BIO 221 Exam 3
1/400
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MCQS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
401 Terms
Which of the following is associated with antigen presentation by phagocytes, but not by epithelial cells?
MHC2 picks up an antigen from the phagolysosome.
Which of the following is NOT common to all three complement activation pathways?
The adaptive immune response is needed for activation of the pathway.
Bacteria respond to phagocytosis by . . .
producing leukocidins
MHC Class II receptors . . .
Are found only on phagocytes and B-cells
How does interferon fight a viral infection in an infected host?
It is produced in virus-infected cells and induces AVP in neighboring cells.
Choose the option with one PHAGOCYTE antigen presenting cell (APC) and one LYMPHOCYTE APC.
Macrophages and B cells
Which of the following is correct regarding the body's interferon defense system?
Interferon induces the production of antiviral proteins in adjacent cells.
The three complement activation systems share many common features, but there are also differences. Which of the following is NOT common to all three complement pathways?
Properdin is required to stabilize the C5 convertasein the alternative pathway only.
Why does a bacterium produce antioxidants?
To survive the harsh environment inside the phagolysosome.
Some bacteria live and divide inside the phagolysosome. What will be a symptom associated with a chronic infection of a patient with such a bacterium?
Clumps of infected macrophages and THcells will be seen in the patient's tissues.
Which of the following is associated with antigen presentation by dendritic cells, but not by epithelial cells?
MHC2 picks up an antigen from the phagolysosome
Which of the following is NOT a consequence of activating the complement cascade on the surface of a bacterium?
Peptide C3a induces B cells to produce antibodies that attach to the bacterium.
One of the complement activation pathways is called the “alternate” pathway. What is different between this pathway and the “classical” pathway?
It can be activated even before the humoral immune response is active.
Which of the following is required for granuloma formation?
persistent antigen presence inside macrophages
Which of the following could be considered to be a phagocyte?
antigen presenting cell
We said that MHC2 is mainly for presentation of exogenous antigens, whereas MHC1 is mainly for presentation of endogenous antigens. Why is this so?
MHC2passes through the endocytic vesicle on its way to the cell surface.
What is the purpose for our immune system to opsonize bacterial cells?
It adds surface features to the bacterium that makes it easier for our cells to recognize.
Granuloma formation involves all of the following EXCEPT . . .
antibodies
Which of the following statements is true of MHC-II, but not of MHC-I?
It mainly displays antigens from the phagolysosome.
How is interferon produced during an infection?
Asecond-messenger pathway induces it when viral RNA binds to an RLR receptor.
Which of the following is true of infections that are characterized by granuloma formation?
Bacteria prevent lysosomes in infected macrophages from fusing with phagosomes.
What is the function of a Toll-like receptor?
It allows macrophages and dendritic cells to bind specifically to pathogens.
What molecule is typically recognized by the immune system to signal that a cell has been infected by a virus?
Double stranded RNA
How does interferon (IFN) function during a viral infection?
IFN is an inducer that turns on genes for antiviral proteins in neighboring cells.
Some bacteria have evolved the ability to prevent lysosome fusion to a phagosome. These bacteria can therefore avoid . . .
the oxidative burst
What is a leukocidin?
a toxin produced by bacteria to kill macrophages
Which of the following is true about antigen presentation on MHC class I?
It requires protein digestion by the proteasome.
Antigens displayed on MHC class II come from . . .
the phagolysosome of the cell that displays them
What is the role of antibodies in the innate immune response?
They can activate the synthesis of antimicrobial peptides.
Which of the following correctly distinguishes MHC-I from MHC-II?
MHC-I can display self antigens on the surface of uninfected cells.
Which of the following is true regarding interferon α and β?
They are released from a cell to bind to receptors on nearby cells.
There are three complement activation pathways. How do these pathways differ?
The way C3 and C5 proteins are hydrolyzed
Two things happen once a pathogen binds specifically to a dendritic cell (DC). They are . .
The pathogen is engulfed, and the DC produces co-stimulatory molecules.
Bacteria that can survive inside the phagolysosome can do so because . . .
they produce antioxidants
Which of the following is a difference between endogenous and exogenous antigen presentation?
Endogenous antigens are processed by the proteasome, exogenous by the phagolysosome
How does interferon prevent viral replication?
By signaling cells to be ready to apoptose if a virus invades
Which complement molecule is correctly matched with its function?
C5a– chemokine signaling molecule
Which of the following are produced inside a phagolysosome?
