Quiz 5 (Social Change, Nationalism, and Globalization)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are 3 factors that influence social change?
Pressures from the environment/population, culture/technology, and cultural diffusion.
What are the 2 forms of collective change and possible examples?
Disruptive and peaceful movements. Disruptive can be raiding the Capitol, and peaceful can be a protest.
What are the 3 types of social movements, their characteristics, and possible examples?
A reform movement is a type of social movement where people come together push for specific goals; these movements do not reform the structure/system (Women’s Rights).
A counter movement is a social movement that takes place to reverse the progress made by a specific movement (White Lives Matter / White Nationalism).
A revolutionary movement is one that seeks to completely change the political system (French revolution).
Why do social movements occur?
Social movements occur when people realize their needs/desires are not being met by the system and there is a possibility for change. It stems from frustration.
What role does ideology play in social movements?
Ideologies are an important part of social movements as they help provide moral frameworks, distinguishing friend vs. foe, and helps identify end goals (things the social movement wishes to attain).
What role does deprivation and expectations play in social movements?
Social movements occur when people have rising expectations. When people feel change is possible, it sparks movements. Rising expectations can come from education or the internet. Movements are far less likely to occur when people are deprived/in poverty.
What is relative deprivation and how does it relate to social change?
Relative deprivation is when people feel that they should have more than they currently have based on comparison. It leads to social change as it sparks feelings of inequality or unfairness. In contrast, absolute deprivation is when people struggle with having bare necessities, and as such, they are more worried on surviving rather than bringing about social change.
What role does a political system play in fostering social change?
Social movements only occur when there is a possibility to make a change. If a political system is constraining, then social change is less likely to occur.
What are the characteristics of political systems that inhibit and induce social change?
A stable, repressive government (such as a totalitarian dictatorship) would inhibit social change. A government that is divided or creates opportunities (elections and policy change) are more likely to induce social change.
What are the two main arguments surrounding globalization and how it affects culture?
Pessimistic hyperglobalizers argue that cultures are losing their diversity; cultures are homogenizing, according to them, and the world is Westernizing/Americanizing. Optimistic hyperglobalizers argue that Westernization is not necessarily a bad thing; it leads to free market and democracy.
What is glocalization?
As argued by Ronald Robertson, glocalization is the principle that global and local cultures interact with one another and don’t necessarily homogenize. He emphasizes that global cultures adapt to local cultures (McDonaldization) and local cultures are adapted globally (sushi).
What is the difference between globalism and globalization?
Globalism refers to the interconnectedness of the world in different domains. In contrast, globalization refers to the process of whether the world is increasing or decreasing in its globalism.
How has globalization been historicized?
Scholars have always tried to explain globalization and the historical events/developments that have facilitated it.
What are the phases of globalization and their characteristics?
Phase 1.0: Large to medium; resource and conquest; 1492-1800
Phase 2.0: Medium to small; companies globalizing for more markets and labor; 1800-2000
Phase 3.0: Small to tiny; Individuals drive globalization
What did Walter Rodney posit about colonization and how it relates to globalization?
Rodney argues that globalization did not solely rise from European modernization. He posits that European development depended on colonizing Africa. Ultimately, Africa lagged as it was dependent on Europe. Africa can only develop if it breaks away from international ties and focuses on itself.
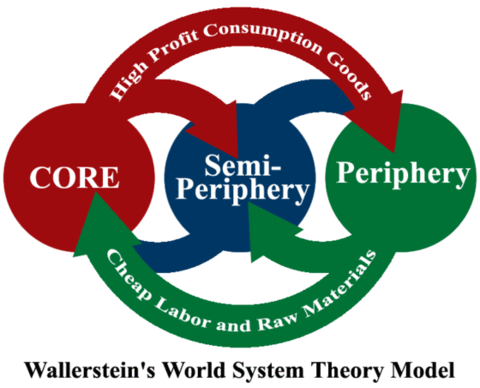
What does the World Systems Theory focus on?
Posited by Immanuel Wallerstein, the World System Theory explores the concept of global capitalism. The world is structured into the core (powerful countries), the periphery (resource-rich nations that are dependent on the core), and the semi-periphery (“2nd class core countries”)
What is Network Society Theory?
Posited by Manuell Castell, the Network Society Theory examines the interplay of technology and information, relating it to globalization. This theory focuses on technological determinism, emphasizing that information is a new economy (“information capitalism”).
What are the 3 goals of nationalism?
National autonomy (self-rule/free from external control), National Unity (bringing together fragmented cultures), and National Identity (distinguishing one natino from another and creating shared values)
What are examples of different ways the 3 goals of nationalism have manifested?
National autonomy = India wanting to be free of British control
National unity = Bringing fragmented Italian states together
National identity = Mongolia distinguishing itself from foreign influences
What things define a nation?
Lives in a location recognized by others. Have common myths and a distinct culture. Their own set of laws.
When defining a nation, what is the difference between objective and subjective factors?
Objective factors that influence the formulation of a nation include language. Subjective factors can include perception and sentiment. Subjective factors are more inclusive.
What is the difference between a nation and an ethnie?
Nations have political goals and their own land, while ethnies have shared ancestry/history/culture but no poltiical goals.
What is the definition of nationalism?
An ideology revolving around the nation that seeks to preserve culture using language and symbolism. It is the principle behind self-determination, and it differs from patriotism in that nationalism asserts one’s nation is superior to others.