AP Literature - Literary Terms
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
allegory
A story, poem, or picture that can be interpreted to reveal a hidden meaning, typically a moral or political one.
alliteration
It is a stylistic device in which a number of words, having the same first consonant sound, occur close together in a series.

anaphora
A rhetorical figure of repetition in which the same word or phrase is repeated in (and usually at the beginning of) successive lines, clauses, or sentences.
anastrophe
Inversion of the natural or usual word order

blank verse
Poetry written in unrhymed iambic pentameter

dactyl
A stressed syllable followed by two unstressed syllables
dirge
a funeral hymn or mournful speech

hamartia
tragic flaw which causes a character's downfall
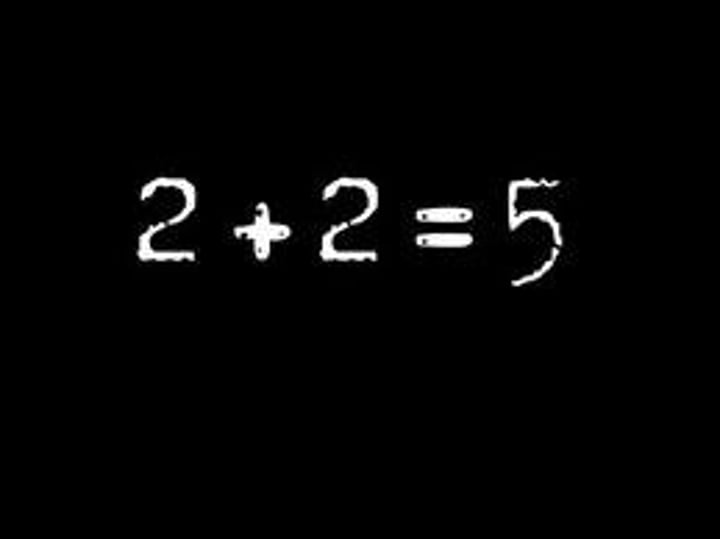
iamb
A common meter in poetry consisting of an unrhymed line with five feet or accents, each foot containing an unaccented syllable and an accented syllable.
novelette
When a novel is short and has chapters reffered to as vignettes

antimetabole
repetition of words in successive clauses in reverse grammatical order. Moliere: "one should eat to live, not live to eat." In poetry, this is called chiasmus
fable
a very short story told in prose or poetry that teaches a practical lesson about how to succeed in life
hypotactic
sentence marked by the use of connecting words between clauses or sentences, explicitly showing the logical or other relationships between them. "I am tired because it is hot."
allusion
A brief and indirect reference to a person, place, thing or idea of historical, cultural, literary or political significance.
antecedent
The word, phrase, or clause referred to by a pronoun.

antagonist
A character or force in conflict with the main character

antithesis
A balancing of two opposite or contrasting words, phrases, or clauses.

aphorism
A brief, cleverly worded statement that makes a wise observation about life.

apostrophe
A figure of speech that directly addresses an absent or imaginary person or a personified abstraction, such as liberty or love.
assonance
Repetition of a vowel sound within two or more words in close proximity

asyndeton
A series of words separated by commas (with no conjunction), e.g. "I came, I saw, I conquered." The parts of the sentence are emphasized equally; in addition, the use of commas with no intervening conjunction speeds up the flow of the sentence.

caesura
A natural pause or break in a line of poetry, usually near the middle of the line.

cacophony
Harsh, discordant, or meaningless mixture of sounds

cadence
Rhythmic rise and fall
conceit
A fanciful expression, usually in the form of an extended metaphor or surprising analogy between seemingly dissimilar objects.

connotation
All the meanings, associations, or emotions that a word suggests
consonance
Repetition of a consonant sound within two or more words in close proximity.

couplet
A pair of rhymed lines that may or may not constitute a separate stanza in a poem.

denotation
Dictionary definition of a word

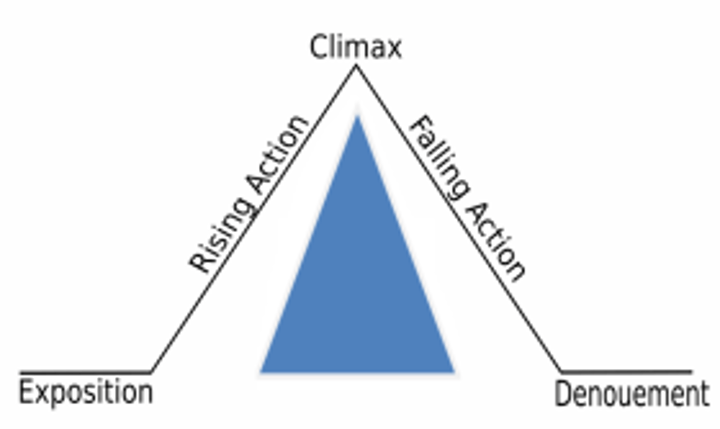
denouement
an outcome or solution; the unraveling of a plot
diction
The choice and use of words and phrases in speech or writing

didactic
Intended to instruct; teaching, or teaching a moral lesson

euphemism
An indirect, less offensive way of saying something that is considered unpleasant

end-stopped line
A line that ends with a natural speech pause, usually marked by punctuation

enjambment
A run-on line of poetry in which logical and grammatical sense carries over from one line into the next.

