(Unit 3) Gestalt Principles + Binocular/Monocular Cues
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Gestalt
Organized visual sensations into a whole that makes sense
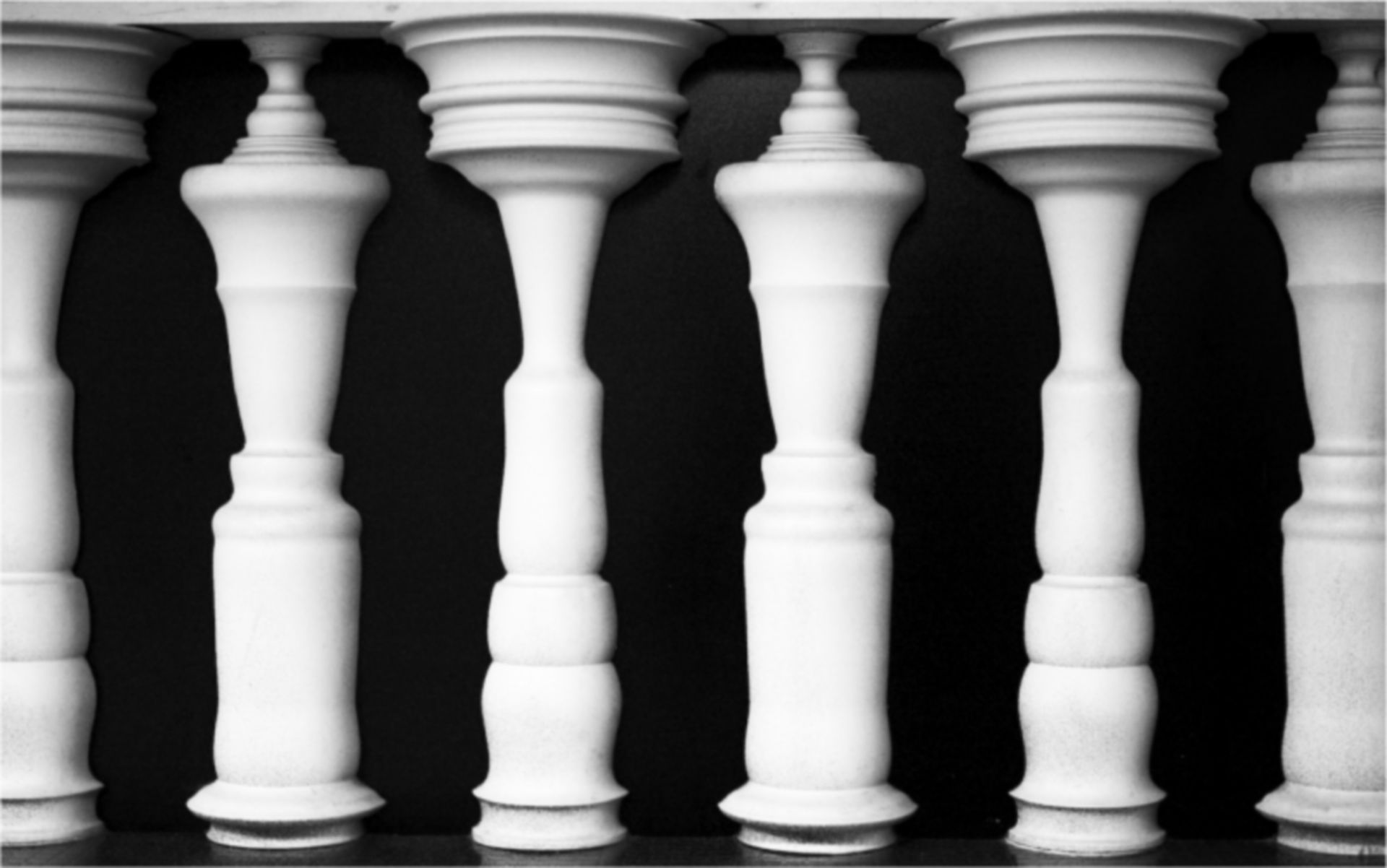

Which Gestalt Principle is this?
Figure/Ground
Figure-Ground
Gestalt principle where we separate objects (‘figure’) from their background (‘ground’)
(ex: vase or two faces illusion)
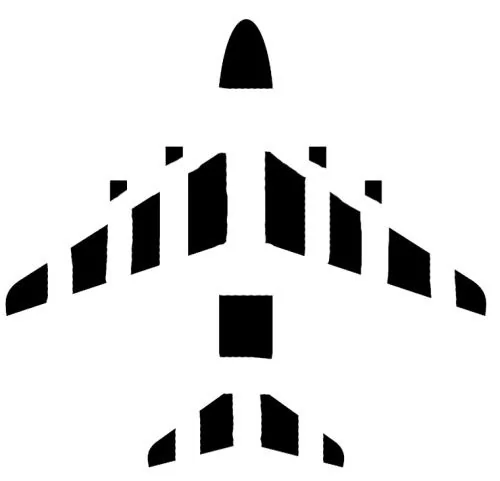

