Marine Biology - Exam 3
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Radial symmetry
symmetry about a central axis like corals & jelly fish
Bilateral symmetry
symmetry on either side of plane like worms & lobsters
How many cell layers do cnidarians have?
2
What type of organisms have 3 cell layers?
Endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm
Coelom
- cavity that develops in embryo within mesoderm
- allows body compartmentalization
What types of organisms have coeloms?
Arthropods & mollusks
Gut
- may be absent
- open at only one end (blind)
- complete with a mouth & anus
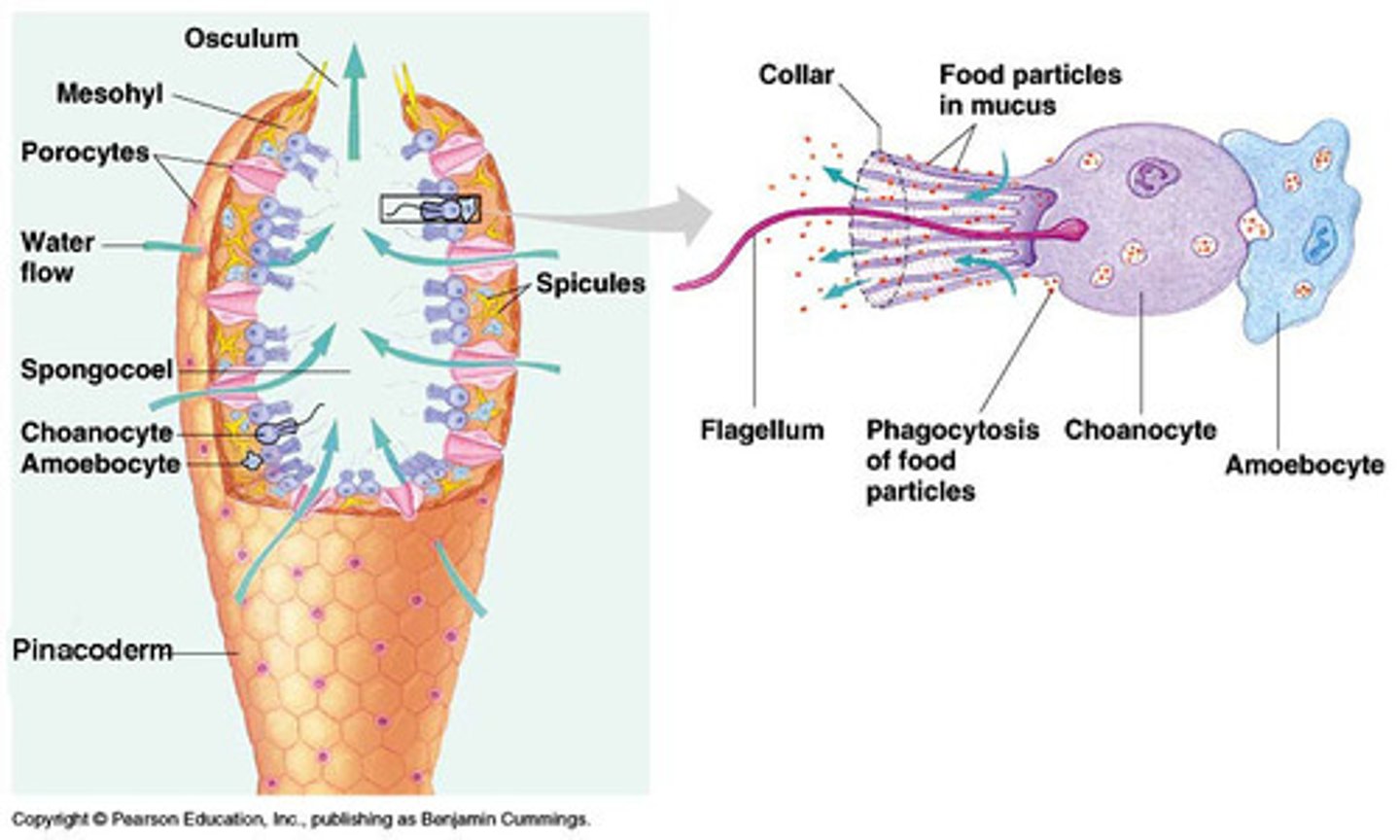
What do sponges feed on?
Feed on bacteria by trapping bacteria via choanocytes flagellae
Amoebacytes
move digested food to other parts, carry waste
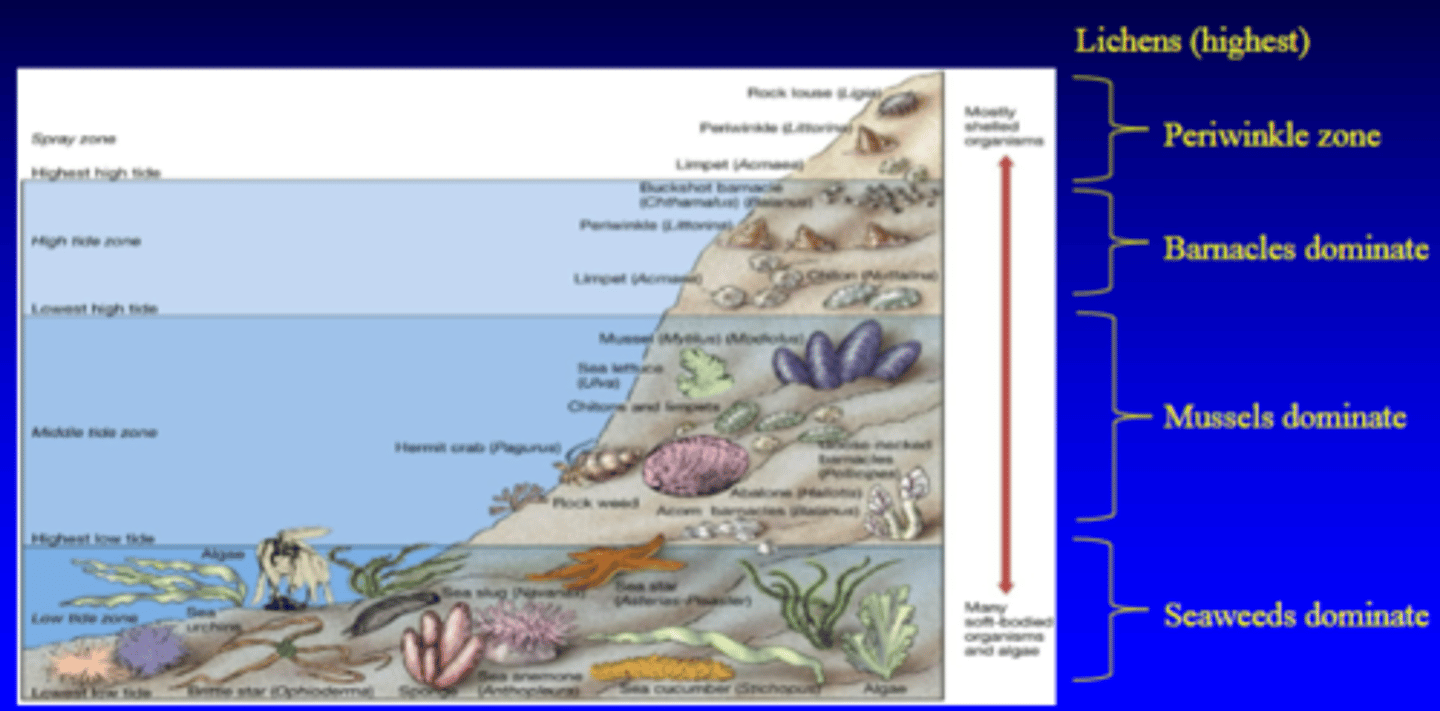
Zonation
- universal feature of rocky shores
- not as pronounced in soft sediment shores
- 3D due to burrowing organisms
Typical zonation pattern (high to low)
1. black lichen zone
2. periwinkle zone with sparse barnacles
3. barnacle-dominated zone
4. seaweeds dominate
Horizontal spatial gradients
changing wave exposure (outlets vs. inlets)
Inlets on the shore experience
low wave energy and less pronounced zones
Outlets on the shore experience
high wave energy and more pronounced zones
Vertical spatial gradient
- changing current exposure (up/down shore)
- biotic & abiotic factors
Vertical gradient attributes
- Temperature
- Desiccation
- Reduced feeding time
- Oxygen stress
- Wave energy
Bigger animals have:
- lower surface area to volume
- pro for water loss
- con for heat dissipation
Heat Stress/Desiccation
- varies on small spatial scales
- body size, shape are important
- evaporative cooling & circulation of body fluids aids in heat loss
- well-sealed exoskeletons aid in reducing water loss (acorn barnacles)
Heat shock proteins (HSP)
- chaperone proteins that help refold misfolded proteins
- interact with seasonal acclimation
Do HSP interact with seasonal acclimation?
Yes, summer acclimates mussels produce less HSP at a higher threshold temp than winter acclimated mussels.
Higher intertidal organisms
