lab 15 - additional biochemical tests to identify gram-negative bacteria
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
further testing is needed to definitively identify gram-negative bacteria. what kinds of biochemical testing is done?
IMViC series
esculin hydrolysis test
DNase test
oxidase test
nitrate reduction test
most gram-negative bacteria fall under which family?
Enterobacteriaceae, which is enteric gram-negative bacilli
Enterobacteriaceae are separated into what 2 groups?
coliforms, which are lactose-fermenting enteric bacilli (such as Escherichia or Enterobacter)
non-coliforms, which are non-lactose fermenting bacilli (such as salmonella and serratia)
which 2 gram-negative bacteria aren’t a part of Enterobacteriaceae?
Pseudomonas, because although it is a bacillus, it doesn’t ferment carbohydrates and is oxidase positive
Neisseria, because it is a diplococcus that is also oxidase positive
what is the IMViC series tests?
it is a series of tests used to differentiate members of Enterobacteriaceae. it stands for indole, methyl red, voges-proskauer, and citrate utilization
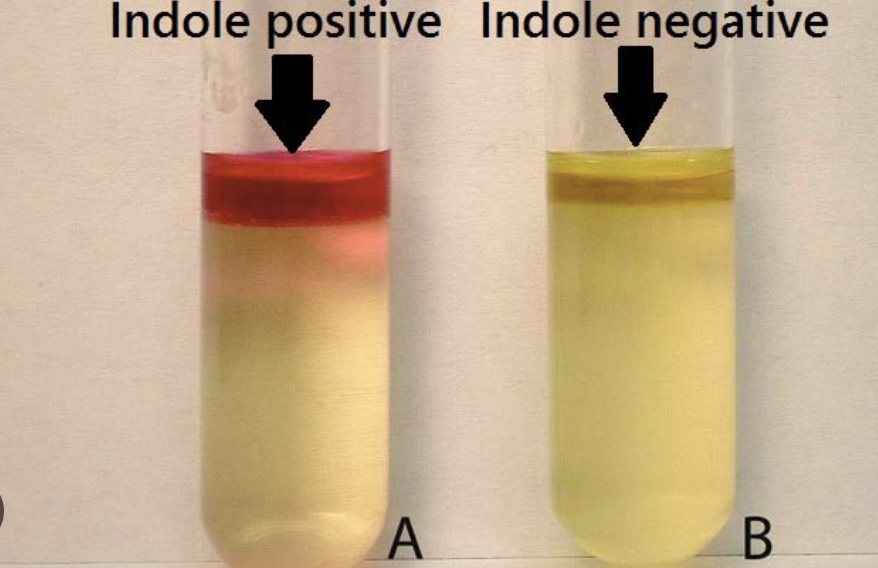
what is the indole test?
it tests an organism’s ability to hydrolyze the amino acid tryptophan and produce indole. it grows the organisms in a broth rich in tryptophan (such as TSB). after incubation, kovac’s reagent is added. if indole is present, it will combine with the reagent to form a distinctive red-colored phase on top of the denser broth
the methyl red and voges-proskauer tests detect the presence of different end products resulting from the metabolism of _
glucose. both tests are performed by inoculating the organism into tubes of MRVP broth which contains glucose
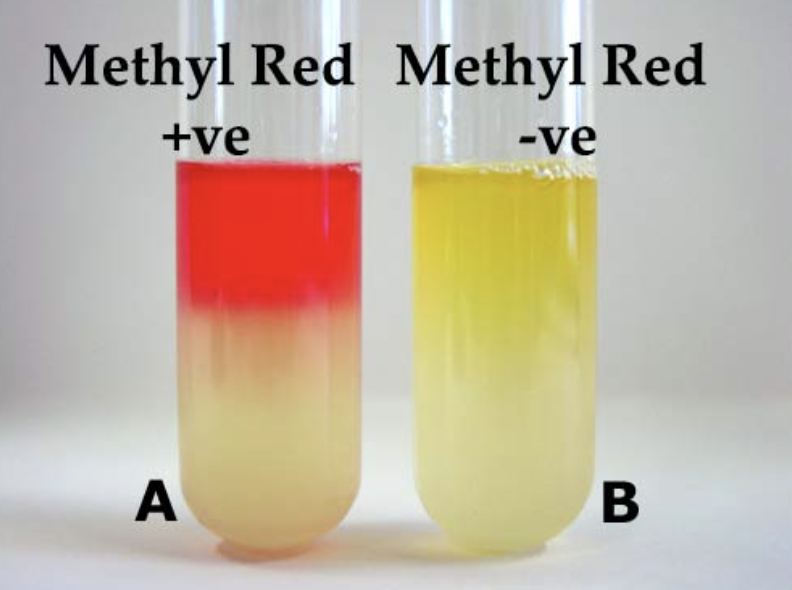
what is the MR test?
the methyl red reagent detects the presence of acids produced by organisms that perform a mixed acid fermentation. a positive MR test is indicated by a red color immediately after adding the reagent
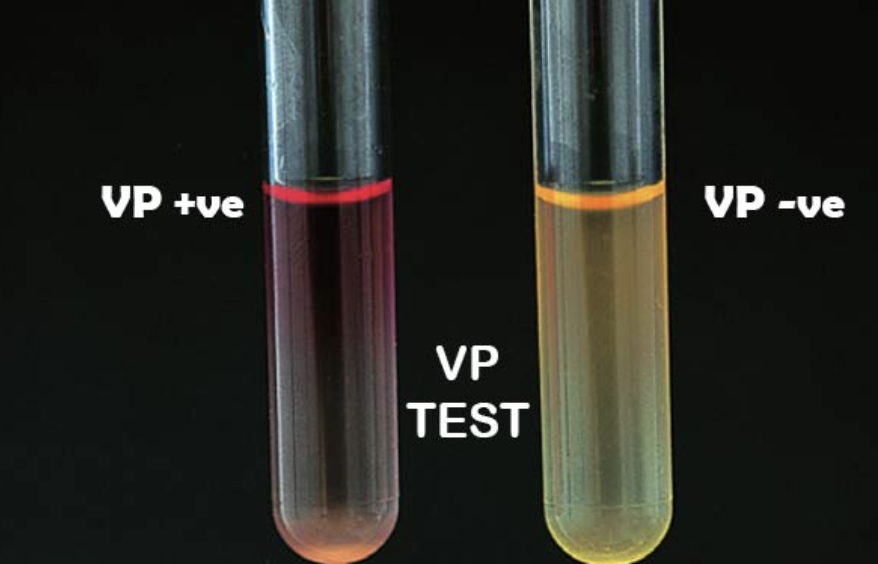
what is the VP test?
barritt’s a and barritt’s b reagents detect the presence of an unusual, non-acidic compound, which is formed by pyruvate

