T1:Atomic structure
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What are all substances made of?
Atoms.
What is an atom?
An atom is the smallest part of an element that can exist.
How many different elements are there?
118.
What is an element?
An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom.
What do chemical reactions always involve?
The formation of one or more new substances
A detectable energy change.
What is a compound?
A compound contains two or more different elements chemically combined in fixed proportions.
What is the only way in which compounds can be formed/separated into elements?
A chemical reaction.
What is a molecule?
A molecule is two or more atoms chemically bonded together, which can be of the same or different elements
What is a mixture?
A mixture consists of two or more different elements or compounds not chemically combined together.
Are the chemical properties of each substance in a mixture unchanged?
Yes.
What do you need to do to separate a mixture?
You need to use a physical separation technique.
What are 4 physical processess by which a mixture can be seperated?
Filtration
Crystallisation
Simple distillation
Fractional distillation
Chromatography
mixture notes here
What may lead to a scientific model being changed or replaced?
New experimental evidence.
What did James Dalton think about atoms before the discovery of the electron?
Atoms were thought to be tiny spheres that could not be divided
Which model did the discovery of the electron lead JJ Thompson to create?
The plum pudding model.
What did the plum pudding model suggest?
The atom is a ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded throughout it.
What three conclusions did the results from the Alpha Scattering experiment lead to?
Most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus
The nucleus has a positive charge
Most of the atom is empty space
Which model replaced the Plum Pudding model?
The nuclear model.
How did Neil Bohr adapt the Nuclear model?
By suggesting that electrons orbit the nucleus at specific distances on shells.
What sub-particle was discovered after later experiments?
The proton.
What did James Chadwick discover 20 years after the nucleus became an accepted scientific idea?
The Neutron.
Differences of Plum Pudding vs Nuclear model?
Mostly empty space
The positive charge is in the nucleus
The mass is concentrated in the nucleus
The electrons and the nucleus are separate
What are the relative electrical charges of the sub-particles in atoms?
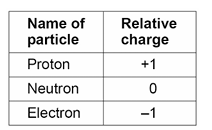
Why do atoms have no overall electrical charge?
The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus.
Therefore, the positive charges on the protons are cancelled out by the negative charges on the electrons
What is the number of protons in an atom of an element called?
Atomic number.
What do all atoms of a particular element have which is the same?
All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons.
What do atoms of different elements have?
Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons.
What is the radius of an atom?
1 x 10-10 m
What is the radius of the nucleus compared to the radius of the atom?
The radius of a nucleus is less than 1/10 000 the radius of an atom.
Where is almost all of the mass of an atom concentrated?
The Nucleus.
What is the relative masses of the 3 sub-atomic particles?
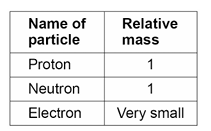
What is the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom called?
The mass number.
What is an isotope of an element?
An isotope of an element has the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons.

What does 23 and 11 represent for Sodium?
23:Mass number
11:Atomic number

This is an ion of fluorine.Calculate the number of neutrons,protons and electrons.

What is the relative atomic mass of an element?
The relative atomic mass of an element is an average value that takes account of the abundance of the isotopes of the element.
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy the first,second and third shell in an atom?
2,8,8
What are the elements in the periodic table arranged in order of?
Atomic number.
Why were elements arranged in order of their atomic number?
So that elements with similair properties were in the same groups.
Why is the table called the periodic table?
Similar properties occur at regular intervals.
What doeelements in the same group have?
The same number of electrons in their outer shell.
developing periodic table
What are elements that react to form positive ions?
metals
What are elements that do not react to form positive ions?
Non-metals.
Where are metals and non-metals found in the periodic table?
Metals are found to the left and towards the bottom of the periodic table.
Non-metals are found towards the right and top of the periodic table
What are 4 properties of a metal?
Strong
shiny
Malleable
good conductors of electricity and heat
high melting/boiling points
What are 5 properties of a non-metal?
Brittle
Dull-looking
don’t coduct electricity
lower melting/boiling points
lower denisty
What are elements in Group 0 of the periodic table called?
The noble gases
Why are the noble gases unreactive and do not easily form molecules?
They have a full outer hsell of eelctrons which makes them stable.
The noble gases all ahve 8 electrons in their outer shell except for which element?
Helium.
Does the boiling points of the noble gases increase or decrease going down the group?
Increase.
Why does the boiling points of the noble gases increase as you go down the group?
The boiling point increases as you go down the group
because there is an increase in the nuber of electrons in each atom
leading to greater intermolecular forces between them that needs to be overcome
What are the elements in group 1 of the periodic table known as?
The alkali metals.
Whhy do the alkali metals have similar properties and are very reactive?
They all have one elctron in their outer shell.
recations with chlorine,oxygen and water
Does the reactivity increase or decrease going down group 1?
Increase.
Why does the reactivity increase going down group 1?
The reactivity increases down group 1 beacuse the