- more heat resistant
- more desiccation
- less time to feed
- avoid mobile carnivores
Wave stress is higher in what intertidal zone?
Lower intertidal zones
Abrasion
particles in suspension scrape delicate structures
Pressure
hydrostatic pressure of break waves can crush structures
Drag
- impact of water can exert drag, pull organisms from their attachments to surfaces
- erode particles from beaches & carry organisms from burrows
Swash riders
move up and down as tides change to maintain burrowing position in moist sand (burrowing mole crab)
Why are there vertical zones, with dominance often of single sessile species within a zone?
1. differences in tolerance at different tidal heights
2. competitive interactions
Oxygen gradient
- only respire when submerged, can't respire at low tide
- reduce metabolic rate at low tide
- high intertidal animals respire from air
Larval settlement
settle at different areas in intertidal, different species may settle differently & respond to different cue
Interspecific competition
space is a limiting resource, competitive displacement can occur
Predation
important for preventing competitive dominants
Robert Paine
Removal of sea stars decreased biodiversity because muscles out competed everything else
Why are coral reefs restricted to warm shallow clear water?
subject to high calcification, need sunlight
Connell experiment conclusions
- predation important in lower intertidal
- biological factors control lower limit of species occurrence
- physical factors control upper limit
- community structure a function of very local processes
Soft Sediment Intertidal
- zonation not as distinct
- water retention due to porous sediments reduced vertical desiccation & temp
- higher intertidal species burrow more deeply
Vertical Stratification in soft sediments
- dominant species found at different levels below sediment-water interface
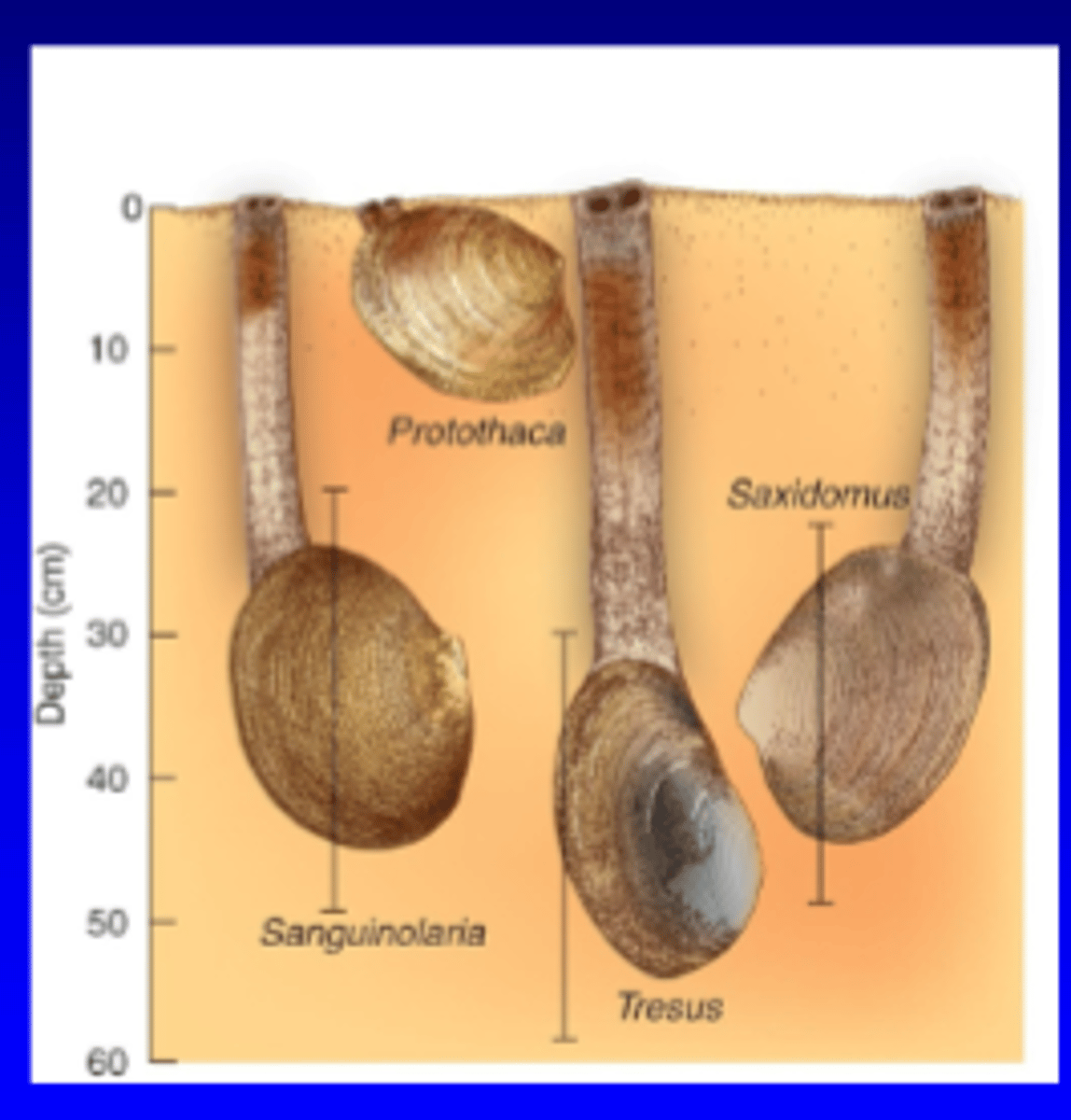
Food Supply in soft sediments
1. Suspended phytoplankton for suspension feeders
2. Microalgae & bacteria for deposit feeders
3. Decomposing organic matter (phytodetritus)
Why do sediments gain particulate organic matter & become anoxic patches?