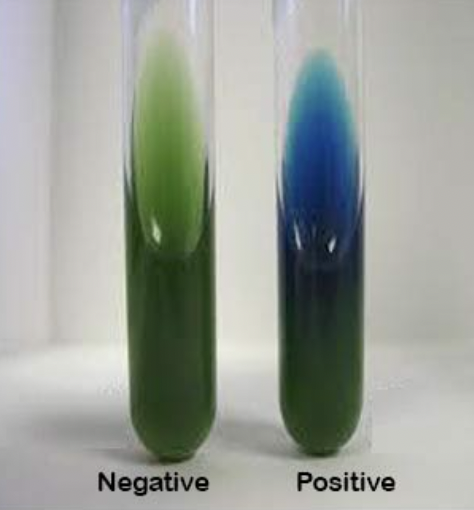
what is the citrate utilization test?
it determines if an organism can use citrate as its only carbon source. the simmons citrate agar slant contains sodium citrate as the sole carbon source, ammonium phosphate as the sole nitrogen source, and a bromthymol blue pH indicator. if citrate is utilized, alkaline end products are released, which increases the pH and changes the indicator color from green to blue

a positive oxidase test is useful in the confirmatory identification of which 2 gram-negative organisms?
pseudomonas and neisseria
bacteria that perform aerobic respiration have
cytochromes, or heme-containing proteins. together with flavoproteins and ubiquinones, they serve as electron carriers in the ETC
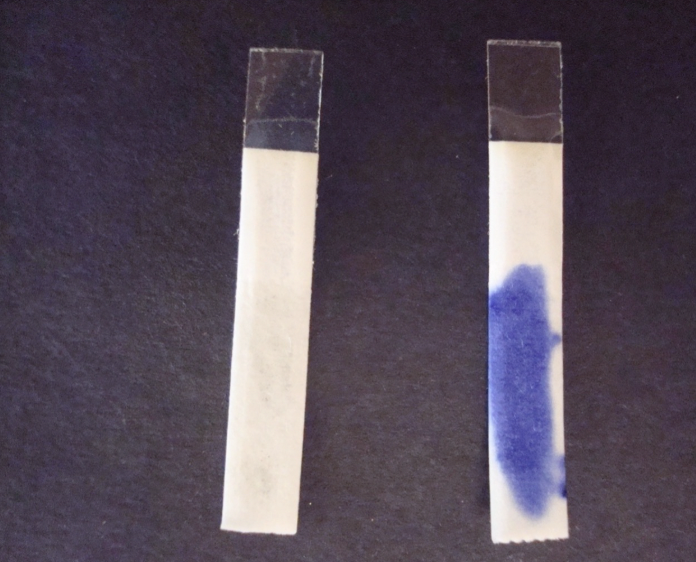
what does a positive oxidase test look like?
the development of a dark purple coloration on the filter

what is the nitrate reduction test?
it determines the ability of different bacteria to reduce nitrate to nitrite, ammonia, or other reduced forms of nitrogen using nitrate reductase or nitrite reductase
what is the function of a reagent?
to initiate/test a chemical reaction
nitrate reduction indicates that the organism is performing _ metabolism
anaerobic
how can you speed up a reaction that is progressing slowly?
by increasing the temperature
in the typical 24-48 hour citrate-positive test, the citrate agar slant is blue in the upper portion but green at the bottom. why?
because of the pH change caused by the bacterial metabolism of citrate
in which metabolic pathway is citrate an important intermediate?
Krebs cycle
what is reduction?
a chemical reaction where a substance gains electrons, decreasing its oxidation state