OSI MODEL
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
OSI model
Open System Interconnection different vendors networks could become compatible and work together by creating interoperable network devices and software in the form of protocols or standards.
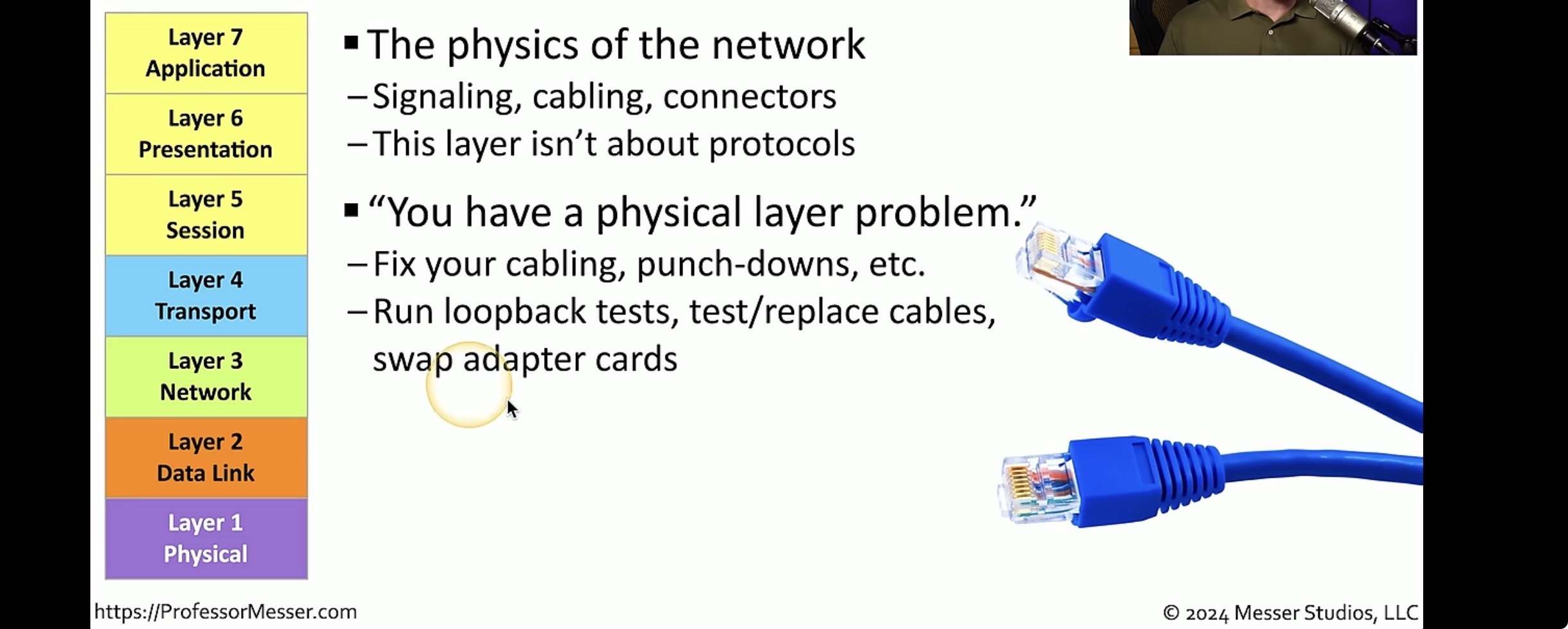
Physical Layer
Data terminal equipment DTE is the attached device. Data communication equipment is located at the customer specifying the layout of the transmission media. And a physical layer describes the way cabling is physically laid specifies the layout of the transmission media.
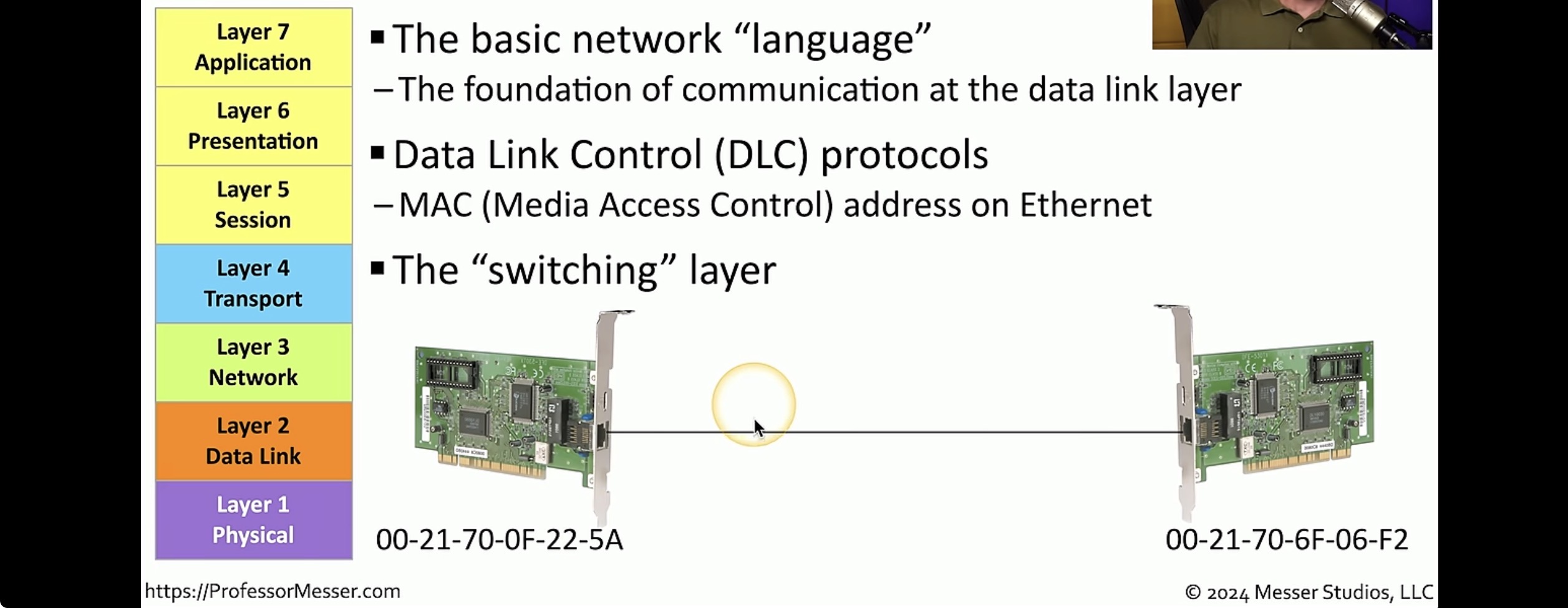
Data Link Layer
Media access control defines how packets are placed on the media.
logical link control is responsible for identifying network layer protocols and then encapsulating them an LLC header to find out where the packet is