Which Gestalt Principle is this?
Closure
Closure
Gestalt principle where our brains fill in gaps to make a whole image
(ex: seeing faces in clouds or filling in the gaps of a circle outline)

Which Gestalt Principle is this?
Similarity
Similarity
Gestalt principle where we group things that look alike
(ex: seeing different colored flowers as distinct groups)
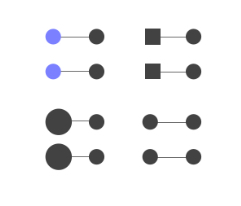
Which Gestalt Principle is this?
Connectedness
Connectedness
Gestalt principle where things that are linked/connected by lines or arrows are seen as one unit
(ex: circles joined by lines look like pairs)
Which Gestalt Principle is this?
Proximity
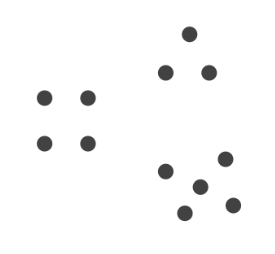
Proximity
Gestalt principle where we group things that are close together
(ex: dots close to each other appear as one group)
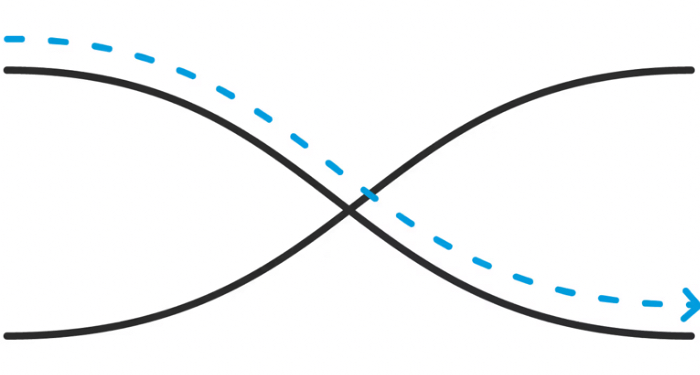
Which Gestalt Principle is this?
Continuity
Continuity
Gestalt principle where we prefer smooth, continuous patterns instead of abrupt changes
(ex: Lines crossing appear to flow smoothly rather than being split)
Monocular Cues
Visual cues that allow the brain to perceive depth and distance using only one eye
(ex: Linear Perspective, Interposition, Perceptual Constancies (size, shape, and color), and Phi Phenomenon)
Linear Perspective
(Monocular Cue) Parallel lines seem to meet as they go into the distance .The closer the lines look, the farther away we are
(ex: railroad tracks converging on the horizon)
Interposition
(Monocular Cue) When one object partially blocks another, it gets interpreted as being closer
(ex: a tree covering part of a house)
Perceptual Constancy (Size)
(Monocular Cue) Top-down process of perceiving an image as having unchanging size even as distance varies
(ex: man holding apple close to camera so that it looks bigger than his head, however we know that his head is actually bigger in reality)
Perceptual Constancy (Shape)
(Monocular Cue) Top-down process of perceiving the form of an object as constant even as the retina recieves changing images of them
(ex: different shapes of door being perceived as it opens, but we know the door is staying the same shape)
Perceptual Constancy (Color)
(Monocular Cue) Top-down process of perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color even as illuminations (shadows/filters) seem to change it. Visual stimuli sees change in color, but brain perceives as same consistent color
(ex: filter on a picture of a rubix cube)
Phi Phenomenon
(Monocular Cue) The optical illusion of one continuous moving object due to the flickering of adjacent stationary objects in quick succession
Binocular Cues
Visual cues that allow the brain to perceive depth and distance using both eyes
(ex: Retinal Disparity, Convergence)
Retinal Disparity
(Binocular Cue) Eyes take in two slightly different images because of the space between them, brain merges the images to create a single view of the world. The size of disparity (difference) between the two images helps to determine distance (bigger disparity, closer object).
Convergence
(Binocular Cue) Both eyes lock onto an object to judge your distance from it. Strain from eyes determines distance (more inward strain, closer to object)