Peroxides and Antimicrobial complement peptides
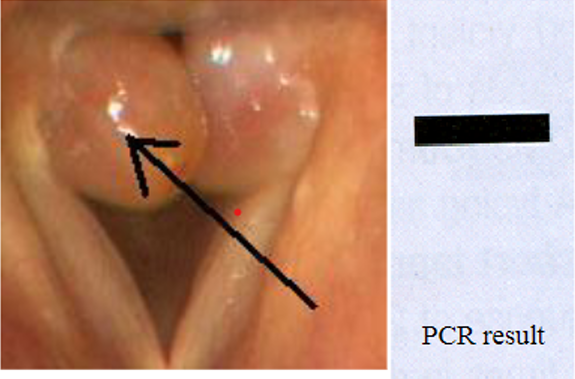
A patient comes to your clinic with the structures shown below on his vocal cords. You take a biopsy of the structure indicated by the arrow. PCR primers are prepared complementary to the 3' ends of a bacterial gene, and a reaction is performed on the biopsied tissue. The results are shown after electrophoresis. What is the best interpretation of this data?
The patient has a granuloma, and may need long term antibiotics to treat it.
Which complement-associated term is NOT correctly matched with its function?
Lectin– digests the C5 protein
In general, antibodies can defend against pathogens in any of six ways. However, IgM and IgA can only use a few of these methods. Which of the following could be used by IgM or IgA to inactivate pathogens?
Agglutination
What parts of antibodies have great variability due to somatic recombination?
the Fab part only
The antibody type that is secreted by plasma cells one day after primary infection would most likely be:
IgM
Some antigens (T-independent) can activate B cells without the involvement of cellular immunity. Which of the following would still occur in response to these antigens?
B cell receptors would bind to the antigen
A Bcell recognizes an antigen, but there is no THcell that also recognizes the antigen. What will happen?
The B cell will become anergic.
The process that ensures no circulating B cells recognize self antigens is called:
clonal deletion
How do antibodies actually kill foreign bacteria?
They opsonize the bacterium, making it easier to phagocytize.
What is the major difference between IgG and IgA?
The Fc region of the IgA heavy chain allows dimerization.
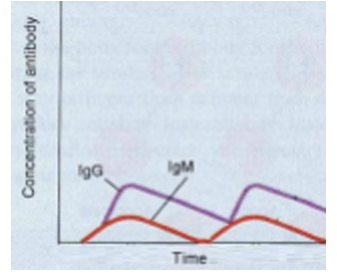
A patient is infected with Pasteurella multocida from a dog bite. Two weeks later, the same patient is bitten and infected with P. multocida again. The antibody titers were determined after the two bites, and found to be as shown. What best explains this result?
This patient cannot develop memory B cells.
Which antibody class can cross the placenta to protect the fetus?
IgG
What parts of antibodies have great variability due to somatic recombination?
the Fab part only
What causes a B cell to become anergic?
Its MHC2 receptors present an antigen that is not recognized by a TH cell.
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) . . .
is the first antibody produced in response to an infection
The process responsible for antibody diversity . . .
is a genetic recombination that can only happen once in each B cell
How are TH cells involved in the humoral immune response?
Cytokines from THcells cause B cells to turn into antibody-producing plasma cells
Why are only a very small number of B cells activated in response to an infection?
Only a few B cells bind to both the specific antigen and a TH cell
What is the most correct statement about the selection process B cells must undergo before they are released to the blood?
Recognizing any antigens in bone marrow causes B cells to apoptose.
Which of the following can antibodies do to “fight” against both bacteria and viruses?
neutralize receptor binding proteins
The antibody type shown at right has what special feature?
It is the major antibody found in mucus membranes.
What cellular process allows billions of different antibody Fab fragments to be produced from only a few hundred genes?
Somatic Recombination
Antibodies can "fight" bacterial infections in all of the following ways EXCEPT . . .
activate TH cells to secrete cytokines

What can you conclude if you find the structure at the right in a patient?
The patient has been recently infected
What is the role of T cells in the antibody response?
TH cells stimulate B cell division and differentiation.
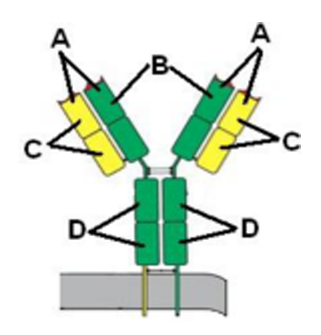
Which parts of the antibody shown at the right undergo somatic recombination?
all 4 parts labeled 'A'

The antibody shown below can help your body "fight" against pathogens in all of the following ways EXCEPT . . .
activation of ADCC
How are T cells involved in antibody production?
Cytokines from TH cells cause proliferation and differentiation of B cells into plasma cells.
When does a B cell undergo the genetic switch to begin producing IgG instead of IgM?
several days after the initial infection with a pathogen
What happens during the process called "clonal deletion"?
B cells apoptose if their receptors recognize proteins present in bone marrow
Which of the following statements about antibody types is TRUE?
The most effective antibody for agglutinating antigens is IgM.
Which of the following steps occurs during the immune response to BOTH polysaccharide vaccines AND protein-conjugate vaccines?
B cell receptors bind to polysaccharide components of vaccine antigens
Which of the following B cells would become anergic?
A B-cell that is displaying an antigen to which no T-cell has bound
What is meant by the abbreviation ADCC?
