Exam 1: Skin, Hair, Nails
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
What is the purpose of the skin, hair, and nails? (10)
protection against penetration
perception
fluid balance
temp. regulation
identification
communication
wound repair
absorption
excretion
vitamin D production
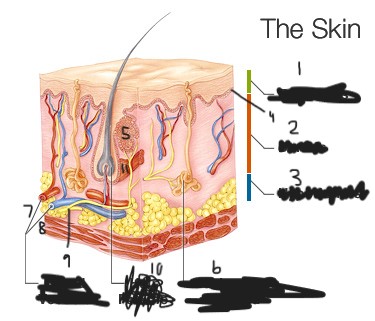
Identify all 11 structures.
epidermis
dermis
subcutaneous layer
sensory receptors
sebaceous gland
sweat gland
artery
vein
nerve
hair follicle
arrector pili muscle
What is the difference between sebaceous glands and sweat glands (and 2 types of sweat glands)?
sebaceous glands: secrete sebum (oily) for lubrication through hair follicles
sweat glands: secrete sweat for temp. regulation (eccrine: sweat; apocrine: thick milk)
Identify whether this data is subjective (S) or objective (O).
edema
skin disease history
mobility/turgor
pigmentation changes
mole changes
moisture
shape/contour of nails
xerosis
seborrhea
temperature
excessive bruising
nail consistency
rash
vascularity/bruising
lesions
nail color
medications
lesions of scalp
skin color
alopecia
nail changes
environmental/occupational hazards
self-care
texture
thickness
capillary refill
pruritus
O
S
O
S
S
O
O
S
S
O
S
O
S
S
O
O
S
O
O
S
S
S
S
O
O
O
S
Pallor
pale
Keratin
tough, fibrous protein that forms new skin cells
Melanin
pigment that gives brown tones to skin/hair; protects skin from UV rays
T or F: melanocytes are in interspersed along the epidermis.
T
What is the difference between the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous layer?
e: outer, highly differentiated, stratified, inner basal cell layer, avascular
d: inner, supportive, collagen (CT), elasticity, vascular, nerves, sensory receptors, lymphatics, hair, glands
s: inner-most; adipose (fat) tissue, energy storage, temp. control, protection, mobility (loose)
What is hair made up of?
types? (2)
What are the parts?
keratin
types:
vellus: fine, covers body (not palms/soles)
terminal: dark, thick that grows on scalp, eyebrows, axillae, pubic area, face/chest in M
parts:
shaft: visible above skin
root: bellow surface
bulb matrix: new cells produced in expanded area of root
Erythema
red
Cyanosis
blue
Jaundice
yellow
Uremia
green/frosty
When assessing skin color, you should include these 5 things…
general pigmentation
freckles
moles
birthmarks
widespread change
Why do you use back of hands to palpate skin for temperature?
thinner skin on dorsa of hand
Palpate
examine by touch
Skin should be warm and equal bilaterally because warmth suggests…
normal circulatory status
Hypothermia
body heat is lost faster than produced, using up body’s stored energy and lowering body’s temp.
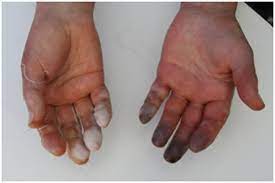
This is an example of what condition?
hypothermia
Hyperthermia
abnormally high body temp.
