ecology slide deck 6 (population ecology part 2)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
changes in population over time is the difference in
the arrival (birth and immigration) and loss of individuals (death and emigration)
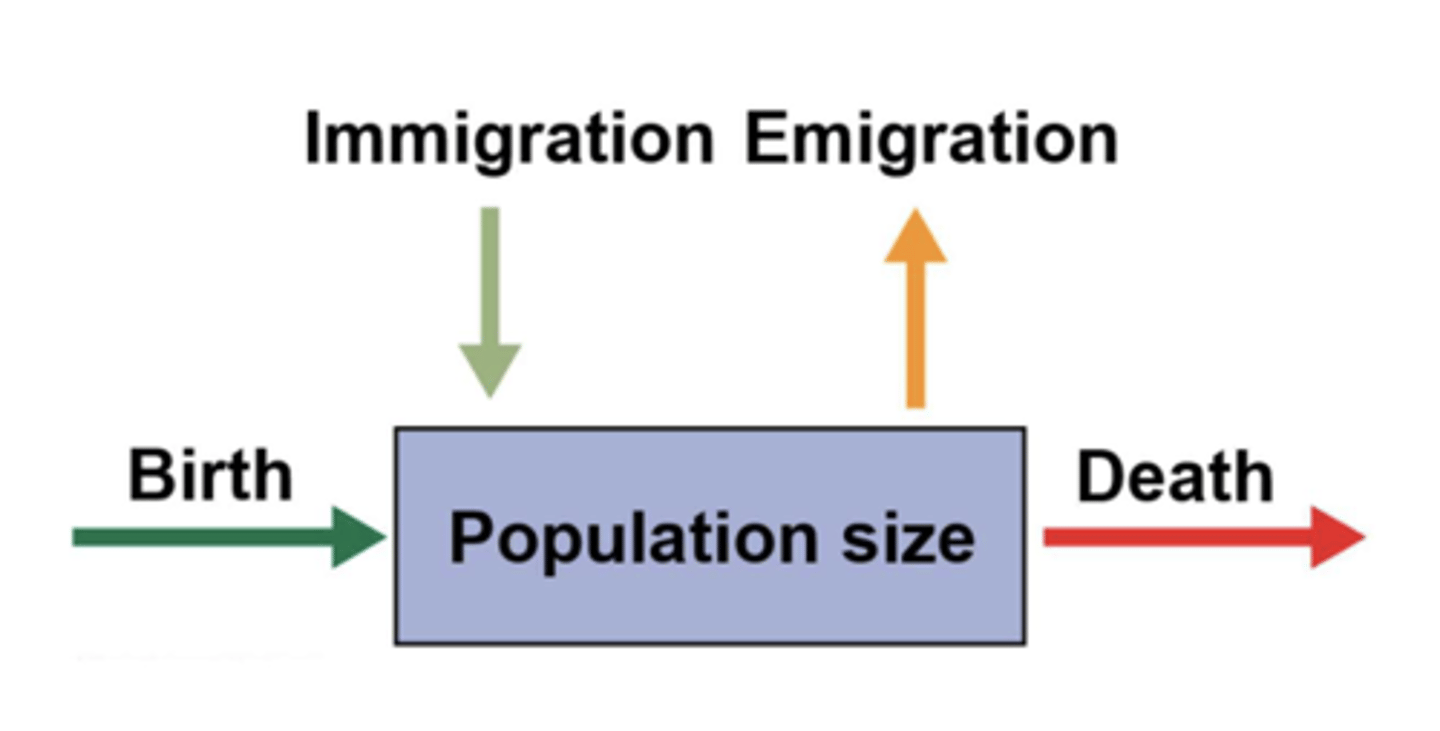
an open population has
immigrations and emigration
a closed population does not have or has a very low level of
immigration and emigration that doesn't influence population growth
fertility
ability to produce offspring
natality (birthrate)
number of births related to population size
fecundity
number of offspring/female/unit time
potential fecundity
potential reproductive capacity of individual (under optimal conditions)
realized fecundity
actual reproduction of individual
potential longevity
maximum lifespan under optimal conditions
realized longevity
actual life span
disease, predation, natural disasters ->
lower longevity
net reproductive rate (Ro)
average number of female offspirng produced by an average female during lifetime
equation for net reproductive rate
Ro=Σlxbx
lx survivorship
the number of individuals surviving to a given age (x) as a proportion of the original cohort size nx/no)
bx fecundity
the mean number of females born to each female in an age group