Tagging a cell so that NK cells bind to and destroy it
Which of the following antibody types is correctly matched with a feature of that antibody?
IgM– only Ig produced in response to T-independent antigens
Why does a second exposure to the same pathogen usually result in a much stronger immune response against it?
When a second infection occurs, B memory cells produce IgG without class switching.
What happens if you are exposed to an antigen but none of your circulating B cells has receptors that recognize it?
New B cells can be released from your bone marrow that may recognize it, even though no circulating B cells do.
Which of the following is one way our immune system avoids producing antibodies that recognize self antigens?
B cells become anergic if they are not also stimulated by TH cells.
You are working in pharmaceutical research, and you want to make a vaccine against a bacterial polysaccharide slime layer. You know that you will need to make a conjugated vaccine. Which of the following is true about such a vaccine?
The conjugated protein may be the antigen that is displayed on a B cell's MHC-II.
How can IgG prevent a viral infection?
It can neutralize viral binding to host receptors.
In a T-dependent B cell response . . .
a B cell must endocytose an antigen and display it on MHC-II
Which of the following is correctly associated with a B cell that has become anergic?
The B cell displays an antigen that no T cell recognizes.
How many type(s) of antibody is produced from a single B cell?
1
Can B-cells produce antibodies without TH cell help, and what type of antibody is predominantly produced in this scenario?
Yes, a small population of B cells can produce IgM antibodies without TH cell help.
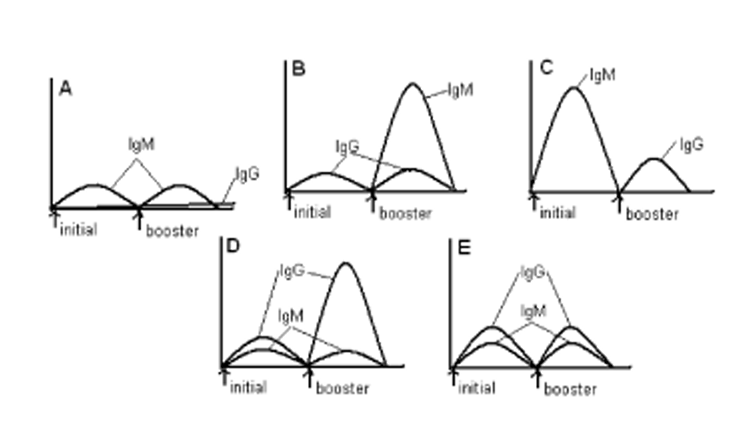
In DiGeorge's Syndrome, the patient is born without a thymus. Such a patient obviously lacks some of his immune system. Which of the following best represents his antibody titer after initial and booster vaccination?
A. No thymus = no T cells
What is the main function of TC cells in the immune system?
to release perforin and granzymes
What happens when an effector TC cell binds to an antigen on an epithelial cell’s MHC1?
The TC cell kills the epithelial cell.
Which of the following does NOT happen once TH cells have become activated?
The TH cells produce MHC2 on their surface
Immune tolerance in T cells involves positive selection. What does that mean?
T cells are only released if their TCR recognizes thymus cells’ MHC1.
What is the difference between TH and TC cells?
TH cells secrete cytokines, TC cells secrete perforin.
If a TH cell binds to an MHC on “cell A” that is presenting an antigen, but binds to nothing else, what happens?
The body assumes this is a mistake; the TH cell becomes unresponsive.
Effector TH cells can do all of the following EXCEPT . . .
Phagocytize nearby bacteria
What is the most correct statement about the selection process T cells must undergo before they are released to the blood?
TCRs must recognize self MHCs, but must not recognize antigens on the MHCs.
What type of cells do NK cells kill?
any cells without MHC1 (or its equivalent) on their surface
What is the role of the B7 protein in the immune response?
It is produced by infected macrophages to help stimulate T cells.
A TH cell is secreting interleukin-2 (IL-2). This means that . . .
nearby TC cells will become activated once they bind to an antigen-MHC1 complex.
How do activated macrophages differ from non-activated (naïve) macrophages?
They contain more lysosomes.
What is the role of NK cells in the immune response?
They participate in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
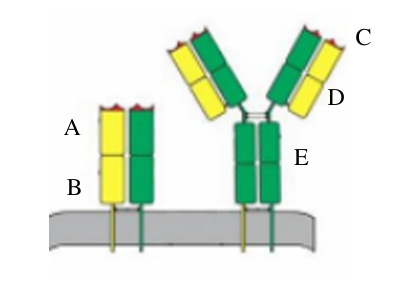
Which of the letters in the diagram at the right refers to the variable region of a T cell receptor (TCR)?
A
What is a major difference between TH and TC cells?
TC can bind to almost any infected cell; TH only bind infected antigen presenting cells
Which of the following correctly refers to the second signal that is required for T cell activation?
It is only produced when a pathogen is recognized by the immune system.
Upon receipt of cytokine signals from effector TH cells, macrophages . . .
produce a more potent oxidative burst that includes nitric oxide.