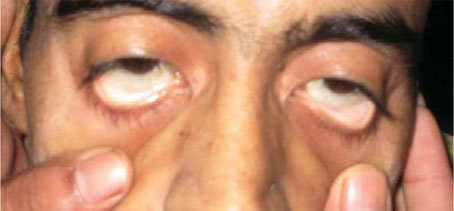
This color is an example of…
pallor
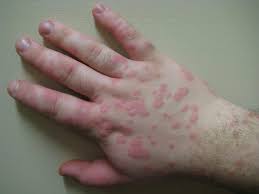
This color is an example of…
erythema

This color is an example of…
cyanosis
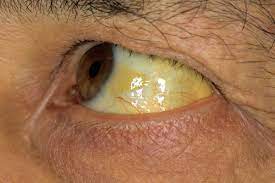
This color is an example of…
jaundice
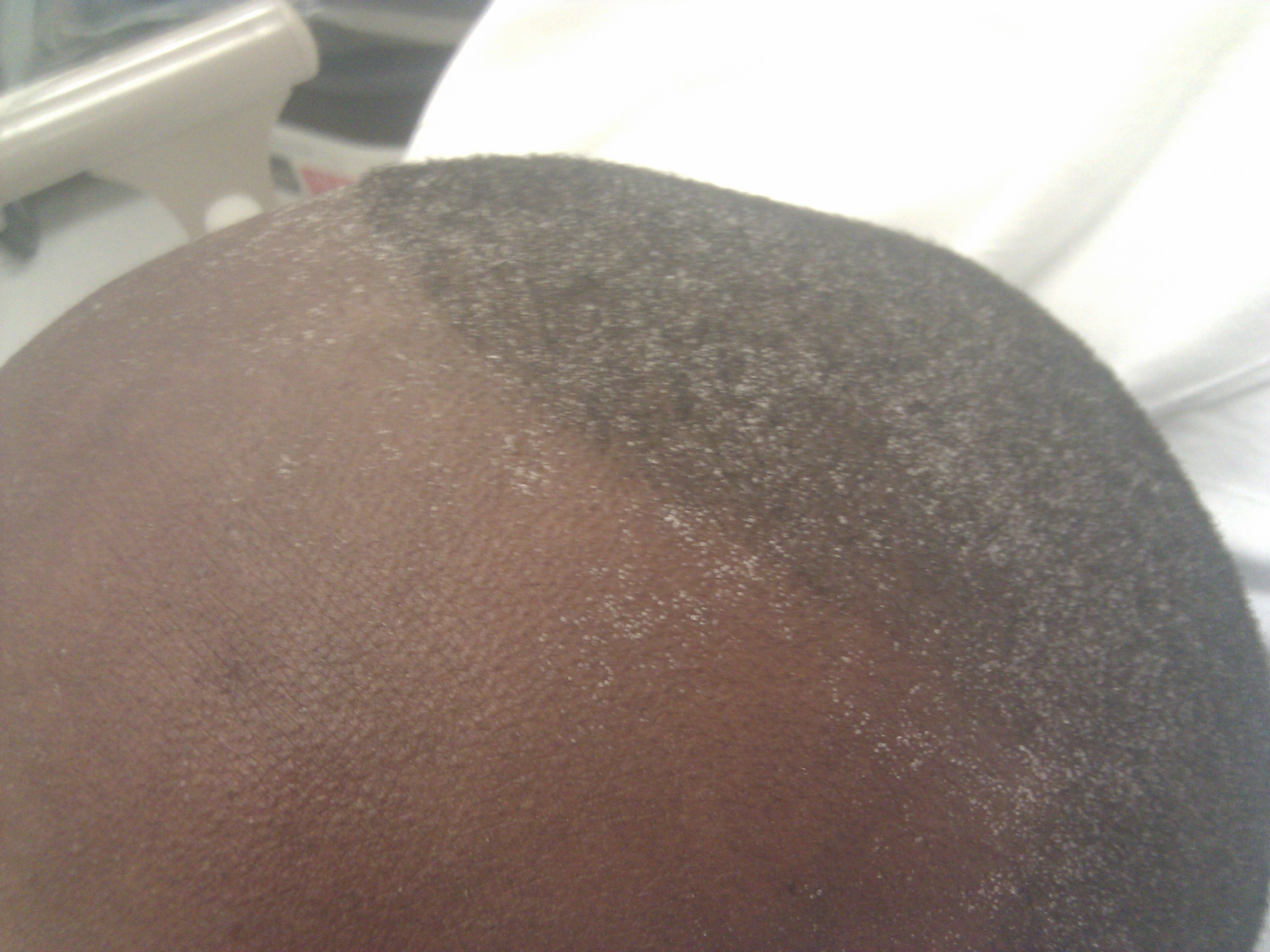
This color is an example of…
uremia
Xerosis
excessive dryness of skin
Seborrhea
excessive oil of skin
Alopecia
hair loss
Pruritus
itchiness
What are 5 external factors of skin color?
emotions
environment
disease processes
physical
nutritional status
Diaphoresis
sweating
The nurse is assessing a patient who has been admitted for liver failure. What finding would the nurse expect?