a life table is an
age-specific account of mortality
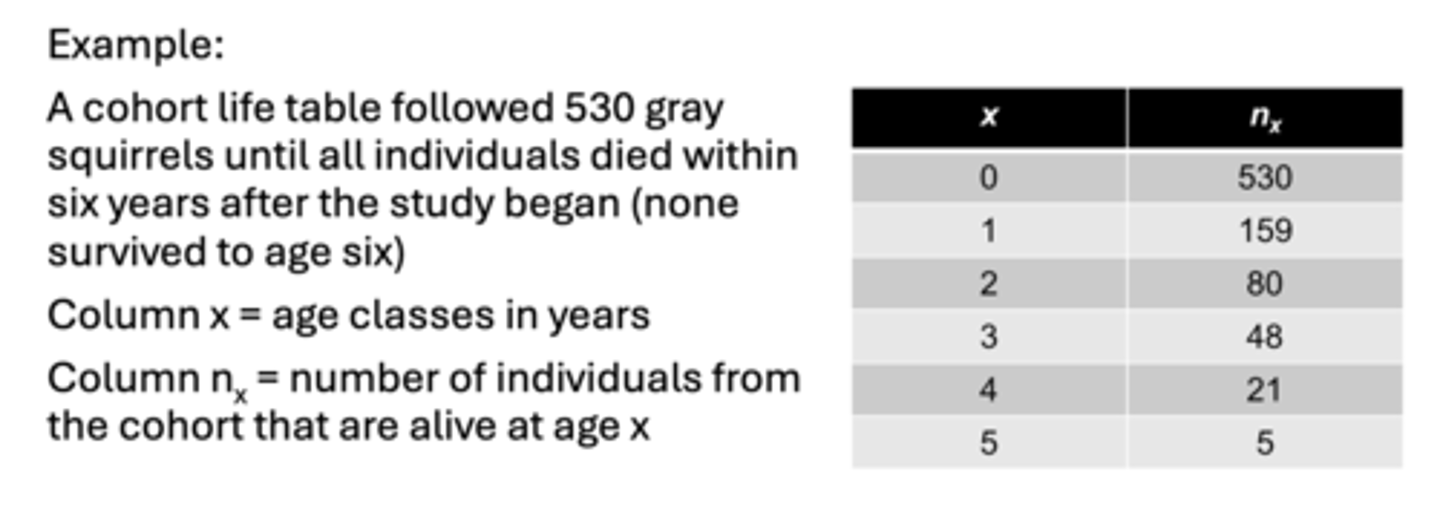
if Ro = 1.0
females on average produce on daughter, replacing themselves; population is stable
if Ro > 1.0
females on average produce more than one daughter; population is growing
if Ro < 1.0
females on average produce less than one daughter; population is declining
discrete
all individuals in a population reproduce in roughly the same time window
overlapping
multiple age classes coexist and reproduce at the same time
intrinsic rate of increase (r)
per capita rate of growth of population with stable age distribution
geometric growth model
predicts changes in population size in discrete intervals where birth and death are not continuous processes
exponential growth model
continuous, unlimited growth, overlapping generations
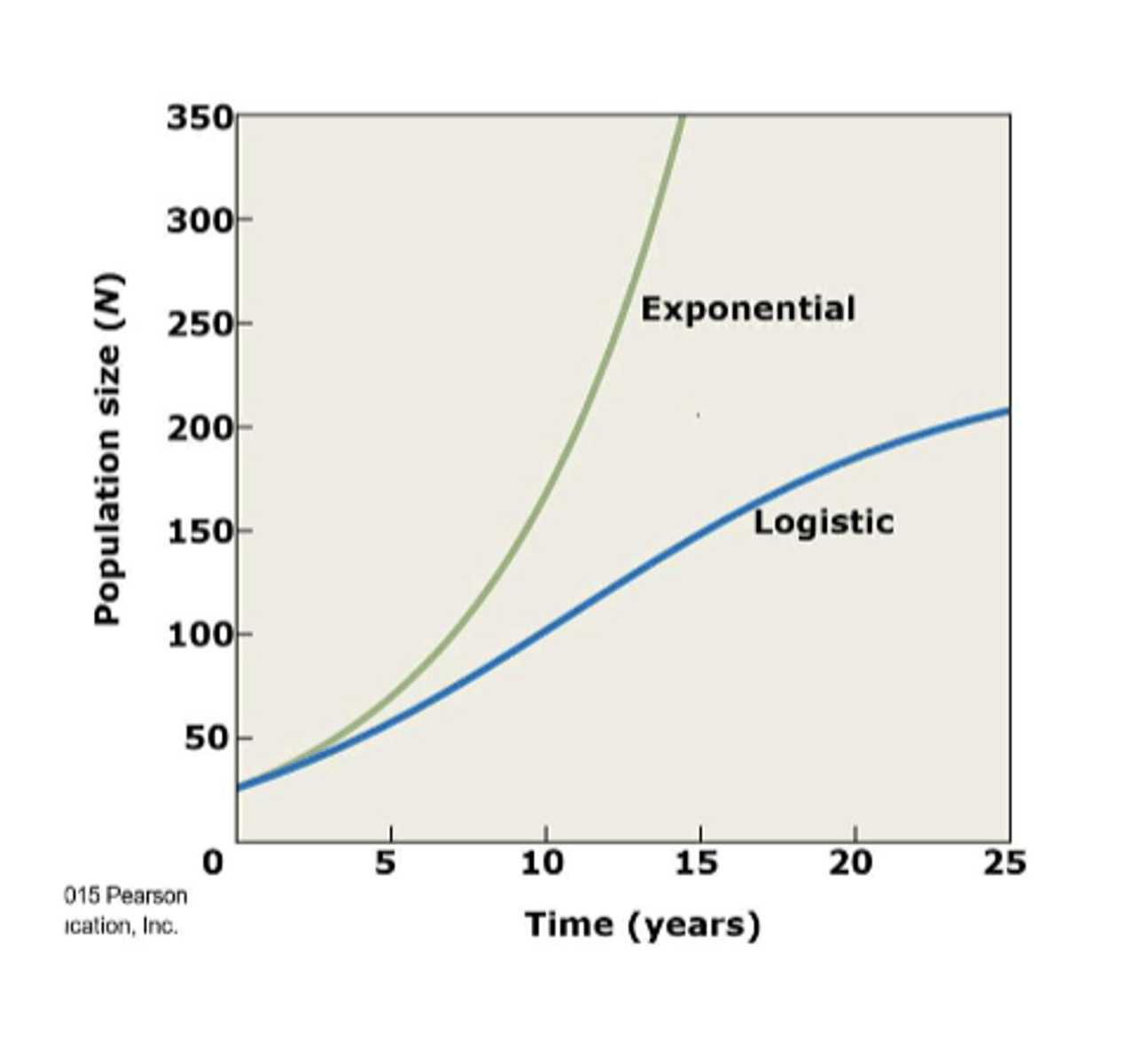
logistic growth
found where environmental limit exist, growth rate is influenced by population size
K=
maximum population size that the environment can support
the effect of K on population growth is
(1-N/K), where N=population size
geometric growth=
discrete generations (stepwise, j-shaped curve with plotted points)
exponential growth=
overlapping generations (smooth, continuous J-shaped curve)
logistic growth=
overlapping generations (smooth, continuous S-shaped curve)
N=
number of individuals in the population
t=
time
N(t)=
number of individuals in the population at a given time
when r=0, b=d
the population size does not change
when r>0, b>d
the population increases exponentially
when r<0, b
the population decreases exponentially
the exponential growth model assumes
unlimited essential resources, a constant environment
logistic growth describes population growth when resources are ___________ and growth is density dependent
limited
to this point, population growth has been considered to be a
deterministic process
stochasticity
random, unpredictable fluctuations that influencepopulation dynamics
demographic stochasticity
variation in birthrates and death ratesoccurring in populations from year to year
environmental stoachasticity
random variation in environmentthat can influence birthrates and death rates in population
generally ______ populations are more vulnerable to extinction
small
small populations are more vulnerable to extinction because of
loss of genetic variability, increased vulnerability to demographic and environmental stochasticity