Sediment colonized by populations of smaller polychaetes becomes oxygenated, strong spatial variation in worm densities
Predation in soft sediments
- seasonal influxes of predators (birds/fish), predators focus on most abundant
- caging experiments demonstrate this effect
Salt Marches
- Bare intertidal sediment
- Early colonization of patches of grasses
- Extension of grass patches & trapping of sediment (rhizome system)
- Gradual rise of sediment surface (accretion)
- Development of higher march dominated by terrestrial plants
Aerenchyma tissue
allow Spartina to exchange gases, even when surrounded by anoxic soil
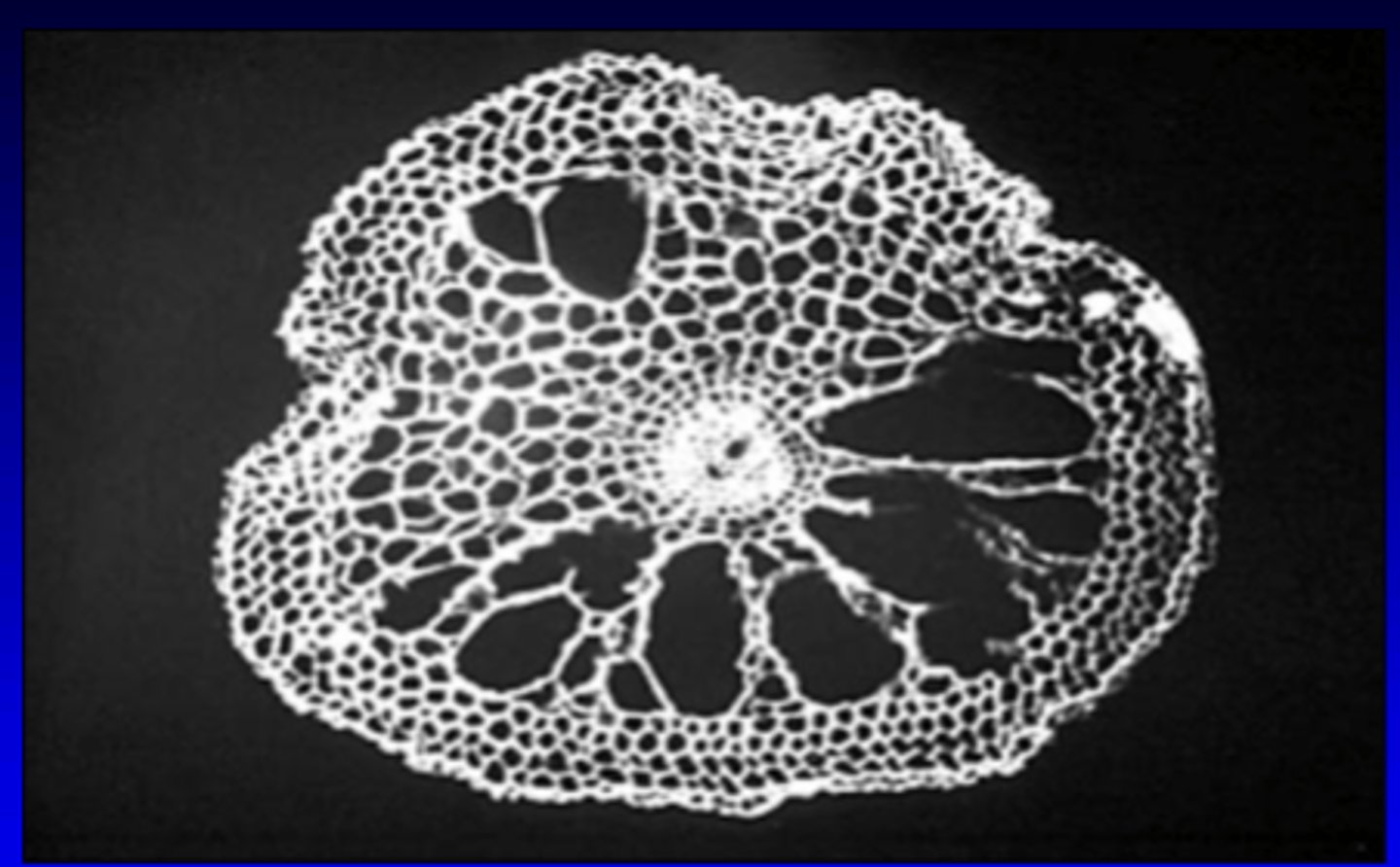
Salt Marsh Creeks
- Creeks are tidal: fill with saltwater at high tide, drain at low tide
- High nutrient input, support large populations of invertebrates & are often nursery grounds for juvenile fishes & crustaceans
Salt Marsh Vertical Zonation
- lower intertidal species are more salt tolerant
- higher intertidal species are competitively superior, not able to survive the longer exposure lower down to salt
Mangrove Forests
- broadly rooted but only to shallow depth in quite anoxic soils
- underground roots have projections into air that allow gathering of oxygen
Key Features of Salt Marshes/Mangrove Forests:
- High supply of particulate organic matter
- Both stabilize coastal intertidal soils
- Both maintain water quality
- Support rich assemblage
Estuaries
- controlled by seaward flow of freshwater combined w tidal mixing