Cyanosis
Flushing
Rubor
Jaundice
4
If there is a presence of edema, document on a scale of to ____
0; 4+
What is normal mobility? Turgor?
mobile; <1 second
Edema
accumulation of fluid in interstitial spaces (extracellular), causing swelling
Compare pitting and dependent edema.
pitting: when you depress on swelled skin, it leaves an indentation that remains
dependent: specific to parts that gravity pulls the blood down (extremities)
When is edema considered normal?
pregnancy
The production of ______ impacts hair color.
melanin
How do you identify lesions of the scalp?
divide hair into sections
Normal nails are angled at _____ degrees. Curved nails are angled at ____ degrees. Clubbing of the nails occurs when the profile angle is ___ degrees.
160; <160; 180
Capillary refill
when you depress edge of nail and then release
T or F: people with darker skin have a higher amount of melanocytes.
F
What produces melanin?
melanocytes
What 4 things can affect melanin production?
sun exposure
keratin
underlying vascular bed
genetics
Lesion
area of skin that has suffered damage
Name 2 medications that affect the skin.
Accutane
birth control
What is the first step of assessment?
skin inspection
Mobility
pinching (tempting) skin
Turgor
how fast skin goes down once let it out of the pinch
If you are _____________, turgor is slower.
dehydrated
Which part of the nail do you look at when determining color?
nail bed
What is the symbol for with? without?
c with line over; s with line over
What 7 things do you document for lesions of the skin?
color
quantity
elevation (macular/piacular)
pattern/shape (grouped/scattered; distinctness)
size (cm)
location and distribution
exudate (color; odor)
Exudate
fluid that leaks out; drainage
Macular
flat
Piacular
raised
What are the 9 shapes/configurations of lesions?
annular
confluent
discrete
grouped
gyrate
target
linear
polycyclic
zosteriform
Annular
circular
Linear
scratch, streak, line, stripe
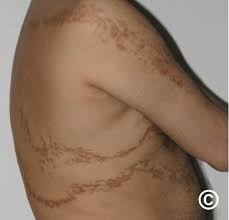
What lesion shape/configuration is this? What condition can cause this?
linear; Blaschko’s lines
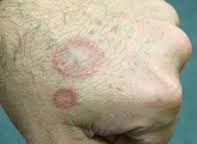
What lesion shape/configuration is this? What condition can cause this?
annular; tinea corporis: ringworm
Confluent
run/grown together
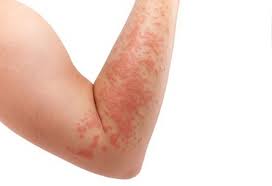
What lesion shape/configuration is this? What condition can cause this?
confluent; urticaria: hives
Discrete
separate, individual
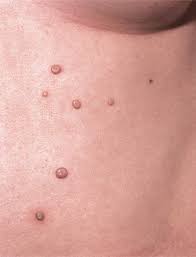
What lesion shape/configuration is this? What condition can cause this?
discrete; acne
Grouped
clustered together
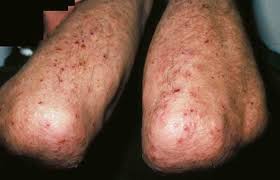
What lesion shape/configuration is this? What condition can cause this?