destined. The Data Link layer formats the message into pieces, each called a data frame, and adds a customized header containing the destination and source hardware addresses. The Data Link layer provides the physical transmission of the data and handles error notification, network topology, and flow control.
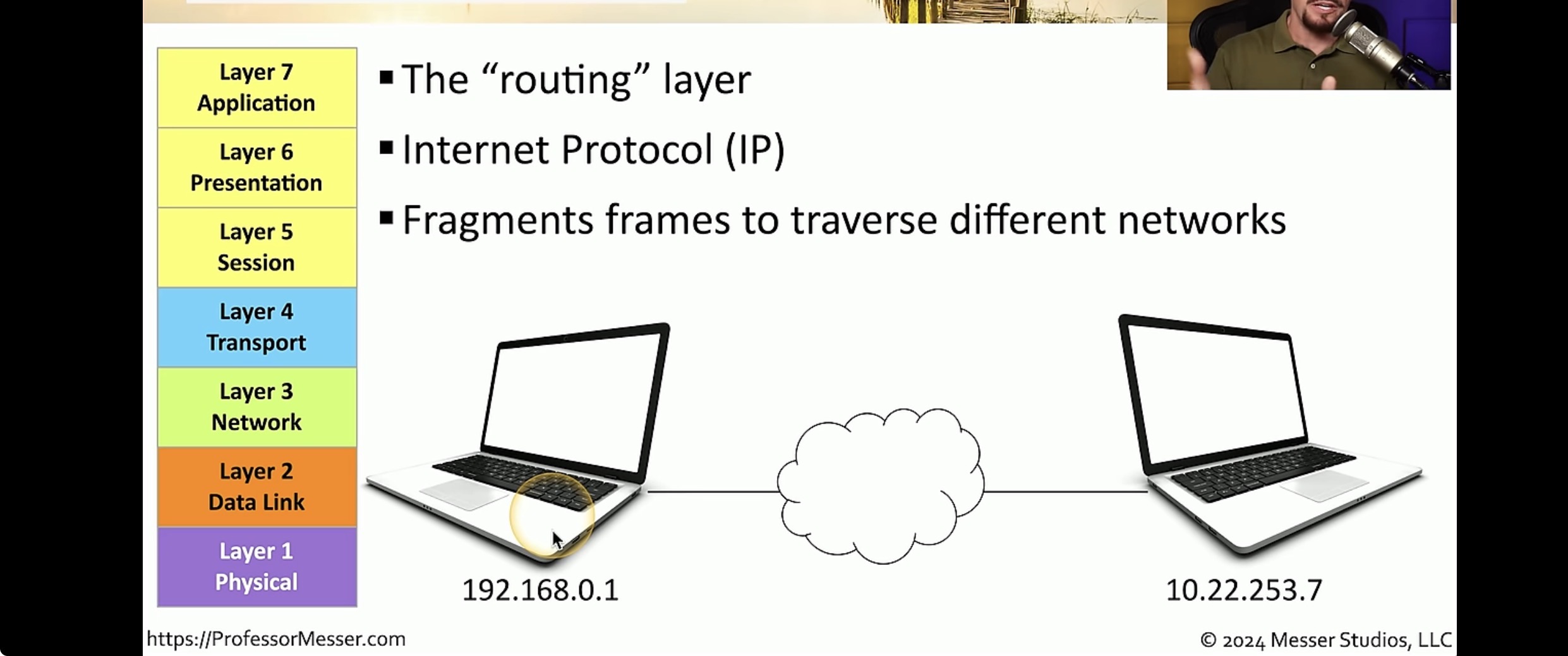
Network layer
Manages logical device, device addressing, tracks the location of devices on the network and determines the best way to move data data packets used to transport user data through the Internet network route update packets used to update neighboring routers about the networks connected to all routers within the internetwork.
Transport
Segmenting and resembling data into a data stream
Session layer
Responsible for setting up managing and then tearing down session between presentation layer entries