- decreasing salinity zones to freshwater & associated creeks, decreasing biodiversity
- ephemeral but biologically rich
Sea Grasses
- angiosperm (flowering plants) that are confined to shallow water
- surface rhizome systems within soft sediment
- tropical & temperate oceans
- shallow, high light, modest current flow
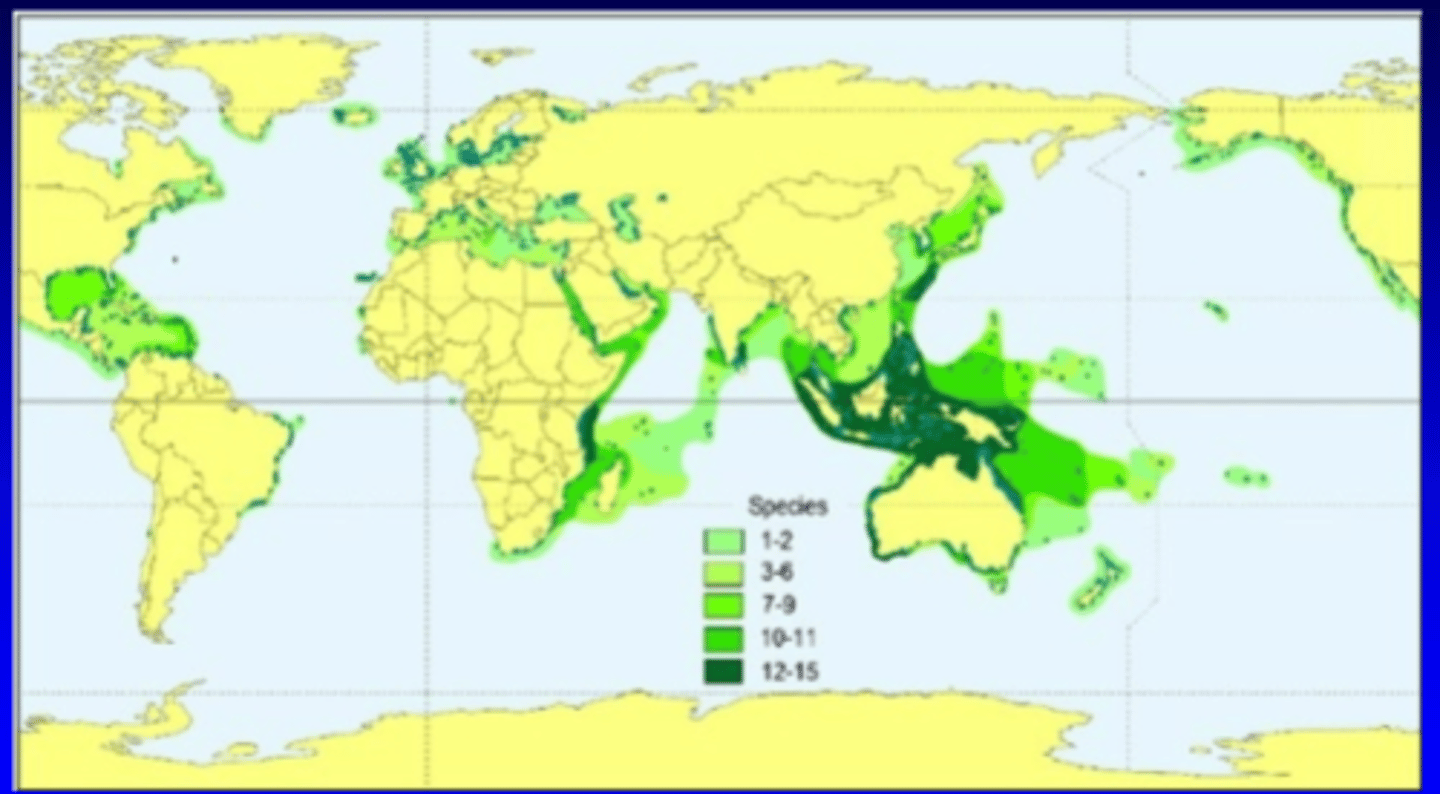
Why do sea grasses lack flower?
- Sexual reproduction is secondary to asexual
- Rely on water dispersal of pollen rather than pollinators
Production/Ecology of sea grasses
- high primary production, support diversity
- reduce current flow
- refuge for prey
- enhance growth of infaunal suspension feeders near edge
Grazing/Community Structure
- grazing on eel grass is minimal (temperate zone)
- different species are grazed differently bc of different toughness/cellulose content (tropics)
- tough grasses consumed by turtles, urchins, dugongs
Decline of sea grasses:
- vulnerable eutrophication, phytoplankton shade sea grasses
- possible overfishing results in reduced grazing/overgrowth of epiphytes
- dredging, boat traffic
- fungi that causes sporadic diseases in tropical sea grasses
Kelp Forests
- brown seaweeds in Laminariales
- nutrient rich, shallow water, exposed to open sea
- high growth rates (cm/day)
- 10-20 m high
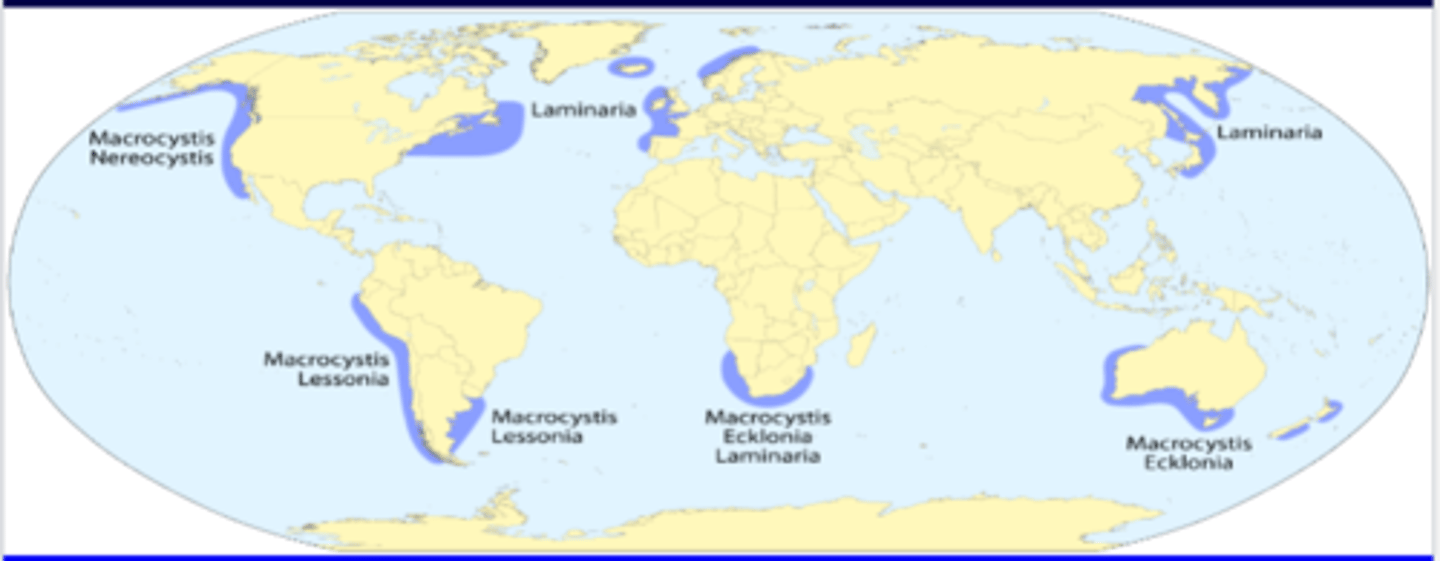
Diversity of kelp forests
- sometimes dominated by 1 species
- sessile benthic species living on hard substrata, suspension feeders
What happened in Kuluk Bay, Alaska?
