)
-flush before and after medication w/ 15 mL
-use an automatic flush pump
what is “water” with flushing tubes?
purified or sterile water
what is the role of the pharmacist in enteral feedings?
1.review medication formulations
2.determine the compatibility of the medication
3.assess the appropriateness of the medication route of administration
4.evaluate methods to optimize the medication regimen and prevent complications
what are preferred medication formulations w/ EN?
Liquids (avoid sugars, preservatives, thickening agents)
IR caps/tabs (crush)
what are medication formulations that we should avoid in EN?
enteric-coated (can clump and clog)
ER (crushed may result in erratic or toxic drug levels)
Sublingula/buccal tablets (erratic drug levels)
High-viscosity, high-osmolality (decreased delivery and may clog)
Hazardous (only crushed in a biological safety cabinet)
T/F
drugs requiring an acidic environment may have altered bsorption when given via J-tube
true, because they will have bypassed the acidic environment of the stomach
how should we administer phenytoin with enteral feeds?
hold the feed 1-2 hours before and after administration as enteral feeds may reduce absorption
how should we administer warfarin with enteral feeds?
the absorption may be variable, monitor INR
how should we administer fluoroquinolones with enteral feeds
2 hours before or 6 hours after
-may chelate w/ calcium and magnesium and clog
how should we administer levothyroxine with enteral feeds?
shouldn’t
these bind to enteral nutrition = reduced bioavailability and efficacy
what type of pill can we use for EN fluoroquinolones?
IR tablets
t/f
we can use fluoroquinolone suspensions
false, clogging risk due to high-osmolality and high-viscosity
what form of omeprazole can we use for EN?
oral packet for suspension
ODT or delayed-release
what form of lansoprazole can we use for EN?
delayed release oral capsule, ODT
can form of pantoprazole can we use for EN?
oral packet for suspension, delayed-release
t/f
we can use the oral capsule of levothyroxine for EN
false
how can we administer levothyroxine oral solution as EN?
hold tube feeding 1 hour before and up to 1 hour after
how can we administer levothyroxine oral tablet as EN?
hold tube feeding 1 hour before and after administration
how can we manage tube clogs?
instill warm water, apply a gentle back & forth motion
enzyme-based declogging solution (1 uncoated pancreatic enzyme + 325 mg NaHCO3 + 5mL water
mechanical declogging device
tube replacement
generally when can someone be switched from IV to PO?
when they have tolerated a full liquid diet for 24 hours
when there is a feeding tube in place
when they are receiving other oral/enteral medications
what are general exclusion to switching form IV to PO?
NPO
risk of aspiration
ileus/GI obstruction
severe/life-threatening infection
actively seizing