Viral replication
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Stages of viral replication [9]
Recognition, attachment, penetration, uncoating, transcription, protein synthesis, replication, assembly, lysis and release
Virus host movement
virus movement is driven by Brownian forces, diffusion, electrostatic interactions
how viruses attach to host cells?
viral attachment proteins (VAP) bind to certain cellular surface proteins
What molecules can be receptors for viruses
proteins, carbohydrates, glycolipids, glycoproteins
Define affinity in terms of virus binding
strength of interaction between a single receptor and a singel virus attachment protein (one to one)
Define avidity in terms of virus binding
measure of overall binding of receptor with ligand, involving multiple binding sites
The change in strength of binding
at first the affinity is low, then due to VAPs and receptors results in high avidity interaction
Penetration of enveloped viruses
fusion of envelope with cell membrane
Enveloped viruses which fuse at the membrane
HIV, herpes virus
Enveloped viruses which fuse after receptor mediated endocytosis
influenza
Penetration of non-enveloped viruses
viropexis - direct entry
viropexis
hydrophobic viral protein interacts directly with membrane and injects the genome through the membrane
HIV-1 receptor binding, two proteins [2]
gp120 - mediates binding to the viral receptors, an antigenic target for antibodies gp41 - mediates fusion
DNA from DNA viruses is transported to
the nucleus
RNA from RNA viruses is transported to
the cytoplasm
Where can synthesis of nucleic acids also occur (not in the nucleus or the cytoplasm)
partially assembled capsids
Viruses which replicate in partially assembled capsids [4]
reovirus, poxvirus, retrovirus, hepadnavirus
Why does the virus uncoats?
to initiate viral gene expression, and replication of viruses
DNA virus cellular characteristics [2]
replication and transcription occurs in the nucleus, uses cellular enzymes and proof-reading mechanisms
DNA virus non-cellular characteristics [3]
no histones episomal circular DNA frame shifts
What is ori
origin of replication typically on circular DNA viruses such as polyomavirus
Rolling circle replication
a DNA replication mechanism in which one strand is nicked and unrolled for use as a template to synthesize a complementary strand
Which viruses replicate by rolling circle?
herpes viruses
All DNA viruses replicate in the nucleus except
Poxvirus
Main enzyme for RNA replicatio
RdRp (RNA dependent RNA polymerase)
Which RNA virus does not replicate in the cytoplasm?
orthomyxovirus
+ RNA replication
Can be directly translated into proteins Synthesized negative strand serves for genome replication
+RNA strand is the same as mRNA?
yes
VPg function
Viral protein genome-linked acts as a primer during RNA synthesis
-RNA virus replication
RNA is synthesized acts as a template for mRNA synthesis and production of new genome
In the cytoplasm, what proteins associate with the synthesized genome to form the nucleocapsid?
N, L and NS proteins
Which protein associates with the G protein modified membrane
the matrix protein
retrovirus replication
have their own enzymes for transcription use cellular enzymes for replication form viral dsDNA in the nucleus
Which viruses produce polyproteins
RNA viruses polyproteins are processed by viral and cellular proteases
What is the nucleocapsid composed of
DNA or RNA + structural proteins (capsid)
Virus assembly general steps [6]
formation of a structural units of the protein shell
assembly of the protein shell via interaction of units
selective packaging of the nucleic acid genome and other virion components
acquisition of an envelope (only for enveloped viruses)
release from host cell virion
maturation (only for some viruses)
Define virion
a completely assembled, infectious virus outside its host cell
Virus assembly cellular machineries [2]
ER -> Golgi -> PM secretory pathway transport viral glycoproteins nuclear import and export
machinery moves viral proteins and nucleic acids
How do viruses localize their proteins [5]
nuclear localization sequences signal sequences,
CHO-,
lipid modifications
ER retention signals
interactions with microtubules, actin filaments
Virus which forms an icosahedral particle
poliovirus
5S structural unit is composed of
VP1, VP2, VP3, VP4
Complete icosahedral particle is composed of
12 pentamers (5S) and RNA
Viral scaffolding proteins
Establish transient intermediate structures
Viral proteases packaged in these intermediate structures become activated to finalize structure
Where is the nucleocapsid with scaffolding proteins assembled
in the nucleus
How is viral genome identified during packaging
Via packaging signals on the genome which are recognized by structural proteins. Binding of one structural protein initiates subsequent binding.
How does poliovirus achieve genome specificity
packaging of viral proteins and RNA synthesis are coupled
Enveloped virus assembly (idk man)
viral membrane proteins are co translationally translocated into the ER membrane they become processed and glycosylated for by viral and cellular chaperones and transported out to the PM then they travel to the site of viral budding lateral interactions build a matrix of proteins which often excludes cellular proteins
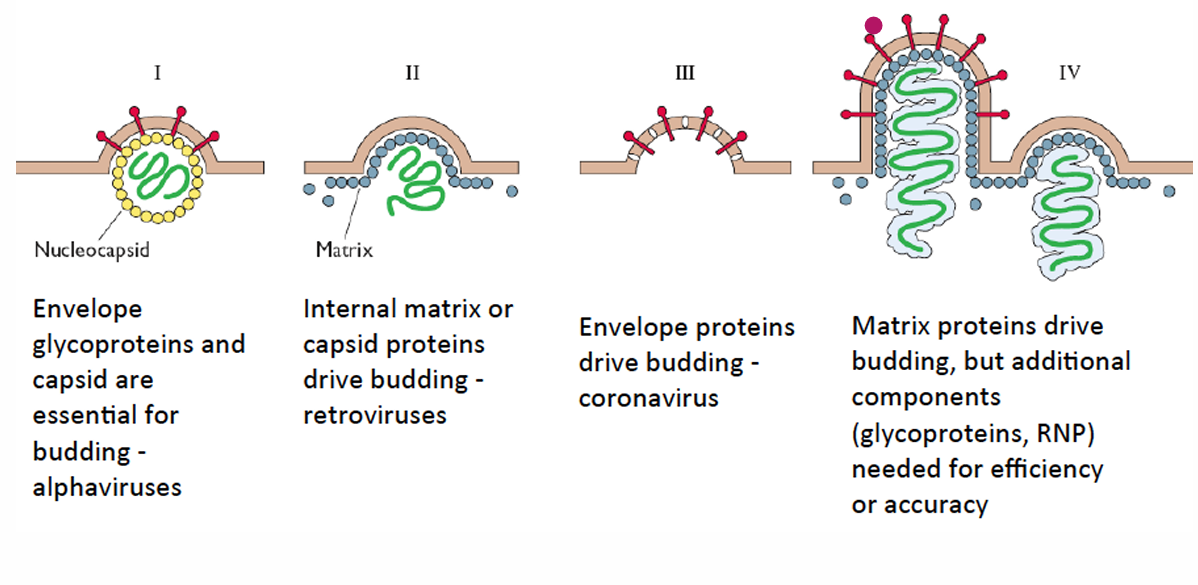
Viral budding strategies [4]
Alphaviruses - envelope glycoproteins and capsid drive budding retroviruses - internal matrix or capsid proteins drive budding coronavirus - envelope proteins drive budding matrix proteins and additional glycoproteins or RNP drive budding efficiently and accurately
Maturation of viruses include
virion components are processed to make them infectious
Viruses which require viral or/and cellular proteases
HIV, poxvirus, HCV
Viruses which process sialic acids
influenza