epitaph
A brief statement written on a tomb or gravestone

epic
A long narrative poem, written in heightened language, which recounts the deeds of a heroic character who embodies the values of a particular society

flashback
A method of narration in which present action is temporarily interrupted so that the reader can witness past events

foreshadowing
A narrative device that hints at coming events; often builds suspense or anxiety in the reader.
foot
A metrical unit composed of stressed and unstressed syllables.
free verse
Poetry that does not have a regular meter or rhyme scheme

genre
A category or type of literature (or of art, music, etc.) characterized by a particular form, style, or content.

heroic couplet
A pair of rhymed, iambic pentameter lines.
hexameter
A line of poetry that has six metrical feet.

hubris
Excessive pride or arrogance that results in the downfall of the protagonist of a tragedy

hyperbole
A figure of speech that uses exaggeration to express strong emotion, make a point, or evoke humor

imagery
Descriptive or figurative language in a literary work; the use of language to create sensory impressions.
irony
A contrast or discrepancy between what is stated and what is really meant, or between what is expected to happen and what actually does happen.

verbal irony
In this type of irony, the words literally state the opposite of the writer's true meaning

situational irony
Occurs when the outcome of a work is unexpected, or events turn out to be the opposite from what one had expected

dramatic irony
Irony that occurs when the meaning of the situation is understood by the audience but not by the characters in the play.

jargon
Special words or expressions that are used by a particular profession or group and are difficult for others to understand

juxtaposition
Placement of two things closely together to emphasize comparisons or contrasts

metaphor
A comparison that establishes a figurative identity between objects being compared.

meter
A regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables in a line of poetry
metonymy
A figure of speech in which something is referred to by using the name of something that is associated with it
mood
Feeling or atmosphere that a writer creates for the reader

motif
(n.) a principal idea, feature, theme, or element; a repeated or dominant figure in a design
motivation
A psychological factor that provides a directional force or reason for behavior.

narration
The purpose of this type of rhetorical mode is to tell the story or narrate an event or series of events.

novel
A long fictional narrative written in prose, usually having many characters and a strong plot.

novella
A short novel usually under 100 pages.
octave
a verse form consisting of eight lines of iambic pentameter
ode
A lyric poem usually marked by serious, respectful, and exalted feelings toward the subject.

onomatopoeia
A figure of speech in which natural sounds are imitated in the sounds of words.
oxymoron
A figure of speech that combines opposite or contradictory terms in a brief phrase.

paean
song of joy or triumph; a fervent expression of joy

parable
A simple story used to illustrate a moral or spiritual lesson

paradox
A statement or proposition that seems self-contradictory or absurd but in reality expresses a possible truth.

parallelism
Phrases or sentences of a similar construction/meaning placed side by side, balancing each other

parody
A work that closely imitates the style or content of another with the specific aim of comic effect and/or ridicule.

pedantic
An adjective that describes words, phrases, or general tone that is overly scholarly, academic, or bookish.

pentameter
a rhythm in poetry that has five stressed syllables in each line (five metrical feet)

persona
A pattern of relatively permanent traits, dispositions, or characteristics that give some consistency to people's behavior.

personification
A figure of speech in which an object or animal is given human feelings, thoughts, or attitudes

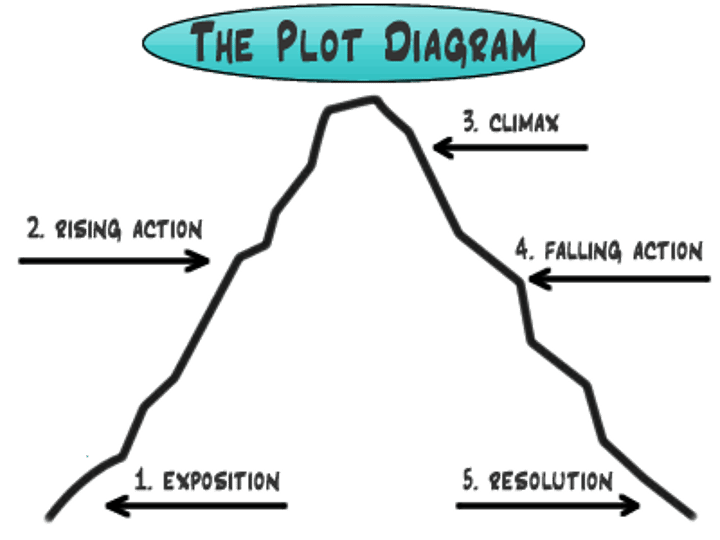
plot
Sequence of events in a story
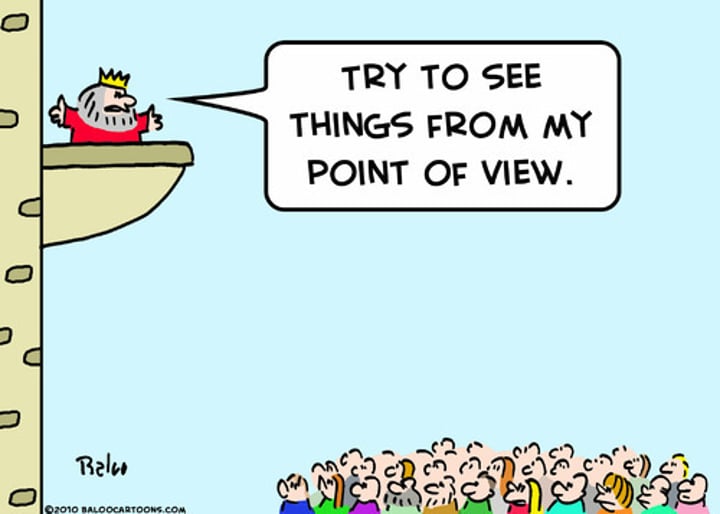
point of view
The perspective from which a story is told
polysyndeton
Deliberate use of many conjunctions in close succession, especially where some might be omitted. Hemingway and the Bible both use extensively. Ex. "he ran and jumped and laughed for joy"