Presentation layer
It represents data to the application layer and responsible for data translation and code formatting
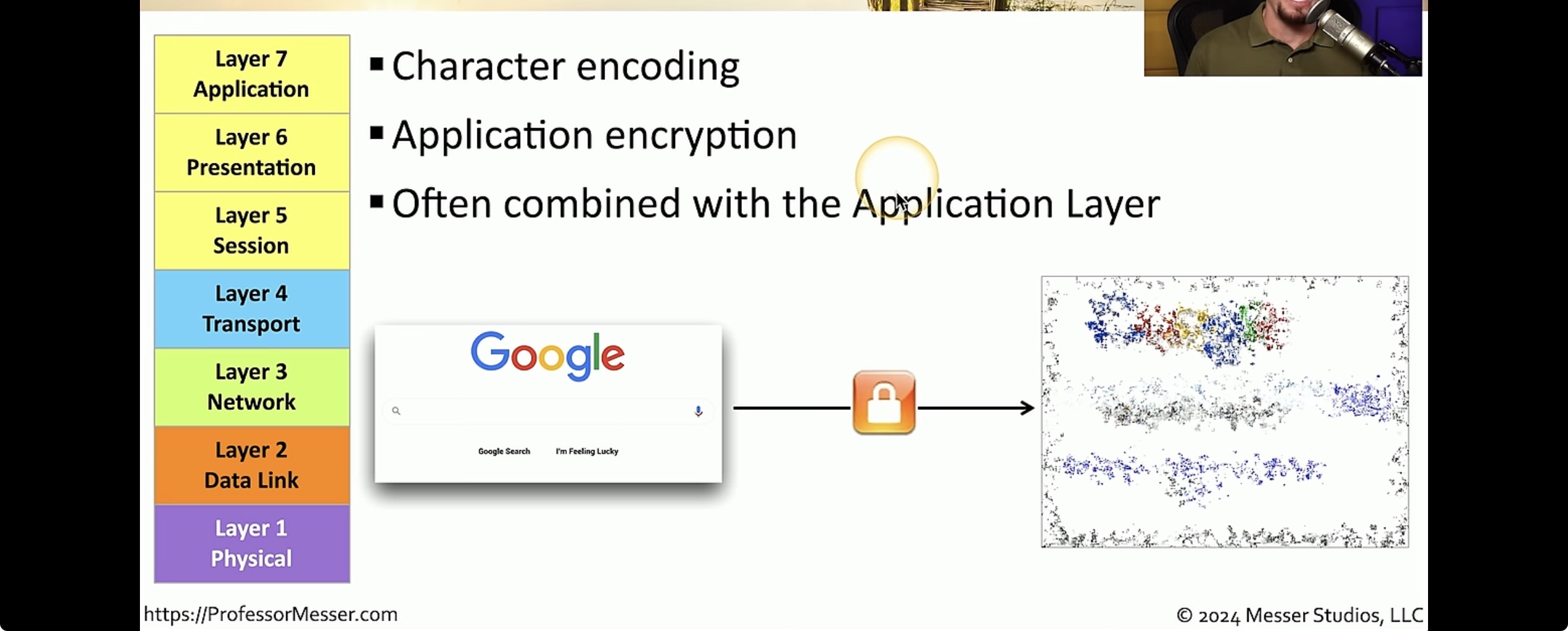
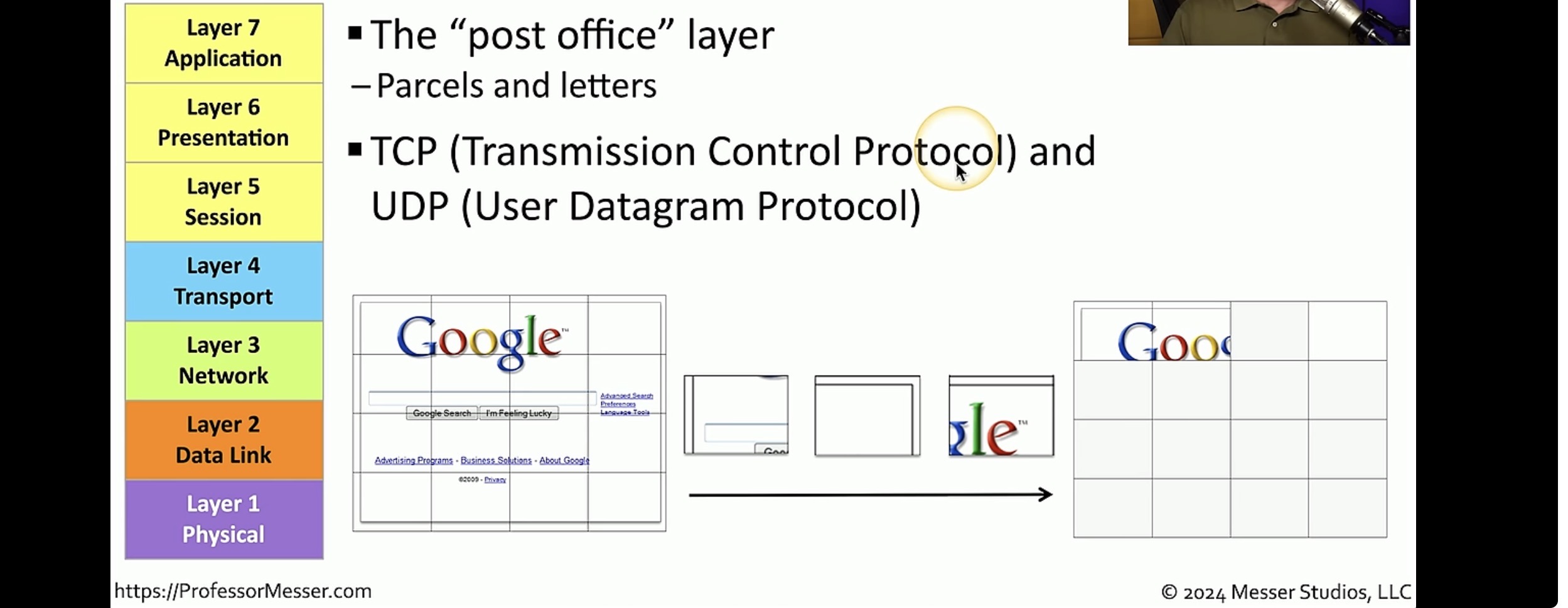
Application layer
Marks the spot where users actually communicate or interact with a computer the application layer acts as an interface by providing ways for the application to send information down through the protocol stacks. it’s responsible for identifying and establishing availability of the intended communication partner and determines whether sufficient resource resources for requested communication exists.
OSI

Function of Upper 3 Layer and lower

Three-way handshake


Flow control
1. The segments delivered are acknowledged back to the sender upon their reception,
Any segments not acknowledged are retransmitted.
Segments are sequenced back into their proper order upon arrival at their destination.
A manageable data flow is maintained in order to avoid congestion, overloading, and data loss.

Windowing
The quantity of data segments (measured in bytes) that the transmitting machine is allowed to send without receiving an acknowledgment is represented by something

Acknowledgement
technique that requires a receiving machine to communicate with the transmitting source by sending an acknowledgment message back to the sender when it receives data
Routers

DL Layer MAC & LLC

Data Encapsulation Method