- Over fishing decreased number of fish for sea lions, decreasing killer whale prey
- whales started to eat sea otters which increased urchin population to over graze kelp
Grazing of kelp forest
- shallow water kelps lack chemical defense
- deep water kelps contain more chemical defense
- Australian kelps better defended than North Pacific kelps
North Pacific kelps
- otters reduce urchins
- low herbivory
- relatively few defenses
Australasia
- less predation on urchins
- results in high herbivory
- phlorotannin conc in helps are 5-6x higher
How much of the marine environment do coral reefs make up?
0.25%
Reef
wave-resistant structure hazardous to shipping, formed by biotic or abiotic processes
Coral reef
structure resulting from cementation processes & skeletal construction of hermatypic corals, calcareous algae
Coral community
scleractinian corals, not necessarily built on or actively accreting wave-structure
Why Phylum is coral in?
Cnidaria
Coral Feeding
- Symbiotic Zooxanthelle
- Carnivory: Nematocysts
- Mesenterial filaments
Hard corals
- reef builders (hermatypic)
- produce hard CaCO3 skeleton
- rely on symbiotic algae
- limited to warm, clear shallow water
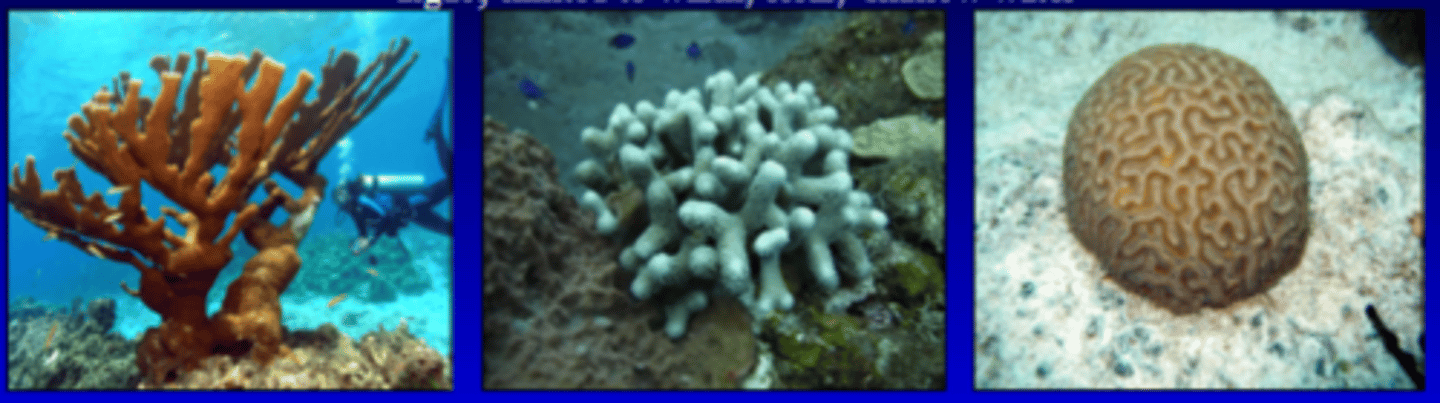

Soft corals
- may or may not have symbiotic algae
- broader habitat range

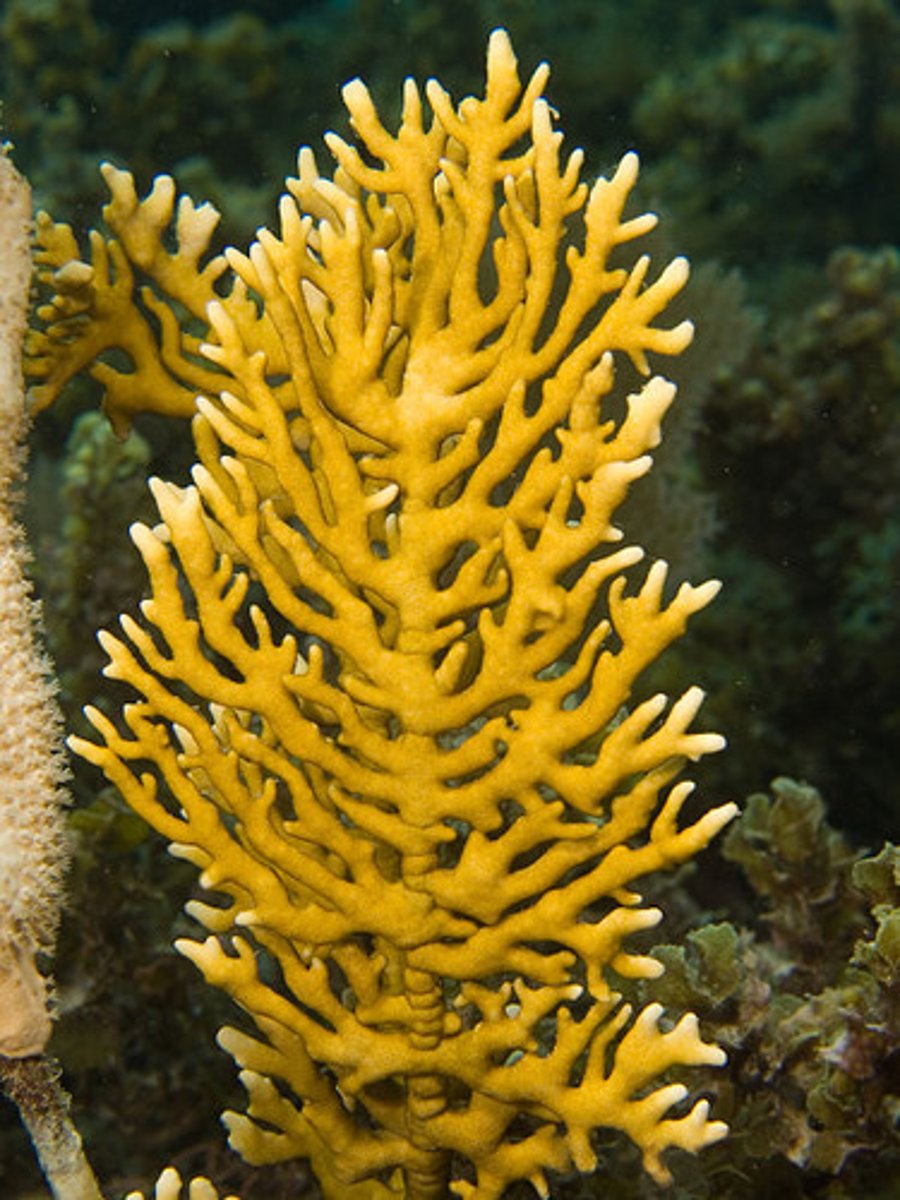
Hydrazoa corals
fire corals

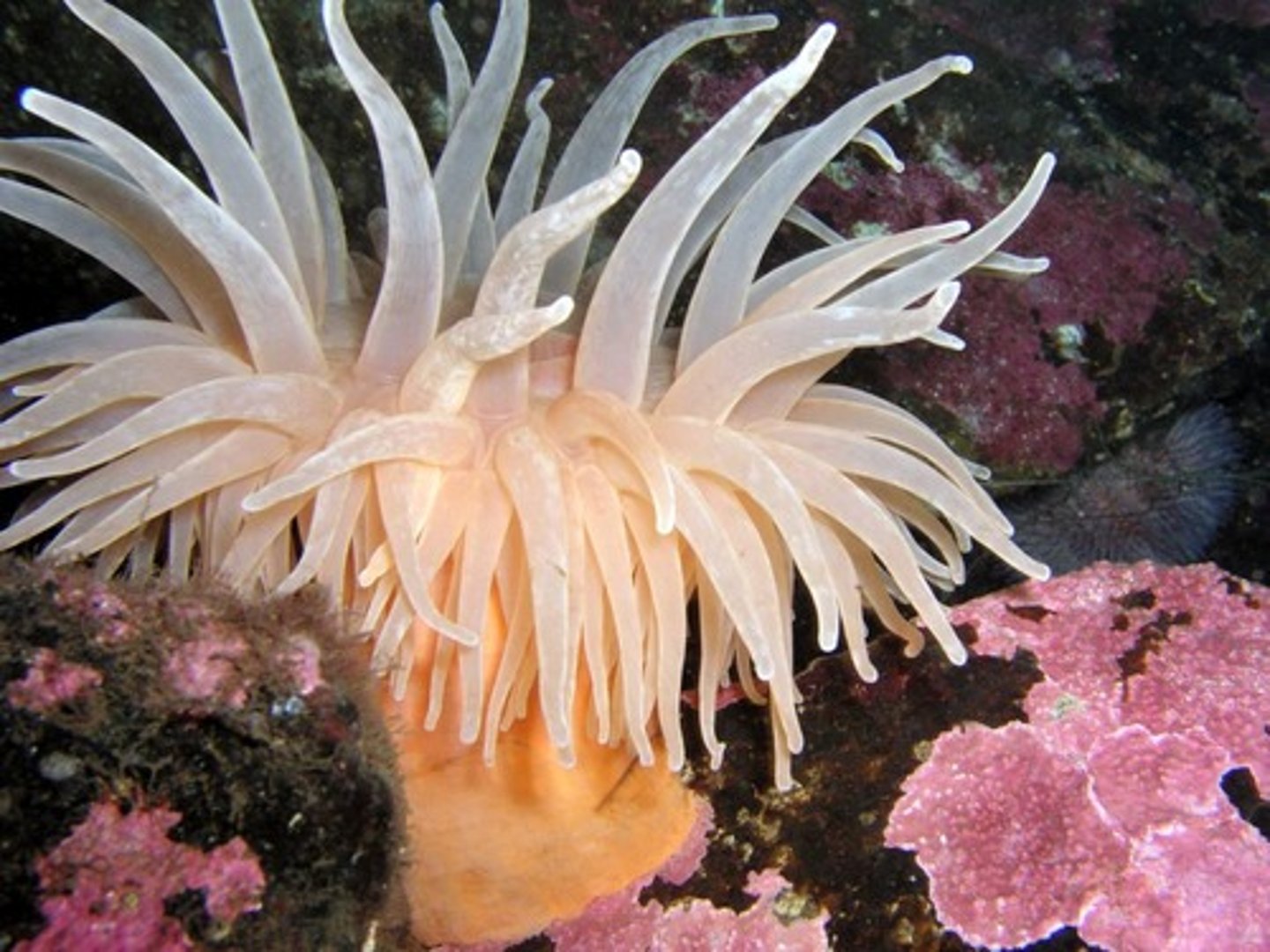
Actinaria corals
anemones, not colonial

Scleractinia corals
stony corals, reef builders

Antipatharia corals
black/thorny corals (little spines on surface)

Stolonifera corals
soft coral, produces CaCO3 skeleton

Alcyonaria (octocorallia) corals
soft coral, polyps all have 8 tentacles
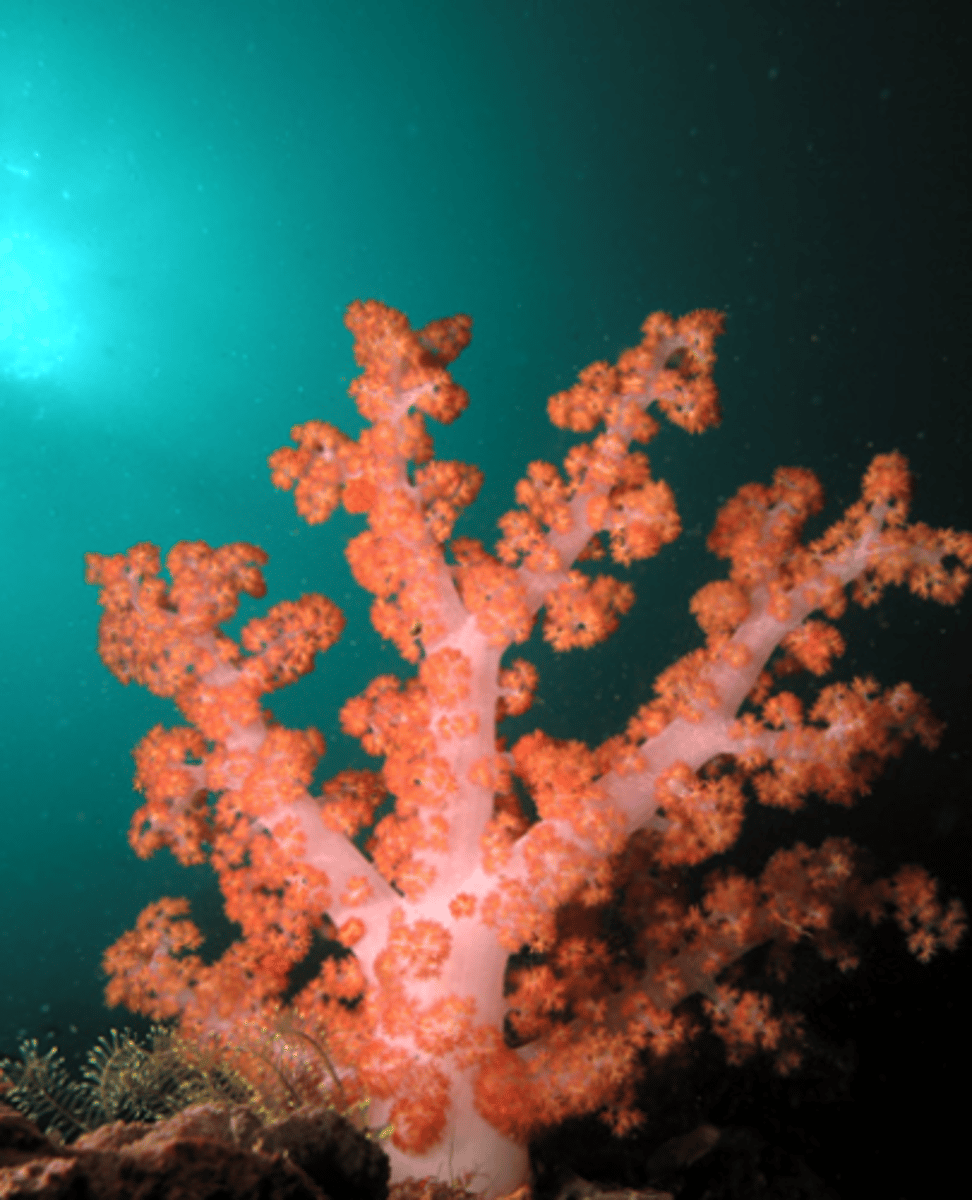
Gorgonacea corals
sea whips, sea fans
Types of shallow reef builders:
- Scleractinan corals
- Coralline algae
- Fire corals
- Calcareous green algae
- Mollusks
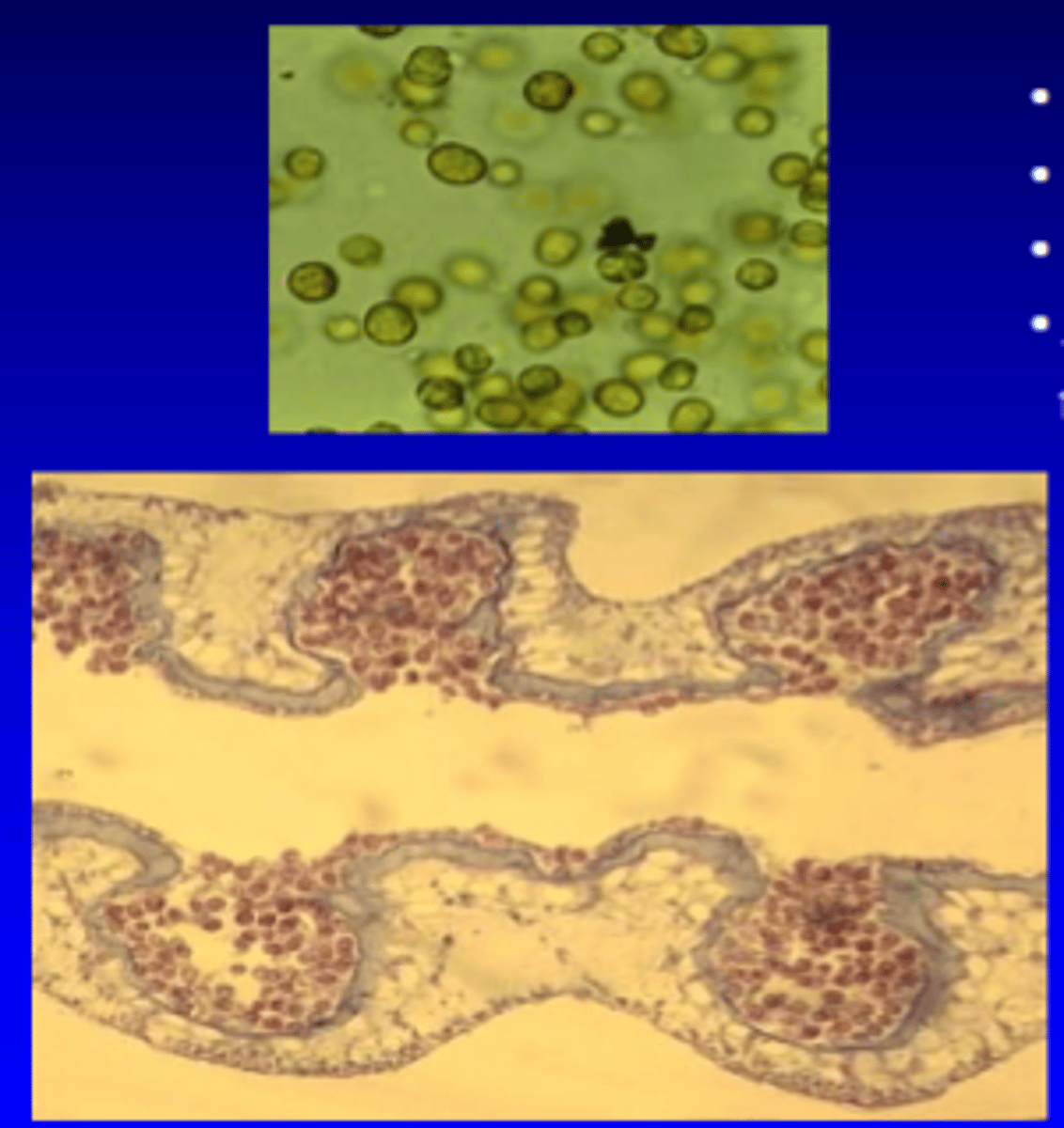
Zooxanthelae Dinoflagellate (Symbiodinium)
- coccoid stage, nonmotile (lack flagella)
- Ch a, c; peridinin pigments
- acquired from environment or maternally transmitted through eggs/planulae larva
Benefits of Xenia
- supply reduced carbon
- increased growth & reproduction
- increased calcification rate
Costs of Xenia
- algal growth regulation & production perialgal vacuoles
- restrictions to photic zone
- defenses against high oxygen tension, high light, UV
- rejections of foreein or excess algae
Benefits of Zooxanthellae
- supply CO2 & nutrients
- maintenance in photic zone
- protection from UV damage by animal tissues
- maintenance of high population density under uniform conditions
- protection from grazers
Costs of Zooxanthellae
- translocation of significant fraction of photosynthetic carbon to animal (85%)
- regulation growth rate, slower in coral than free-living
- expulsion from host
Why are coral reefs restricted to warm, shallow, clean water?