grouped; dermatitis
Gyrate
twisted, coiled spiral, snakelike
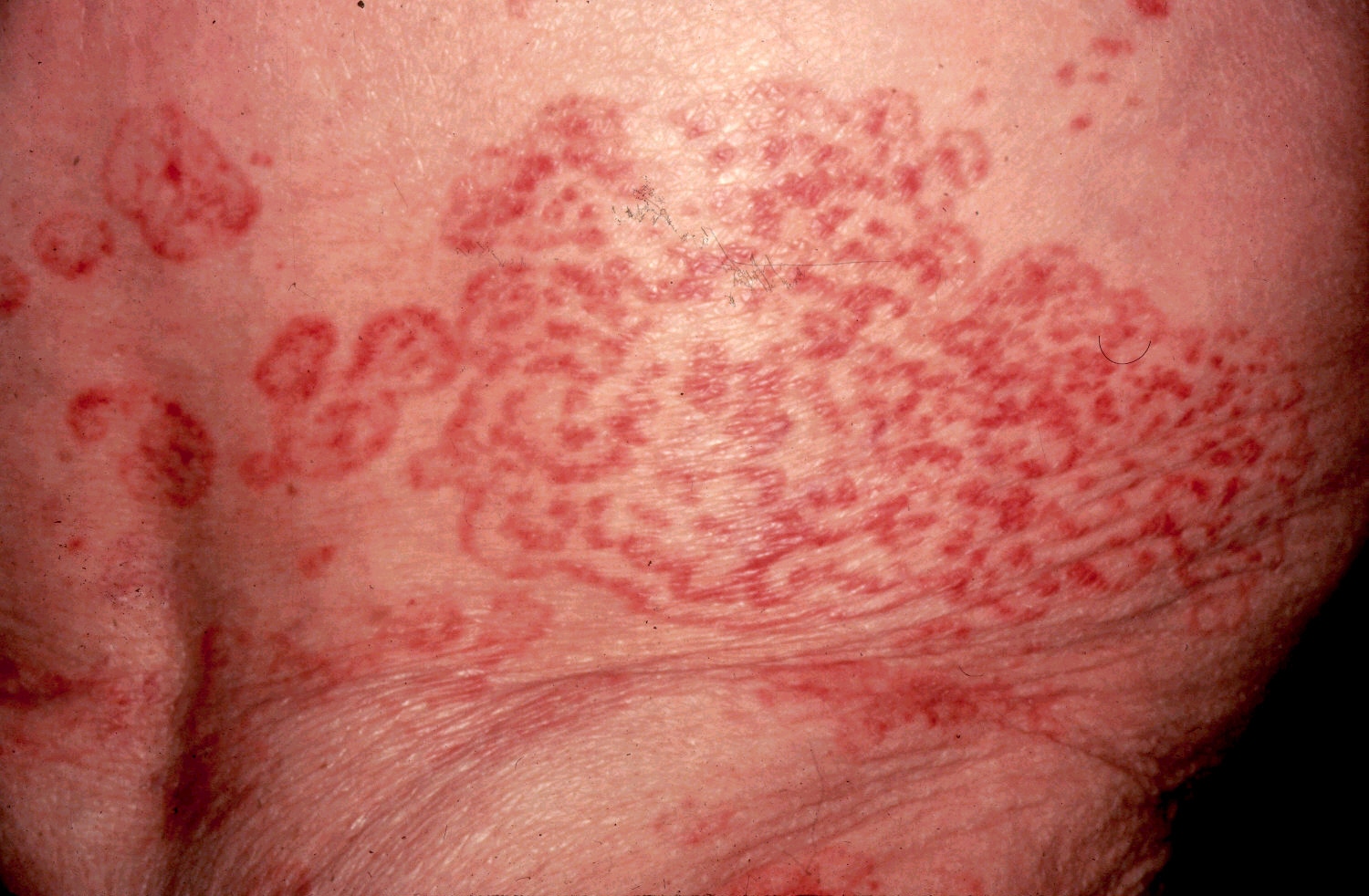
What lesion shape/configuration is this? What condition can cause this?
gyrate; erythema gyratum repens
Target
iris/bullseye/concentric rings
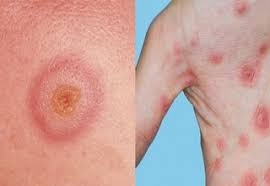
What lesion shape/configuration is this? What condition can cause this?
target; erythema multiforme
Polycyclic
annular lesions that link together like a Venn-diagram
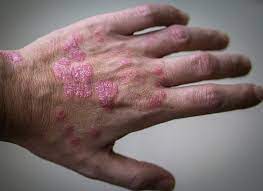
What lesion shape/configuration is this? What condition can cause this?
polycyclic; psoriasis
zosteriform
linear arrangement along a nerve
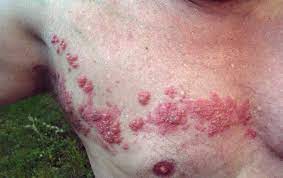
What lesion shape/configuration is this? What condition can cause this?
zosteriform; herpes zoster: shingles
What are the 12 primary lesion types?
papules
patches
plaques
nodules
wheals
urticaria
vesicles
cysts
bullas
pustules
macules
tumors
Tumors
benign/malignant; deep in dermis; > few cm.