prosody
Appropriate expression when reading. Includes pitch (intonation), loudness, stressing phrases, etc.

protagonist
Chief character in a dramatic or narrative work, usually trying to accomplish some objective or working toward some goal.

pun
A joke exploiting the different possible meanings of a word or the fact that there are words that sound alike but have different meanings.

quatrain
4 line stanza

refrain
A line or set of lines repeated several times over the course of a poem.
rhetorical question
A question asked merely for rhetorical effect and not requiring an answer

end rhyme
A word at the end of one line rhymes with a word at the end of another line

eye rhyme
rhyme that appears correct from spelling but does not rhyme because of pronunciation

forced rhyme
when two words don't really rhyme together, but an author uses similar spelled, or sounding words to try to create a rhyme; Ex: stone, one
internal rhyme
A word inside a line rhymes with another word on the same line

slant rhyme
rhyme in which the vowel sounds are nearly, but not exactly the same (i.e. the words "stress" and "kiss"); sometimes called half-rhyme, near rhyme, or partial rhyme

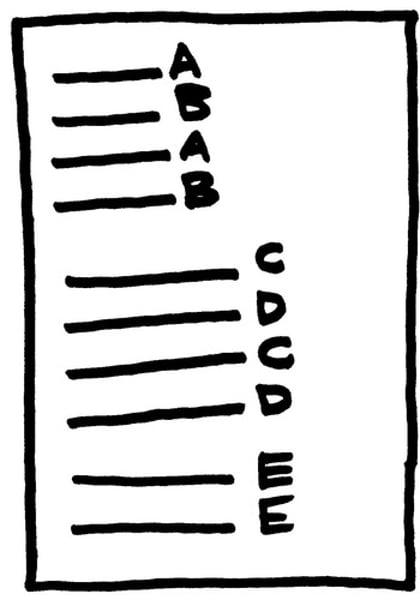
rhyme scheme
A regular pattern of rhyming words in a poem
satire
A literary work that criticizes human misconduct and ridicules vices, stupidities, and follies.
sestet
a rhythmic group of six lines of verse

shifts/turns
Changes in the speaker's attitude. Look for key words such as but, yet, however, and although, punctuation, and stanza division.
sonnet
14-line lyric poem focused on a single theme; usually written in iambic pentameter

symbol
A thing that represents or stands for something else, especially a material object representing something abstract.

synecdoche
a figure of speech in which a part is made to represent the whole or vice versa

syntax
Arrangement of words in phrases and sentences

theme
A topic of discussion or writing; a major idea broad enough to cover the entire scope of a literary work.

tone
A writer's attitude toward his or her subject matter revealed through diction, figurative language, and organization on the sentence and global levels.

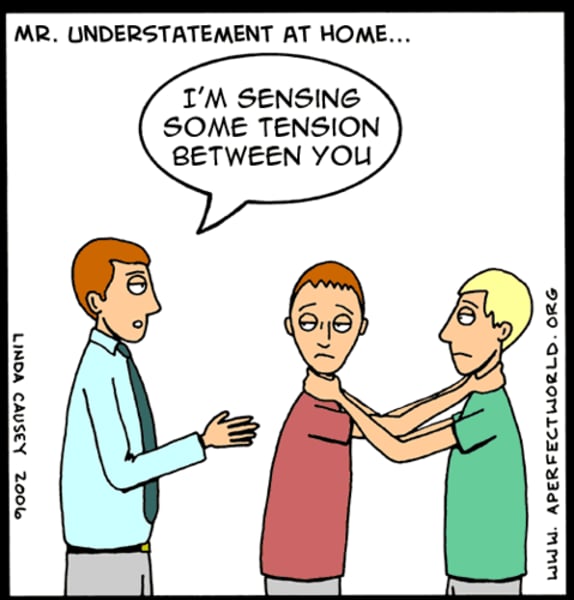
understatement
the presentation of something as being smaller, worse, or less important than it actually is.