- calcification rates
- photosynthetic algae
- sensitive to pollution
- need firm substrate for attachment
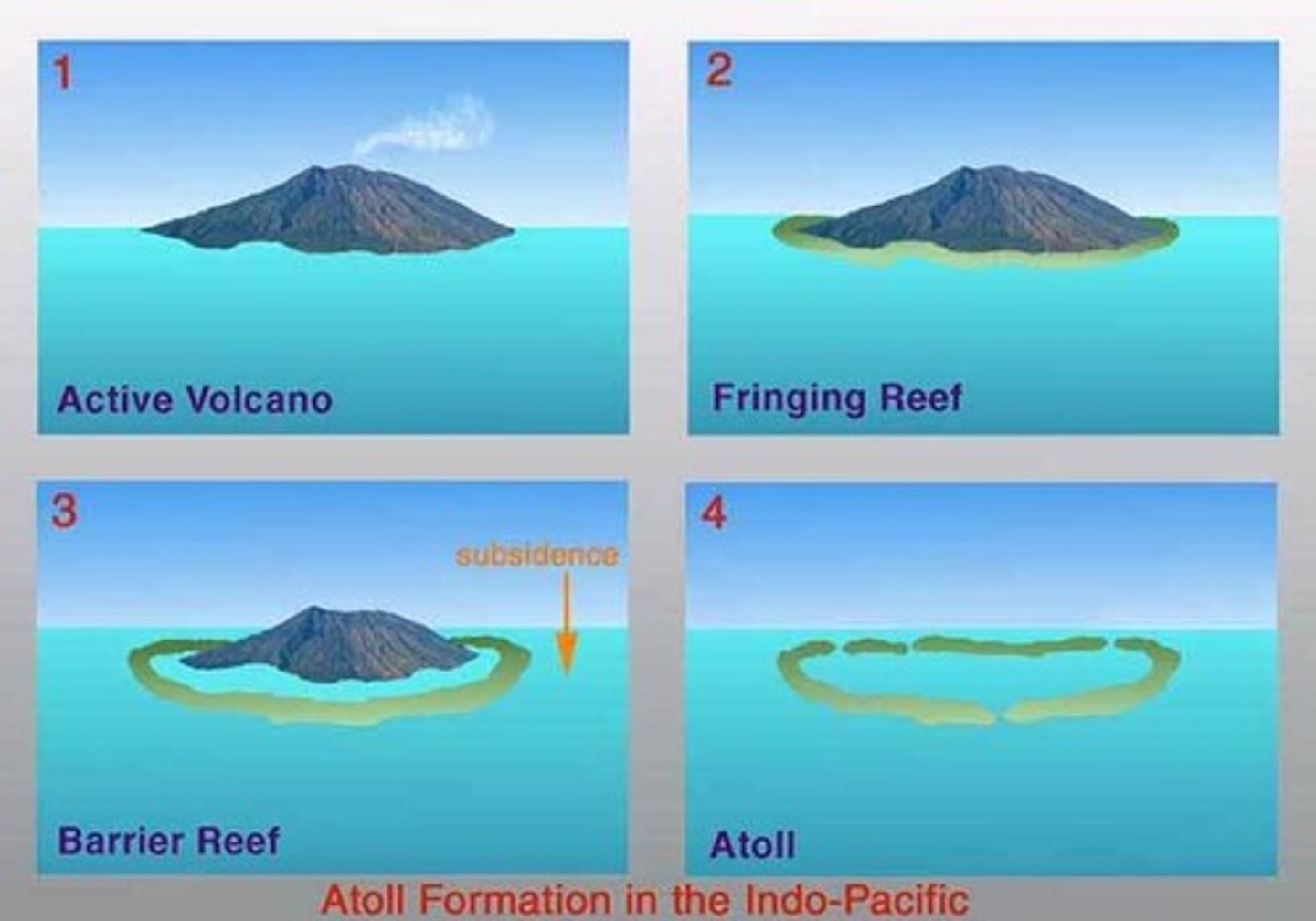
Atoll formation:
- volcanic island
- fringing reef forms around islands
- islands sinks, corals continue to grow up, form barrier reef with lagoon
Parrot fish
- key reef grazers
- strong, hard teeth to scrape algae off corals
- take chunks out of coral to either eat polyps or extract symbiotic algae
- form mucus cocoon at night
Why are beaches in Caribbean so white?
Parrot fish grind up coal skeleton to produce white sandy beaches
Dredges
any device with heavy metal frames & cutting edges that dig & drag into sediment
Sleds/Anchor dredges
dredges with metal plane allow only shallow sampling of sediment or sampling at defined depth
Grabs
samplers that sample only defined area at time
Corers
small tubes that are dropped into sediment (useful for microbiota, sediment samples)
Disadvantages of sampling subtidal soft-bottom benthos:
- cannot be precisely located
- difficult to control spatial distribution
- drift makes exact locations impossible
- small sample sizes
- reduced pressure & increased temp does not keep specimens alive
ROV Jason
- remotely operated vehicle, tethered to ship
- equipped with variety of sensors & cameras
- explored Titanic
ROV Ventana
- operated by Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute
AUV Abe
- Autonomous underwater vehicle (lost at sea)
- AUV's requires no surface input
HOV Alvin (Human Occupied Vehicle)
- deep submergence vehicle is one of the most famous (4000 m)
- explored Titanic
- First to explore hydrothermal vents
HOV Johnson Sea-Link
- operated by Harbor branch
- 1000 m diving depth
- exploring space shuttle challenger wreckage
Muddy sediment
- quiet water environments favor fine-grained organic matter
- deposit feeders dominate
- seasonality based on primary production (Spring diatom bloom)
Sandy sediment
- sandy bottoms have faster currents
- favors suspension feeders, which rely on currents to deliver plankton
Sediment Impacts on Trophic Groups:
- instability of muddy & near-bottom turbidity have negative effect of efficiency, growth, survival (suspension feeders)
- Deposit feeders deteriorate environment more than suspension feeders (trophic amensalism)
- water content high in muddy
Clam Rangia cuneata
- over 2 yrs. clams in sandy sediments had higher condition index than clams in muddy sediments
- in muddy sediments, suspended particles during day were higher
- suspended particles can clog feeding organs of suspension feeders
Microhabitats of burrowers
sea cucumber creates fecal mounds which rise above & attract suspension feeders
How do large, mobile predators impact marine communities by feeding on benthic invertebrates?
Localized destruction of communities and create heterogeneity in sediment topography
Bottom currents
- exert shear stress on sediment
- movement of particles results in variety of structures
- local environments of troughs & crests can be quite different
Suspension feeders are found in
crests