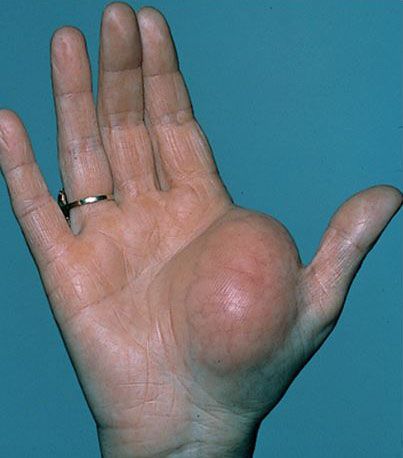
What type of skin lesion is this? Give an example.
tumors; lipoma
Bullas
unilocular (1 cavity); superficial; thin walls (easily rupture); > 1 cm
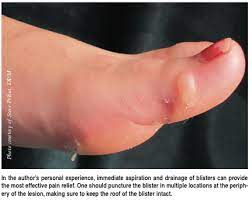
What type of skin lesion is this? Give an example.
bullas; friction blister
Urticaria
hives: wheals unite to form extensive reaction, itching
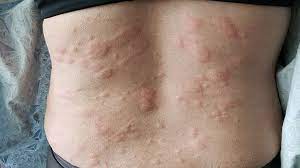
What type of skin lesion is this? Give an example
urticaria; hives
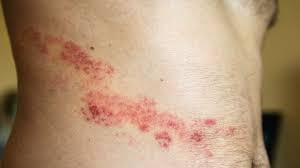
What type of skin lesion is this? Give an example.
vesicle; herpes zoster (shingles)
Vesicles
elevated, fluid, <1 cm
Papules
superficial thickening of epidermis <1 cm, so elevated
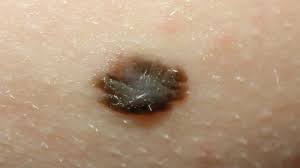
What type of skin lesion is this? Give an example.
papule; nevus: mole
Macules
color change <1 cm

What type of skin lesion is this? Give an example.
macule; freckles
Patches
macules >1 cm

What type of skin lesion is this? Give an example.
patch; vitiligo
Plaque
united papules >1 cm (plateau)
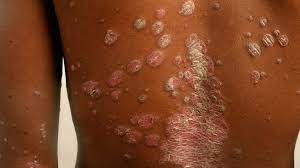
What type of skin lesion is this? Give an example.
plaque; psoriasis
Nodule
solid, elevated, hard/soft; > 1cm
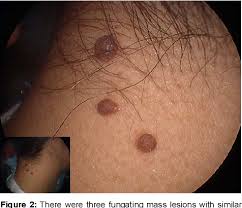
What type of skin lesion is this? Give an example.
nodule; intradermal nevi
Wheal
superficial, raised, short-term, erythematous, irregular shape from edema
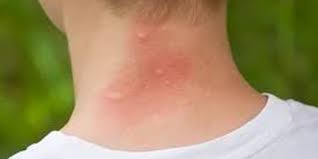
What type of skin lesion is this? Give an example.
wheal; mosquito bite
Cysts
encapsulated fluid-filled balloon in dermis/subcutaneous layer, so elevated skin
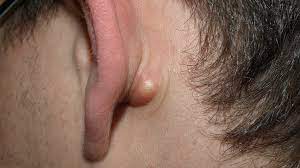
What type of skin lesion is this? Give an example.
cyst; sebaceous cyst
Pustules
elevated and filled with pus